python实现wc
Posted universityofleeds
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python实现wc相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
github address:https://github.com/langliang/wcpy.git
项目要求:
wc.exe 是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数。它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
具体功能要求:
程序处理用户需求的模式为:
wc.exe [parameter] [file_name]
基本功能列表:
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数 (已实现)
wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目 (已实现)
wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数 (已实现)
额外功能:
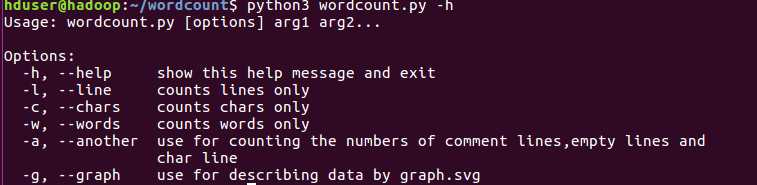
-h 显示帮助命令
-g 将输出的结果用pygal模块绘制svg图像
扩展功能:
-s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件。(已实现)
-a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)。(已实现)
[file_name]: 文件或目录名,可以处理一般通配符。(已实现)
高级功能:
-x 参数。这个参数单独使用。如果命令行有这个参数,则程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息。(未实现)
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
30 | 60 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
20 | 30 |
|
Development |
开发 |
180 | 230 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
100 | 120 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
50 | 60 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
30 | 30 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
40 | 50 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
