Linux基础19 Gdisk, 挂载命令mount与配置文件, fstab文件的详细信息, Swap介绍与案例, 修改/etc/fstab错误重启系统, 修复(单用户模式登陆)
Posted 战斗小人
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux基础19 Gdisk, 挂载命令mount与配置文件, fstab文件的详细信息, Swap介绍与案例, 修改/etc/fstab错误重启系统, 修复(单用户模式登陆)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
gdisk
gdisk分区,分区表是GPT,支持更大的容量分区。128个。
#需要安装 [root@oldboy ~]# yum install -y gdisk
1.添加硬盘,3TB
在vmware里面添加
2.查看是否能识别出来。
[root@oldboy ~]# lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sda 8:0 0 50G 0 disk ├─sda1 8:1 0 200M 0 part /boot ├─sda2 8:2 0 2G 0 part [SWAP] └─sda3 8:3 0 47.8G 0 part / sdb 8:16 0 20G 0 disk ├─sdb1 8:17 0 1G 0 part /data2 ├─sdb2 8:18 0 2G 0 part ├─sdb3 8:19 0 7G 0 part ├─sdb4 8:20 0 1K 0 part ├─sdb5 8:21 0 5G 0 part └─sdb6 8:22 0 5G 0 part sdc 8:32 0 3T 0 disk sr0 11:0 1 4.3G 0 rom [root@oldboy ~]# ll /dev/sd* brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 0 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sda brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 1 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sda1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 2 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sda2 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 3 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sda3 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 16 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sdb brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 17 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sdb1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 18 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sdb2 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 19 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sdb3 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 20 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sdb4 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 21 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sdb5 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 22 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sdb6 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 32 Jul 16 19:09 /dev/sdc
3.进行分区
[root@oldboy ~]# gdisk /dev/sdc GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.10 Partition table scan: MBR: not present BSD: not present APM: not present GPT: not present Creating new GPT entries. Command (? for help): ? b back up GPT data to a file #将GPT数据备份到文件中 c change a partition\'s name #更改分区的名称 ** d delete a partition #删除分区 i show detailed information on a partition #显示分区的详细信息 ** l list known partition types #列出已知的分区类型 ** n add a new partition #添加一个新的分区 o create a new empty GUID partition table (GPT) #创建一个新的空GUID分区表(GPT) ** p print the partition table #打印分区表 ** q quit without saving changes #没有保存更改就退出 r recovery and transformation options (experts only) #恢复和转换选项(仅限专家使用) s sort partitions #年代分类分区 t change a partition\'s type code #不要更改分区的类型代码 v verify disk #验证磁盘 ** w write table to disk and exit #将表写入磁盘并退出 x extra functionality (experts only) #额外功能(仅限专家使用) ** ? print this menu #打印菜单 Command (? for help): n #创建分区 Partition number (1-128, default 1): #选择分区表的编号,选择默认,直接回车键 First sector (34-6442450910, default = 2048) or +-sizeKMGTP: #扇区的开始位置,选择默认,直接回车键 Last sector (2048-6442450910, default = 6442450910) or +-sizeKMGTP: # 这里就分一个区,直接回车 #该分区扇区的结束位置,选择默认,只做一个分区,直接回车键,最大值 Current type is \'Linux