python教程18python操作Mysql,pymysql,SQLAchemy
Posted bksts
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python教程18python操作Mysql,pymysql,SQLAchemy相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、MySQL
1、概述
什么是数据库 ?
答:数据的仓库,和Excel表中的行和列是差不多的,只是有各种约束和不同数据类型的表格
什么是 MySQL、Oracle、SQLite、Access、MS SQL Server等 ?
答:他们均是一个软件,都有两个主要的功能:
- a. 将数据保存到文件或内存
- b. 接收特定的命令,然后对文件进行相应的操作
PS:如果有了以上软件,无须自己再去创建文件和文件夹,而是直接传递 命令 给上述软件,让其来进行文件操作,他们统称为数据库管理系统(DBMS,Database Management System)
什么是SQL ?
答:上述提到MySQL等软件可以接受命令,并做出相应的操作,由于命令中可以包含删除文件、获取文件内容等众多操作,对于编写的命令就是是SQL语句。SQL语句是结构化语言(Structured Query Language)的缩写,SQL是一种专门用来与数据库通信的语言。
2、下载安装
MySQL是一个关系型数据库管理系统,由瑞典MySQL AB 公司开发,目前属于 Oracle 旗下公司。MySQL 最流行的关系型数据库管理系统,在 WEB 应用方面MySQL是最好的 RDBMS (Relational Database Management System,关系数据库管理系统) 应用软件之一。
想要使用MySQL来存储并操作数据,则需要做几件事情:
a. 安装MySQL服务端
b. 安装MySQL客户端
b. 【客户端】连接【服务端】
c. 【客户端】发送命令给【服务端MySQL】服务的接受命令并执行相应操作(增删改查等)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
下载 http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/安装 windows: 点点点 Linux: yum install mysql-server Mac: 点点点 |
3、数据库操作
(1)、显示数据
|
1
|
SHOW DATABASES; |
默认数据库:
mysql - 用户权限相关数据
test - 用于用户测试数据
information_schema - MySQL本身架构相关数据
(2)、使用数据库
|
1
|
USE db_name; |
(3)、显示所有表
|
1
|
SHOW TABLES; |
(4)、用户授权
用户管理:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
创建用户 create user \'用户名\'@\'IP地址\' identified by \'密码\';删除用户 drop user \'用户名\'@\'IP地址\';修改用户 rename user \'用户名\'@\'IP地址\'; to \'新用户名\'@\'IP地址\';;修改密码 set password for \'用户名\'@\'IP地址\' = Password(\'新密码\') PS:用户权限相关数据保存在mysql数据库的user表中,所以也可以直接对其进行操作(不建议) |
授权管理:
|
1
2
3
|
show grants for \'用户\'@\'IP地址\' -- 查看权限grant 权限 on 数据库.表 to \'用户\'@\'IP地址\' identified by \'密码\' -- 授权并创建密码revoke 权限 on 数据库.表 from \'用户\'@\'IP地址\' -- 取消权限 |
-->有哪些权限:
 View Code
View Code-->数据库范围:
对于目标数据库以及内部其他:
数据库名.* 数据库中的所有
数据库名.表 指定数据库中的某张表
数据库名.存储过程 指定数据库中的存储过程
*.* 所有数据库
-->用户范围:
用户名@IP地址 用户只能在改IP下才能访问 用户名@192.168.1.% 用户只能在改IP段下才能访问(通配符%表示任意) 用户名@% 用户可以再任意IP下访问(默认IP地址为%)
4、表操作
(1)、创建表
|
1
2
3
4
|
create table 表名( 列名 类型 是否可以为空, 列名 类型 是否可以为空) |
约束(1)是否可空null
是否可空,null表示空,非字符串
not null - 不可空
null - 可空
约束(2)默认值default
默认值,创建列时可以指定默认值,当插入数据时如果未主动设置,则自动添加默认值
create table tb1(
nid int not null defalut 2,
num int not null
)
约束(3)自增auto_increment
自增,如果为某列设置自增列,插入数据时无需设置此列,默认将自增(表中只能有一个自增列)
create table tb1(
nid int not null auto_increment primary key,
num int null
)
或
create table tb1(
nid int not null auto_increment,
num int null,
index(nid)
)
注意:1、对于自增列,必须是索引(含主键)。
2、对于自增可以设置步长和起始值
show session variables like \'auto_inc%\';
set session auto_increment_increment=2;
set session auto_increment_offset=10;
