Windows7 上运行docker实战
Posted Linux无限探索
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Windows7 上运行docker实战相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
| Docker 是一种容器技术,它可以将应用和环境等进行打包,形成一个独立的,类似于 iOS 的 APP 形式的「应用」,这个应用可以直接被分发到任意一个支持 Docker 的环境中,通过简单的命令即可启动运行, 是一种最流行的容器化实现方案。和虚拟化技术类似,它极大的方便了应用服务的部署。本文我们介绍如何在windows7上面安装使用docker。 |
安装包 https://github.com/boot2docker/windows-installer/releases(这个地址国内下载很慢)
用这个: https://get.daocloud.io/toolbox/
下载最新版本的:Docker-install.exe即可。
该安装包安装完成后,系统上会多出三个软件:
Oracle VM VirtualBox Git Boot2Docker for Windows
以上三个默认安装即可。
PS:windows必须是64位的
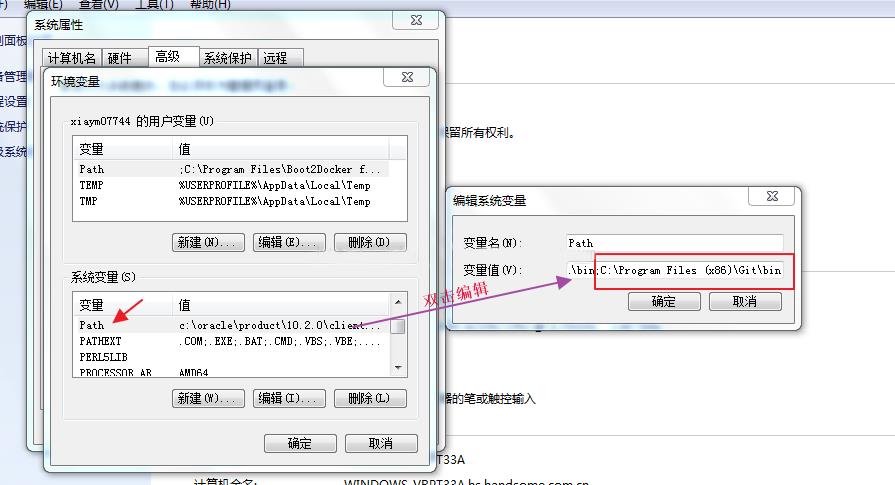
在命令窗口中,输入ls 如果能找到命令说明环境添加正确。
在命令窗口中,切到docker的安装目录下
输入sh:
然后输入start.sh,等待启动
第一次启动中,如果有新版本会更新,时间比较长。
如果第二次启动,就非常快了。
#!/bin/bashset -e
# clear the MSYS MOTD
clear
cd "$(dirname "$BASH_SOURCE")"
ISO="$HOME/.boot2docker/boot2docker.iso"
if [ ! -e "$ISO" ]; then
echo \'copying initial boot2docker.iso (run "boot2docker.exe download" to update)\'
mkdir -p "$(dirname "$ISO")"
cp ./boot2docker.iso "$ISO"fi
echo \'initializing...\'
./boot2docker.exe init
echo
echo \'starting...\'
./boot2docker.exe start
echo
./boot2docker.exe ip
echo \'connecting...\'
./boot2docker.exe ssh
echo
echoecho \'[Press any key to exit]\'read
从内容上看主要是执行,如下语句
boot2docker.exe init boot2docker.exe start boot2docker.exe ssh
所有在命令行下执行 sh start.sh 即可
在windows命令行进入docker后,不能复制,而且操作也不方便,因此用支持SSH的工具来管理是很好的,比如SECURECRT, PUTTY等,推荐用SECURECRT.
