Linux驱动开发笔记:helloworld驱动源码编写makefile编写以及驱动编译基本流程
Posted 红胖子(红模仿)
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux驱动开发笔记:helloworld驱动源码编写makefile编写以及驱动编译基本流程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
基于linux的驱动开发学习笔记,本篇是描述了一个字符驱动的基础开发流程,以便做嵌入式开发多年的应用或者系统学习驱动开发。
笔者拥有硬件基础,单片机软硬基础,linux系统基础等各种,就是没有linux驱动框架基础,未做过linux系统移植和驱动移植开发了。所以补完linux系统移植和驱动开发就基本可以打通嵌入式整套流程了,作为技术leader不一定亲自动手做,但是一定要对产品构架中的每一块业务和技术要基本清楚。
建议参考xun为的视频教程,教程整个过程非常清晰,直接给拥有很多知识基础的资深研发,可以不陷入某山的固有思维误区,也不用imx6的太过庞从汇报理解大而冗余,它能直接以最终实现目标为目的,不用从什么裸机开始做开发学习,怎么做也告诉你为什么都交代清楚,再结合多年相关从业工作经验,说实在的,一通百通可以融会贯通。从业多年,第一次推荐,因为确实真的是好东西。
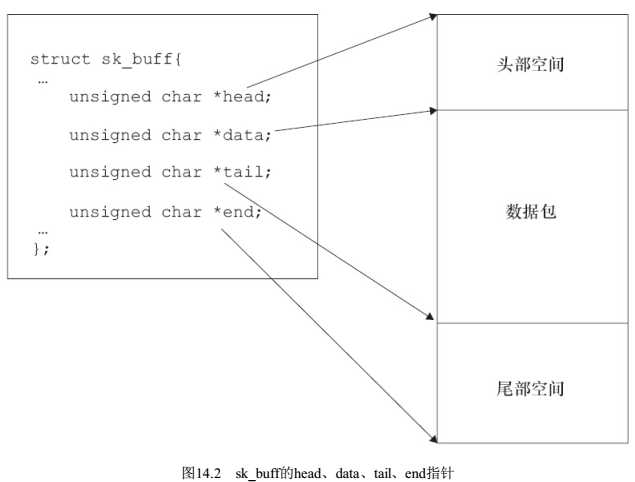
- 头文件:宏定义等等
- 驱动模块的入口和出口宏:linux驱动框架
- 声明信息:linux内核模块的必要声明
- 功能实现:真正实现驱动的实体代码
包含宏定义的头文件init.h,是一些初始化和宏头文件,一些module_init,module_exit等。
#include <linux/init.h>
包含了初始化加载模块的头文件
#include <linux/module.h>
module_init()和module_exit()入口和出口宏。(PS:这里括号内实际上需要填入入口出口函数,后续再填入)
module_init();
module_exit();
告诉内核,本模块驱动有开源许可证。
MODULE_LICENSE(“GPL”);
入口函数
static int hello_init(void)
// 在内核里面无法使用基础c库printf,需要使用内核库printk
printk(“Hello, I’m hongPangZi\\n”);
return 0;
出口函数
static void hello_exit(void)
printk(“bye-bye!!!\\n”);
此时可以修改,步骤二的出口入口宏了
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
总结,按部就班四步法,搭建了基础的驱动代码框架。
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
static int hello_init(void)
// 在内核里面无法使用基础c库printf,需要使用内核库printk
printk(“Hello, I’m hongPangZi\\n”);
return 0;
static void hello_exit(void)
printk(“bye-bye!!!\\n”);
MODULE_LICENSE(“GPL”);
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
把驱动编译城模块,然后加载到内核里面。
把驱动直接编译到内核,运行内核则会直接加载驱动。
obj-m += helloworld.o
内核在哪,实际路径在哪
KDIR:=
PWD?=$(shell pwd)
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
make进去KDIR路径,当前路径编译成模块。
obj-m = helloworld.o
KDIR:=
PWD?=$(shell pwd)
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
编译驱动之前有几点要注意:
与驱动编译成的目标系统,获取对应的内核且需要编译通过。
开发板或者系统跑的内核版本需要与编译内核驱动的内核源码版本一致。
注意3:编译目标环境要确认是否是需要的构架,在内核目录下:
make menu configure
export ARCH=arm
修改构架后,可使用menu configure查看标题栏的内核构架
找到使用的arm编译器(实际为arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc,取gcc前缀)
export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf-
直接输入make,编译驱动,会生成hellowold.ko文件,ko文件就是编译好的驱动模块。
将驱动拷贝到开发板或者目标系统,然后使用加载指令:
insmod helloworld.ko
会打印入口加载的printk输出。
lsmod
可以查看到加载的驱动模块
rmmod helloworld
可以移除指定驱动模块(PS:卸载驱动不需要.ko后缀),卸载成功会打印之前的printk输出。
学习了驱动的基础框架,那么为了方便很好的测试,让大家都有基础环境,下一篇,将使用ubuntu18.04,编译ubuntu18.04的驱动,然后做好本篇文章的相关实战测试。
《linux设备驱动开发详解》笔记——14 linux网络设备驱动
14.1 网络设备驱动结构
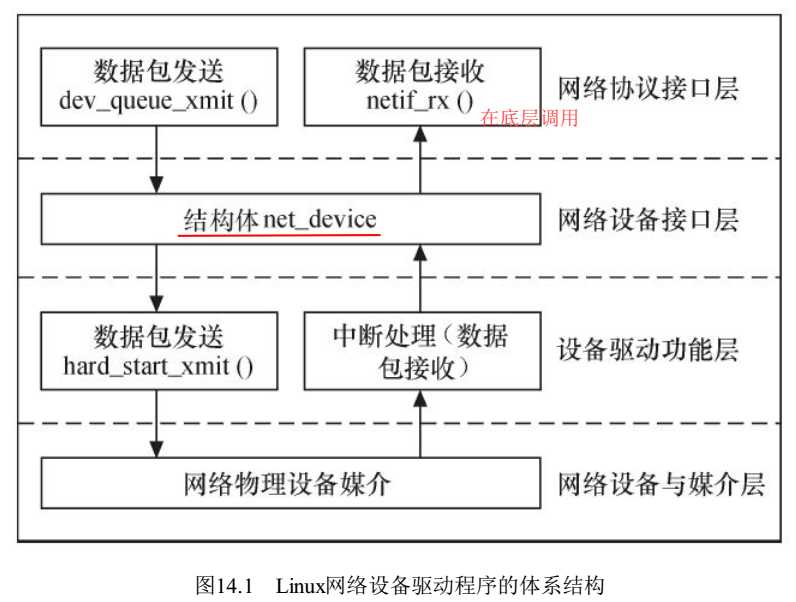
- 网络协议接口层:硬件无关,标准收发函数dev_queue_xmit()和netif_rx(); 注意,netif_rx是将接收到的数据给上层,有时也在驱动收到数据以后调用。
- 网络设备接口层,net_device,统一接口名称,使上层独立于具体硬件。
- 设备驱动功能层,实现net_device的各成员
- 物理层
在整个以太网架构里,有两个数据结构非常重要,即sk_buff和net_device,后面两节有说明。
还有一些与内核交互的函数,需要掌握,如netif_start_queue(),netif_stop_queue(),netif_wakeup_queue(),netif_rx(),netif_carrier_on/off_ok()
14.1.1 sk_buff
以太网各层之间用sk_buff结构体传递数据,该结构体是很多函数的形参。
#include <linux/skbuff.h> /** * struct sk_buff - socket buffer * @next: Next buffer in list * @prev: Previous buffer in list * @tstamp: Time we arrived * @sk: Socket we are owned by * @dev: Device we arrived on/are leaving by * @cb: Control buffer. Free for use by every layer. Put private vars here * @_skb_refdst: destination entry (with norefcount bit) * @sp: the security path, used for xfrm * @len: Length of actual data * @data_len: Data length * @mac_len: Length of link layer header * @hdr_len: writable header length of cloned skb * @csum: Checksum (must include start/offset pair) * @csum_start: Offset from skb->head where checksumming should start * @csum_offset: Offset from csum_start where checksum should be stored * @priority: Packet queueing priority * @local_df: allow local fragmentation * @cloned: Head may be cloned (check refcnt to be sure) * @ip_summed: Driver fed us an IP checksum * @nohdr: Payload reference only, must not modify header * @nfctinfo: Relationship of this skb to the connection * @pkt_type: Packet class * @fclone: skbuff clone status * @ipvs_property: skbuff is owned by ipvs * @peeked: this packet has been seen already, so stats have been * done for it, don‘t do them again * @nf_trace: netfilter packet trace flag * @protocol: Packet protocol from driver * @destructor: Destruct function * @nfct: Associated connection, if any * @nf_bridge: Saved data about a bridged frame - see br_netfilter.c * @skb_iif: ifindex of device we arrived on * @tc_index: Traffic control index * @tc_verd: traffic control verdict * @rxhash: the packet hash computed on receive * @queue_mapping: Queue mapping for multiqueue devices * @ndisc_nodetype: router type (from link layer) * @ooo_okay: allow the mapping of a socket to a queue to be changed * @l4_rxhash: indicate rxhash is a canonical 4-tuple hash over transport * ports. * @wifi_acked_valid: wifi_acked was set * @wifi_acked: whether frame was acked on wifi or not * @no_fcs: Request NIC to treat last 4 bytes as Ethernet FCS * @dma_cookie: a cookie to one of several possible DMA operations * done by skb DMA functions * @napi_id: id of the NAPI struct this skb came from * @secmark: security marking * @mark: Generic packet mark * @dropcount: total number of sk_receive_queue overflows * @vlan_proto: vlan encapsulation protocol * @vlan_tci: vlan tag control information * @inner_protocol: Protocol (encapsulation) * @inner_transport_header: Inner transport layer header (encapsulation) * @inner_network_header: Network layer header (encapsulation) * @inner_mac_header: Link layer header (encapsulation) * @transport_header: Transport layer header * @network_header: Network layer header * @mac_header: Link layer header * @tail: Tail pointer * @end: End pointer * @head: Head of buffer * @data: Data head pointer * @truesize: Buffer size * @users: User count - see {datagram,tcp}.c */ struct sk_buff { /* These two members must be first. */ struct sk_buff *next; struct sk_buff *prev; ktime_t tstamp; struct sock *sk; struct net_device *dev; /* * This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every * layer. Please put your private variables there. If you * want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone() * first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM. */ char cb[48] __aligned(8); unsigned long _skb_refdst; #ifdef CONFIG_XFRM struct sec_path *sp; #endif unsigned int len, // data段的长度 data_len; __u16 mac_len, hdr_len; union { __wsum csum; struct { __u16 csum_start; __u16 csum_offset; }; }; __u32 priority; kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags1); __u8 local_df:1, cloned:1, ip_summed:2, nohdr:1, nfctinfo:3; __u8 pkt_type:3, fclone:2, ipvs_property:1, peeked:1, nf_trace:1; kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags1); __be16 protocol; void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb); #if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE) struct nf_conntrack *nfct; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER struct nf_bridge_info *nf_bridge; #endif int skb_iif; __u32 rxhash; __be16 vlan_proto; __u16 vlan_tci; #ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED __u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */ #ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT __u16 tc_verd; /* traffic control verdict */ #endif #endif __u16 queue_mapping; kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags2); #ifdef CONFIG_IPV6_NDISC_NODETYPE __u8 ndisc_nodetype:2; #endif __u8 pfmemalloc:1; __u8 ooo_okay:1; __u8 l4_rxhash:1; __u8 wifi_acked_valid:1; __u8 wifi_acked:1; __u8 no_fcs:1; __u8 head_frag:1; /* Encapsulation protocol and NIC drivers should use * this flag to indicate to each other if the skb contains * encapsulated packet or not and maybe use the inner packet * headers if needed */ __u8 encapsulation:1; /* 6/8 bit hole (depending on ndisc_nodetype presence) */ kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags2); #if defined CONFIG_NET_DMA || defined CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL union { unsigned int napi_id; dma_cookie_t dma_cookie; }; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK __u32 secmark; #endif union { __u32 mark; __u32 dropcount; __u32 reserved_tailroom; }; __be16 inner_protocol; __u16 inner_transport_header; __u16 inner_network_header; __u16 inner_mac_header; __u16 transport_header; __u16 network_header; __u16 mac_header; /* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */ sk_buff_data_t tail; sk_buff_data_t end; unsigned char *head, *data; unsigned int truesize; atomic_t users; };
- 接收时,各层去掉自己的协议,把数据给上层;
- 发送时,各层添加自己的协议,最终给物理网口。
- 上图指针可以动态调整,下面是若干函数
/** tail后移,即在data中增加数据 * skb_put - add data to a buffer * @skb: buffer to use * @len: amount of data to add * * This function extends the used data area of the buffer. If this would * exceed the total buffer size the kernel will panic. A pointer to the * first byte of the extra data is returned. */ unsigned char *skb_put(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) { unsigned char *tmp = skb_tail_pointer(skb); SKB_LINEAR_ASSERT(skb); skb->tail += len; skb->len += len; if (unlikely(skb->tail > skb->end)) skb_over_panic(skb, len, __builtin_return_address(0)); return tmp; } /** * skb_push - add data to the start of a buffer,data前移 * @skb: buffer to use * @len: amount of data to add * * This function extends the used data area of the buffer at the buffer * start. If this would exceed the total buffer headroom the kernel will * panic. A pointer to the first byte of the extra data is returned. */ unsigned char *skb_push(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) { skb->data -= len; skb->len += len; if (unlikely(skb->data<skb->head)) skb_under_panic(skb, len, __builtin_return_address(0)); return skb->data; } /** * skb_pull - remove data from the start of a buffer,data后移 * @skb: buffer to use * @len: amount of data to remove * * This function removes data from the start of a buffer, returning * the memory to the headroom. A pointer to the next data in the buffer * is returned. Once the data has been pulled future pushes will overwrite * the old data. */ unsigned char *skb_pull(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) { return skb_pull_inline(skb, len); } static inline unsigned char *skb_pull_inline(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) { return unlikely(len > skb->len) ? NULL : __skb_pull(skb, len); } static inline unsigned char *__skb_pull(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) { skb->len -= len; BUG_ON(skb->len < skb->data_len); return skb->data += len; }
/** * skb_reserve - adjust headroom * @skb: buffer to alter * @len: bytes to move * * Increase the headroom of an empty &sk_buff by reducing the tail * room. This is only allowed for an empty buffer. */ static inline void skb_reserve(struct sk_buff *skb, int len) { skb->data += len; skb->tail += len; }
// 例子:
skb=alloc_skb(len+headspace, GFP_KERNEL); // 分配
skb_reserve(skb, headspace); // tail=data=起始位置+headspace
skb_put(skb,len); // tail += len
memcpy_fromfs(skb->data,data,len);
pass_to_m_protocol(skb);
-
sk_buff的动态分配和释放
static inline struct sk_buff *alloc_skb(unsigned int size, gfp_t priority);/* legacy helper around netdev_alloc_skb() */ static inline struct sk_buff *dev_alloc_skb(unsigned int length);void kfree_skb(struct sk_buff *skb);
void dev_kfree_skb)(struct sk_buff * skb); /* * It is not allowed to call kfree_skb() or consume_skb() from hardware * interrupt context or with hardware interrupts being disabled. * (in_irq() || irqs_disabled()) * * We provide four helpers that can be used in following contexts : * * dev_kfree_skb_irq(skb) when caller drops a packet from irq context, * replacing kfree_skb(skb) * * dev_consume_skb_irq(skb) when caller consumes a packet from irq context. * Typically used in place of consume_skb(skb) in TX completion path * * dev_kfree_skb_any(skb) when caller doesn‘t know its current irq context, * replacing kfree_skb(skb) * * dev_consume_skb_any(skb) when caller doesn‘t know its current irq context, * and consumed a packet. Used in place of consume_skb(skb) */ static inline void dev_kfree_skb_irq(struct sk_buff *skb); static inline void dev_kfree_skb_any(struct sk_buff *skb);
14.1.2 net_device
net_device有点类似字符设备中的file_opretions,里面定义了很多标准成员函数,驱动需要实现里面的函数。
/* * The DEVICE structure. * Actually, this whole structure is a big mistake. It mixes I/O * data with strictly "high-level" data, and it has to know about * almost every data structure used in the INET module. * * FIXME: cleanup struct net_device such that network protocol info * moves out. */ struct net_device { /* * This is the first field of the "visible" part of this structure * (i.e. as seen by users in the "Space.c" file). It is the name * of the interface. */ char name[IFNAMSIZ]; /* device name hash chain, please keep it close to name[] */ struct hlist_node name_hlist; /* snmp alias */ char *ifalias; /* * I/O specific fields * FIXME: Merge these and struct ifmap into one */ unsigned long mem_end; /* shared mem end */ unsigned long mem_start; /* shared mem start */ unsigned long base_addr; /* device I/O address */ int irq; /* device IRQ number */ /* * Some hardware also needs these fields, but they are not * part of the usual set specified in Space.c. */ unsigned long state; struct list_head dev_list; struct list_head napi_list; struct list_head unreg_list; struct list_head close_list; /* directly linked devices, like slaves for bonding */ struct { struct list_head upper; struct list_head lower; } adj_list; /* all linked devices, *including* neighbours */ struct { struct list_head upper; struct list_head lower; } all_adj_list; /* currently active device features */ netdev_features_t features; /* user-changeable features */ netdev_features_t hw_features; /* user-requested features */ netdev_features_t wanted_features; /* mask of features inheritable by VLAN devices */ netdev_features_t vlan_features; /* mask of features inherited by encapsulating devices * This field indicates what encapsulation offloads * the hardware is capable of doing, and drivers will * need to set them appropriately. */ netdev_features_t hw_enc_features; /* mask of fetures inheritable by MPLS */ netdev_features_t mpls_features; /* Interface index. Unique device identifier */ int ifindex; int iflink; struct net_device_stats stats; // 各种统计信息 atomic_long_t rx_dropped; /* dropped packets by core network * Do not use this in drivers. */ #ifdef CONFIG_WIRELESS_EXT /* List of functions to handle Wireless Extensions (instead of ioctl). * See <net/iw_handler.h> for details. Jean II */ const struct iw_handler_def * wireless_handlers; /* Instance data managed by the core of Wireless Extensions. */ struct iw_public_data * wireless_data; #endif /* Management operations */ const struct net_device_ops *netdev_ops; // 具体函数,需驱动填充 const struct ethtool_ops *ethtool_ops; const struct forwarding_accel_ops *fwd_ops; /* Hardware header description */ const struct header_ops *header_ops; unsigned int flags; /* interface flags (a la BSD) ,接口标记,以IFF_开头,说明设备接口的能力和特性*/ unsigned int priv_flags; /* Like ‘flags‘ but invisible to userspace. * See if.h for definitions. */ unsigned short gflags; unsigned short padded; /* How much padding added by alloc_netdev() */ unsigned char operstate; /* RFC2863 operstate */ unsigned char link_mode; /* mapping policy to operstate */ unsigned char if_port; /* Selectable AUI, TP,..