50 | 40 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
120 | 230 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
60 | 80 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
60 | 45 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
45 | 80 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
35 | 25 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
15 | 20 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划
|
25 | 20 |
|
合计 |
825 |
1120 |
解题思路:
使用python的optparse 模块中的OptionParser类来获取命令行选项和参数,选项包括-l, -w ,-d ,-a,-s,-g. 参数为单文件或多文件或目录路径
使用os模块来判断输入路径为文件或目录
使用pygal模块来绘制svg图,把数据作为y轴
文件处理:使用with open()打开文件,再用for line in file.readlines()来分别处理每行文本
寻找资料:主要是上网搜索os,optparse模块的使用及其方法
设计实现过程:
add_option()方法添加参数,选项
is_not_dir()函数判断文件是否存在,是文件还是目录,并且使用0,1,2返回值来对应
read_file()函数读取单个文件,并统计其相应的数据
read_files()通过循环调用read_file()来读取多个文件或目录
show_data()打印数据到控制台
use_pygal() 将结果函数绘制到svg文件
代码说明:
usage = "usage: %prog [options] arg1 arg2..." parser = OP(usage) # 往OptionParser对象中添加Options parser.add_option(‘-l‘, ‘--line‘,# 对应-l 选项 dest=‘lines‘, action=‘store_true‘, default=False, help=‘counts lines only‘ ) parser.add_option(‘-c‘, ‘--chars‘,# 对应 -c选项 dest=‘chars‘, action=‘store_true‘, default=False, help=‘counts chars only‘ ) parser.add_option(‘-w‘, ‘--words‘,# 对应-w选项 dest=‘words‘, action=‘store_true‘, default=False, help=‘counts words only‘ ) parser.add_option(‘-a‘, ‘--another‘,# 对应-a选项 