python语句
Posted 小禹哥。
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python语句相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
if语句
第一种
if 4>5:
print("你该去幼儿园好好学习学习了")
print("不错啊,知道啊")
第二种
if 4>5: print("你该去幼儿园好好学习学习了") else: print("不错啊,知道啊")
第三种
num = input ("请输入你猜的数字:") #input里边的都是字符型,字符型必须引号引起来
if num == "1":
print ("你请我吃饭")
elif num == "2":
print ("我请你吃饭")
elif num == "3":
print ("你说谁请就谁请")
else:
print ("我说谁请就谁请")

第四种
score = int (input("请输入成绩:")) if score >= 90: print("A") elif score >= 80: print("B") elif score >= 70: print("C") elif score >= 60: print("D") else: print("你没有及格,明年继续加油吧!")

注:这里将字符型转化成了整型,所以后边的不带引号。只有数字的字符型才可以转化成整型。
第五种
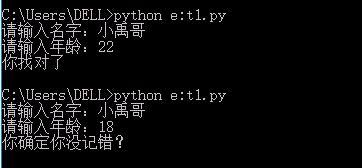
name = input("请输入名字:") age = input("请输入年龄:") if name == "小禹哥": if age == "22": print("你找对了") else: print("你确定你没记错?") else: print("对不起,你找的人查询不到,请到别处查找")
while循环
在循环的过程中,如果你不想继续循环就用到break 或 continue 语句
- break用于完全结束一个循环,跳出循环体执行循环后面的语句
- continue和break有点类似,区别在于continue只是终止本次循环,接着还执行后面的循环,break则完全终止
第一种
输出1到100(当出现False时循环停止)
count = 1 flag = True #标志位 while flag: print(count) count = count + 1 if count > 100 : flag = False
count = 1 while count <= 100: print(count) count = count + 1

第二种
count = 1 sum = 0 while count <= 100: sum = sum + count count = count + 1 print(sum)
第三种
count = 0 while count <= 100 : count += 1 if count > 5 and count <95: continue print("loop",count) print(".......out of while loop.....")
while循环训练
1.使用while循环输入1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10
2.用户登录,三次机会
i = 0 while i < 3: username = input(\'請輸入賬號:\') password = input(\'請輸入密碼: \') if username == \'小禹哥\' and password == 123456: print(\'登陸成功\') else: print(\'登錄失敗,請重新登錄\') i += 1
username = \'小禹哥\' password = \'123456\' i = 0 while i < 3: name = input(\'请输入你的用户名:\') paw = input(\'请输入你的密码:\') if username == name and password == paw: print(\'登陆成功\') break else: print(\'登录失败,你还有%d次机会\'%(2-i)) if (2-i) == 0: result = input(\'是否再试试?yes\') if result == \'yes\': i = 0 continue i += 1 else: print(\'你要不要脸\')
2.格式化输出
用%s代表字符串占位符,除此之外,还有%d,是数字占位符
注:用%这种方法必须与后边的一一对应,否则会出错。
name = input(\'请输入你的名字: \') age = input(\'请输入你的年龄:\') job = input(\'请输入你的工作: \') hobble=input(\'请输入你的爱好:\') msg = \'\'\'........info of %s........ name : %s age : %d job: %s hobble : %s .........end............ \'\'\' %(name,name,int(age),job,hobble) print(msg)
3.验证用户并输出用户名和密码
username = \'小禹哥\' password = \'123456\' i = 3 while i > 0: name = input(\'请输入你的用户名:\') i -= 1 if name == username: paw = input(\'请输入你的密码:\') if paw == password: print(\'验证成功,正在登录,请稍后……\') print(\'\'\'恭喜你登录成功! 欢迎用户进入 用户名:%s 密码 :%s \'\'\'%(name,paw)) break else: if i == 0: print(\'你的机会已经用完了\') print(\'密码错误,请重新输入\') print("你还有"+ str(i)+"次机会") else: print(\'请输入正确的用户名!\') if i == 0: print(\'你的机会已经用完了\') print("你还有"+ str(i)+"次机会")
以上是关于python语句的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章