*/ unsigned char dma; /* DMA channel */ unsigned int mtu; /* interface MTU value,最单传输单元 */ unsigned short type; /* interface hardware type,硬件类型 */ unsigned short hard_header_len; /* hardware hdr length,Dmac+Smac+type=14 */ /* extra head- and tailroom the hardware may need, but not in all cases * can this be guaranteed, especially tailroom. Some cases also use * LL_MAX_HEADER instead to allocate the skb. */ unsigned short needed_headroom; unsigned short needed_tailroom; /* Interface address info. */ unsigned char perm_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* permanent hw address */ unsigned char addr_assign_type; /* hw address assignment type */ unsigned char addr_len; /* hardware address length */ unsigned short neigh_priv_len; unsigned short dev_id; /* Used to differentiate devices * that share the same link * layer address */ spinlock_t addr_list_lock; struct netdev_hw_addr_list uc; /* Unicast mac addresses */ struct netdev_hw_addr_list mc; /* Multicast mac addresses */ struct netdev_hw_addr_list dev_addrs; /* list of device * hw addresses */ #ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS struct kset *queues_kset; #endif bool uc_promisc; unsigned int promiscuity; unsigned int allmulti; /* Protocol specific pointers */ #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_VLAN_8021Q) struct vlan_info __rcu *vlan_info; /* VLAN info */ #endif #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_NET_DSA) struct dsa_switch_tree *dsa_ptr; /* dsa specific data */ #endif #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_TIPC) struct tipc_bearer __rcu *tipc_ptr; /* TIPC specific data */ #endif void *atalk_ptr; /* AppleTalk link */ struct in_device __rcu *ip_ptr; /* IPv4 specific data */ struct dn_dev __rcu *dn_ptr; /* DECnet specific data */ struct inet6_dev __rcu *ip6_ptr; /* IPv6 specific data */ void *ax25_ptr; /* AX.25 specific data */ struct wireless_dev *ieee80211_ptr; /* IEEE 802.11 specific data, assign before registering */ /* * Cache lines mostly used on receive path (including eth_type_trans()) */ unsigned long last_rx; /* Time of last Rx * This should not be set in * drivers, unless really needed, * because network stack (bonding) * use it if/when necessary, to * avoid dirtying this cache line. */ /* Interface address info used in eth_type_trans() */ unsigned char *dev_addr; /* hw address, (before bcast because most packets are unicast) */ #ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS struct netdev_rx_queue *_rx; /* Number of RX queues allocated at register_netdev() time */ unsigned int num_rx_queues; /* Number of RX queues currently active in device */ unsigned int real_num_rx_queues; #endif rx_handler_func_t __rcu *rx_handler; void __rcu *rx_handler_data; struct netdev_queue __rcu *ingress_queue; unsigned char broadcast[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw bcast add */ /* * Cache lines mostly used on transmit path */ struct netdev_queue *_tx ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp; /* Number of TX queues allocated at alloc_netdev_mq() time */ unsigned int num_tx_queues; /* Number of TX queues currently active in device */ unsigned int real_num_tx_queues; /* root qdisc from userspace point of view */ struct Qdisc *qdisc; unsigned long tx_queue_len; /* Max frames per queue allowed */ spinlock_t tx_global_lock; #ifdef CONFIG_XPS struct xps_dev_maps __rcu *xps_maps; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_RFS_ACCEL /* CPU reverse-mapping for RX completion interrupts, indexed * by RX queue number. Assigned by driver. This must only be * set if the ndo_rx_flow_steer operation is defined. */ struct cpu_rmap *rx_cpu_rmap; #endif /* These may be needed for future network-power-down code. */ /* * trans_start here is expensive for high speed devices on SMP, * please use netdev_queue->trans_start instead. */ unsigned long trans_start; /* Time (in jiffies) of last Tx */ int watchdog_timeo; /* used by dev_watchdog() */ struct timer_list watchdog_timer; /* Number of references to this device */ int __percpu *pcpu_refcnt; /* delayed register/unregister */ struct list_head todo_list; /* device index hash chain */ struct hlist_node index_hlist; struct list_head link_watch_list; /* register/unregister state machine */ enum { NETREG_UNINITIALIZED=0, NETREG_REGISTERED, /* completed register_netdevice */ NETREG_UNREGISTERING, /* called unregister_netdevice */ NETREG_UNREGISTERED, /* completed unregister todo */ NETREG_RELEASED, /* called free_netdev */ NETREG_DUMMY, /* dummy device for NAPI poll */ } reg_state:8; bool dismantle; /* device is going do be freed */ enum { RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZED, RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZING, } rtnl_link_state:16; /* Called from unregister, can be used to call free_netdev */ void (*destructor)(struct net_device *dev); #ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL struct netpoll_info __rcu *npinfo; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_NET_NS /* Network namespace this network device is inside */ struct net *nd_net; #endif /* mid-layer private */ union { void *ml_priv; struct pcpu_lstats __percpu *lstats; /* loopback stats */ struct pcpu_sw_netstats __percpu *tstats; struct pcpu_dstats __percpu *dstats; /* dummy stats */ struct pcpu_vstats __percpu *vstats; /* veth stats */ }; /* GARP */ struct garp_port __rcu *garp_port; /* MRP */ struct mrp_port __rcu *mrp_port; /* class/net/name entry */ struct device dev; /* space for optional device, statistics, and wireless sysfs groups */ const struct attribute_group *sysfs_groups[4]; /* space for optional per-rx queue attributes */ const struct attribute_group *sysfs_rx_queue_group; /* rtnetlink link ops */ const struct rtnl_link_ops *rtnl_link_ops; /* for setting kernel sock attribute on TCP connection setup */ #define GSO_MAX_SIZE 65536 unsigned int gso_max_size; #define GSO_MAX_SEGS 65535 u16 gso_max_segs; #ifdef CONFIG_DCB /* Data Center Bridging netlink ops */ const struct dcbnl_rtnl_ops *dcbnl_ops; #endif u8 num_tc; struct netdev_tc_txq tc_to_txq[TC_MAX_QUEUE]; u8 prio_tc_map[TC_BITMASK + 1]; #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FCOE) /* max exchange id for FCoE LRO by ddp */ unsigned int fcoe_ddp_xid; #endif #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CGROUP_NET_PRIO) struct netprio_map __rcu *priomap; #endif /* phy device may attach itself for hardware timestamping */ struct phy_device *phydev; struct lock_class_key *qdisc_tx_busylock; /* group the device belongs to */ int group; struct pm_qos_request pm_qos_req; };
