Python交互图表可视化Bokeh:4. 折线图| 面积图
Posted kris12
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python交互图表可视化Bokeh:4. 折线图| 面积图相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
折线图与面积图
① 单线图、多线图
② 面积图、堆叠面积图
1. 折线图--单线图
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt % matplotlib inline import warnings warnings.filterwarnings(\'ignore\') # 不发出警告 from bokeh.io import output_notebook output_notebook() # 导入notebook绘图模块 from bokeh.plotting import figure,show # 导入图表绘制、图标展示模块

source = ColumnDataSource(data = df) 这里df中index、columns都必须有名称字段
p.line(x=\'index\',y=\'value\',source = source, line_width=1, line_alpha = 0.8, line_color = \'black\',line_dash = [10,4])
# 绘制折线图
p.circle(x=\'index\',y=\'value\',source = source, size = 2,color = \'red\',alpha = 0.8) # 绘制折点
# 1、折线图 - 单线图 from bokeh.models import ColumnDataSource # 导入ColumnDataSource模块 # 将数据存储为ColumnDataSource对象 # 参考文档:http://bokeh.pydata.org/en/latest/docs/user_guide/data.html # 可以将dict、Dataframe、group对象转化为ColumnDataSource对象 df = pd.DataFrame({\'value\':np.random.randn(100).cumsum()}) # 创建数据 df.index.name = \'index\' source = ColumnDataSource(data = df) # 转化为ColumnDataSource对象 # 这里注意了,index和columns都必须有名称字段 p = figure(plot_width=600, plot_height=400) p.line(x=\'index\',y=\'value\',source = source, # 设置x,y值, source → 数据源 line_width=1, line_alpha = 0.8, line_color = \'black\',line_dash = [10,4]) # 线型基本设置 # 绘制折线图 p.circle(x=\'index\',y=\'value\',source = source, size = 2,color = \'red\',alpha = 0.8) # 绘制折点 show(p) df.head()


可以将dict、Dataframe、group对象转化为ColumnDataSource对象
