Python基于皮尔逊系数实现股票预测(多线程)
Posted 云山之巅
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python基于皮尔逊系数实现股票预测(多线程)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 """ 3 Created on Tue Dec 4 08:53:08 2018 4 5 @author: zhen 6 """ 7 from dtw import fastdtw 8 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 9 import numpy as np 10 import pandas as pd 11 import threading 12 import time 13 from datetime import datetime 14 15 def normalization(x): # np.std:计算矩阵的标准差(方差的算术平方根) 16 return (x - np.mean(x)) / np.std(x) 17 18 def corrcoef(a,b): 19 corrc = np.corrcoef(a,b) # 计算皮尔逊相关系数,用于度量两个变量之间的相关性,其值介于-1到1之间 20 corrc = corrc[0,1] 21 return (16 * ((1 - corrc) / (1 + corrc)) ** 1) # ** 表示乘方 22 23 startTimeStamp = datetime.now() # 获取当前时间 24 # 加载数据 25 filename = \'C:/Users/zhen/.spyder-py3/sh000300_2017.csv\' 26 # 获取第一,二列的数据 27 all_date = pd.read_csv(filename,usecols=[0, 1], dtype = \'str\') 28 all_date = np.array(all_date) 29 data = all_date[:, 0] 30 times = all_date[:, 1] 31 32 data_points = pd.read_csv(filename,usecols=[3]) 33 data_points = np.array(data_points) 34 data_points = data_points[:,0] #数据 35 36 topk = 10 #只显示top-10 37 baselen = 100 # 假设在50到150之间变化 38 basebegin = 365 39 basedata = data[basebegin]+\' \'+times[basebegin]+\'~\'+data[basebegin+baselen-1]+\' \'+times[basebegin+baselen-1] 40 length = len(data_points) #数据长度 41 42 # 定义自定义线程类 43 class Thread_Local(threading.Thread): 44 def __init__(self, thread_id, name, counter): 45 threading.Thread.__init__(self) 46 self.thread_id = thread_id 47 self.name = name 48 self.counter = counter 49 self.__running = threading.Event() # 标识停止线程 50 self.__running.set() # 设置为True 51 52 def run(self): 53 print("starting %s" % self.name) 54 split_data(self, self.counter) # 执行代码逻辑 55 56 def stop(self): 57 self.__running.clear() 58 59 # 分割片段并执行匹配,多线程 60 def split_data(self, split_len): 61 base = data_points[basebegin:basebegin+split_len] # 获取初始要匹配的数据 62 subseries = [] 63 dateseries = [] 64 for j in range(0, length): 65 if (j < (basebegin - split_len) or j > (basebegin + split_len - 1)) and j <length - split_len: 66 subseries.append(data_points[j:j+split_len]) 67 dateseries.append(j) #开始位置 68 search(self, subseries, base, dateseries) # 调用模式匹配 69 70 # 定义结果变量 71 result = [] 72 base_list = [] 73 date_list = [] 74 def search(self, subseries, base, dateseries): 75 # 片段搜索 76 listdistance = [] 77 for i in range(0, len(subseries)): 78 tt = np.array(subseries[i]) 79 # dist, cost, acc, path = fastdtw(base, tt, dist=\'euclidean\') 80 # listdistance.append(dist) 81 distance = corrcoef(base, tt) 82 listdistance.append(distance) 83 # 排序 84 index = np.argsort(listdistance, kind=\'quicksort\') #排序,返回排序后的索引序列 85 result.append(subseries[index[0]]) 86 print("result length is %d" % len(result)) 87 base_list.append(base) 88 date_list.append(dateseries[index[0]]) 89 # 关闭线程 90 self.stop() 91 92 # 变换数据(收缩或扩展),生成50到150之间的数据,间隔为10 93 loc = 0 94 for split_len in range(round(0.5 * baselen), round(1.5 * baselen), 10): 95 # 执行匹配 96 thread = Thread_Local(1, "Thread" + str(loc), split_len) 97 loc += 1 98 # 开启线程 99 thread.start() 100 101 boo = 1 102 103 while(boo > 0): 104 if(len(result) < 10): 105 if(boo % 100 == 0): 106 print("has running %d s" % boo) 107 boo += 1 108 time.sleep(1) 109 else: 110 boo = 0 111 112 # 片段搜索 113 listdistance = [] 114 for i in range(0, len(result)): 115 tt = np.array(result[i]) 116 distance = corrcoef(base_list[i], tt) 117 listdistance.append(distance) 118 # 最终排序 119 index = np.argsort(listdistance, kind=\'quicksort\') #排序,返回排序后的索引序列 120 print("closed Main Thread") 121 endTimeStamp = datetime.now() 122 # 结果集对比 123 plt.figure(0) 124 plt.plot(normalization(base_list[index[0]]),label= basedata,linewidth=\'2\') 125 length = len(result[index[0]]) 126 begin = data[date_list[index[0]]] + \' \' + times[date_list[index[0]]] 127 end = data[date_list[index[0]] + length - 1] + \' \' + times[date_list[index[0]] + length - 1] 128 label = begin + \'~\' + end 129 plt.plot(normalization(result[index[0]]), label=label, linewidth=\'2\') 130 plt.legend(loc=\'upper left\') 131 plt.title(\'normal similarity search\') 132 plt.show() 133 print(\'run time\', (endTimeStamp-startTimeStamp).seconds, "s")
结果:
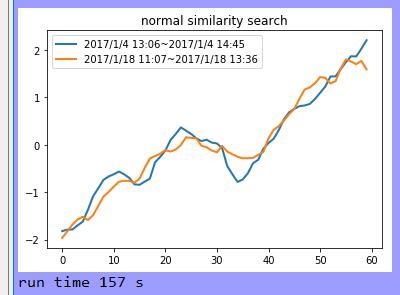
分析:
皮尔逊相关系数(corrcoef)运算速度远超DTW或FASTDTW,但DTW或FASTDTW应用范围更广,适用于等长或变长的比较。
以上是关于Python基于皮尔逊系数实现股票预测(多线程)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章