* Standard interface flags (netdevice->flags). */
#define IFF_UP 0x1 /* interface is up */
#define IFF_BROADCAST 0x2 /* broadcast address valid */
#define IFF_DEBUG 0x4 /* turn on debugging */
#define IFF_LOOPBACK 0x8 /* is a loopback net */
#define IFF_POINTOPOINT 0x10 /* interface is has p-p link */
#define IFF_NOTRAILERS 0x20 /* avoid use of trailers */
#define IFF_RUNNING 0x40 /* interface RFC2863 OPER_UP */
#define IFF_NOARP 0x80 /* no ARP protocol */
#define IFF_PROMISC 0x100 /* receive all packets */
#define IFF_ALLMULTI 0x200 /* receive all multicast packets*/
#define IFF_MASTER 0x400 /* master of a load balancer */
#define IFF_SLAVE 0x800 /* slave of a load balancer */
#define IFF_MULTICAST 0x1000 /* Supports multicast */
#define IFF_PORTSEL 0x2000 /* can set media type */
#define IFF_AUTOMEDIA 0x4000 /* auto media select active */
#define IFF_DYNAMIC 0x8000 /* dialup device with changing addresses*/
#define IFF_LOWER_UP 0x10000 /* driver signals L1 up */
#define IFF_DORMANT 0x20000 /* driver signals dormant */
#define IFF_ECHO 0x40000 /* echo sent packets */
#define IFF_VOLATILE (IFF_LOOPBACK|IFF_POINTOPOINT|IFF_BROADCAST|IFF_ECHO|\\
IFF_MASTER|IFF_SLAVE|IFF_RUNNING|IFF_LOWER_UP|IFF_DORMANT)
/* Private (from user) interface flags (netdevice->priv_flags). */
#define IFF_802_1Q_VLAN 0x1 /* 802.1Q VLAN device. */
#define IFF_EBRIDGE 0x2 /* Ethernet bridging device. */
#define IFF_SLAVE_INACTIVE 0x4 /* bonding slave not the curr. active */
#define IFF_MASTER_8023AD 0x8 /* bonding master, 802.3ad. */
#define IFF_MASTER_ALB 0x10 /* bonding master, balance-alb. */
#define IFF_BONDING 0x20 /* bonding master or slave */
#define IFF_SLAVE_NEEDARP 0x40 /* need ARPs for validation */
#define IFF_ISATAP 0x80 /* ISATAP interface (RFC4214) */
#define IFF_MASTER_ARPMON 0x100 /* bonding master, ARP mon in use */
#define IFF_WAN_HDLC 0x200 /* WAN HDLC device */
#define IFF_XMIT_DST_RELEASE 0x400 /* dev_hard_start_xmit() is allowed to
* release skb->dst
*/
#define IFF_DONT_BRIDGE 0x800 /* disallow bridging this ether dev */
#define IFF_DISABLE_NETPOLL 0x1000 /* disable netpoll at run-time */
#define IFF_MACVLAN_PORT 0x2000 /* device used as macvlan port */
#define IFF_BRIDGE_PORT 0x4000 /* device used as bridge port */
#define IFF_OVS_DATAPATH 0x8000 /* device used as Open vSwitch
* datapath port */
#define IFF_TX_SKB_SHARING 0x10000 /* The interface supports sharing
* skbs on transmit */
#define IFF_UNICAST_FLT 0x20000 /* Supports unicast filtering */
#define IFF_TEAM_PORT 0x40000 /* device used as team port */
#define IFF_SUPP_NOFCS 0x80000 /* device supports sending custom FCS */
#define IFF_LIVE_ADDR_CHANGE 0x100000 /* device supports hardware address
* change when it‘s running */
#define IFF_MACVLAN 0x200000 /* Macvlan device */
net_device中的一个重要结构体是net_device_ops,驱动需要填充里面的成员。
/* * This structure defines the management hooks for network devices. * The following hooks can be defined; unless noted otherwise, they are * optional and can be filled with a null pointer. * * int (*ndo_init)(struct net_device *dev); * This function is called once when network device is registered. * The network device can use this to any late stage initializaton * or semantic validattion. It can fail with an error code which will * be propogated back to register_netdev * * void (*ndo_uninit)(struct net_device *dev); * This function is called when device is unregistered or when registration * fails. It is not called if init fails. * * int (*ndo_open)(struct net_device *dev);一般在次获取设备需要的IO地址、IRQ、DMA通道等 * This function is called when network device transistions to the up * state. * * int (*ndo_stop)(struct net_device *dev); * This function is called when network device transistions to the down * state. * * netdev_tx_t (*ndo_start_xmit)(struct sk_buff *skb, * struct net_device *dev); * Called when a packet needs to be transmitted. * Must return NETDEV_TX_OK , NETDEV_TX_BUSY. * (can also return NETDEV_TX_LOCKED iff NETIF_F_LLTX) * Required can not be NULL. 不能为空,必须实现,启动发送 * * u16 (*ndo_select_queue)(struct net_device *dev, struct sk_buff *skb, * void *accel_priv, select_queue_fallback_t fallback); * Called to decide which queue to when device supports multiple * transmit queues. * * void (*ndo_change_rx_flags)(struct net_device *dev, int flags); * This function is called to allow device receiver to make * changes to configuration when multicast or promiscious is enabled. * * void (*ndo_set_rx_mode)(struct net_device *dev); * This function is called device changes address list filtering. * If driver handles unicast address filtering, it should set * IFF_UNICAST_FLT to its priv_flags. * * int (*ndo_set_mac_address)(struct net_device *dev, void *addr); * This function is called when the Media Access Control address * needs to be changed. If this interface is not defined, the * mac address can not be changed. * * int (*ndo_validate_addr)(struct net_device *dev); * Test if Media Access Control address is valid for the device. * * int (*ndo_do_ioctl)(struct net_device *dev, struct ifreq *ifr, int cmd); * Called when a user request an ioctl which can‘t be handled by * the generic interface code. If not defined ioctl‘s return * not supported error code. * * int (*ndo_set_config)(struct net_device *dev, struct ifmap *map); * Used to set network devices bus interface parameters. This interface * is retained for legacy reason, new devices should use the bus * interface (PCI) for low level management. 配置接口,也可以改变设备IO地址和中断号 * * int (*ndo_change_mtu)(struct net_device *dev, int new_mtu); * Called when a user wants to change the Maximum Transfer Unit * of a device. If not defined, any request to change MTU will * will return an error. * * void (*ndo_tx_timeout)(struct net_device *dev); * Callback uses when the transmitter has not made any progress * for dev->watchdog ticks. 