python入门isinstance内置函数常用运算等
Posted 月亮上的花园
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python入门isinstance内置函数常用运算等相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. isinstance(变量名,类型) #判断什么类型
ps:
只支持输入两个参数,输入3个参数会报错
>>> isinstance (a,int,float)
Traceack (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: isinstance expected 2 arguments, got 3
>>> isinstance (a,int)
True
>>> b=1.1234
>>> isinstance(b,float)
True
>>> c=1+1j
>>> isinstance(c,complex)
True
>>> d=[1,2,3,4]
>>> isinstance(d,list)
True
>>> e=(1,2,3,4)
>>> isinstance (e,tuple)
True
>>> f="abc"
>>> isinstance(f,str)
True
>>> g={1:4,a:b}
>>> isinstance(g,dict)
True
>>> h={1,2,3,4}
>>> type(h)
<class \'set\'>
>>> isinstance (h,set)
True
>>> isinstance(False,bool)
True
>>> isinstance(False,bool)
True
>>> bool(a)
True
>>> bool(1)
True
>>> bool(-1)
True
>>> bool(1+1j)
True
>>> bool([])
False
>>> bool({})
False
>>> bool( )
False
>>> bool("")
False
>>> bool(0)
False
用途:在实现函数时,需要传入一些变量,因为python是弱语言类型,实现不需要声明变量类型就可以使用的。赋予什么值,就默认为什么类型。所以在给函数传参的时候,事先要判断一下是什么类型。如果类型不对,就会报错儿。
>>> a=1
>>> b="2"
>>> a+b
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: \'int\' and \'str\'
>>> type=1.2
>>> isinstance(type,float)
True
>>> type(1.2)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: \'float\' object is not callable
类型错误:\'float\'对象不可调用
原因:将关键字赋了值,在代码里重内置类型.新定义了type,如type=1.2,这时你自己调用的是代码里定义的type,而不是python
解决方法:删掉重新定义的关键字del type
2. 常用的计算:
1) 加+
>>> 1+1
2
2) 减-
>>> 1-1
0
3) 乘*
>>> 56*2
112
4) 除/
>>> 1/2
0.5
>>> 1/3
0.3333333333333333 #自动取小数,而非取整。
>>> 1/0
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero #0不能做除数:
5) 取整//
>>> 1//2
0
>>> 9//2
4
>>> 9//10
0 #不存在四舍五入的情况,只取商。
6) 四舍五入round(数字,保留的位数)
>>> round(1.25,1) #小数点要保留的位数后面如果是5,5会更加靠近偶数。
1.2 如果5前面是偶数,那不会进位
>>> round(1.25,0) 如果5前面是奇数,那就会进位
1.0
>>> round(1.5) #如果没有写明保留几位,默认输出整数
2 保留0位和保留1的结果一样。
>>> round(0.5)
0
>>> round(2.675,2)
2.67 #结果都应该是2.68的,结果它偏偏是2.67,为什么?这跟浮点数的精度有关。我们知道在机器中浮点数不一定能精确表达,因为换算成一串1和0后可能是无限位数的,机器已经做出了截断处理。那么在机器中保存的2.675这个数字就比实际数字要小那么一点点。这一点点就导致了它离2.67要更近一点点,所以保留两位小数时就近似到了2.67。
除非对精确度没什么要求,否则尽量避开用round()函数
浮点数精度要求如果很高的话,请用decimal模块
>>> round(-100.55,1) #负数也可使用round
-100.5
7) 取余%
>>> 8%3
2
>>> 100%3
1
8) 取商取余divmod(,)
>>> divmod(10,3)
(3, 1)
>>> divmod(9,2)
(4, 1)
>>> divmod(9,2)[0] #只取商
4
>>> divmod(9,2)[1] #只取余
1
9) 取最大值max
>>> max([1,2,3,45])
45
>>> max(1,2,3,45)
45
10) 乘方**/pow
>>> 2**3
8
>>> 2*2*2
8
>>> 10**3
1000
>>> pow(2,3)
8
>>> pow(10,3)
1000
11) 开方math.sqrt
>>> math.sqrt(8)
2.8284271247461903
>>> math.sqrt(4)
2.0
>>> math.pi
3.141592653589793
3. dir(__builtins__) #查看内置函数
[\'ArithmeticError\', \'AssertionError\', \'AttributeError\', \'BaseException\', \'BlockingIOError\', \'BrokenPipeError\', \'BufferError\', \'BytesWarning\', \'ChildProcessError\', \'ConnectionAbortedError\', \'ConnectionError\', \'ConnectionRefusedError\', \'ConnectionResetError\', \'DeprecationWarning\', \'EOFError\', \'Ellipsis\', \'EnvironmentError\', \'Exception\', \'False\', \'FileExistsError\', \'FileNotFoundError\', \'FloatingPointError\', \'FutureWarning\', \'GeneratorExit\', \'IOError\', \'ImportError\', \'ImportWarning\', \'IndentationError\', \'IndexError\', \'InterruptedError\', \'IsADirectoryError\', \'KeyError\', \'KeyboardInterrupt\', \'LookupError\', \'MemoryError\', \'ModuleNotFoundError\', \'NameError\', \'None\', \'NotADirectoryError\', \'NotImplemented\', \'NotImplementedError\', \'OSError\', \'OverflowError\', \'PendingDeprecationWarning\', \'PermissionError\', \'ProcessLookupError\', \'RecursionError\', \'ReferenceError\', \'ResourceWarning\', \'RuntimeError\', \'RuntimeWarning\', \'StopAsyncIteration\', \'StopIteration\', \'SyntaxError\', \'SyntaxWarning\', \'SystemError\', \'SystemExit\', \'TabError\', \'TimeoutError\', \'True\', \'TypeError\', \'UnboundLocalError\', \'UnicodeDecodeError\', \'UnicodeEncodeError\', \'UnicodeError\', \'UnicodeTranslateError\', \'UnicodeWarning\', \'UserWarning\', \'ValueError\', \'Warning\', \'WindowsError\', \'ZeroDivisionError\', \'_\', \'__build_class__\', \'__debug__\', \'__doc__\', \'__import__\', \'__loader__\', \'__name__\', \'__package__\', \'__spec__\', \'abs\', \'all\', \'any\', \'ascii\', \'bin\', \'bool\', \'bytearray\', \'bytes\', \'callable\', \'chr\', \'classmethod\', \'compile\', \'complex\', \'copyright\', \'credits\', \'delattr\', \'dict\', \'dir\', \'divmod\', \'enumerate\', \'eval\', \'exec\', \'exit\', \'filter\', \'float\', \'format\', \'frozenset\', \'getattr\', \'globals\', \'hasattr\', \'hash\', \'help\', \'hex\', \'id\', \'input\', \'int\', \'isinstance\', \'issubclass\', \'iter\', \'len\', \'license\', \'list\', \'locals\', \'map\', \'max\', \'memoryview\', \'min\', \'next\', \'object\', \'oct\', \'open\', \'ord\', \'pow\', \'print\', \'property\', \'quit\', \'range\', \'repr\', \'reversed\', \'round\', \'set\', \'setattr\', \'slice\', \'sorted\', \'staticmethod\', \'str\', \'sum\', \'super\', \'tuple\', \'type\', \'vars\', \'zip\']
12) 与或非
1) and:
>>> True and True
True
>>> True and False
False
>>> False and True
False
>>> False and False
False
>>> a=10
>>> a<5 and a<11 and isinstance (a,floassss)
False #floassss是一个错误的字符,但是依然正确输出False,是因为前面的条件a<5为False,直接输出False,短路了后面的字符。
>>> 1 and 9 #如果两边都为真,则返回第二个值
9
>>> 5 and 3
3
2) or:
>>> True or False
True
>>> True or True
True
>>> False or True
True
>>> False or False
False
>>> a<5 or a<11 or isinstance (a,floassss)
True #依然存在短路效应
3) not:
>>> not False
True
>>> not True
False
>>> not(0)
True
>>> not(1)
False
>>> not[]
True
>>> not{}
True
>>> not("")
True
>>> not()
True
>>> 1 and 2 or not 3 #不加括号的情况下 not的优先级大于and, and的优先级大于 or
2
>>> (1 and 2) or (not 3)
2
>>> not False #一般用这个
True
>>> not(False) #用的是函数,但是两者输出结果一样。
True
4. help(函数名) #查看函数的用法
>>> help(round)
Help on built-in function round in module builtins:
round(...)
round(number[, ndigits]) -> number
Round a number to a given precision in decimal digits (default 0 digits).
This returns an int when called with one argument, otherwise the
same type as the number. ndigits may be negative.
>>> help(pow)
Help on built-in function pow in module builtins:
pow(x, y, z=None, /)
Equivalent to x**y (with two arguments) or x**y % z (with three arguments)
Some types, such as ints, are able to use a more efficient algorithm when
invoked using the three argument form.
>>> pow(2,3)
8
>>> pow(10,10)
10000000000
>>> pow(2,3,2) #2的3次方后除2取余=0
0
>>> pow(2,3,3) #2的3次方后除3取余=2
2
>>> help(math)
Help on built-in module math:
NAME
math
DESCRIPTION
This module is always available. It provides access to the
mathematical functions defined by the C standard.
FUNCTIONS
acos(...)
acos(x)
Return the arc cosine (measured in radians) of x.
pow(...)
pow(x, y)
Return x**y (x to the power of y).