dic = {\'index\':df.index.tolist(), \'value\':df[\'value\'].tolist()} #一般把它先变成字典的格式
source = ColumnDataSource(data=dic)
#不转换为字典也可以,把index提取出来df.index.name = \'a\' --->>> source = ColumnDataSource(data = df)
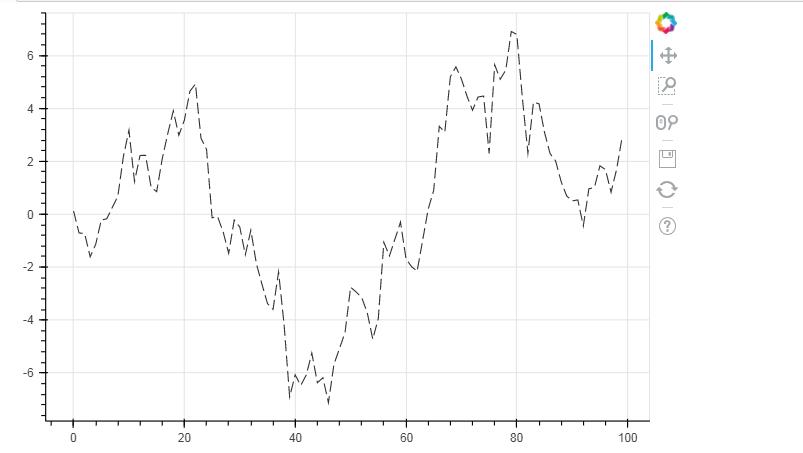
from bokeh.models import ColumnDataSource # 导入ColumnDataSource模块 # 将数据存储为ColumnDataSource对象 # 参考文档:http://bokeh.pydata.org/en/latest/docs/user_guide/data.html # 可以将dict、Dataframe、group对象转化为ColumnDataSource对象 dic = {\'index\':df.index.tolist(), \'value\':df[\'value\'].tolist()} #一般把它先变成字典的格式 source = ColumnDataSource(data=dic) print(source) p = figure(plot_width=600, plot_height=400) p.line(x=\'index\',y=\'value\',source = source, # 设置x,y值, source → 数据源 line_width=1, line_alpha = 0.8, line_color = \'black\',line_dash = [10,4]) # 线型基本设置 # 绘制折线图 show(p)
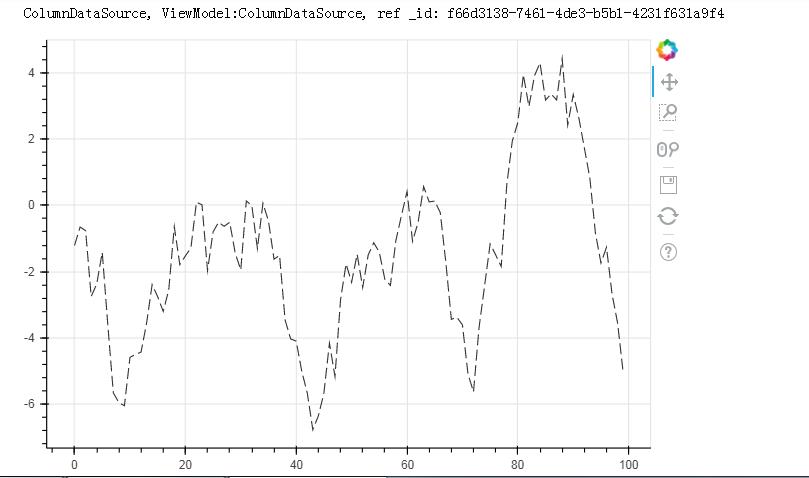
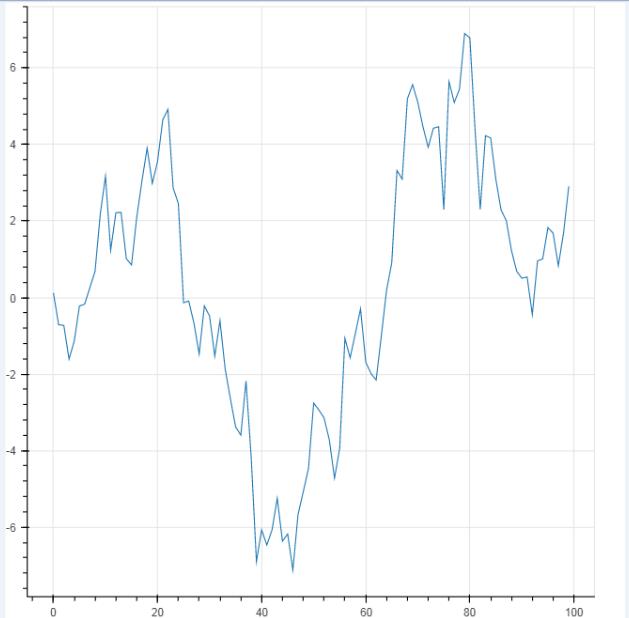
df.index.name = \'a\' #不转换为字典也可以,把index提取出来 source = ColumnDataSource(data = df) p = figure(plot_width=600, plot_height=400) p.line(x=\'a\',y=\'value\',source = source, # 设置x,y值, source → 数据源 line_width=1, line_alpha = 0.8, line_color = \'black\',line_dash = [10,4]) # 线型基本设置 # 绘制折线图 show(p)
df.index.name = \'a\' source = ColumnDataSource(data = df) p = figure() p.line(x=\'a\',y=\'value\',source = source) # 设置x,y值, source → 数据源 show(p)
2. 折线图--多线图
① multi_line
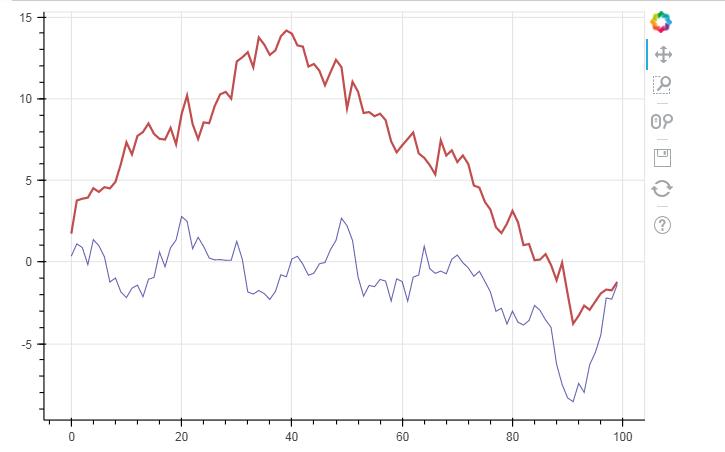
p.multi_line([df.index, df.index], [df[\'A\'], df[\'B\']], color=["firebrick", "navy"], alpha=[0.8, 0.6], line_width=[2,1],)