在命令行下用boot2docker ip 可以查询到IP


默认的用户名和密码是: docker/tcuser
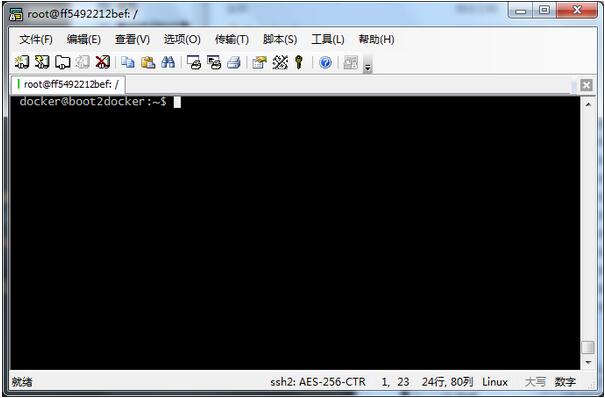
登录后的界面:
http://download.openvz.org/template/precreated
选择下载 ubuntu-14.04-x86_64.tar.gz
推荐使用:FileZilla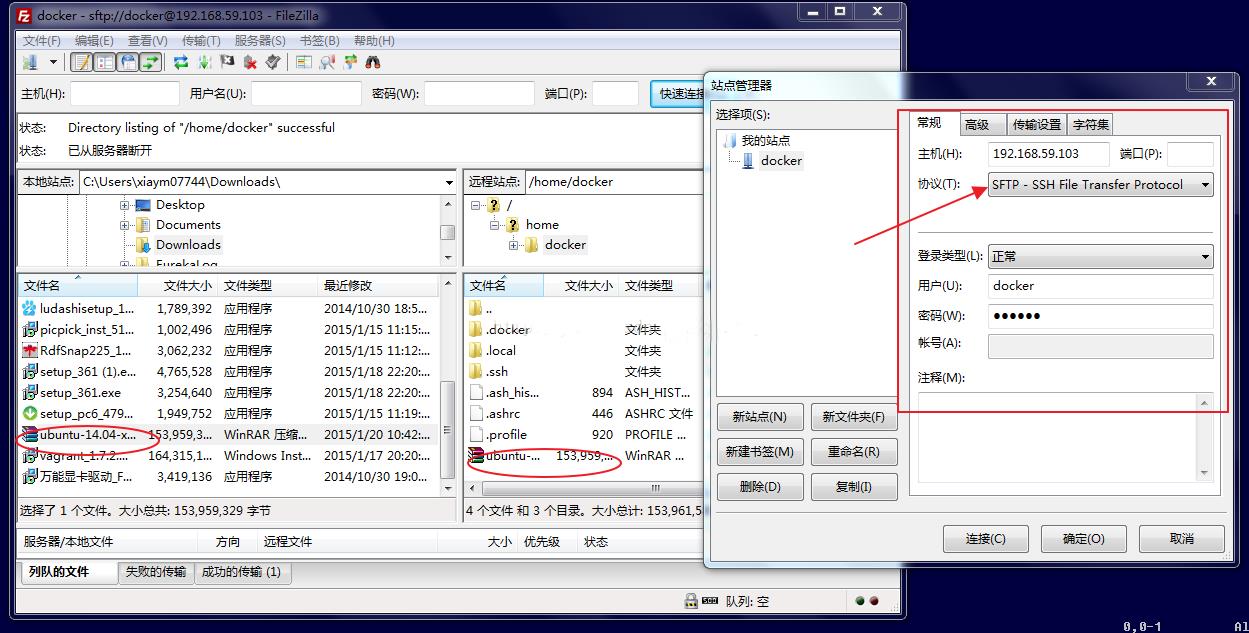
cat ubuntu-14.04-x86_64.tar.gz |docker import - ubuntu:ubuntu14
速度非常快,大概10几秒就完成了。
查看: docker images
docker run -i -t ubuntu:ubuntu14 /bin/bash

可以开始DOCKER旅行了。
原文来自:http://blog.csdn.net/zistxym/article/details/42918339作者:xiaym
本文来自博客园,作者:linux_pro,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/linuxpro/p/17392716.html
Ansible 实战:基于docker运行ansible
准备好安装了Ansible的主机,作为实验环境。有一台新安装的Centos7系统,利用ansible在主机上完成以下操作:
- 主机初始化设置,主要是yum
- 安装python3
- 安装docker,并且制作一个ansible的镜像
- SSH和用户账号安全设置
准备工作
准备好一台安装了Centos7系统的主机,然后去ansible的主机上对目标主机进行操作。
我这里的ansible也是新安装的,所以如果遇到一些没有的工具,也会在遇到的时候一步一步进行添加。下面是汇总的内容。
对于一台新装好的ansible,还是会缺少很多依赖项,有些和特定模块关联的比较紧密,可以在使用特定模块的时候再安装。
还有一些使用范围比较广,建议先装好:
- yum 安装 sshpass
- 目标主机安装了python3,就需要将pip更新到最新,并且安装好selinux
修改ansible.cfg配置文件
我的实验环境,为了测试方便,暂时只有下面3项做了设置:
[defaults]
#host_key_checking = False
inventory = ~/hosts
vault_password_file = ~/vault_password_file配置文件第一行的[defaults]不能省。
添加主机
编辑 /etc/ansible/hosts 添加主机信息:
host1 ansible_host=192.168.24.172我的实验环境是直接放到了家目录里了
先用ping模块测试一下连通性:
[root@Ansible ~]# ansible host1 -m ping -k
SSH password:
host1 | SUCCESS =>
"ansible_facts":
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
,
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
[root@Ansible ~]# 这里使用了-k参数,手动输入密码。
测试联通性,可以再加上-c参数,指定local。不过这里要验证一下ssh连接。
安装 sshpass
如果是第一次使用,可能会提示需要安装sshpass。这个简单,yum安装即可:
$ yum install sshpass添加密码信息
最好的做法是用SSHKey实现免密码登录。这里讲使用密码的情况。
为了方便,也可以把密码加到配置中,这样不用每次都输入密码:
host2 ansible_host=192.168.24.172 ansible_ssh_pass=123456这样做,密码就是明码存放了,很不安全。下面有更安全的做法。
加密保存密码
使用 ansible-vault 来加密敏感信息
修改配置文件
这步不是必须的,运行命令的时候可以加上参数 --vault_password_file 来指定你的密码文件。不过通过设置就可以把这个参数省了:
$ vi /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
# If set, configures the path to the Vault password file as an alternative to
# specifying --vault-password-file on the command line.
vault_password_file = ~/vault_password_file使用openssl来生成随机密码
使用 openssl 来生成随机的base64编码的内容:
$ openssl rand -base64 128 -out vault_password_file
$ chmod a-w vault_password_file
$ chattr +i vault_password_file文件生成后,对文件做了一些保护,防止文件被修改。修改文件的ugo权限只对普通用户有效,root依然可以修改文件。后面的命令可以锁定文件,即使root也无法修改了,防止对文件的意外操作。
如果需要修改或者删除文件,可以先把文件解锁,只要把命令的 +i 改成 -i 就可以了:
$ chattr -i vault_password_file生成加密后的字符串
下面是使用 ansible-vault 来生成加密后的字符串:
[root@Ansible ~]# ansible-vault encrypt_string "123456" --name ansible_ssh_pass
ansible_ssh_pass: !vault |
