Python tkinter之Frame(容器)
Posted 南风丶轻语
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python tkinter之Frame(容器)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、Frame的基本属性
# -*- encoding=utf-8 -*- import tkinter from tkinter import * if __name__ == \'__main__\': win = tkinter.Tk() # 窗口 win.title(\'南风丶轻语\') # 标题 screenwidth = win.winfo_screenwidth() # 屏幕宽度 screenheight = win.winfo_screenheight() # 屏幕高度 width = 500 height = 400 x = int((screenwidth - width) / 2) y = int((screenheight - height) / 2) win.geometry(\'{}x{}+{}+{}\'.format(width, height, x, y)) # 大小以及位置 frame = Frame( master=win, # 父容器 bg=\'yellow\', # 背景颜色 relief=\'groove\', # 边框的3D样式 flat、sunken、raised、groove、ridge、solid。 bd=3, # 边框的大小 height=100, # 高度 width=100, # 宽度 padx=1, # 内间距,字体与边框的X距离 pady=1, # 内间距,字体与边框的Y距离 cursor=\'circle\', # 鼠标移动时样式 arrow, circle, cross, plus... ) frame.pack() win.mainloop()
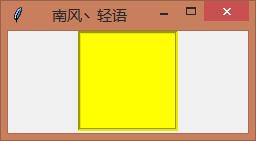
2、不同的Frame使用不同的布局
# -*- encoding=utf-8 -*- import tkinter from tkinter import * if __name__ == \'__main__\': pass w = tkinter.Tk() # 窗口 w.title(\'测试\') # 标题 w.geometry(\'200x100+30+30\') # 大小以及位置 frame = Frame() # 定义容器 Button( master=frame, # 父容器为frame text=\'容器1上的按钮\', # 文本 ).pack() frame2 = Frame() # 定义容器 Button( master=frame2, # 父容器为frame2 text=\'容器2上的按钮\', # 文本 ).grid(row=0, column=0) Label(frame2, text=\'容器2上的Lable\', bg=\'yellow\', fg=\'pink\').grid(row=0, column=1) frame.pack() frame2.pack() w.mainloop()
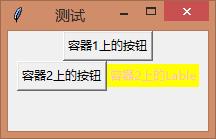
3、是否自动根据子组件改变自身大小
备注:
①默认自动根据子组件改变自身大小,可通过.propagate(False或True)进行设置
# -*- encoding=utf-8 -*-
import tkinter
from tkinter import *
if __name__ == \'__main__\':
win = tkinter.Tk() # 窗口
win.title(\'南风丶轻语\') # 标题
screenwidth = win.winfo_screenwidth() # 屏幕宽度
screenheight = win.winfo_screenheight() # 屏幕高度
width = 500
height = 400
x = int((screenwidth - width) / 2)
y = int((screenheight - height) / 2)
win.geometry(\'{}x{}+{}+{}\'.format(width, height, x, y)) # 大小以及位置
frame1 = Frame(
master=win, # 父容器
bg=\'yellow\', # 背景颜色
relief=\'groove\', # 边框的3D样式 flat、sunken、raised、groove、ridge、solid。
bd=3, # 边框的大小
height=100, # 高度
width=100, # 宽度
padx=1, # 内间距,字体与边框的X距离
pady=1, # 内间距,字体与边框的Y距离
cursor=\'circle\', # 鼠标移动时样式 arrow, circle, cross, plus...
)
frame1.pack()
frame2 = Frame(
master=win, # 父容器
bg=\'yellow\', # 背景颜色
relief=\'groove\', # 边框的3D样式 flat、sunken、raised、groove、ridge、solid。
bd=3, # 边框的大小
height=100, # 高度
width=100, # 宽度
padx=1, # 内间距,字体与边框的X距离
pady=1, # 内间距,字体与边框的Y距离
cursor=\'circle\', # 鼠标移动时样式 arrow, circle, cross, plus...
)
frame2.pack()
# 未设置propagate(False)时自动根据子组件改变自身大小
frame3 = Frame(
master=win, # 父容器
bg=\'yellow\', # 背景颜色
relief=\'groove\', # 边框的3D样式 flat、sunken、raised、groove、ridge、solid。
bd=3, # 边框的大小
height=100, # 高度
width=100, # 宽度
padx=1, # 内间距,字体与边框的X距离
pady=1, # 内间距,字体与边框的Y距离
cursor=\'circle\', # 鼠标移动时样式 arrow, circle, cross, plus...
)
frame3.pack()
frame3.propagate(False) # 不自动根据子组件改变自身大小
Label(frame2, text=\'标签\', width=3, height=1).pack(side=TOP)
Button(frame2, text=\'按钮\', ).pack(side=TOP)
Label(frame3, text=\'标签\', ).pack(side=TOP)
Button(frame3, text=\'按钮\', ).pack(side=TOP)
win.mainloop()
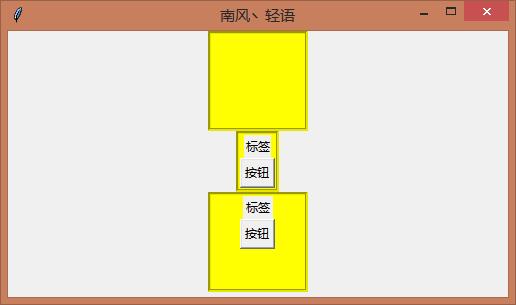
以上是关于Python tkinter之Frame(容器)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章