shwo global variables like \'auto_inc%\';
set global auto_increment_increment=2;
set global auto_increment_offset=10;
约束(4)主键primary key
主键,一种特殊的唯一索引,不允许有空值,如果主键使用单个列,则它的值必须唯一,如果是多列,则其组合必须唯一。
create table tb1(
nid int not null auto_increment primary key,
num int null
)
或
create table tb1(
nid int not null,
num int not null,
primary key(nid,num)
)
约束(5)唯一键unique key
create table tb1(
nid int not null auto_increment primary key,
num int null unique key,
)
约束(6)外键foreign key
外键,一个特殊的索引,只能是指定内容
creat table color(
nid int not null primary key,
name char(16) not null
)
create table fruit(
nid int not null primary key,
smt char(32) null ,
color_id int not null,
constraint fk_cc foreign key (color_id) references color(nid)
)
(2)、删除表
|
1
|
drop table 表名 |
(3)、清空表
|
1
2
|
delete from 表名truncate table 表名 # 和上面的区别在于,这条语句能够使自增id恢复到0 |
(4)、修改表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
添加列:alter table 表名 add 列名 类型删除列:alter table 表名 drop column 列名修改列: alter table 表名 modify column 列名 类型; -- 类型 alter table 表名 change 原列名 新列名 类型; -- 列名,类型 添加主键: alter table 表名 add primary key(列名);删除主键: alter table 表名 drop primary key; alter table 表名 modify 列名 int, drop primary key; 添加外键:alter table 从表 add constraint 外键名称(形如:FK_从表_主表) foreign key 从表(外键字段) references 主表(主键字段);删除外键:alter table 表名 drop foreign key 外键名称 修改默认值:ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl ALTER i SET DEFAULT 1000;删除默认值:ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl ALTER i DROP DEFAULT; |
(5)、基本数据类型
MySQL的数据类型大致分为:数值、时间和字符串
http://www.runoob.com/mysql/mysql-data-types.html
五、基本操作
1、增加数据
insert into 表 (列名,列名...) values (值,值,值...) insert into 表 (列名,列名...) values (值,值,值...),(值,值,值...) insert into 表 (列名,列名...) select (列名,列名...) from 表
2、删除数据
delete from 表 delete from 表 where id=1 and name=\'alex\'
3、修改数据
update 表 set name = \'alex\' where id>1
4、查询数据
select * from 表 select * from 表 where id > 1 select nid,name,gender as gg from 表 where id > 1
5、其他
 View Code
View Code六、视图
视图是一个虚拟表(非真实存在),其本质是【根据SQL语句获取动态的数据集,并为其命名】,用户使用时只需使用【名称】即可获取结果集,并可以将其当作表来使用。
 临时表搜索
临时表搜索1、创建视图
 View Code
View Code2、删除视图
 View Code
View Code3、修改视图
 View Code
View Code4、使用视图
使用视图时,将其当作表进行操作即可,由于视图是虚拟表,所以无法使用其对真实表进行创建、更新和删除操作,仅能做查询用。
 View Code
View Code七、触发器
对某个表进行【增/删/改】操作的前后如果希望触发某个特定的行为时,可以使用触发器,触发器用于定制用户对表的行进行【增/删/改】前后的行为。
1、创建基本语法
 View Code
View Code 插入前触发器
插入前触发器 插入后触发器
插入后触发器特别的:NEW表示即将插入的数据行,OLD表示即将删除的数据行。
2、删除触发器
DROP TRIGGER tri_after_insert_tb1;
3、使用触发器
触发器无法由用户直接调用,而知由于对表的【增/删/改】操作被动引发的。
insert into tb1(num) values(666)
八、存储过程
存储过程是一个SQL语句集合,当主动去调用存储过程时,其中内部的SQL语句会按照逻辑执行。
