python Dom
Posted python|一路向前
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python Dom相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Dom(Document) 称为:文档对象模型,是一种用于HTML和XML文档的编程接口。它给文档提供了一种结构化的表示方法,可以改变文档的内容和呈现方式。DOM把网页和脚本以及其他的编程语言联系了起来。DOM属于浏览器,而不是JavaScript语言规范里的规定的核心内容。
一、查找元素
1、直接查找
document.getElementById(\'il\') 根据ID获取一个标签
document.getElementsByName(\'div\') 根据name属性获取标签集合document.getElementsByClassName(\'c1\') 根据class属性获取标签集合document.getElementsByTagName(\'\') 根据标签名获取标签集合parentNode // 父节点
childNodes // 所有子节点firstChild // 第一个子节点lastChild // 最后一个子节点nextSibling // 下一个兄弟节点previousSibling // 上一个兄弟节点parentElement // 父节点标签元素children // 所有子标签firstElementChild // 第一个子标签元素lastElementChild // 最后一个子标签元素nextElementtSibling // 下一个兄弟标签元素previousElementSibling // 上一个兄弟标签元素二、操作
innerText 文本 例如:document.getElementById(\'il\').innerText 输出标签中的内容。
outerTextinnerHTML HTML内容innerHTML value 值className // 获取所有类名 classList.remove(cls) // 删除指定类 classList.add(cls) // 添加类
tag=document.getElementById(\'il\') tag.classname=\'c1\' #输出html结构图 tag.classlist #输出列表
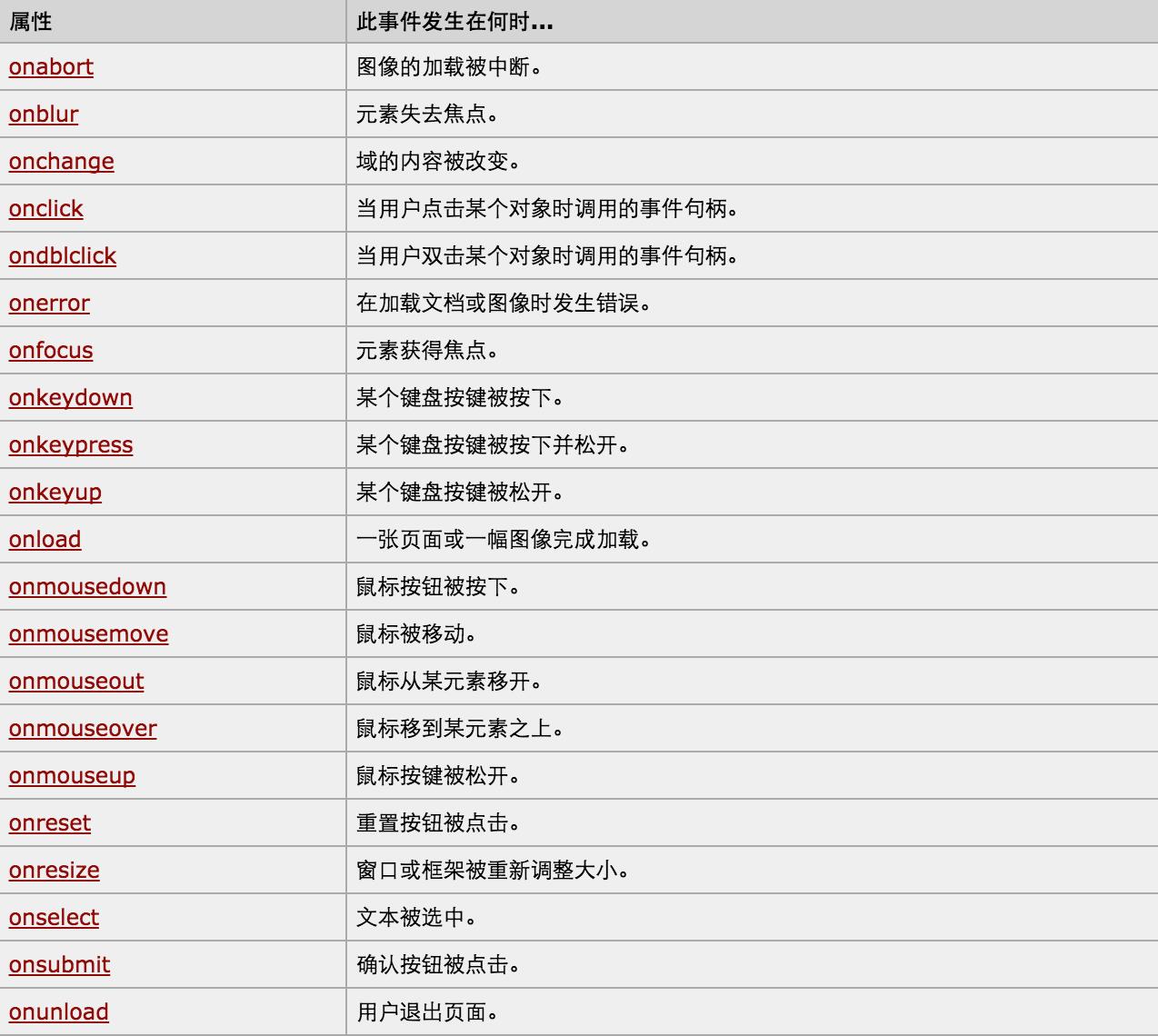
事件操作:
弹窗实例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<style>
.hide{
display: none;
}
.c1{
position: fixed;
left: 0;
top: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
background-color: black;
opacity: 0.6;
z-index: 9;
}
.c2{
width: 500px;
height: 400px;
background-color: white;
position: fixed;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
margin-left: -250px;
margin-top: -200px;
z-index: 10;
}
</style>
</head>
<body style=\'margin:0;\'>
<div>
<input type="button" value="点我" onclick=\'ShowModel();\'></input>
</div>
<!--遮罩开始-->
<div class=\'c1 hide\' id=\'i1\'></div>
<!-- 遮罩结束 -->
<div class=\'c2 hide \' id="i2">
<input type="button" value="取消" onclick=\'HideModel();\'></input>
</div>
<script >
function ShowModel(){
document.getElementById(\'i1\').classList.remove(\'hide\');
document.getElementById(\'i2\').classList.remove(\'hide\');
}
function HideModel(){
document.getElementById(\'i1\').classList.add(\'hide\');
document.getElementById(\'i2\').classList.add(\'hide\');