filesystem\' Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300): L #显示其他文件类型 0700 Microsoft basic data 0c01 Microsoft reserved 2700 Windows RE 3000 ONIE boot 3001 ONIE config 4100 PowerPC PReP boot 4200 Windows LDM data 4201 Windows LDM metadata 7501 IBM GPFS 7f00 ChromeOS kernel 7f01 ChromeOS root 7f02 ChromeOS reserved 8200 Linux swap 8300 Linux filesystem 8301 Linux reserved 8302 Linux /home 8400 Intel Rapid Start 8e00 Linux LVM a500 FreeBSD disklabel a501 FreeBSD boot a502 FreeBSD swap a503 FreeBSD UFS a504 FreeBSD ZFS a505 FreeBSD Vinum/RAID a580 Midnight BSD data a581 Midnight BSD boot a582 Midnight BSD swap a583 Midnight BSD UFS a584 Midnight BSD ZFS a585 Midnight BSD Vinum a800 Apple UFS a901 NetBSD swap a902 NetBSD FFS a903 NetBSD LFS a904 NetBSD concatenated a905 NetBSD encrypted a906 NetBSD RAID ab00 Apple boot af00 Apple HFS/HFS+ af01 Apple RAID af02 Apple RAID offline af03 Apple label af04 AppleTV recovery af05 Apple Core Storage be00 Solaris boot bf00 Solaris root bf01 Solaris /usr & Mac Z bf02 Solaris swap bf03 Solaris backup bf04 Solaris /var bf05 Solaris /home bf06 Solaris alternate se bf07 Solaris Reserved 1 bf08 Solaris Reserved 2 bf09 Solaris Reserved 3 bf0a Solaris Reserved 4 bf0b Solaris Reserved 5 c001 HP-UX data c002 HP-UX service ea00 Freedesktop $BOOT eb00 Haiku BFS ed00 Sony system partitio ed01 Lenovo system partit Press the <Enter> key to see more codes: #翻页 ef00 EFI System ef01 MBR partition scheme ef02 BIOS boot partition fb00 VMWare VMFS fb01 VMWare reserved fc00 VMWare kcore crash p fd00 Linux RAID Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300): #选择默认,直接回车 Changed type of partition to \'Linux filesystem\' Command (? for help): p #打印分区的信息 Disk /dev/sdc: 6442450944 sectors, 3.0 TiB Logical sector size: 512 bytes Disk identifier (GUID): C783DB62-2CE8-44B1-A2C2-3589541AF6E0 Partition table holds up to 128 entries First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 6442450910 Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries Total free space is 2014 sectors (1007.0 KiB) Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name 1 2048 6442450910 3.0 TiB 8300 Linux filesystem Command (? for help): w #保存并退出 Final checks complete. About to write GPT data. THIS WILL OVERWRITE EXISTING PARTITIONS!! Do you want to proceed? (Y/N): y #确认操作 OK; writing new GUID partition table (GPT) to /dev/sdc. The operation has completed successfully.
4.格式化,进行创建文件系统,centos7系列,统一使用(系统默认)xfs文件系统。
[root@oldboy ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/sdc1 meta-data=/dev/sdc1 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=201326527 blks = sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1 = crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0 data = bsize=4096 blocks=805306107, imaxpct=5 = sunit=0 swidth=0 blks naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1 log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=393215, version=2 = sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1 realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
5.挂载,先创建一个挂载点