dest=‘more‘, action=‘store_true‘, default=False, help=‘use for counting the numbers of comment lines,empty lines and char line‘ ) # 如果使用-g参数,会保存相关数据到SVG文件 parser.add_option(‘-g‘, ‘--graph‘,#对应-g选项 dest=‘graph‘, action=‘store_true‘, default=False, help=‘use for describing data by graph.svg‘ ) # 调用optionparser的解析函数 (options, args) = parser.parse_args()
# 以下是判断路径为文件或者目录的函数
def is_not_dir(files): if not os.path.exists(files):# 判断路径是否存在 sys.stderr.write("%s No such file or directory " % files) return 0 if os.path.isdir(files):# 判断是否为目录 sys.stderr.write("%s Is a directory " % files) return return 2
读取并处理单个文件的函数:
def read_file(file): with open(file, ‘r‘) as f: l = 0 c = 0 w = 0 comment_lines = 0 space_lines = 0 char_lines = 0 for line in f.readlines():#对每行文本分别处理 l += 1 c += len(line.strip()) # 统计单词数 match_list = re.findall(‘[a-zA-Z]+‘, line.lower()) w += len(match_list)# 统计字符数,不算前后的空格 # to judge if a line is a comment line line = line.strip()#剥除前后的空格 if line.startswith("#") or line.startswith(r‘"""‘) or line.endswith("#") or line.endswith(r‘"""‘):#注释行判断条件 comment_lines += 1 elif not line: space_lines += 1 else: char_lines += 1 print(‘the current file is: %s‘ % f) l -= 1# 不算最好一行空白行 # 打印数据 show_data(l, c, w, comment_lines, space_lines, char_lines) # 使用列表返回行数,注释行,空白行,字符行以便于测试 return list(l, comment_lines, space_lines, char_lines)
循环处理多文件或者目录:
