基于matlab的归一化阵列响应幅值极坐标图仿真,对比四阵元,八阵元以及十六阵元
Posted 51matlab
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于matlab的归一化阵列响应幅值极坐标图仿真,对比四阵元,八阵元以及十六阵元相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.算法仿真效果
matlab2022a仿真结果如下:
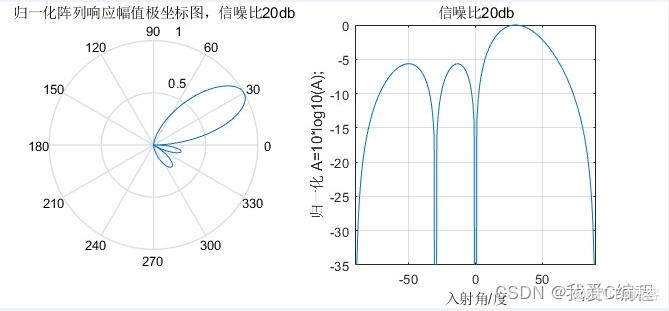
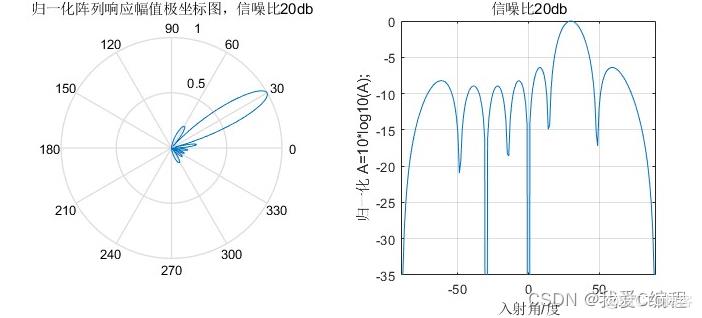
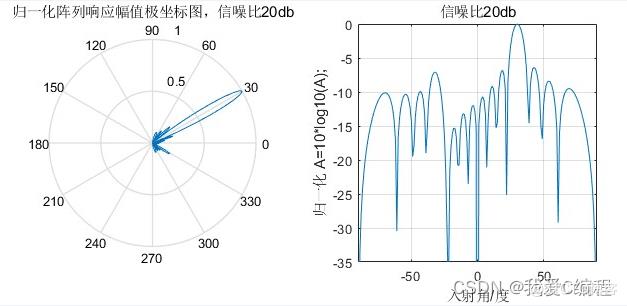
2.算法涉及理论知识概要
直线阵:由N个相同的单元天线等间距地排列在一条直线上构成。均匀直线阵:若各单元上的馈电电流大小相同,而相位沿线均匀递增或递减,这样的直线阵称为均匀直线阵。
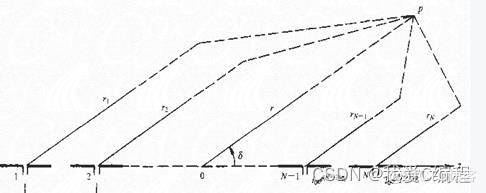

3.MATLAB核心程序
m=4 ;% array阵元 p=4; % signal number信号数 N=3000;% recursive number 迭代次数 或快拍数 A=zeros(m,p); % array pattern阵列流型 theta=[30 0 -45 60]*pi/180;% the signal from the direction of 30 degree is expected. DOA 30为期望信号方向 j=sqrt(-1); w=[0.01 0.2 0.3 0.4]*pi; % frequency for each signal.各个信号的数字频率 %% s=to_get_s(w,N,p); s_rec=get_s_rec(s,m,p,theta); S=s_rec; % output date matrix .m*N 的阵元输出数据矩阵 %%%%——————————————%% 自适应调节权 y=S;% input data of GSC; ad=exp(-j*pi*[0:m-1]\'*sin(theta(1))) %steering vector in the direction of expected. 期望信号方向导向矢量 c=10;% condition 波束形成条件 C=ad\'; Wc=C\'*inv(C*C\')*c; %main path weight 主通道固定权 wa(1:m-1,1)=0; % auxiliary path 辅助通道自适应权 B=get_B(m,theta); % get Block Matrix 得到阻塞矩阵 u=0.000001; ................................................................. %%%%------------ %%%main path 主通道 wop=Wc; drawpp(m,wop); %%%%auxiliary path 辅助通道 wop=B\'*wa(:,N) drawpp(m,wop); %%array response 总的阵列响应 wop=Wc-B\'*wa(:,N); drawpp(m,wop);
在多显示器环境中计算 SendInput() 的归一化坐标
【中文标题】在多显示器环境中计算 SendInput() 的归一化坐标【英文标题】:Calculate normalized coordinates for SendInput() in a multi-monitor environment 【发布时间】:2020-07-06 15:15:40 【问题描述】:我想以编程方式将鼠标输入发送到我连接的任何显示器。
我知道我可以使用 SendInput 函数来执行此操作,但我目前的方法不适用于多显示器设置。
我正在使用以下方法:
-
获取点击点相对于当前屏幕的像素坐标;
使用 GetMonitorInfoW 函数和适当的 HMONITOR 句柄获取当前屏幕左上角像素的像素坐标;
获取相对于整个虚拟屏幕的像素坐标:为此,我们将当前屏幕边缘的坐标(左上角像素)与点击点的坐标相加;
将生成的像素坐标转换为绝对坐标 (0-65535),供 SendInput 函数使用;
将SendInput 函数与MOUSEEVENTF_ABSOLUTE 一起使用| MOUSEEVENTF_VIRTUALDESK 标志和相对于整个虚拟桌面的绝对坐标。