[root@oldboy ~]# mkdir /gpt [root@oldboy ~]# mount /dev/sdc1 /gpt [root@oldboy ~]# df -h |grep sdc1 /dev/sdc1 3.0T 33M 3.0T 1% /gpt [root@oldboy ~]# [root@oldboy ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/gpt/test.txt bs=100M count=20 # 创建文件 bs每次传输多大 20+0 records in 20+0 records out 2097152000 bytes (2.1 GB) copied, 7.11174 s, 295 MB/s [root@oldboy ~]# ll /gpt/ total 2048000 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2097152000 Jul 17 17:34 test.txt [root@oldboy ~]# ll -h /gpt/ total 2.0G -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2.0G Jul 17 17:34 test.txt [root@oldboy ~]# df -h |grep sdc1 /dev/sdc1 3.0T 2.0G 3.0T 1% /gpt [root@oldboy ~]# umount /gpt [root@oldboy ~]# ll /gpt total 0 [root@oldboy ~]# mkdir /data [root@oldboy ~]# mount /dev/sdc1 /data [root@oldboy ~]# ll /data total 2048000 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2097152000 Jul 17 17:34 test.txt
6.永久挂载
[root@oldboy ~]# vim /etc/fstab [root@oldboy ~]# tail -1 /etc/fstab /dev/sdc1 /data xfs defaults 0 0 [root@oldboy ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda3 48G 2.9G 45G 6% / devtmpfs 980M 0 980M 0% /dev tmpfs 991M 0 991M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 991M 9.6M 981M 1% /run tmpfs 991M 0 991M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda1 197M 105M 93M 54% /boot tmpfs 199M 0 199M 0% /run/user/0 /dev/sdb1 1014M 533M 482M 53% /data2 /dev/sdc1 3.0T 2.0G 3.0T 1% /data [root@oldboy ~]# umount /data [root@oldboy ~]# mount -a [root@oldboy ~]# echo $? 0 [root@oldboy ~]# vim /etc/fstab [root@oldboy ~]# mount -a mount: special device dev/sdc1 does not exist [root@oldboy ~]# vim /etc/fstab [root@oldboy ~]# mount -a [root@oldboy ~]# df -h |grep sdc1 /dev/sdc1 3.0T 2.0G 3.0T 1% /data
parted #高级分区工具。了解
挂载方式:mount
mount 挂载的命令 选项: -t #文件系统(centos7默认是xfs) [root@oldboy ~]# mount -t xfs /dev/sdc1 /data -o #指定挂载的参数 [root@oldboy ~]# mount -o ro /dev/sdc1 /data # ro只读文件系统 [root@oldboy ~]# touch /data/123 touch: cannot touch ‘/data/123’: Read-only file system -a #重新挂载配置/etc/fstab文件的分区表 [root@oldboy ~]# mount -a
umount 卸载的命令 [root@oldboy ~]# umount /dev/sdc1 # 设备名或者挂载点 -l #强制卸载(即使在该目录下,使用中也可以卸载) -f #勉强的卸载,不一定能卸载成功。 #退出当前目录进行卸载。
[root@oldboy data]# umount -f /data umount: /data: target is busy. (In some cases useful info about processes that use the device is found by lsof(8) or fuser(1)) [root@oldboy data]# umount -lf /data [root@oldboy data]# cd [root@oldboy ~]# mount -a [root@oldboy ~]# cd /data [root@oldboy data]# umount /data umount: /data: target is busy. (In some cases useful info about processes that use the device is found by lsof(8) or fuser(1)) [root@oldboy data]# cd [root@oldboy ~]# umount /data [root@oldboy ~]# man umount [root@oldboy ~]# mount -a [root@oldboy ~]# [root@oldboy ~]# [root@oldboy ~]# cd /data [root@oldboy data]# [root@oldboy data]# umount /data umount: /data: target is busy. (In some cases useful info about processes that use the device is found by lsof(8) or fuser(1)) [root@oldboy data]# umount -l /data
#使用UUID进行挂载(推荐, 因为设备名有可能重)
[root@oldboy ~]# blkid # 查看uuid /dev/sda1: UUID="e7d2d29d-d679-4f0f-8acb-e86ffbe9b5f9" TYPE="xfs" /dev/sda2: UUID="7b4436bc-2748-49ba-9ff8-a5923eaf2127" TYPE="swap" /dev/sda3: UUID="8a332f48-6869-4866-9e8d-698aaaf744df" TYPE="xfs" /dev/sdb1: UUID="8cb952e5-136d-4f9d-807b-662f3cc521d7" TYPE="xfs" /dev/sdc1: UUID="813aae2a-b3eb-4f24-bef2-9a669abaf90e" TYPE="xfs" PARTLABEL="Linux filesystem" PARTUUID="c79e5fdf-1ea9-46a7-b5b9-931cf80fa3cb" /dev/sr0: UUID="2018-11-25-23-54-16-00" LABEL="CentOS 7 x86_64" TYPE="iso9660" PTTYPE="dos" [root@oldboy ~]# blkid |grep sdc /dev/sdc1: UUID="813aae2a-b3eb-4f24-bef2-9a669abaf90e" TYPE="xfs" PARTLABEL="Linux filesystem" PARTUUID="c79e5fdf-1ea9-46a7-b5b9-931cf80fa3cb" [root@oldboy ~]# mount UUID="813aae2a-b3eb-4f24-bef2-9a669abaf90e" /data [root@oldboy ~]# vim /etc/fstab [root@oldboy ~]# tail -1 /etc/fstab UUID="813aae2a-b3eb-4f24-bef2-9a669abaf90e" /data xfs defaults 0 0 [root@oldboy ~]# mount -a