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
33336539373437373161326537323836343163633532396235383334326562303134626565613537
3134313631393931376361363761313165393966613831360a343338353765326331663433613533
31636238613133363639336130613264386366363931663230333663363062333836323730383563
6562626265393535310a623732633863633765363066636265303265316661373464323961666131
6561
Encryption successful
[root@Ansible ~]# 接下来需要把这里获得的信息复制到配置文件中。
修改主机配置文件
这里对配置文件进行了大修改,原来是INI格式的,现在改成了YAML格式:
---
all:
hosts:
host1:
ansible_host: 192.168.24.172
ansible_ssh_pass: !vault |
$ANSIBLE_VAULT;1.1;AES256
33336539373437373161326537323836343163633532396235383334326562303134626565613537
3134313631393931376361363761313165393966613831360a343338353765326331663433613533
31636238613133363639336130613264386366363931663230333663363062333836323730383563
6562626265393535310a623732633863633765363066636265303265316661373464323961666131
6561
...要使用YAML是因为INI格式不支持内嵌vault,官方的说明如下:
This is an example using an extract from a YAML inventory, as the INI format does not support inline vaults:
INI格式的主机配置文件,可读性感觉更好。如果依然希望使用INI格式的配置,可以另外再创建vars文件,把额外的参数以YAML格式写在另一个文件中。
验证
这次用command模块了进行验证:
$ ansible host1 -a hostname
host1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Host1
$ 至此准备工作都做完了,已经能成功连接到主机。
python3 版本的问题
python多个版本并存是很常见的情况。Centos7系统安装后默认就有一个python2,一般自己要使用python3就会再安装一个,这个就会带来一些问题。
之前遇到的问题,就是ansible使用了目标主机的python3来执行任务,而有模块使用python3会有问题。
之前有问题的主机是将系统的python命令指向了python3。并且去yum相关的命令中修改了开头的#!/usr/bin/python2来保证yum可以正常运行。
而ansible默认就会去目标主机查找 /usr/bin/python 来执行,这就造成了默认使用python3来执行的情况。
这里就强行将ansible_python_interpreter的值指向目标主机的python3来将问题再现出来。
yum 模块
yum 是用python2写的,所以不支持python3。下面是报错的情况:
[root@Ansible ~]# ansible host1 -m yum -a "name=wget state=present" -e "ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3"
host1 | FAILED! =>
"ansible_facts":
"pkg_mgr": "yum"
,
"changed": false,
"msg": "The Python 2 bindings for rpm are needed for this module. If you require Python 3 support use the `dnf` Ansible module instead.. The Python 2 yum module is needed for this module. If you require Python 3 support use the `dnf` Ansible module instead."
[root@Ansible ~]#根据msg的提示。建议使用dnf,但是尝试之后还是失败了。
简单的办法就是指定 ansible_python_interpreter 参数,使用Python2。
使用yum模块必须指定python2,暂时没别的办法。
selinux
在使用 get_utl 模块的时候,就会遇到selinux的问题。这类问题应该只要把selinux关掉应该就解决了(没试过),不过这里看看不关的情况。
[root@Ansible ~]# ansible host1 -m get_url -a ‘url="http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo" dest="/etc/yum.repos.d/epel-7.repo"‘ -e "ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3"
host1 | FAILED! =>