但是,在我当前的代码中,鼠标输入的位置错误。 我对如何正确计算绝对坐标感到困惑。
目前,我确实使用another question 上讨论的公式检索绝对坐标。 要获取虚拟屏幕的宽度/高度,我使用GetSystemMetrics 和 SM_CXVIRTUALSCREEN/SM_CYVIRTUALSCREEN 参数。
// ________________________________________________
//
// GetAbsoluteCoordinate
//
// PURPOSE:
// Convert pixel coordinate to absolute coordinate (0-65535).
//
// RETURN VALUE:
// Absolute Coordinate
// ________________________________________________
//
UINT16 GetAbsoluteCoordinate(INT PixelCoordinate, INT ScreenResolution)
UINT16 AbsoluteCoordinate = ( (65536 * PixelCoordinate) / ScreenResolution ) + 1;
return AbsoluteCoordinate;
// ________________________________________________
//
// GetAbsoluteCoordinates
//
// PURPOSE:
// Retrieve virtual screen absolute coordinates from pixel coordinates.
//
// PARAMETERS:
// x, y coordinates passed by reference. These will be changed by the function and used as return values.
//
// RETURN VALUE:
// None (see parameters)
// ________________________________________________
//
void GetAbsoluteCoordinates(INT32 &X, INT32 &Y)
// Get multi-screen coordinates
MONITORINFO MonitorInfo = 0 ;
MonitorInfo.cbSize = sizeof(MonitorInfo);
if (GetMonitorInfoW(hMonitor, &MonitorInfo))
// 1) Get pixel coordinates of topleft pixel of target screen, relative to the virtual desktop ( coordinates should be 0,0 on Main screen);
// 2) Get pixel coordinates of mouse cursor, relative to the target screen;
// 3) Sum topleft margin pixel coordinates with mouse cursor coordinates;
X = MonitorInfo.rcMonitor.left + X;
Y = MonitorInfo.rcMonitor.top + Y;
// 4) Transform the resulting pixel coordinates into absolute coordinates.
X = GetAbsoluteCoordinate(X, GetSystemMetrics(SM_CXVIRTUALSCREEN));
Y = GetAbsoluteCoordinate(Y, GetSystemMetrics(SM_CYVIRTUALSCREEN));
// ________________________________________________
//
// SendMouseInput
//
// PURPOSE:
// Send mouse input, supporting any of the connected displays
//
// PARAMETERS:
// X, Y are pixel coordinates, relative to the current screen.