/etc/fstab 文件的详细信息
/dev/sdb1 /data1 xfs defaults 0 0 第一列:挂载的设备(可以是uuid) 第二列:挂载点 第三列:文件系统的类型 第四列:挂载的参数,defaults表示默认。 参数 含义 async/sync 是否同步方式运行,默认async(异步)。 user/nouser 是否允许普通用户使用mount命令挂载,默认nouser。 exec/noexec 是否允许可执行文件执行,默认exec。 suid/nosuid 是否允许存在suid属性的文件,默认suid。 auto/noauto 执行mount -a时,此文件系统是否被主动挂载,默认auto。 rw/ro 是否只读或者读写模式进行挂载。默认rw。 default 具有rw,suid,exec,auto,nouser,async等默认参数的设定。 第五列:是否使用dump进行备份。默认选择0 0 #不备份 1 #每天进行备份 2 #不定时的进行备份 第六列:是否通过fsck这个命令磁盘检测,默认是0 0 #不检查 1 #检查,如果存在根分区,这个值只能是根分区上面。 如果挂载点是/,要检查只能是1 2 #检查,按照顺序进行检查。
swap的介绍
企业案例:
java使用内存过大,出现oom故障,系统会随机kill掉一个进程。 tailf /var/log/messages可以查看系统日志 一旦内存用完,会大量占用swap 1.临时增加内存,需要找个1G的分区 2.使这个分区成为swap [root@oldboy ~]# mkswap /dev/sdb2 # 此时通过free -m还是不变 3.扩容swap [root@oldboy ~]# swapon /dev/sdb2 4.检查(查看内存) [root@oldboy ~]# free -m total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1980 100 1692 9 188 1695 Swap: 4095 0 4095 5.缩减swap内存 [root@oldboy ~]# swapoff /dev/sdb2 [root@oldboy ~]# free -m total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1980 100 1691 9 188 1695 Swap: 2047 0 2047 6.禁用所有的swap(云服务会禁用) [root@oldboy ~]# swapoff -a [root@oldboy ~]# free -m total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1980 98 1694 9 187 1697 Swap: 0 0 0 7.恢复swap [root@oldboy ~]# swapon -a [root@oldboy ~]# free -m total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1980 98 1694 9 187 1697 Swap: 2047 0 2047 8.检查swap在使用的设备 [root@oldboy ~]# swapon -s Filename Type Size Used Priority /dev/sda2 partition 2097148 0 -2 /dev/sdb2 partition 2097148 0 -3 9.通过一个大文件的方式添加临时内存 [root@oldboy ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/data/swap_file bs=100M count=10 # 生成1G的文件 10+0 records in 10+0 records out 1048576000 bytes (1.0 GB) copied, 0.992418 s, 1.1 GB/s [root@oldboy ~]# ll /data data/ data1/ data2/ [root@oldboy ~]# ll /data/swap_file -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1048576000 Jul 17 19:00 /data/swap_file [root@oldboy ~]# chmod 600 /data/swap_file [root@oldboy ~]# file /data/swap_file # 查看文件类型 /data/swap_file: data [root@oldboy ~]# mkswap -f /data/swap_file # 指定文件需要-f参数 Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 1023996 KiB no label, UUID=d822190d-7826-4fb4-9f1c-e011cd421eca [root@oldboy ~]# file /data/swap_file /data/swap_file: Linux/i386 swap file (new style), version 1 (4K pages), size 255999 pages, no label, UUID=d822190d-7826-4fb4-9f1c-e011cd421eca [root@oldboy ~]# swapon /data/swap_file # 通过文件添加swap swapon: /data/swap_file: insecure permissions 0644, 0600 suggested. [root@oldboy ~]# free -m total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1980 99 663 9 1217 1682 Swap: 3047 0 3047
随意修改/etc/fstab重启系统, 进入修复.
能够进入系统,直接修改
# 修改为读写模式, 重新挂载
[root@web ~]# mount -o rw,remount UUID=8a332f48-6869-4866-9e8d-698aaaf744df /
无法进入系统,单用户模式登陆(忘记root密码,使用这种模式进行修改)
1. 启动界面下,按e进入单用户模式
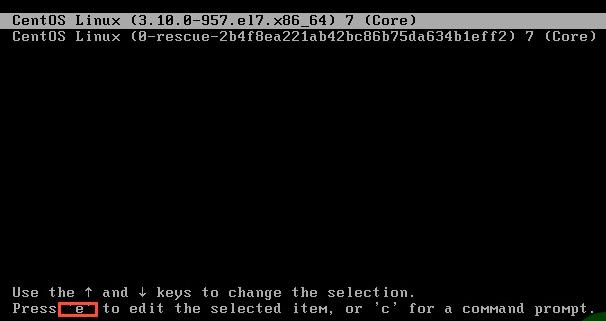
2.找到linux16,把ro只读改为rw读写,输入命令解释器 init=/bin/bash,把selinux关闭 enforcing=0 (如果已经关闭,可以不管)

3. ctrl+x 启动
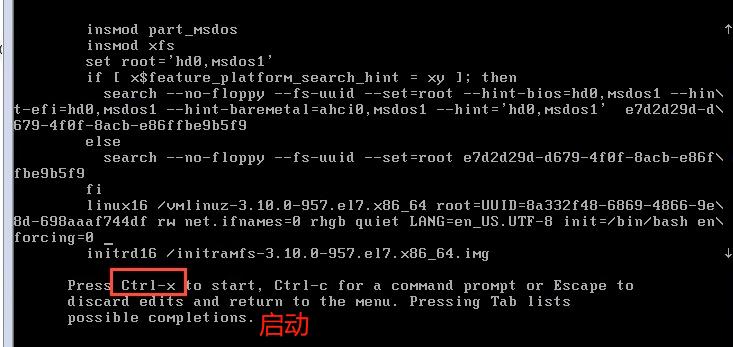
4. 然后重新修改/etc/fstab文件
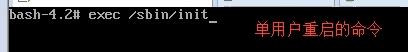
5. exec /sbin/init # 进行单用户模式下的重启
Linux系统的目录绑定配置
Linux系统的目录绑定配置
一.源目录与目标目录情况
1、源目录文件及inode
[root@docker data]# pwd
/data
[root@docker data]# ll