# 2、折线图 - 多线图 # ① multi_line df = pd.DataFrame({\'A\':np.random.randn(100).cumsum(),"B":np.random.randn(100).cumsum()}) # 创建数据 p = figure(plot_width=600, plot_height=400) p.multi_line([df.index, df.index], #第一条线的横坐标和第二条线的横坐标 [df[\'A\'], df[\'B\']], # 注意x,y值的设置 → [x1,x2,x3,..], [y1,y2,y3,...] 第一条线的Y值和第二条线的Y值 color=["firebrick", "navy"], # 可同时设置 → color= "firebrick";也可以统一弄成一个颜色。 alpha=[0.8, 0.6], # 可同时设置 → alpha = 0.6 line_width=[2,1], # 可同时设置 → line_width = 2 ) # 绘制多段线 # 这里由于需要输入具体值,故直接用dataframe,或者dict即可 show(p)
② 多个line
p.line(x, 10**(x**2), legend="y=10^(x^2)",line_color="coral", line_dash="dashed", line_width=2)
# 2、折线图 - 多线图 # ② 多个line x = np.linspace(0.1, 5, 100) # 创建x值 p = figure(title="log axis example", y_axis_type="log",y_range=(0.001, 10**22)) # 这里设置对数坐标轴 p.line(x, np.sqrt(x), legend="y=sqrt(x)", line_color="tomato", line_dash="dotdash") # line1 p.line(x, x, legend="y=x") p.circle(x, x, legend="y=x") # line2,折线图+散点图 p.line(x, x**2, legend="y=x**2") p.circle(x, x**2, legend="y=x**2",fill_color=None, line_color="olivedrab") # line3 p.line(x, 10**x, legend="y=10^x",line_color="gold", line_width=2) # line4 p.line(x, x**x, legend="y=x^x",line_dash="dotted", line_color="indigo", line_width=2) # line5 p.line(x, 10**(x**2), legend="y=10^(x^2)",line_color="coral", line_dash="dashed", line_width=2) # line6 p.legend.location = "top_left" p.xaxis.axis_label = \'Domain\' p.yaxis.axis_label = \'Values (log scale)\' # 设置图例及label show(p)

3. 面积图
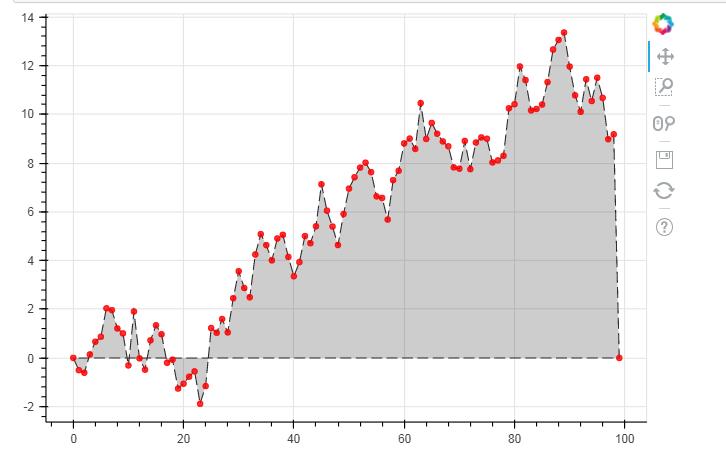
