005 python语法
Posted 汁虫
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了005 python语法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

/* 时间:2018/09/29 目录: 一: python 1 基本介绍 2 编码规范 二: print 1 打印字符串 2 打印字符串和数字 3 使用通用转换类型 4 查看函数 三: 数字 1 整型 2 浮点型 3 布尔类型 四: 字符串 1 编码原理 2 编码显示 3 编码转换: Unicode - ascii/utf-8 4 编码转换: bytes - ascii/utf-8 5 len 6 索引和截取 五: 元组 1 基本语法 2 内置函数 */
一: python
1 基本介绍
1 语言: 是面向对象编程语言,每个数据类型都是对象,每个对象都其方法。 2 大小写: 区分大小写 3 拥有类型: 数字、字符串、元组、列表、字典、集合 4 没有类型: 对比C/C++ - 字符、i++、++i、指针、引用
2 编码规范
1 分号: python结尾不要加分号 2 行长度: 每行不要超过80个字符 3 括号: 除非是行隐式和元组,否则不要在返回语句中使用括号 4 缩进: tab和4个空行,不要混着用 5 空行: 顶级定义之间空两行,方法定义空一行; 6 空格: 括号内不要有空格; 按照标准排版规范使用标点两边的空格 7 注释: 确保对模块/函数/方法。 8 导入: 模块注释和文档字符串之间; 每个导入应该独占一行 9 语句: 每个语句独占一行 10 命名: 单字符名称:包/模块中对连字符, 双下划线开头并结尾对名称,不能命名 12 命名规范: 小写 _ 驼峰命名规范
二: print
1 打印字符串
# coding:utf-8 print("hello world") # 打印 - hello world
# Result hello world Process finished with exit code 0
2 打印字符串和数字
占位符 替换内容 %d 整数 %f 浮点数 %s 字符串 %x 十六进制整数
# coding:utf-8 name = "ZhangSan" age = 27 print("%s age is %d" %(name, age)) # 打印 - 字符串和数字
# Result ZhangSan age is 27 Process finished with exit code 0
3 使用通用转换类型
# coding:utf-8 name = "ZhangSan" age = 27 print("%r age is %r" %(name, age)) # 使用 - 通用转换类型
# Result \'ZhangSan\' age is 27 Process finished with exit code 0
4 查看函数
def print(self, *args, sep=\' \', end=\'\\n\', file=None): # known special case of print """ print(value, ..., sep=\' \', end=\'\\n\', file=sys.stdout, flush=False) Prints the values to a stream, or to sys.stdout by default. Optional keyword arguments: file: a file-like object (stream); defaults to the current sys.stdout. sep: string inserted between values, default a space. end: string appended after the last value, default a newline. flush: whether to forcibly flush the stream. """
三: 数字
1 整型
# coding:utf-8 nNum = 3 # nNum整形 strNum = input() # 输入内容 nResult = nNum + int(strNum) # 数字相加 print(nResult) # 打印结果 print(type(nResult)) # 打印类型
# Run Result 2 5 <class \'int\'> Process finished with exit code 0
2 浮点型
# coding:utf-8 fNum = 3.2 nResult = fNum * 2 print(nResult) # 打印结果 print(type(nResult)) # 打印类型
# Run Result 6.4 <class \'float\'> Process finished with exit code 0
3 布尔类型
# coding:utf-8 nTrue = True nFalse = False print(nTrue) # 打印结果 print(type(nTrue)) # 打印类型 print(False) # 打印结果 print(type(False)) # 打印类型
# Run Result True <class \'bool\'> False <class \'bool\'> Process finished with exit code 0
四: 字符串
1 编码原理
1 发展过程: ASCII -> GB2312(中文) Shift_JIS(韩文) Euc-kr(韩文) -> Unicode -> UTF-8 2 Python3: 字符串是Unicode编码
