python文本挖掘输出权重,词频等信息
Posted 蔡军帅
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python文本挖掘输出权重,词频等信息相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from pandas import read_csv import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets.base import Bunch import pickle # 导入cPickle包并且取一个别名pickle #持久化类 from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer import jieba import operator # 排序用 from sklearn import metrics from sklearn.externals import joblib import xlwt def importSmallContentdata(file, data, art, label, f, Slast, Snew): dataset = read_csv(file) Sdata = dataset.values[:, :] print(type(Sdata)) if f == 1: for line in Sdata: ls = [] ls.append(line[14]) ls.append(line[15]) ls.append(line[16]) ls.append(line[17]) Slast.append(ls) # print(len(Slast)) # print("需要对照的小类数据准备完毕") \'\'\'找到smalli不为0的装入Straindata,把数据分开\'\'\' for smalli in range(14, 18): # print(smalli) count = 0 for line in Sdata: count = count + 1 if line[smalli] != \'0\' and line[smalli] != 0: k = 1 ls = [] for i in line: if k == 1: #art.append(i) k = k + 1 continue if k == 11: # k为14并不代表是line[14],因为line是从0开始 break ls.append(float(i)) k = k + 1 data.append(ls) label.append(line[smalli]) if f == 1: Snew.append(count) for line in Sdata: art.append(line[0]) # print("为什么都超限",len(Snew)) def getKvector(train_set, vec, n): class obj: def __init__(self): self.key = 0 self.weight = 0.0 nonzero = train_set.tdm.nonzero() k = 0 lis = [] gather = [] p = -1 for i in nonzero[0]: p = p + 1 if k == i: a = obj() a.key = nonzero[1][p] a.weight = train_set.tdm[i, nonzero[1][p]] lis.append(a) else: lis.sort(key=lambda obj: obj.weight, reverse=True) # 对链表内为类对象的排序 gather.append(lis) while k < i: k = k + 1 lis = [] a = obj() a.key = nonzero[1][p] a.weight = train_set.tdm[i, nonzero[1][p]] lis.append(a) gather.append(lis) # gather存储的是每条数据的事实描述的特征向量,已经从小到大排好了,只不过每个存既有key又有weight # 我们只要key,不再需要weight sj = 1 for i in gather: ls = [] for j in i: sj = sj + 1 ls.append(float(j.key)) while sj <= n: sj = sj + 1 ls.append(-1) sj = 1 vec.append(ls) \'\'\'读取停用词\'\'\' def _readfile(path): with open(path, "rb") as