1、创建存储过程和执行过程
 View Code
View Code对于存储过程,可以接收参数,其参数有三类:
- in 仅用于传入参数用
- out 仅用于返回值用
- inout 既可以传入又可以当作返回值
 有参数的存储过程
有参数的存储过程2、删除存储过程
drop procedure proc_name;
3、执行存储过程
-- 无参数 call proc_name() -- 有参数,全in call proc_name(1,2) -- 有参数,有in,out,inout DECLARE @t1 INT; DECLARE @t2 INT default 3; call proc_name(1,2,@t1,@t2)
 pymysql执行存储过程
pymysql执行存储过程九、函数
MySQL中提供了许多内置函数,例如:
 部分内置函数
部分内置函数更多:
http://doc.mysql.cn/mysql5/refman-5.1-zh.html-chapter/functions.html#encryption-functions
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/string-functions.html
1、自定义函数
 View Code
View Code2、删除函数
drop function func_name;
3、执行函数
 View Code
View Code十、索引
事务用于将某些操作的多个SQL作为原子性操作,一旦有某一个出现错误,即可回滚到原来的状态,从而保证数据库数据完整性。
 支持事务的存储过程
支持事务的存储过程 执行存储过程
执行存储过程十一、索引
索引,是数据库中专门用于帮助用户快速查询数据的一种数据结构。类似于字典中的目录,查找字典内容时可以根据目录查找到数据的存放位置,然后直接获取即可。
MySQL中常见索引有:
- 普通索引
- 唯一索引
- 主键索引
- 组合索引
1、普通索引
普通索引仅有一个功能:加速查询
 创建表+索引
创建表+索引 创建索引
创建索引 删除索引
删除索引 查看索引
查看索引注意:对于创建索引时如果是BLOB 和 TEXT 类型,必须指定length。
 View Code
View Code2、唯一索引
唯一索引有两个功能:加速查询 和 唯一约束(可含null)
 创建表+索引
创建表+索引 创建唯一键索引
创建唯一键索引 删除唯一键索引
删除唯一键索引3、主键索引
主键有两个功能:加速查询 和 唯一约束(不可含null)
 创建表+主键索引
创建表+主键索引 创建主键
创建主键 删除主键
删除主键4、组合索引
组合索引是将n个列组合成一个索引
其应用场景为:频繁的同时使用n列来进行查询,如:where n1 = \'redhat\' and n2 = 666。
 创建表
创建表 创建组合索引
创建组合索引如上创建组合索引之后,查询:
- name and email -- 使用索引
- name -- 使用索引
- email -- 不使用索引
注意:对于同时搜索n个条件时,组合索引的性能好于多个单一索引合并。
其他
1、条件语句
 View Code
View Code2、循环语句
 while循环
while循环 repeat循环
repeat循环 loop循环
loop循环3、动态执行SQL语句
 View Code
View Code二、pymsql模块
pymsql是Python中操作MySQL的模块,其使用方法和MySQLdb几乎相同。这里介绍pymysql
一、下载安装:
|
1
|
pip install pymysql |
二、使用
# 先往数据库插入点数据
mysql> CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS testdb DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
mysql> use testdb;
mysql> CREATE TABLE hosts (id int not null auto_increment primary key,ip varchar(20) not null,port int not null);
mysql> INSERT INTO hosts (ip,port) values
(\'1.1.1.1\',22),(\'1.1.1.2\',22),
(\'1.1.1.3\',22),(\'1.1.1.4\',22),
(\'1.1.1.5\',22);
1、执行SQL
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import pymysql# 创建连接conn = pymysql.connect(host=\'127.0.0.1\', port=3306, user=\'root\', passwd=\'123456\', db=\'testdb\', charset=\'utf8\')# 创建游标cursor = conn.cursor()# 执行SQL,并返回收影响行数r = effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set ip = \'1.1.1.2\'")print(r)# 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set ip = \'1.1.1.6\' where id > %s", (6,))# 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数effect_row = cursor.executemany("insert into hosts(ip,port) values(%s,%s)", [("1.1.1.7",21),("1.1.1.8",23)])# 提交,不然无法保存新建或者修改的数据conn.commit()# 关闭游标cursor.close()# 关闭连接conn.close() |