发送超时以后调用 * * struct rtnl_link_stats64* (*ndo_get_stats64)(struct net_device *dev, * struct rtnl_link_stats64 *storage); * struct net_device_stats* (*ndo_get_stats)(struct net_device *dev); 返回的结构体包含若干统计信息 * Called when a user wants to get the network device usage * statistics. Drivers must do one of the following: * 1. Define @ndo_get_stats64 to fill in a zero-initialised * rtnl_link_stats64 structure passed by the caller. * 2. Define @ndo_get_stats to update a net_device_stats structure * (which should normally be dev->stats) and return a pointer to * it. The structure may be changed asynchronously only if each * field is written atomically. * 3. Update dev->stats asynchronously and atomically, and define * neither operation. * * int (*ndo_vlan_rx_add_vid)(struct net_device *dev, __be16 proto, u16t vid); * If device support VLAN filtering this function is called when a * VLAN id is registered. * * int (*ndo_vlan_rx_kill_vid)(struct net_device *dev, unsigned short vid); * If device support VLAN filtering this function is called when a * VLAN id is unregistered. * * void (*ndo_poll_controller)(struct net_device *dev); * * SR-IOV management functions. * int (*ndo_set_vf_mac)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, u8* mac); * int (*ndo_set_vf_vlan)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, u16 vlan, u8 qos); * int (*ndo_set_vf_tx_rate)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, int rate); * int (*ndo_set_vf_spoofchk)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, bool setting); * int (*ndo_get_vf_config)(struct net_device *dev, * int vf, struct ifla_vf_info *ivf); * int (*ndo_set_vf_link_state)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, int link_state); * int (*ndo_set_vf_port)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, * struct nlattr *port[]); * int (*ndo_get_vf_port)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, struct sk_buff *skb); * int (*ndo_setup_tc)(struct net_device *dev, u8 tc) * Called to setup ‘tc‘ number of traffic classes in the net device. This * is always called from the stack with the rtnl lock held and netif tx * queues stopped. This allows the netdevice to perform queue management * safely. * * Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) offload functions. * int (*ndo_fcoe_enable)(struct net_device *dev); * Called when the FCoE protocol stack wants to start using LLD for FCoE * so the underlying device can perform whatever needed configuration or * initialization to support acceleration of FCoE traffic. * * int (*ndo_fcoe_disable)(struct net_device *dev); * Called when the FCoE protocol stack wants to stop using LLD for FCoE * so the underlying device can perform whatever needed clean-ups to * stop supporting acceleration of FCoE traffic. * * int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_setup)(struct net_device *dev, u16 xid, * struct scatterlist *sgl, unsigned int sgc); * Called when the FCoE Initiator wants to initialize an I/O that * is a possible candidate for Direct Data Placement (DDP). The LLD can * perform necessary setup and returns 1 to indicate the device is set up * successfully to perform DDP on this I/O, otherwise this returns 0. * * int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_done)(struct net_device *dev, u16 xid); * Called when the FCoE Initiator/Target is done with the DDPed I/O as * indicated by the FC exchange id ‘xid‘, so the underlying device can * clean up and reuse resources for later DDP requests. * * int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_target)(struct net_device *dev, u16 xid, * struct scatterlist *sgl, unsigned int sgc); * Called when the FCoE Target wants to initialize an I/O that * is a possible candidate for Direct Data Placement (DDP). The LLD can * perform necessary setup and returns 1 to indicate the device is set up * successfully to perform DDP on this I/O, otherwise this returns 0. * * int (*ndo_fcoe_get_hbainfo)(struct net_device *dev, * struct netdev_fcoe_hbainfo *hbainfo); * Called when the FCoE Protocol stack wants information on the underlying * device. This information is utilized by the FCoE protocol stack to * register attributes with Fiber Channel management service as per the * FC-GS Fabric Device Management Information(FDMI) specification. * * int (*ndo_fcoe_get_wwn)(struct net_device *dev, u64 *wwn, int type); * Called when the underlying device wants to override default World Wide * Name (WWN) generation mechanism in FCoE protocol stack to pass its own * World Wide Port Name (WWPN) or World Wide Node Name (WWNN) to the FCoE * protocol stack to use. * * RFS acceleration. * int (*ndo_rx_flow_steer)(struct net_device *dev, const struct sk_buff *skb, * u16 rxq_index, u32 flow_id); * Set hardware filter for RFS. rxq_index is the target queue index; * flow_id is a flow ID to be passed to rps_may_expire_flow() later. * Return the filter ID on success, or a negative error code. * * Slave management functions (for bridge, bonding, etc). * int (*ndo_add_slave)(struct net_device *dev, struct net_device *slave_dev); * Called to make another netdev an underling. * * int (*ndo_del_slave)(struct net_device *dev, struct net_device *slave_dev); * Called to release previously enslaved netdev. * * Feature/offload setting functions. * netdev_features_t (*ndo_fix_features)(struct net_device *dev, * netdev_features_t features); * Adjusts the requested feature flags according to device-specific * constraints, and returns the resulting flags. Must not modify * the device state. * * int (*ndo_set_features)(struct net_device *dev, netdev_features_t features); * Called to update device configuration to new features. Passed * feature set might be less than what was returned by ndo_fix_features()). * Must return >0 or -errno if it changed dev->features itself. * * int (*ndo_fdb_add)(struct ndmsg *ndm, struct nlattr *tb[], * struct net_device *dev, * const unsigned char *addr, u16 flags) * Adds an FDB entry to dev for addr. * int (*ndo_fdb_del)(struct ndmsg *ndm, struct nlattr *tb[], * struct net_device *dev, * const unsigned char *addr) * Deletes the FDB entry from dev coresponding to addr. * int (*ndo_fdb_dump)(struct sk_buff *skb, struct netlink_callback *cb, * struct net_device *dev, int idx) * Used to add FDB entries to dump requests. Implementers should add * entries to skb and update idx with the number of entries. * * int (*ndo_bridge_setlink)(struct net_device *dev, struct nlmsghdr *nlh) * int (*ndo_bridge_getlink)(struct sk_buff *skb, u32 pid, u32 seq, * struct net_device *dev, u32 filter_mask) * * int (*ndo_change_carrier)(struct net_device *dev, bool new_carrier); * Called to change device carrier. Soft-devices (like dummy, team, etc) * which do not represent real hardware may define this to allow their * userspace components to manage their virtual carrier state. Devices * that determine carrier state from physical hardware properties (eg * network cables) or protocol-dependent mechanisms (eg * USB_CDC_NOTIFY_NETWORK_CONNECTION) should NOT implement this function. * * int (*ndo_get_phys_port_id)(struct net_device *dev, * struct netdev_phys_port_id *ppid); * Called to get ID of physical port of this device. If driver does * not implement this, it is assumed that the hw is not able to have * multiple net devices on single physical port. * * void (*ndo_add_vxlan_port)(struct net_device *dev, * sa_family_t sa_family, __be16 port); * Called by vxlan to notiy a driver about the UDP port and socket * address family that vxlan is listnening to. It is called only when * a new port starts listening. The operation is protected by the * vxlan_net->sock_lock. * * void (*ndo_del_vxlan_port)(struct net_device *dev, * sa_family_t sa_family, __be16 port); * Called by vxlan to notify the driver about a UDP port and socket * address family that vxlan is not listening to anymore. The operation * is protected by the vxlan_net->sock_lock. * * void* (*ndo_dfwd_add_station)(struct net_device *pdev, * struct net_device *dev) * Called by