def read_files(files): file_list = []#文件路径列表 for file in files:# 每个文件单独处理 judge = is_not_dir(file) if judge == 2: # 此路径为文件 # use the function of with open to automatically open and close files read_file() elif judge == 1: #此路径为目录 for item in os.listdir(file): item_path = os.path.join(file, item) #合并路径 file_list.append(item_path)# 添加到文件列表 read_files(file_list) else: continue if len(files) > 1: # 如果有多个文件,则输出总数 print(‘the total number is:‘) show_data(sum_l, sum_c, sum_w, sum_comment, sum_space, sum_char_line)
use_pygal函数:
def use_pygal(x_list, y_list, svg_name): # 设置风格 my_style = LS(‘#333366‘, base_style=LCS) my_config = pygal.Config() my_config.show_legend = False # 坐标旋转25度 my_config.x_label_rotation = 25 my_config.title_font_size = 24 # x,y轴坐标大小 my_config.label_font_size = 16 # 主坐标大小 my_config.major_label_font_size = 18 my_config.show_y_guides = True # 设置width 充分利用浏览器界面 my_config.width = 1000 # 使用pygal绘制直方图 chart = pygal.Bar(my_config, style=my_style) chart.title = "source file‘s data of wordcount" chart.x_labels = x_list chart.add(‘‘, y_list) # 保存svg图 chart.render_to_file(svg_name)
show_data打印结果:
def show_data(ll, cc, ww, cl, sl, chl): global sum_l #总行数 global sum_c global sum_w global sum_comment #总注释行数 global sum_space global sum_char_line
#记录总数据