fp: content = fp.read() return content \'\'\' 读取bunch对象\'\'\' def _readbunchobj(path): with open(path, "rb") as file_obj: bunch = pickle.load(file_obj) return bunch \'\'\'写入bunch对象\'\'\' def _writebunchobj(path, bunchobj): with open(path, "wb") as file_obj: pickle.dump(bunchobj, file_obj) def buildtrainbunch(bunch_path, art_train, trainlabel): bunch = Bunch(label=[], contents=[]) for item1 in trainlabel: bunch.label.append(item1) # trainContentdatasave=[] #存储所有训练和测试数据的分词 for item2 in art_train: item2 = str(item2) item2 = item2.replace("\\r\\n", "") item2 = item2.replace(" ", "") content_seg = jieba.cut(item2) save2 = \'\' for item3 in content_seg: if len(item3) > 1 and item3 != \'\\r\\n\': # trainContentdatasave.append(item3) save2 = save2 + "," + item3 bunch.contents.append(save2) with open(bunch_path, "wb") as file_obj: pickle.dump(bunch, file_obj) print("构建训练数据文本对象结束!!!") def buildtestbunch(bunch_path, art_test, testlabel): bunch = Bunch(label=[], contents=[]) for item1 in testlabel: bunch.label.append(item1) # testContentdatasave=[] #存储所有训练和测试数据的分词 for item2 in art_test: item2 = str(item2) item2 = item2.replace("\\r\\n", "") item2 = item2.replace(" ", "") content_seg = jieba.cut(item2) save2 = \'\' for item3 in content_seg: if len(item3) > 1 and item3 != \'\\r\\n\': # testContentdatasave.append(item3) save2 = save2 + "," + item3 bunch.contents.append(save2) with open(bunch_path, "wb") as file_obj: pickle.dump(bunch, file_obj) print("构建测试数据文本对象结束!!!") def vector_space(stopword_path, bunch_path, space_path): stpwrdlst = _readfile(stopword_path).splitlines() # 读取停用词 bunch = _readbunchobj(bunch_path) # 导入分词后的词向量bunch对象 # 构建tf-idf词向量空间对象 tfidfspace = Bunch(label=bunch.label, tdm=[], vocabulary={}) # 权重矩阵tdm,其中,权重矩阵是一个二维矩阵,tdm[i][j]表示,第j个词(即词典中的序号)在第i个类别中的IF-IDF值 # 使用TfidVectorizer初始化向量空间模型 vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words=stpwrdlst, sublinear_tf=True, max_df=0.5, min_df=0.0001, use_idf=True, max_features=15000) # print(vectorizer) # 文本转为词频矩阵,单独保存字典文件 tfidfspace.tdm = vectorizer.fit_transform(bunch.contents) tfidfspace.vocabulary = vectorizer.vocabulary_ # 创建词袋的持久化 _writebunchobj(space_path, tfidfspace) print("if-idf词向量空间实例创建成功!!!") def testvector_space(stopword_path, bunch_path, space_path, train_tfidf_path): stpwrdlst = _readfile(stopword_path).splitlines() # 把停用词变成列表 bunch = _readbunchobj(bunch_path) tfidfspace = Bunch(label=bunch.label, tdm=[], vocabulary={}) # 导入训练集的TF-IDF词向量空间 ★★ trainbunch = _readbunchobj(train_tfidf_path) tfidfspace.vocabulary = trainbunch.vocabulary vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words=stpwrdlst, sublinear_tf=True, max_df=0.7, vocabulary=trainbunch.vocabulary, min_df=0.001) tfidfspace.tdm = vectorizer.fit_transform(bunch.contents) _writebunchobj(space_path, tfidfspace) print("if-idf词向量空间实例创建成功!!!")
if __name__=="__main__": Stestdata = [] Stestlabel = [] Sart_test = [] Slast = [] Snew = [] \'\'\'============================先导入数据==================================\'\'\' file_test = \'F:/goverment/excel operating/all_tocai_train.csv\' importSmallContentdata(file_test, Stestdata, Sart_test, Stestlabel, 1, Slast, Snew) #print(Sart_test) # print("Stestlabel" ,len(Stestlabel)) # print("小类导入数据完毕") # print("大类标签导入完毕")#共1329*4 \'\'\'==========================================================tf-idf对Bar进行文本特征提取============================================================================\'\'\' # 导入分词后的词向量bunch对象 test_bunch_path = "F:/goverment/excel operating/trainbunch.bat" test_space_path = "F:/goverment/excel operating/traintfdifspace.dat" stopword_path = "F:/goverment/excel operating/hlt_stop_words.txt" \'\'\'============================================================tf-idf对Sart进行文本特征提取==============================================================================\'\'\' buildtestbunch(test_bunch_path, Sart_test, Stestlabel) testvector_space(stopword_path, test_bunch_path, test_space_path, test_space_path) test_set = _readbunchobj(test_space_path) \'\'\'测试数据\'\'\' #获取已知 id 找 文本 dic={} for i in test_set.vocabulary.keys(): dic[test_set.vocabulary[i]]=i #print(dic)
test_set分为三部分
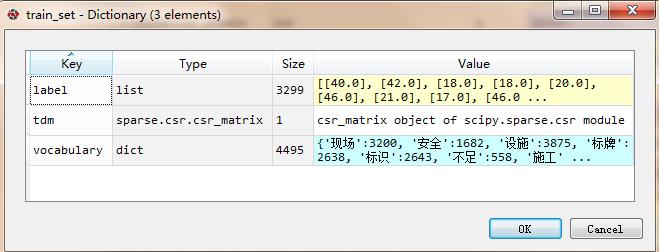
查看test_set.tdm