total 140648
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 205 Dec 11 13:59 backdata.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 11 13:54 file1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 11 13:54 file10
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 11 13:54 file2
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 11 13:54 file3
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 11 13:54 file4
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 11 13:54 file5
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 11 13:54 file6
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 11 13:54 file7
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 11 13:54 file8
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 11 13:54 file9
-rw------- 1 root root 144015872 Dec 11 14:11 web01.tar
[root@docker data]# ls -lid /data
2401630 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 177 Dec 11 14:11 /data
2、目标目录的文件及inode
[root@docker backup]# pwd
/backup
[root@docker backup]# ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 17 17:00 test1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 17 17:00 test2
[root@docker backup]# ls -lid /backup/
38821596 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 32 Dec 17 17:00 /backup/
[root@docker backup]#
二、将两个目录进行绑定
1.moun --bind进行绑定
将test1挂载到test2上,inode号都变为test1的inode
root@docker backup]# mount --bind /data/ /backup/
2.检查绑定后的两个目录情况
[
[root@docker backup]# ls /data/
backdata.tar.gz file1 file10 file2 file3 file4 file5 file6 file7 file8 file9 web01.tar
[root@docker backup]# ls /backup/
backdata.tar.gz file1 file10 file2 file3 file4 file5 file6 file7 file8 file9 web01.tar
[root@docker backup]# lls -lid /data/ /backup/
bash: lls: command not found...
Similar command is: 'ls'
[root@docker backup]# ls -lid /data/ /backup/
2401630 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 177 Dec 11 14:11 /backup/
2401630 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 177 Dec 11 14:11 /data/
3.moun --bind绑定注意事项
#注意,mount --bind重启后会丢失挂载,包括/dev/shm目录重启后也会清空,要解决该问题,可以添加开机自启脚本
#添加到/etc/rc.local文件中
三、解挂载
1.对两个目录进行解挂载
[root@docker /]# umount /backup
2.查看解挂载后的情况
[root@docker ~]# ls /data
backdata.tar.gz file1 file10 file2 file3 file4 file5 file6 file7 file8 file9 web01.tar
[root@docker ~]# ls /backup/
test1 test2
[root@docker ~]# ls -lid /data /backup/
38821596 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 32 Dec 17 17:00 /backup/
2401630 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 177 Dec 11 14:11 /data
四、应用场景
1.场景描述
在固件开发过程中常常遇到这样的情况:为测试某个新功能,必需修改某个系统文件。而这个文件在只读文件系统上(总不能为一个小小的测试就重刷固件吧),或者是虽然文件可写,但是自己对这个改动没有把握,不愿意直接修改。这时候mount --bind就是你的好帮手。
2.测试系统文件
[root@docker ~]# mount -o ro /dev/sdb1 /soft
[root@docker ~]# cd /soft/
[root@docker soft]# touch file1
touch: cannot touch 'file1': Read-only file system
[root@docker soft]#
[root@docker soft]# mount --bind /test/ /soft/
[root@docker soft]# cd /test
[root@docker test]# touch test1..10.txt
[root@docker test]# ls
test10.txt test1.txt test2.txt test3.txt test4.txt test5.txt test6.txt test7.txt test8.txt test9.txt
[root@docker test]# ls /soft/
test10.txt test1.txt test2.txt test3.txt test4.txt test5.txt test6.txt test7.txt test8.txt test9.txt
[root@docker test]#
以上是关于Linux基础19 Gdisk, 挂载命令mount与配置文件, fstab文件的详细信息, Swap介绍与案例, 修改/etc/fstab错误重启系统, 修复(单用户模式登陆)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章