# 3、面积图 - 单维度面积图 s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(100).cumsum()) s.iloc[0] = 0 s.iloc[-1] = 0 # 创建数据 # 注意设定起始值和终点值为最低点 p = figure(plot_width=600, plot_height=400) p.patch(s.index, s.values, # 设置x,y值 line_width=1, line_alpha = 0.8, line_color = \'black\',line_dash = [10,4], # 线型基本设置 fill_color = \'black\',fill_alpha = 0.2 ) # 绘制面积图 # .patch将会把所有点连接成一个闭合面 show(p)
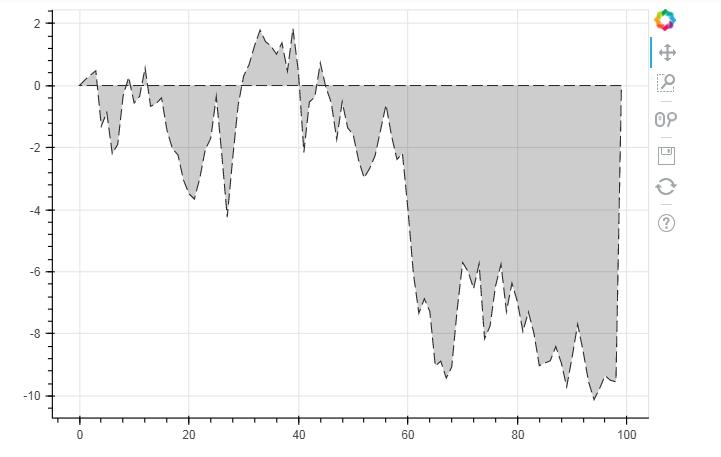
p.circle(s.index, s.values,size = 5,color = \'red\',alpha = 0.8) # 绘制折点
# 3、面积图 - 面积堆叠图 from bokeh.palettes import brewer # 导入brewer模块 N = 20 cats = 10 #分类 rng = np.random.RandomState(1) df = pd.DataFrame(rng.randint(10, 100, size=(N, cats))).add_prefix(\'y\') # 创建数据,shape为(20,10) df_top = df.cumsum(axis=1) # 每一个堆叠面积图的最高点 df_bottom = df_top.shift(axis=1).fillna({\'y0\': 0})[::-1] # 每一个堆叠面积图的最低点,并反向 df_stack = pd.concat([df_bottom, df_top], ignore_index=True) # 数据合并,每一组数据都是一个可以围合成一个面的散点集合 # 得到堆叠面积数据 # print(df.head()) # print(df_top.tail()) # print(df_bottom.head()) # df_stack colors = brewer[\'Spectral\'][df_stack.shape[1]] # 根据变量数拆分颜色 x = np.hstack((df.index[::-1], df.index)) # 得到围合顺序的index,这里由于一列是20个元素,所以连接成面需要40个点 print(x) p = figure(x_range=(0, N-1), y_range=(0, 700)) p.patches([x] * df_stack.shape[1], # 得到10组index [df_stack[c].values for c in df_stack], # c为df_stack的列名,这里得到10组对应的valyes color=colors, alpha=0.8, line_color=None) # 设置其他参数 show(p)
[19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19]

以上是关于Python交互图表可视化Bokeh:4. 折线图| 面积图的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章