upper layer devices to accelerate switching or other * station functionality into hardware. ‘pdev is the lowerdev * to use for the offload and ‘dev‘ is the net device that will * back the offload. Returns a pointer to the private structure * the upper layer will maintain. * void (*ndo_dfwd_del_station)(struct net_device *pdev, void *priv) * Called by upper layer device to delete the station created * by ‘ndo_dfwd_add_station‘. ‘pdev‘ is the net device backing * the station and priv is the structure returned by the add * operation. * netdev_tx_t (*ndo_dfwd_start_xmit)(struct sk_buff *skb, * struct net_device *dev, * void *priv); * Callback to use for xmit over the accelerated station. This * is used in place of ndo_start_xmit on accelerated net * devices. */ struct net_device_ops { int (*ndo_init)(struct net_device *dev); void (*ndo_uninit)(struct net_device *dev); int (*ndo_open)(struct net_device *dev); int (*ndo_stop)(struct net_device *dev); netdev_tx_t (*ndo_start_xmit) (struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev); u16 (*ndo_select_queue)(struct net_device *dev, struct sk_buff *skb, void *accel_priv, select_queue_fallback_t fallback); void (*ndo_change_rx_flags)(struct net_device *dev, int flags); void (*ndo_set_rx_mode)(struct net_device *dev); int (*ndo_set_mac_address)(struct net_device *dev, void *addr); int (*ndo_validate_addr)(struct net_device *dev); int (*ndo_do_ioctl)(struct net_device *dev, struct ifreq *ifr, int cmd); int (*ndo_set_config)(struct net_device *dev, struct ifmap *map); int (*ndo_change_mtu)(struct net_device *dev, int new_mtu); int (*ndo_neigh_setup)(struct net_device *dev, struct neigh_parms *); void (*ndo_tx_timeout) (struct net_device *dev); struct rtnl_link_stats64* (*ndo_get_stats64)(struct net_device *dev, struct rtnl_link_stats64 *storage); struct net_device_stats* (*ndo_get_stats)(struct net_device *dev); int (*ndo_vlan_rx_add_vid)(struct net_device *dev, __be16 proto, u16 vid); int (*ndo_vlan_rx_kill_vid)(struct net_device *dev, __be16 proto, u16 vid); #ifdef CONFIG_NET_POLL_CONTROLLER void (*ndo_poll_controller)(struct net_device *dev); int (*ndo_netpoll_setup)(struct net_device *dev, struct netpoll_info *info, gfp_t gfp); void (*ndo_netpoll_cleanup)(struct net_device *dev); #endif #ifdef CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL int (*ndo_busy_poll)(struct napi_struct *dev); #endif int (*ndo_set_vf_mac)(struct net_device *dev, int queue, u8 *mac); int (*ndo_set_vf_vlan)(struct net_device *dev, int queue, u16 vlan, u8 qos); int (*ndo_set_vf_tx_rate)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, int rate); int (*ndo_set_vf_spoofchk)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, bool setting); int (*ndo_get_vf_config)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, struct ifla_vf_info *ivf); int (*ndo_set_vf_link_state)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, int link_state); int (*ndo_set_vf_port)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, struct nlattr *port[]); int (*ndo_get_vf_port)(struct net_device *dev, int vf, struct sk_buff *skb); int (*ndo_setup_tc)(struct net_device *dev, u8 tc); #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FCOE) int (*ndo_fcoe_enable)(struct net_device *dev); int (*ndo_fcoe_disable)(struct net_device *dev); int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_setup)(struct net_device *dev, u16 xid, struct scatterlist *sgl, unsigned int sgc); int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_done)(struct net_device *dev, u16 xid); int (*ndo_fcoe_ddp_target)(struct net_device *dev, u16 xid, struct scatterlist *sgl, unsigned int sgc); int (*ndo_fcoe_get_hbainfo)(struct net_device *dev, struct netdev_fcoe_hbainfo *hbainfo); #endif #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_LIBFCOE) #define NETDEV_FCOE_WWNN 0 #define NETDEV_FCOE_WWPN 1 int (*ndo_fcoe_get_wwn)(struct net_device *dev, u64 *wwn, int type); #endif #ifdef CONFIG_RFS_ACCEL int (*ndo_rx_flow_steer)(struct net_device *dev, const struct sk_buff *skb, u16 rxq_index, u32 flow_id); #endif int (*ndo_add_slave)(struct net_device *dev, struct net_device *slave_dev); int (*ndo_del_slave)(struct net_device *dev, struct net_device *slave_dev); netdev_features_t (*ndo_fix_features)(struct net_device *dev, netdev_features_t features); int (*ndo_set_features)(struct net_device *dev, netdev_features_t features); int (*ndo_neigh_construct)(struct neighbour *n); void (*ndo_neigh_destroy)(struct neighbour *n); int (*ndo_fdb_add)(struct ndmsg *ndm, struct nlattr *tb[], struct net_device *dev, const unsigned char *addr, u16 flags); int (*ndo_fdb_del)(struct ndmsg *ndm, struct nlattr *tb[], struct net_device *dev, const unsigned char *addr); int (*ndo_fdb_dump)(struct sk_buff *skb, struct netlink_callback *cb, struct net_device *dev, int idx); int (*ndo_bridge_setlink)(struct net_device *dev, struct nlmsghdr *nlh); int (*ndo_bridge_getlink)(struct sk_buff *skb, u32 pid, u32 seq, struct net_device *dev, u32 filter_mask); int (*ndo_bridge_dellink)(struct net_device *dev, struct nlmsghdr *nlh); int (*ndo_change_carrier)(struct net_device *dev, bool new_carrier); int (*ndo_get_phys_port_id)(struct net_device *dev, struct netdev_phys_port_id *ppid); void (*ndo_add_vxlan_port)(struct net_device *dev, sa_family_t sa_family, __be16 port); void (*ndo_del_vxlan_port)(struct net_device *dev, sa_family_t sa_family, __be16 port); void* (*ndo_dfwd_add_station)(struct net_device *pdev, struct net_device *dev); void (*ndo_dfwd_del_station)(struct net_device *pdev, void *priv); netdev_tx_t (*ndo_dfwd_start_xmit) (struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev, void *priv); };
14.2 注册与注销
14.2.1 注册与注销
register时,net_device的net_device_ops的ndo_init()会执行。
/** * register_netdev - register a network device * @dev: device to register * * Take a completed network device structure and add it to the kernel * interfaces. A %NETDEV_REGISTER message is sent to the netdev notifier * chain. 0 is returned on success. A negative errno code is returned * on a failure to set up the device, or if the name is a duplicate. * * This is a wrapper around register_netdevice that takes the rtnl semaphore * and expands the device name if you passed a format string to * alloc_netdev. */ int register_netdev(struct net_device *dev); /** * unregister_netdev - remove device from the kernel * @dev: device * * This function shuts down a device interface and removes it * from the kernel tables. * * This is just a wrapper for unregister_netdevice that takes * the rtnl semaphore. In general you want to use this and not * unregister_netdevice. */ void unregister_netdev(struct net_device *dev);
14.2.2 申请和释放
可以自己定义net_device结构体,也可以动态申请和释放空间。
// sizeof_priv是自定义数据结构的大小
// setup是动态申请后,自动执行的初始化函数,下面两个ether申请函数,都有默认的setup函数