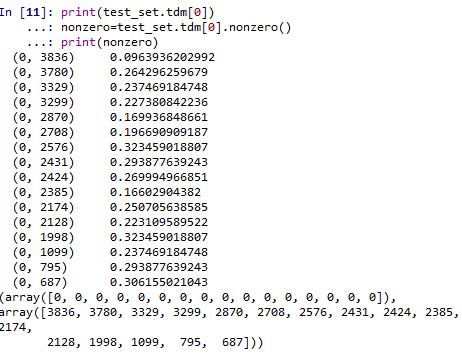
print(test_set.tdm) (0, 3836) 0.0963936202992 (0, 3780) 0.264296259679 (0, 3329) 0.237469184748 (0, 3299) 0.227380842236 (0, 2870) 0.169936848661 (0, 2708) 0.196690909187 (0, 2576) 0.323459018807 (0, 2431) 0.293877639243 (0, 2424) 0.269994966851 (0, 2385) 0.16602904382 (0, 2174) 0.250705638585 (0, 2128) 0.223109589522 (0, 1998) 0.323459018807 (0, 1099) 0.237469184748 (0, 795) 0.293877639243 (0, 687) 0.306155021043 (1, 4127) 0.158745878875 (1, 4075) 0.187148908824 (1, 4066) 0.275285441964 (1, 3506) 0.325600030259 (1, 3329) 0.271913955503 (1, 2512) 0.30263228246 (1, 2385) 0.190111462595 (1, 2121) 0.370376566292 (1, 1555) 0.325600030259 : : (1437, 790) 0.216605181177 (1437, 784) 0.30372112351 (1437, 558) 0.20127256985 (1438, 4279) 0.240643793924 (1438, 4276) 0.118606614328 (1438, 4184) 0.148565457218 (1438, 4107) 0.185731268834 (1438, 4014) 0.154101569448 (1438, 3877) 0.220155031015 (1438, 3298) 0.245309299377 (1438, 2933) 0.318303833306 (1438, 2383) 0.0923818814565 (1438, 2378) 0.213187531379 (1438, 2092) 0.263926619628 (1438, 2091) 0.263926619628 (1438, 1969) 0.15613334884 (1438, 1802) 0.144868484461 (1438, 1714) 0.256704677923 (1438, 1447) 0.309102127772 (1438, 1411) 0.226077842579 (1438, 1010) 0.116062811153 (1438, 997) 0.263926619628 (1438, 648) 0.15613334884 (1438, 640) 0.157728638816 (1438, 565) 0.232695024234
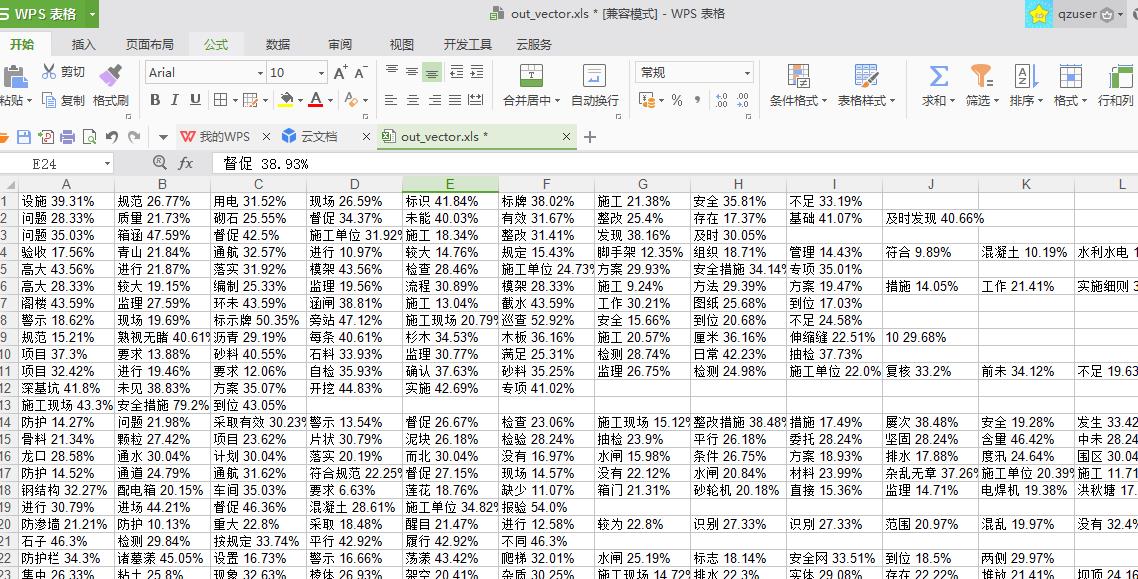
打印出分词及权重
#各个文本的词语及权重 dataset = read_csv(file_test) Sdata = dataset.values[:, :] print(len(Sdata)) #print(nonzero[1]) myexcel = xlwt.Workbook() sheet = myexcel.add_sheet("sheet1") for k in range(len(Sdata)):#遍历每一条文本 nonzero=test_set.tdm[k].nonzero() ls=[] for i in range(len(nonzero[1])): b=test_set.tdm[k, nonzero[1][i]]*100 #test_set.tdm[k, nonzero[1][i]]是第k条文本中,第i个权重非零的词权重 a= dic[nonzero[1][i]] +" "+str(round(b,2))+"%" ls.append(a) for i in range(len(nonzero[1])): sheet.write(k,i,str(ls[i])) myexcel.save("out_vector.xls")
运行结果如下:
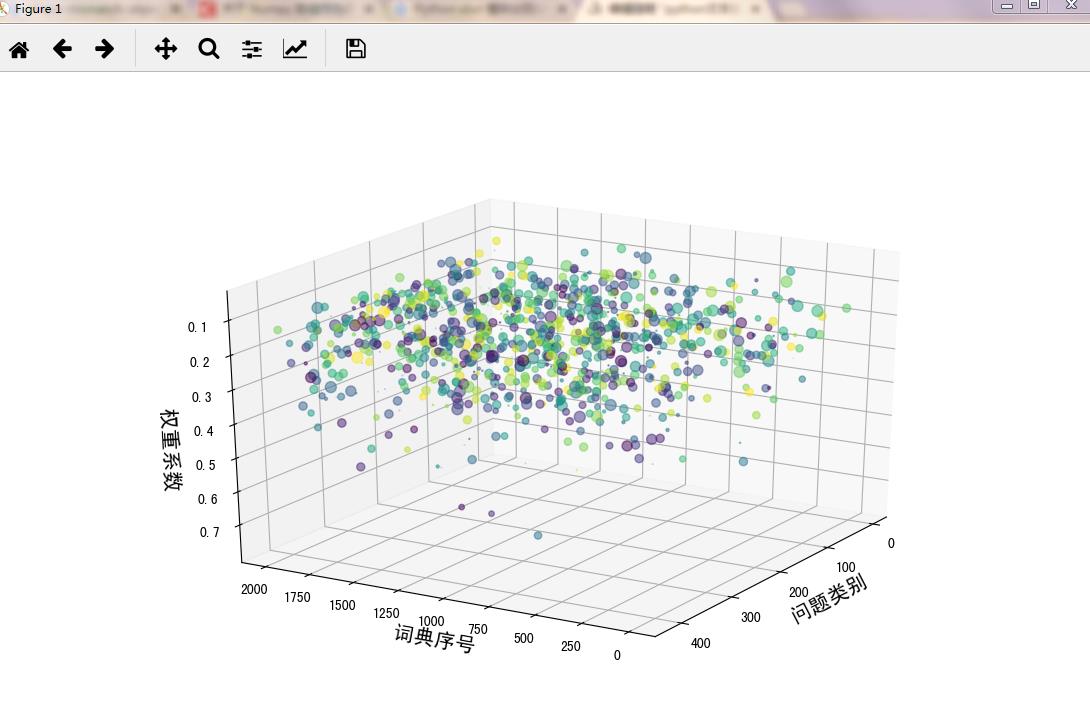
画出3d图:还可以转动呢
以上是关于python文本挖掘输出权重,词频等信息的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