2、获取新创建数据自增ID
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import pymysqlconn = pymysql.connect(host=\'127.0.0.1\', port=3306, user=\'root\', passwd=\'123456\', db=\'testdb\')cursor = conn.cursor()cursor.executemany("insert into hosts(ip,port) values(%s,%s)", [("1.1.1.9",21),("1.1.1.10",222)])conn.commit()cursor.close()conn.close()# 获取最新自增IDnew_id = cursor.lastrowidprint(new_id)<br><br># 获取当前行行号<br>current_row = cursor.rownumber<br>print(current_row) |
3、获取查询数据
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import pymysqlconn = pymysql.connect(host=\'127.0.0.1\', port=3306, user=\'root\', passwd=\'123456\', db=\'testdb\')cursor = conn.cursor()cursor.execute("select * from hosts")# 获取第一行数据row = cursor.fetchone()print(row)print(cursor.rownumber)# 获取第二行数据row_1 = cursor.fetchone()print(row_1)print(cursor.rownumber)# 获取前n行数据row_2 = cursor.fetchmany(3)print(row_2)# 获取所有数据row_3 = cursor.fetchall()print(row_3)conn.commit()cursor.close()conn.close() |
注:在fetch数据时按照顺序进行,可以使用cursor.scroll(num,mode)来移动游标位置,如:
- cursor.scroll(1,mode=\'relative\') # 相对当前位置移动
- cursor.scroll(2,mode=\'absolute\') # 相对绝对位置移动
4、fetch数据类型
关于默认获取的数据是元祖类型,如果想要或者字典类型的数据,即:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-import pymysqlconn = pymysql.connect(host=\'127.0.0.1\', port=3306, user=\'root\', passwd=\'123456\', db=\'testdb\')# 游标设置为字典类型cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)r = cursor.execute("select * from hosts")print(r)result = cursor.fetchone()print(result)conn.commit()cursor.close()conn.close() |
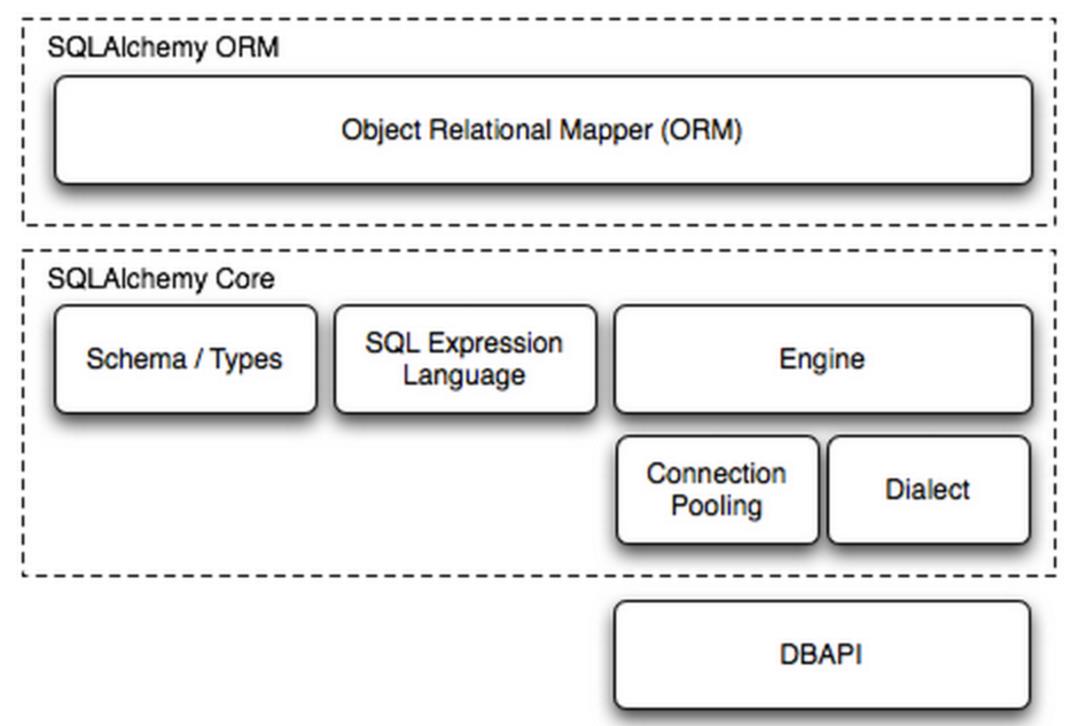
三、SQLAchemy
SQLAlchemy是Python编程语言下的一款ORM框架,该框架建立在数据库API之上,使用关系对象映射进行数据库操作,简言之便是:将对象转换成SQL,然后使用数据API执行SQL并获取执行结果。
SQLAlchemy安装
|
1
|
pip install sqlalchemy |
SQLAlchemy本身无法操作数据库,其必须以来pymsql等第三方插件,Dialect用于和数据API进行交流,根据配置文件的不同调用不同的数据库API,从而实现对数据库的操作,如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
MySQL-Python mysql+mysqldb://<user>:<password>@<host>[:<port>]/<dbname> pymysql mysql+pymysql://<username>:<password>@<host>/<dbname>[?<options>] MySQL-Connector mysql+mysqlconnector://<user>:<password>@<host>[:<port>]/<dbname> cx_Oracle oracle+cx_oracle://user:pass@host:port/dbname[?key=value&key=value...] 更多详见:http://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/latest/dialects/index.html |
一、底层处理
使用 Engine/ConnectionPooling/Dialect 进行数据库操作,Engine使用ConnectionPooling连接数据库,然后再通过Dialect执行SQL语句。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
以上是关于python教程18python操作Mysql,pymysql,SQLAchemy的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
|