#define alloc_netdev(sizeof_priv, name, setup) \\ alloc_netdev_mqs(sizeof_priv, name, setup, 1, 1) #define alloc_etherdev(sizeof_priv) alloc_etherdev_mq(sizeof_priv, 1) #define alloc_etherdev_mq(sizeof_priv, count) alloc_etherdev_mqs(sizeof_priv, count, count) /** * alloc_etherdev_mqs - Allocates and sets up an Ethernet device * @sizeof_priv: Size of additional driver-private structure to be allocated * for this Ethernet device * @txqs: The number of TX queues this device has. * @rxqs: The number of RX queues this device has. * * Fill in the fields of the device structure with Ethernet-generic * values. Basically does everything except registering the device. * * Constructs a new net device, complete with a private data area of * size (sizeof_priv). A 32-byte (not bit) alignment is enforced for * this private data area. */ struct net_device *alloc_etherdev_mqs(int sizeof_priv, unsigned int txqs, unsigned int rxqs) { return alloc_netdev_mqs(sizeof_priv, "eth%d", ether_setup, txqs, rxqs); } /** * alloc_netdev_mqs - allocate network device * @sizeof_priv: size of private data to allocate space for * @name: device name format string * @setup: callback to initialize device * @txqs: the number of TX subqueues to allocate * @rxqs: the number of RX subqueues to allocate * * Allocates a struct net_device with private data area for driver use * and performs basic initialization. Also allocates subqueue structs * for each queue on the device. */ struct net_device *alloc_netdev_mqs(int sizeof_priv, const char *name, void (*setup)(struct net_device *), unsigned int txqs, unsigned int rxqs) { struct net_device *dev; size_t alloc_size; struct net_device *p; BUG_ON(strlen(name) >= sizeof(dev->name)); if (txqs < 1) { pr_err("alloc_netdev: Unable to allocate device with zero queues\\n"); return NULL; } #ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS if (rxqs < 1) { pr_err("alloc_netdev: Unable to allocate device with zero RX queues\\n"); return NULL; } #endif alloc_size = sizeof(struct net_device); if (sizeof_priv) { /* ensure 32-byte alignment of private area */ alloc_size = ALIGN(alloc_size, NETDEV_ALIGN); alloc_size += sizeof_priv; } /* ensure 32-byte alignment of whole construct */ alloc_size += NETDEV_ALIGN - 1; p = kzalloc(alloc_size, GFP_KERNEL | __GFP_NOWARN | __GFP_REPEAT); if (!p) p = vzalloc(alloc_size); if (!p) return NULL; dev = PTR_ALIGN(p, NETDEV_ALIGN); dev->padded = (char *)dev - (char *)p; dev->pcpu_refcnt = alloc_percpu(int); if (!dev->pcpu_refcnt) goto free_dev; if (dev_addr_init(dev)) goto free_pcpu; dev_mc_init(dev); dev_uc_init(dev); dev_net_set(dev, &init_net); dev->gso_max_size = GSO_MAX_SIZE; dev->gso_max_segs = GSO_MAX_SEGS; INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->napi_list); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->unreg_list); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->close_list); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->link_watch_list); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->adj_list.upper); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->adj_list.lower); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->all_adj_list.upper); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->all_adj_list.lower); dev->priv_flags = IFF_XMIT_DST_RELEASE; setup(dev); dev->num_tx_queues = txqs; dev->real_num_tx_queues = txqs; if (netif_alloc_netdev_queues(dev)) goto free_all; #ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS dev->num_rx_queues = rxqs; dev->real_num_rx_queues = rxqs; if (netif_alloc_rx_queues(dev)) goto free_all; #endif strcpy(dev->name, name); dev->group = INIT_NETDEV_GROUP; if (!dev->ethtool_ops) dev->ethtool_ops = &default_ethtool_ops; return dev; free_all: free_netdev(dev); return NULL; free_pcpu: free_percpu(dev->pcpu_refcnt); netif_free_tx_queues(dev); #ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS kfree(dev->_rx); #endif free_dev: netdev_freemem(dev); return NULL; }
// 释放net_device
void free_netdev(struct net_device *dev);
模板:
static int xxx_register(void) { ... /* 分配 net_device 结构体并对其成员赋值 */ xxx_dev = alloc_netdev(sizeof(struct xxx_priv), "sn%d", xxx_init); if (xxx_dev == NULL) ... /* 分配 net_device 失败 */ /* 注册 net_device 结构体 */ if ((result = register_netdev(xxx_dev))) ... } static void xxx_unregister(void) { ... /* 注销 net_device 结构体 */ unregister_netdev(xxx_dev); /* 释放 net_device 结构体 */ free_netdev(xxx_dev); }
14.3 初始化ndo_init()
向内核register时,ndo_init()函数会被执行。
int register_netdev(struct net_device *dev) { int err; rtnl_lock(); err = register_netdevice(dev); rtnl_unlock(); return err; } int register_netdevice(struct net_device *dev) { ... /* Init, if this function is available */ if (dev->netdev_ops->ndo_init) { ret = dev->netdev_ops->ndo_init(dev); if (ret) { if (ret > 0) ret = -EIO; goto out; } } ... }
ndo_init()要干的事:
- 准备硬件
- 初始化net_device结构体的相关内容
- 获取私有指针,并初始化
ndo_init()模板:
xxx_netdev_ops.ndo_init = xxx_init;
void xxx_init(struct net_device *dev) { /* 设备的私有信息结构体 */ struct xxx_priv *priv; /* 检查设备是否存在和设备所使用的硬件资源 */ xxx_hw_init(); /* 初始化以太网设备的公用成员 */ ether_setup(dev); /* 设置设备的成员函数指针 */ ndev->netdev_ops = &xxx_netdev_ops; ndev->ethtool_ops = &xxx_ethtool_ops; dev->watchdog_timeo = timeout; /* 取得私有信息, 并初始化它 */ priv = netdev_priv(dev); ... /* 初始化设备私有数据区 */ }
14.4 打开和释放ndo_open()/ndo_stop()
ndo_open()的工作:
- 使能硬件资源,申请IO区域、中断和DMA通道等;
- 调用netif_start_queue()函数,激活设备发送队列
ndo_stop()的工作:
- 调用netif_stop_queue()函数,停止设备发送队列
- 释放IO区域、中断和DMA资源
原来这两个函数只针对 tx queue
/** * netif_start_queue - allow transmit * @dev: network device * * Allow upper layers to call the device hard_start_xmit routine. */ static inline void netif_start_queue(struct net_device *dev) { netif_tx_start_queue(netdev_get_tx_queue(dev, 0)); }
/** * netif_stop_queue - stop transmitted packets * @dev: network device * * Stop upper layers calling the device hard_start_xmit routine. * Used for flow control when transmit resources are unavailable. */ static inline void netif_stop_queue(struct net_device *dev) { netif_tx_stop_queue(netdev_get_tx_queue(dev, 0)); }
/**
* netif_wake_queue - restart transmit
* @dev: network device
*
* Allow upper layers to call the device hard_start_xmit routine.
* Used for flow control when transmit resources are available.
*/
static inline void netif_wake_queue(struct net_device *dev)
{
netif_tx_wake_queue(netdev_get_tx_queue(dev, 0));
}
模板:
xxx_netdev_ops.ndo_open = xxx_open;
xxx_netdev_ops.ndo_stop = xxx_stop;
static int xxx_open(struct net_device *dev) { /* 申请端口、 IRQ 等, 类似于 fops->open */ ret = request_irq(dev->irq, &xxx_interrupt, 0, dev->name, dev); ... netif_start_queue(dev); ... } static int xxx_stop(struct net_device *dev) { /* 释放端口、 IRQ 等, 类似于 fops->close */ free_irq(dev->irq, dev); ... netif_stop_queue(dev); /* can‘t transmit any more */ ... }
14.5 发送 ndo_start_xmit()/ndo_tx_timeout()
ndo_start_xmit()主要流程:
- 解析sk_buff,缓存有效数据
- 校验数据长度,若小于ETH_ZLEN(60,不包含FCS),则尾部填充0
- 控制硬件发送数据
int xxx_tx(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev) { int len; char *data, shortpkt[ETH_ZLEN]; if (xxx_send_available(...)) { /* 发送队列未满, 可以发送 */ /* 获得有效数据指针和长度 */ data = skb->data; len = skb->len; if (len < ETH_ZLEN) { /* 如果帧长小于以太网帧最小长度, 补 0 */ memset(shortpkt, 0, ETH_ZLEN); memcpy(shortpkt, skb->data, skb->len); len = ETH_ZLEN; data = shortpkt;
} dev->trans_start = jiffies; /* 记录发送时间戳 */ if (avail) {/* 设置硬件寄存器, 让硬件把数据包发送出去 */ xxx_hw_tx(data, len, dev); } else { netif_stop_queue(dev); // 不一定非要这么搞,返回busy也可以,如果调用了,需要在TX结束中断或者超时中断里唤醒 ... } }
}
void xxx_tx_timeout(struct net_device *dev)
{
...