"changed": false,
"msg": "Aborting, target uses selinux but python bindings (libselinux-python) aren‘t installed!"
[root@Ansible ~]#一个办法还是使用python2,因为系统默认已经安装好了python2版本的selnux,应该就是下面这个:
[root@PlayHost ~]# yum info libselinux-python
已加载插件:fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: ftp.sjtu.edu.cn
* extras: ftp.sjtu.edu.cn
* updates: ftp.sjtu.edu.cn
已安装的软件包
名称 :libselinux-python
架构 :x86_64
版本 :2.5
发布 :14.1.el7
大小 :589 k
源 :installed
来自源:anaconda
简介 : SELinux python bindings for libselinux
网址 :https://github.com/SELinuxProject/selinux/wiki
协议 : Public Domain
描述 : The libselinux-python package contains the python bindings for developing
: SELinux applications.
[root@PlayHost ~]# 如果使用python2也就没这个问题了。
使用python3也是可以的,只要把这个包装上。在yum里没有找到对应的python3版本,不过pip里有:
[root@PlayHost ~]# pip install selinux
Collecting selinux
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/59/38/780baac7aafcf44cca8e77318ec935660f93fc30e3de92f8de7a7dbc0513/selinux-0.1.6-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Installing collected packages: selinux
Successfully installed selinux-0.1.6
[root@PlayHost ~]#这里的操作是在目标主机上进行的,也可以用ansible远程来操作。不过这里主要是为了讲明白问题。
建议在目标主机上安装python3之后,就顺便把selinux也装上。这样有些python2和python3都兼容的模块使用任何版本都不会有问题
pip
初始的系统是没有pip的,之后我也只会为python3安装pip。并且所有需要pip安装的python模块都是为python3安装的。
所以在安装pip的时候,需要指定 ansible_python_interpreter 参数,使用Python3。这个和yum模块正好相反。
使用pip模块的时候,可以加参数 extra_args: -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ 来指定pypi源。
不过为方便起见,也可以直接写在配置文件中指定默认的pypi源。配置文件也用命令可以添加,不用编辑文件。使用的命令如下:
$ pip config set global.index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/运行命令可以用command模块来实现。
安装pip和更新
安装我是用yum模块来安装python36-pip(使用easy_install模块安装会有问题,我解决不了)。安装完成后,再用pip模块更新pip。
更新了pip之后,再顺便把selinux也装上,就是上一小节的问题。
实战 playbook
这里要用自己测试环境的ansible去配置一台主机。完成初始配置后,要安装好python3和docker,然后再创建一个ansible的镜像。最后还有SSH和账户的安全设置。
yum 安装工具
主要是设置国内的镜像源,然后使用yum来安装工具:
---
- hosts: host1
vars:
ansible_python_interpreter: /usr/bin/python2 # 指定使用python2,防止有坑
tasks:
- name: 删除默认的repo文件
file:
path: "/etc/yum.repos.d/ item "
state: absent
with_items:
- CentOS-Base.repo
- CentOS-Debuginfo.repo
- CentOS-Media.repo
- CentOS-Vault.repo
- CentOS-CR.repo
- CentOS-fasttrack.repo
- CentOS-Sources.repo
- name: 下载阿里源的 Centos-7.repo epel-7.repo
get_url:
url: "http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/ item.url "
dest: "/etc/yum.repos.d/ item.dest "
with_items:
- url: "Centos-7.repo", dest: "CentOS-7.repo"
- url: "epel-7.repo", dest: "epel-7.repo"
- name: yum安装 wget net-tools bind-utils net-snmp-utils traceroute lrzsz
yum:
name:
- wget
- net-tools