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
样式操作:
className
classList : classList.add/classList.remove
obj.style.fontSize=\'11px\';
obj.style.backgroundColor=\'red\';
obj.style.color=\'red\';
属性操作:
obj.setAttributr(\'\',\'\');
obj.removeAttribute();
创建标签的两中方式:字符串方式和对象方式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type=\'button\' onclick=\'A1();\' value=\'+\'/>
<input type=\'button\' onclick=\'A2();\' value=\'+\'/>
<div id=\'i1\'>
<p><input type=\'text\'/></p>
</div>
<script>
function A1(){
var tag=\'<p><input type="text"/></p>\';
document.getElementById(\'i1\').insertAdjacentHTML(\'beforeEnd\',tag);
}
function A2(){
var tag=document.createElement(\'input\');
tag.setAttribute(\'type\',\'text\');
tag.style.fontSize=\'11px\';
tag.style.color=\'red\';
var p=document.createElement(\'p\');
p.appendChild(tag);
document.getElementById(\'i1\').appendChild(p);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
提交表单
任何标签都可以通过document 提交表单
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<table border=\'1\'; width=\'300px\'>
<tr><td>1</td><td>2</td><td>3</td></tr>
<tr><td>1</td><td>2</td><td>3</td></tr>
<tr><td>1</td><td>2</td><td>3</td></tr>
</table>
<script>
var MT=document.getElementsByTagName(\'tr\');
var len=MT.length
for(var i=0;i<len;i++){
MT[i].onmouseover=function(){
this.style.backgroundColor=\'red\';
}
MT[i].onmouseout=function(){
this.style.backgroundColor=\'\';
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
绑定事件的两种方式:
a.直接标签绑定 onclick=\'xx()\' onfocus
b.先获取dom对象 然后进行绑定
this,当前触发事件的标签
a. 第一绑定方式
<input type=\'button\' onclick=\'A1();\' value=\'+\'/>
function Clickon(self){
//self 当前点击的标签
}
b.第二种绑定方式
<input id=‘i1’ type=\'button\'>
document.getElementById(\'i1\').onclick=function(){
//this 代指当前点击的标签
}
1.冒泡
2.词法分析
function t1(age){
console.log(age); //function age()
var age=27;
console.log(age);//27
function age(){}
console.log(age);//27
}
t1(3)
分析过程,还没正式执行:
active object ====>AO
1.形式参数
2.局部变量
3.函数声明表达式
1.形式参数
AO.age=undefined
AO.age=3;
2.局部变量
AO.age=undefined
3.函数声明表达式
AO.age=function()
以上是关于python Dom的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章