// ________________________________________________
//
void SendMouseInput(INT X, INT Y)
INPUT Input;
GetAbsoluteCoordinates(X, Y);
memset(&Input, 0, sizeof(INPUT));
Input.type = INPUT_MOUSE;
Input.mi.dx = X;
Input.mi.dy = Y;
Input.mi.dwFlags = MOUSEEVENTF_ABSOLUTE | MOUSEEVENTF_VIRTUALDESK | MOUSEEVENTF_MOVE | MOUSEEVENTF_LEFTDOWN;
SendInput(1, &Input, sizeof(Input));
【问题讨论】:
【参考方案1】:获取相对于整个虚拟屏幕的像素坐标:to do 这个,我们将当前屏幕边距的坐标相加(topleft pixel) 与要点击的点的坐标;
看起来您正在使用相对于监视器的坐标 (X,Y)。你是怎么得到坐标的?
如果是这样,那么样品基本没有问题。如果你的鼠标坐标是通过类似于GetCursorPos的东西得到的,那么你就不需要计算相对于虚拟屏幕的坐标了(是的)。
该示例几乎对我有用,我更改了一些代码如下:
#include <windows.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// ________________________________________________
//
// GetAbsoluteCoordinate
//
// PURPOSE:
// Convert pixel coordinate to absolute coordinate (0-65535).
//
// RETURN VALUE:
// Absolute Coordinate
// ________________________________________________
//
INT GetAbsoluteCoordinate(INT PixelCoordinate, INT ScreenResolution)
INT AbsoluteCoordinate = MulDiv(PixelCoordinate, 65535, ScreenResolution);
return AbsoluteCoordinate;
void GetAbsoluteCoordinates(HMONITOR hMonitor, INT32& X, INT32& Y)
// Get multi-screen coordinates
MONITORINFO MonitorInfo = 0 ;
MonitorInfo.cbSize = sizeof(MonitorInfo);
if (GetMonitorInfoW(hMonitor, &MonitorInfo))
// 1) Get pixel coordinates of topleft pixel of target screen, relative to the virtual desktop ( coordinates should be 0,0 on Main screen);
// 2) Get pixel coordinates of mouse cursor, relative to the target screen;
// 3) Sum topleft margin pixel coordinates with mouse cursor coordinates;
X = MonitorInfo.rcMonitor.left + X;
Y = MonitorInfo.rcMonitor.top + Y;
// 4) Transform the resulting pixel coordinates into absolute coordinates.
X = GetAbsoluteCoordinate(X, GetSystemMetrics(SM_CXVIRTUALSCREEN));
Y = GetAbsoluteCoordinate(Y, GetSystemMetrics(SM_CYVIRTUALSCREEN));
void SendMouseInput(HMONITOR hMonitor, INT X, INT Y)
INPUT Input[2];
GetAbsoluteCoordinates(hMonitor, X, Y);
memset(Input, 0, sizeof(INPUT));
Input[0].type = Input[1].type = INPUT_MOUSE;
Input[0].mi.dx = Input[1].mi.dx = X;
Input[0].mi.dy = Input[1].mi.dy = Y;
Input[0].mi.dwFlags = MOUSEEVENTF_ABSOLUTE | MOUSEEVENTF_LEFTDOWN | MOUSEEVENTF_MOVE | MOUSEEVENTF_VIRTUALDESK;
Input[1].mi.dwFlags = MOUSEEVENTF_ABSOLUTE | MOUSEEVENTF_LEFTUP | MOUSEEVENTF_MOVE | MOUSEEVENTF_VIRTUALDESK;
SendInput(2, Input, sizeof(INPUT));
BOOL CALLBACK Monitorenumproc(
HMONITOR Arg1,
HDC Arg2,
LPRECT Arg3,
LPARAM Arg4)
SendMouseInput(Arg1, 725, 85);
return TRUE;
int main(void)
EnumDisplayMonitors(NULL,NULL, Monitorenumproc,0);
return 0;
结果:
我有 2 台具有相同显示分辨率 (1920 x 1080) 的显示器进行测试,例如:
示例将在每个监视器上的相同位置单击。
延伸阅读:The Virtual Screen
【讨论】:
错误确实在于我在转换像素坐标之前如何获取它们。感谢您提供代码示例,它有助于解决问题。以上是关于基于matlab的归一化阵列响应幅值极坐标图仿真,对比四阵元,八阵元以及十六阵元的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章