字符 ASCII Unicode UTF-8 A 01000001 00000000 01000001 01000001 中 x 01001110 00101101 11100100 10111000 10101101
1 内存中,统一使用Unicode编码,当需要保存到硬盘或者需要传输的时候,就转换为UTF-8编码。 2 记事本编辑的时,从文件读取UTF-8字符被转换为Unicode字符到内存里,保存时把Unicode转换为UTF-8保存到文件: 3 浏览网页的时候,服务器会把动态生成的Unicode内容转换为UTF-8再传输到浏览器 1 内存(unicode) - 文件/传输(utf-8) 2 文件读取(utf-8) - 内存操作(unicode) - 文件保存(utf-8) 3 服务器(unicode) - 浏览器(utf-8)
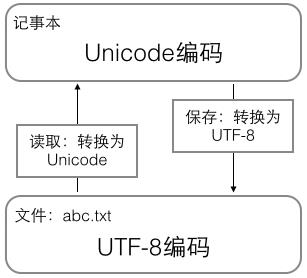
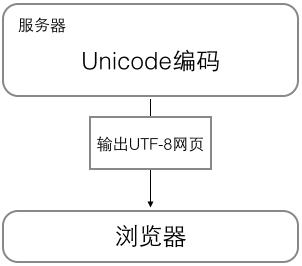
2 编码显示
# coding:utf-8 strName = "ZhangSan" # 字符串 - Unicode编码 print("%s" %strName) print(type(strName)) strName = b"ZhangSan" # 每个字符都只占用一个字节 print("%s" %strName) print(type(strName))
# Run Result ZhangSan <class \'str\'> b\'ZhangSan\' <class \'bytes\'>
3 编码转换: Unicode - ascii/utf-8
# coding:utf-8 strName = "ZhangSan" # Unicode编码 print("%s" %strName) print(type(strName)) print("%s" %strName.encode("utf-8")) # 编码转换: Unicode - utf-8 print(type(strName.encode("utf-8"))) print("%s" %strName.encode("ascii")) # 编码转换: Unicode - ascii print(type(strName.encode("ascii")))
# Run Result ZhangSan <class \'str\'> b\'ZhangSan\' <class \'bytes\'> b\'ZhangSan\' <class \'bytes\'>
4 编码转换: bytes - ascii/utf-8
# coding:utf-8 strName = b"ZhangSan" # 字节流 print("%s" %strName) print(type(strName)) print("%s" %strName.decode("ascii")) # 编码转换: bytes - ascii print(type(strName.decode("ascii"))) print("%s" %strName.decode("utf-8")) # 编码转换: bytes - utf-8 print(type(strName.decode("utf-8")))
# Run Result b\'ZhangSan\' <class \'bytes\'> ZhangSan <class \'str\'> ZhangSan <class \'str\'>
5 len
# coding:utf-8 strName = b"Z" print("%d" %len(strName)) strName = "Z" print("%d" %len(strName)) print("%d" %len(strName.encode("ascii"))) print("%d" %len(strName.encode("utf-8"))) strName = "张" print("%d" %len(strName)) print("%d" %len(strName.encode("utf-8"))) # 汉字字符 - 三个字节
# Run Result 1 1 1 1 1 3
6 索引和截取

# coding:utf-8 str = "Runoob" print(str) # 输出 - 整个字符串 print(str[0]) # 输出 - 第一个字符 print(str[0:-1]) # 输出 - 第一个到倒数第二个 print(str[2:5]) # 输出 - 第三个到第五个 print(str[2:]) # 输出 - 第三个开始 print(str * 2) # 输出 - 两次字符串 print(str + "Test") # 输出 - 字符串拼接
# Run Result Runoob R Runoo noo noob RunoobRunoob RunoobTest
五: 元组
1 基本语法
# coding:utf-8 # 创建元组 tuple = (12, 12.12, True, False, "12.12") # 访问元组 print(tuple) print(type(tuple)) print(tuple[0:5]) print(tuple[0:3]) print(tuple[1:4]) print(tuple[0:-1]) # 删除元组 del tuple print(tuple) # 元素不可以删除,del可以删除整个元组 # 无法修改
2 内置函数

以上是关于005 python语法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章