- bind-utils
- net-snmp-utils
- traceroute
- lrzsz
state: present
...安装 python3
使用yum来安装python3和pip,然后再更新pip到最新版本,并设置国内的pip镜像源:
---
- hosts: host1
tasks:
- name: yum 安装 python3
yum:
name: [python36, python36-setuptools, python36-pip]
state: present
- name: 更新 pip
# 有 easy_install 安装会报错,这里用 pip 更新
pip:
name: pip
state: latest
extra_args: -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
# 用python3的pip要指定python3,否则有可能去调用python2的pip
vars: ansible_python_interpreter: /usr/bin/python3
- name: 检查pip配置文件是否存在
file:
path: ~/.config/pip/pip.conf
state: file
ignore_errors: True
register: result
- name: 如果pip配置文件不存在:设置使用阿里源
command: pip config set global.index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
when: result is failed
- name: 安装 selinux
pip: name: selinux, state: present
vars: ansible_python_interpreter: /usr/bin/python3
...按之前说的,顺便把selinux也安装上。
安装docker
安装docker没有太大问题,需要先把docker-py安装上。用pip安装,所以docker模块只能在python3环境上运行、
之前已经把selinux也装上。这样除了yum,其他都可以在python3环境上运行了。
---
- hosts: host1
vars:
ansible_tag: v1 # 指定ansible镜像的tag(版本号)
tasks:
- name: 下载阿里的安装源
get_url:
url: http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
dest: /etc/yum.repos.d/
- name: yum 安装 docker-ce 指定版本
yum:
name: docker-ce-18.06.0.ce-3.el7
state: present
- name: 启动docker,开机启动
service: name=docker.service state=started enabled=yes
- name: 检查docker配置文件是否存在
file:
path: /etc/docker/daemon.json
state: file
ignore_errors: True
register: result
- name: 如果docker配置文件不存在,则创建初始文件设置镜像加速器
when: result is failed
block:
- name: 文件写入内容,设置设置镜像加速器
lineinfile:
path: /etc/docker/daemon.json
create: yes
line: |
"registry-mirrors": ["http://hub-mirror.c.163.com", "https://docker.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn"]
- name: 重启docker,使镜像加速器生效
service: name=docker.service state=restarted
- name: 安装管理docker的模块,检查镜像是否存在
vars: ansible_python_interpreter: /usr/bin/python3
block:
- name: pip 安装 docker-py selinux
pip:
name: [docker-py, selinux]
state: present
- name: 检查 Ansible 镜像是否存在
vars: ansible_python_interpreter: /usr/bin/python3
docker_image:
name: ansible
tag: " ansible_tag "
source: local
ignore_errors: True
register: result
- name: 制作 Ansible 镜像
vars: ansible_python_interpreter: /usr/bin/python3
when: result is failed
block:
- name: 将 Dockerfile copy 到目标主机
# copy 需要 selinux,所以上面用 pip 安装了 python3 的版本
copy:
src: ansible/Dockerfile
dest: /tmp/docker_file/ansible/
- name: docker build
docker_image:
name: ansible
tag: " ansible_tag "
build:
path: /tmp/docker_file/ansible/
pull: yes
source: build
- name: 删除 Dockerfile
file:
path: /tmp/docker_file/
state: absent
...