>>> math.pow(2,3) #与pow不同的是,返回的是小数
8.0
>>> math.pow(2,3,3)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: pow expected 2 arguments, got 3 #注意,math.pow支持输入两个函数。
5. ord #返回一个字符串的Unicode编码
Return the Unicode code point for a one-character string.
>>> ord("a")
97
>>> ord("z")
122
>>> ord("A")
65
>>> ord("Z")
90
6. chr #返回指定序号的字符
Return a Unicode string of one character with ordinal i; 0 <= i <= 0x10ffff.
>>> chr(97)
\'a\'
>>> chr(65)
\'A\'
>>> chr(90)
\'Z\'
>>> chr(122)
\'z\'
7. print #打印输出
>>> print("hello world!")
hello world! #默认换行输出
>>> print("hello world",end="")
hello world>>> #增加end=” ”后,不会换行
8. input #输入
>>> age=input("how old are you?")
how old are you?10
>>> age
\'10\'
>>> type(age)
<class \'str\'> #input获取到的所有数据的类型均是字串
>>> age+10
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: must be str, not int #字串和数字不能相加
>>> age+"20"
\'1020\' #两个字串相加,是拼字符串
>>> int(age)+10
20 #将age由str强制转换成int,可实现输出数字的相加
>>> age+str(10) #强制类型转换,也可实现拼字符串
\'1010\'
9. if else
>>> score=input("请输入你的数学成绩:")
请输入你的数学成绩:98
>>> if int(score)>85:
... print("优秀")
... elif int(score)>=60 and int(score)<=85:
... print("及格")
... else:
... print("差")
...
优秀
10. len() #求长度
>>> len("gloaryroad")
10
>>> len(121212)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: object of type \'int\' has no len() #int类型没有长度
>>> len(1.123)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: object of type \'float\' has no len() #float类型没有长度
>>> len((1,2,3,4))
4
>>> len([1,2,3,4])
4
>>> len({1,2,2,2,2,2})
2 #集合中重复的元素不算长度
11. ASCII码
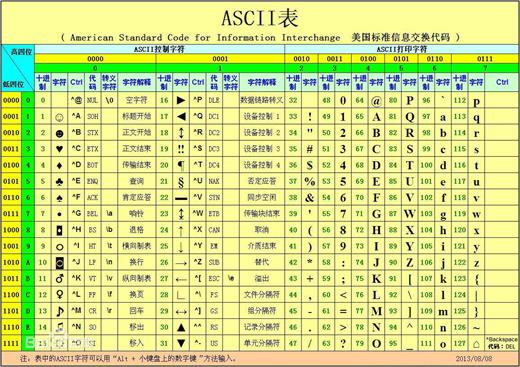
>>> "a">"A"
True #比对的是ASCII码
a-97
A-65 #要牢记!
知识点:
1. 集合{}与列表[]在用法上的区别:
集合值:不能重复
>>> h={1,2,3,3,4,4} #在赋值时可以重复
>>> h
{1, 2, 3, 4} #在查看时,就自动去重了。
列表值:可以重复
>>> i=[1,2,3,3,4,4] #在赋值时也可以重复
>>> i
[1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4] #在查看时也未去重
2. 元祖与列表的区别:
List是[],且是可以改变的
Tuple是(),且是不可以
小练习:
输入一个数,如果可以被2和5整除,打印ok
>>> a=input("请输入一个数字:")
请输入一个数字:10
>>> if int(a)%2==0 and int(a)%5==0:
... print ("ok")
...
ok
小练习:
输入一个数字,如果可以被3或5整除,打印ok
>>> a=input("请输入一个数字:")
请输入一个数字:10
>>> if int(a)%3==0 or int(a)%5==0:
... print ("ok")
...
ok
小练习:
如果输入的数字不等于3,返回ok
方法1:
>>> a=input("请输入一个数字:")
请输入一个数字:4
>>> if int(a)!=3:
... print ("ok")
...
ok
方法2:
>>> a=input("请输入一个数字:")
请输入一个数字:4
>>> if not(a==3):
... print ("ok")
...
ok
小练习:
not 1 or 0 and 1 or 3 and 4 or 5 and 6 or 7 and 8 and 9
not 1=0
0 and 1 = 0
3 and 4 = 4
5 and 6 = 6
7 and 8 = 8
8 and 9 = 9
0 or 0 or 4 or 6 or 9 = 4
#and运算时,如果第一个为False返回第一个值,否则返回第二个值
#or 运算时,如果第一个为False返回第二个值,否则返回第一个值
小练习:
输入一个字符串,长度如果大于3打印大于3,长度小于3打印小于3,长度等于3打印等于3
>>> a=input("请输入一个字符串:")
请输入一个字符串:gloaryroad
>>> if len(a)>3:
... print ("大于3")
... elif len(a)==3:
... print ("等于3")
... else:
... print ("小于3")
...
大于3
以上是关于python入门isinstance内置函数常用运算等的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章