sum_l += ll sum_c += cc sum_w += ww sum_char_line += chl sum_space += sl sum_comment += cl if not (options.words or options.lines or options.chars):#如果不使用参数,则默认输出行数,单词数,字符数 print(ll) print(ww) print(cc) if options.words: print(ww) if options.lines: print(ll) if options.chars: print(cc) if options.more: print("the number of comment lines is:", cl) print("the number of empty lines is:", sl) print("the number of char lines is:", chl) if options.graph: # 列表用以构造svg图 x_list_arg = [‘lines number‘, ‘words number‘, ‘chars number‘, ‘comment lines number‘, ‘empty lines number‘, ‘chars lines number‘] y_list_arg = [ll, ww, cc, cl, sl, chl] use_pygal(x_list_arg, y_list_arg, svg_name=‘word_count.svg‘)#绘图
程序运行截图:
多文件(不使用选项):
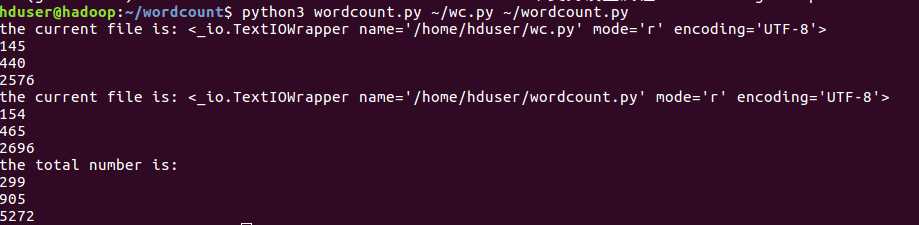
路径为目录目录(使用选项-a,-l,只输出行数和注释行,空白行,字符行):
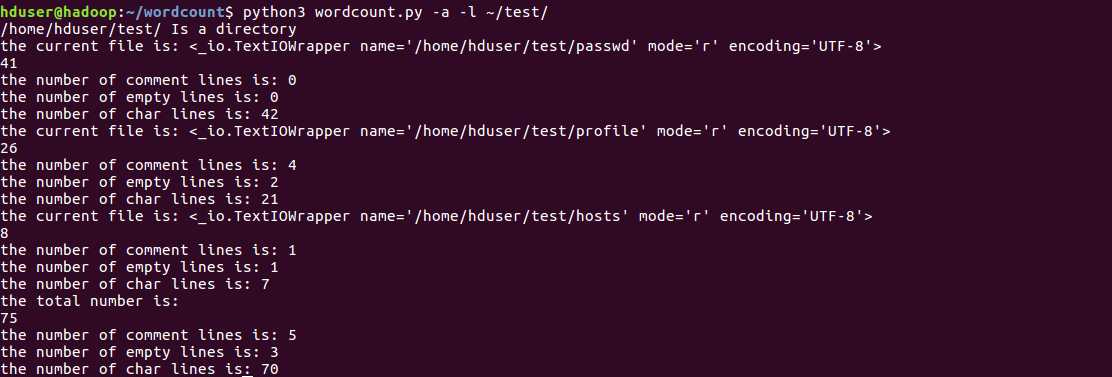
使用通配符*处理所有以p头的文件:
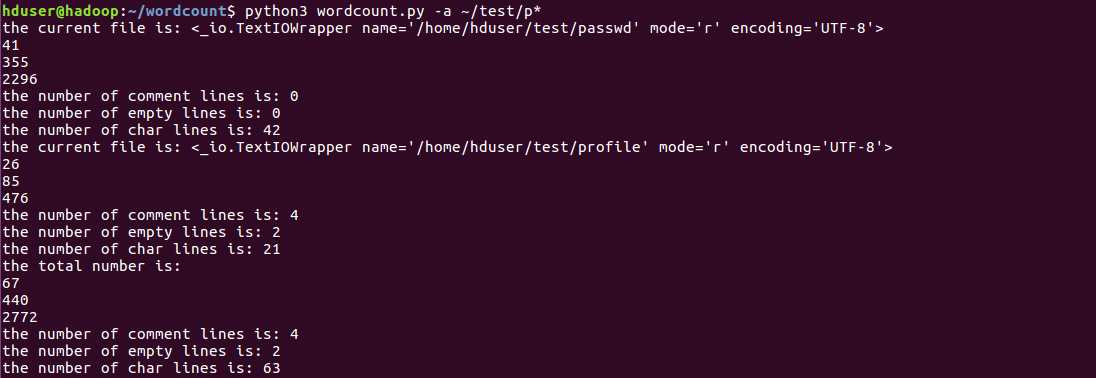
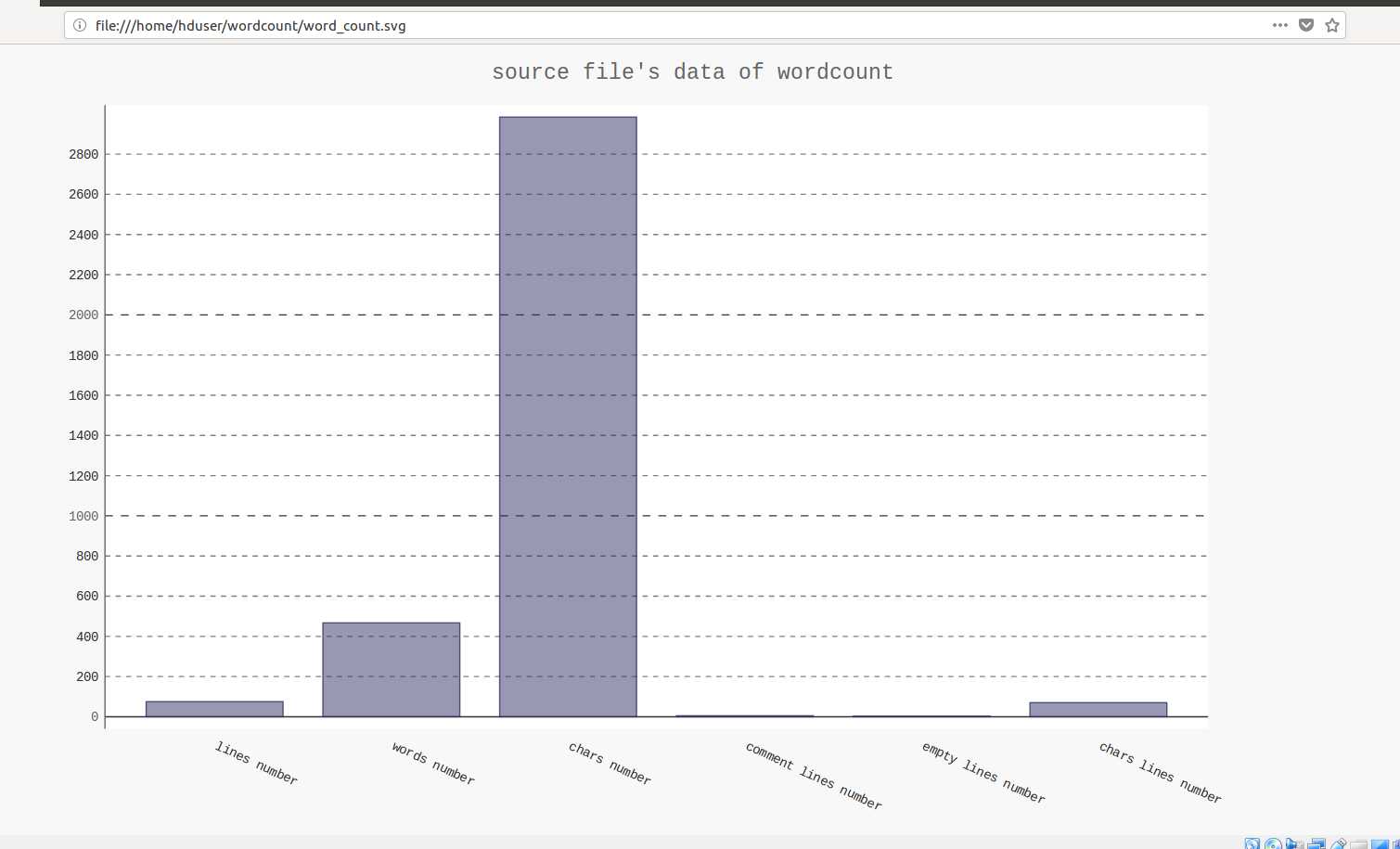
使用-p选项,保存结果并可视化到svg图像

使用firefox打开svg文件

直方图可视化输出结果:
-h选项,打印帮助命令:
测试运行:
测试所用源文件:
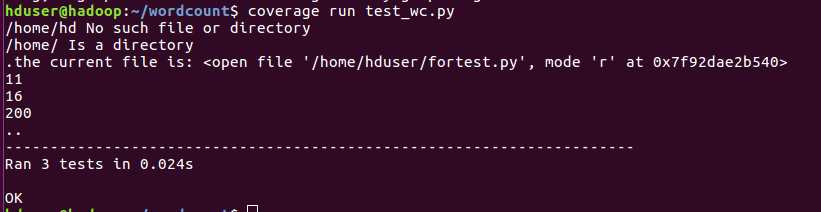
使用coverage模块运行单元测试模块:
使用coverage report命令查看代码覆盖率: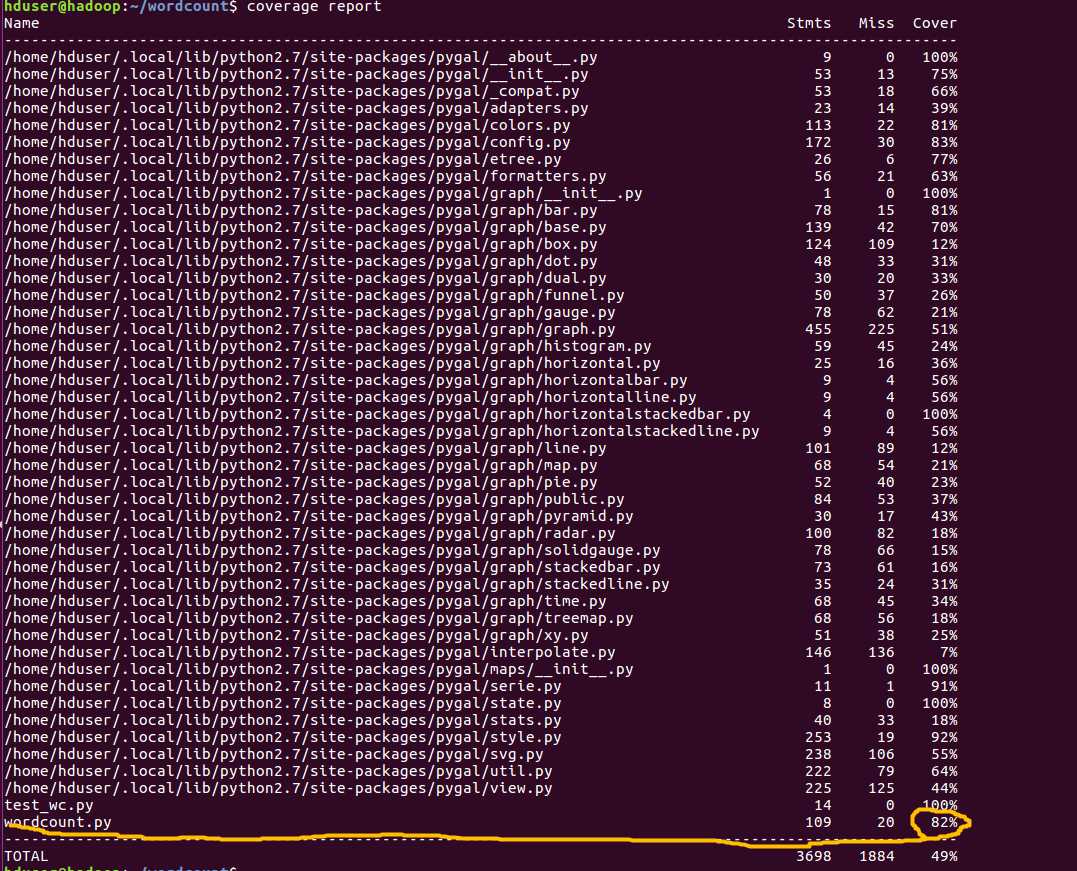
项目总结:
由于本次使用python来实现这个命令行程序,而python本身非常适合处理这方面的作业,在程序方面没有遇到太大困难。主要的困难在于测试方面,之前没有使用过python的unittest模块,不知道应该如何使用。刚开始测试模块总是出现failures,查看文档才发现是权限的问题,于是修改了文件的权限就可以了。还有就是正则表达式的问题,网上查阅了一些资料依然没能写的很好,单词统计方面并不十分准确。其次是optparse模块的使用不熟练,也造成了一些困难,总体而言完成的时间比预期多了很多,主要问题在于前期没有合理审查功能需求,和考虑解决思路,就急于开始编写代码,还有就是对测试方面的知识匮乏,使得测试工作占据了大量时间。通过这次作业我明白了前期对整体流程的规划和功能需求分析的重要性,后期测试是刚需而不是选项。
以上是关于python实现wc的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章