docker的配置文件是json格式的,json没有注释,所以不能用blockinfile模块。可以用lineinfile模块,也可以用copy模块。不过copy模块有个小问题,没法递归创建目录。而lineinfile模块有create参数,并且也支持多行。
通过Dockerfile制作镜像
这个是构架ansible的Dockerfile:
FROM centos:centos7
RUN curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo && yum -y install python36 python36-setuptools python36-pip && yum clean all && pip3 install pip --upgrade -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ && /usr/local/bin/pip3 install ansible -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ && mkdir /opt/ansible_project/etc/ansible -p && ln -s /opt/ansible_project/etc/ansible/ /etc/ansible
VOLUME /opt/ansible_project
CMD ["ansible", "--version"]创建镜像查找的Dockerfile所在的文件夹是在目标主机上的。所以需要先用copy模块将文件夹复制过去。
copy模块使用相对目录时,源文件的起始目录是playbook所在的目录,目标的起始目录有目标主机决定(Centos的系统,默认登录后就在用户的家目录)。
账号和SSH安全优化
主要做了2件事:
- 开启一个管理员账号
- 修改默认ssh使用的端口号
playbook如下:
---
- hosts: host1
vars:
ansible_python_interpreter: /usr/bin/python2 # 指定使用python2,防止有坑
init_ssh_user: admin # 是否创建用户,并且会禁用root密码登录
init_ssh_port: 2849 # 是否修改默认ssh端口
tasks:
# 创建管理员用户,禁用root登录
- block:
- name: 创建用户 init_ssh_user
user:
name: " init_ssh_user "
# 这个是加盐的对称加密,所以可以反解,官网有生成密码的方式:
# https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/reference_appendices/faq.html#how-do-i-generate-encrypted-passwords-for-the-user-module
password: "$6$ my_secret_salt $CSQSsXSoAkwtWDzjlReQ3u0jy1YyxBLouwe403dCVe.ystdi9JQvjSxhoTpYwNoT5nprsJV/UpYb9Ktj.7jLX/"
groups: wheel
state: present
- name: 修改 /etc/ssh/sshd_config 禁止root登录
lineinfile:
dest: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
state: present
regexp: "^#?PermitRootLogin"
line: "PermitRootLogin no"
notify: systemctl restart sshd.service
when: init_ssh_user is defined
# 修改ssh端口
- block:
- name: 防火墙开启端口 init_ssh_port
firewalld:
port: " init_ssh_port /tcp"
state: enabled
permanent: yes
immediate: yes
- name: yum安装 policycoreutils-python
yum: name: policycoreutils-python, state: present
- name: 设置selinux:`semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp init_ssh_port `
seport:
ports: " init_ssh_port "
proto: tcp
setype: ssh_port_t
state : present
- name: 修改 /etc/ssh/sshd_config 的端口设置
lineinfile:
dest: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
state: present
regexp: "^#?Port"
line: "Port init_ssh_port "
notify: systemctl restart sshd.service
when: init_ssh_port is defined
handlers:
- name: systemctl restart sshd.service
service: name=sshd.service state=restarted
...验证
去目标主机上验证:
# docker run --rm ansible:v1
ansible 2.8.4
config file = None
configured module search path = [‘/root/.ansible/plugins/modules‘, ‘/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules‘]
ansible python module location = /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/local/bin/ansible
python version = 3.6.8 (default, Apr 25 2019, 21:02:35) [GCc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-36)]
# 以上是关于Windows7 上运行docker实战的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章