netif_wake_queue(dev); /* 重新启动设备发送队列 */ }
14.6 接收
没有固定形式,在需要的地方调用netif_rx()即可。
static void xxx_interrupt(int irq, void *dev_id) { ... switch (status &ISQ_EVENT_MASK) { case ISQ_RECEIVER_EVENT: /* 获取数据包 */ xxx_rx(dev); break; /* 其他类型的中断 */ } } static void xxx_rx(struct xxx_device *dev) { ... length = get_rev_len (...); /* 分配新的套接字缓冲区 */ skb = dev_alloc_skb(length + 2); skb_reserve(skb, 2); /* 对齐 */ skb->dev = dev; /* 读取硬件上接收到的数据 */ insw(ioaddr + RX_FRAME_PORT, skb_put(skb, length), length >> 1); if (length &1) skb->data[length - 1] = inw(ioaddr + RX_FRAME_PORT); /* 获取上层协议类型 */ skb->protocol = eth_type_trans(skb, dev); /* 把数据包交给上层 */ netif_rx(skb); /* 记录接收时间戳 */ dev->last_rx = jiffies; ... }
14.7 连接状态
一般在定时中断里,检查并更新连接状态。
static inline bool netif_carrier_ok(const struct net_device *dev); // 连接是否ok void netif_carrier_on(struct net_device *dev); // 改变连接状态,on void netif_carrier_off(struct net_device *dev); // 改变连接状态,off
14.8 参数设置和统计数据
参数设置可以通过ioctl(),传入的描述符为socket,linux对命令做了统一规定,如下:
/*路径: include/uapi/linux/sockios.h */ /* * INET An implementation of the TCP/IP protocol suite for the LINUX * operating system. INET is implemented using the BSD Socket * interface as the means of communication with the user level. * * Definitions of the socket-level I/O control calls. * * Version: @(#)sockios.h 1.0.2 03/09/93 * * Authors: Ross Biro * Fred N. van Kempen, <[email protected]> * * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or * modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License * as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version * 2 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. */ #ifndef _LINUX_SOCKIOS_H #define _LINUX_SOCKIOS_H #include <asm/sockios.h> /* Linux-specific socket ioctls */ #define SIOCINQ FIONREAD #define SIOCOUTQ TIOCOUTQ /* output queue size (not sent + not acked) */ /* Routing table calls. */ #define SIOCADDRT 0x890B /* add routing table entry */ #define SIOCDELRT 0x890C /* delete routing table entry */ #define SIOCRTMSG 0x890D /* call to routing system */ /* Socket configuration controls. */ #define SIOCGIFNAME 0x8910 /* get iface name */ #define SIOCSIFLINK 0x8911 /* set iface channel */ #define SIOCGIFCONF 0x8912 /* get iface list */ #define SIOCGIFFLAGS 0x8913 /* get flags */ #define SIOCSIFFLAGS 0x8914 /* set flags */ #define SIOCGIFADDR 0x8915 /* get PA address */ #define SIOCSIFADDR 0x8916 /* set PA address */ #define SIOCGIFDSTADDR 0x8917 /* get remote PA address */ #define SIOCSIFDSTADDR 0x8918 /* set remote PA address */ #define SIOCGIFBRDADDR 0x8919 /* get broadcast PA address */ #define SIOCSIFBRDADDR 0x891a /* set broadcast PA address */ #define SIOCGIFNETMASK 0x891b /* get network PA mask */ #define SIOCSIFNETMASK 0x891c /* set network PA mask */ #define SIOCGIFMETRIC 0x891d /* get metric */ #define SIOCSIFMETRIC 0x891e /* set metric */ #define SIOCGIFMEM 0x891f /* get memory address (BSD) */ #define SIOCSIFMEM 0x8920 /* set memory address (BSD) */ #define SIOCGIFMTU 0x8921 /* get MTU size */ #define SIOCSIFMTU 0x8922 /* set MTU size */ #define SIOCSIFNAME 0x8923 /* set interface name */ #define SIOCSIFHWADDR 0x8924 /* set hardware address */ #define SIOCGIFENCAP 0x8925 /* get/set encapsulations */ #define SIOCSIFENCAP 0x8926 #define SIOCGIFHWADDR 0x8927 /* Get hardware address */ #define SIOCGIFSLAVE 0x8929 /* Driver slaving support */ #define SIOCSIFSLAVE 0x8930 #define SIOCADDMULTI 0x8931 /* Multicast address lists */ #define SIOCDELMULTI 0x8932 #define SIOCGIFINDEX 0x8933 /* name -> if_index mapping */ #define SIOGIFINDEX SIOCGIFINDEX /* misprint compatibility :-) */ #define SIOCSIFPFLAGS 0x8934 /* set/get extended flags set */ #define SIOCGIFPFLAGS 0x8935 #define SIOCDIFADDR 0x8936 /* delete PA address */ #define SIOCSIFHWBROADCAST 0x8937 /* set hardware broadcast addr */ #define SIOCGIFCOUNT 0x8938 /* get number of devices */ #define SIOCGIFBR 0x8940 /* Bridging support */ #define SIOCSIFBR 0x8941 /* Set bridging options */ #define SIOCGIFTXQLEN 0x8942 /* Get the tx queue length */ #define SIOCSIFTXQLEN 0x8943 /* Set the tx queue length */ /* SIOCGIFDIVERT was: 0x8944 Frame diversion support */ /* SIOCSIFDIVERT was: 0x8945 Set frame diversion options */ #define SIOCETHTOOL 0x8946 /* Ethtool interface */ #define SIOCGMIIPHY 0x8947 /* Get address of MII PHY in use. */ #define SIOCGMIIREG 0x8948 /* Read MII PHY register. */ #define SIOCSMIIREG 0x8949 /* Write MII PHY register. */ #define SIOCWANDEV 0x894A /* get/set netdev parameters */ #define SIOCOUTQNSD 0x894B /* output queue size (not sent only) */ /* ARP cache control calls. */ /* 0x8950 - 0x8952 * obsolete calls, don‘t re-use */ #define SIOCDARP 0x8953 /* delete ARP table entry */ #define SIOCGARP 0x8954 /* get ARP table entry */ #define SIOCSARP 0x8955 /* set ARP table entry */ /* RARP cache control calls. */ #define SIOCDRARP 0x8960 /* delete RARP table entry */ #define SIOCGRARP 0x8961 /* get RARP table entry */ #define SIOCSRARP 0x8962 /* set RARP table entry */ /* Driver configuration calls */ #define SIOCGIFMAP 0x8970 /* Get device parameters */ #define SIOCSIFMAP 0x8971 /* Set device parameters */ /* DLCI configuration calls */ #define SIOCADDDLCI 0x8980 /* Create new DLCI device */ #define SIOCDELDLCI 0x8981 /* Delete DLCI device */ #define SIOCGIFVLAN 0x8982 /* 802.1Q VLAN support */ #define SIOCSIFVLAN 0x8983 /* Set 802.1Q VLAN options */ /* bonding calls */ #define SIOCBONDENSLAVE 0x8990 /* enslave a device to the bond */ #define SIOCBONDRELEASE 0x8991 /* release a slave from the bond*/ #define SIOCBONDSETHWADDR 0x8992 /* set the hw addr of the bond */ #define SIOCBONDSLAVEINFOQUERY 0x8993 /* rtn info about slave state */ #define SIOCBONDINFOQUERY 0x8994 /* rtn info about bond state */ #define SIOCBONDCHANGEACTIVE 0x8995 /* update to a new active slave */ /* bridge calls */ #define SIOCBRADDBR 0x89a0 /* create new bridge device */ #define SIOCBRDELBR 0x89a1 /* remove bridge device */ #define SIOCBRADDIF 0x89a2 /* add interface to bridge */ #define SIOCBRDELIF 0x89a3 /* remove interface from bridge */ /* hardware time stamping: parameters in linux/net_tstamp.h */ #define SIOCSHWTSTAMP 0x89b0 /* set and get config */ #define SIOCGHWTSTAMP 0x89b1 /* get config */ /* Device private ioctl calls */ /* * These 16 ioctls are available to devices via the do_ioctl() device * vector. Each device should include this file and redefine these names * as their own. Because these are device dependent it is a good idea * _NOT_ to issue them to random objects and hope. * * THESE IOCTLS ARE _DEPRECATED_ AND WILL DISAPPEAR IN 2.5.X -DaveM */ #define SIOCDEVPRIVATE 0x89F0 /* to 89FF */ /* * These 16 ioctl calls are protocol private */ #define SIOCPROTOPRIVATE 0x89E0 /* to 89EF */ #endif /* _LINUX_SOCKIOS_H */
ndo_get_stats()模板,在程序合适的地方对各种计数进行设置即可。
struct net_device_stats *xxx_stats(struct net_device *dev) { … return &dev->stats; } struct net_device_stats { unsigned long rx_packets; /* 收到的数据包数 */ unsigned long tx_packets; /* 发送的数据包数 */ unsigned long rx_bytes; /* 收到的字节数 */ unsigned long tx_bytes; /* 发送的字节数 */ unsigned long rx_errors; /* 收到的错误数据包数 */ unsigned long tx_errors; /* 发生发送错误的数据包数 */ ... };
14.9 DM9000实例
14.10 总结
以上是关于Linux驱动开发笔记:helloworld驱动源码编写makefile编写以及驱动编译基本流程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章