Python批量搜索和生成数据脚本,含有打包输出exe和msi
Posted eternalnight
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python批量搜索和生成数据脚本,含有打包输出exe和msi相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
搜索和生成脚本
密码字典生存

#author :握着玫瑰的屠夫 #date :2020.10.11 #contact :QQ 2472674814 #project :creat dictionaries #130******37 import itertools as its import time print("使用说明:1.输入有效的关键词如: 0123456789abc", "x0A2.输入字典的长度:每增加1个长度换算就是 关键词^长度,指数级增长。根据自己需求调节", ) inputWords =input("请输入有效的关键词:{}{}".format("_"*20,"x08"*20)) print("{}".format(">")*20,":成功输入。x0A") print("如果你想输出3位至6位的字典就输3和6,如果你只想打10位的字典就输入10和10.") inputLen1 =input("请输入开始的长度值要>0:{}{}".format("_"*3,"x08"*3)) inputLen2 =input("请输入结束的长度值要>=开始的长度:{}{}".format("_"*3,"x08"*3)) lenWords =len(inputWords) if inputLen1 ==inputLen2: countPoint =lenWords**int(inputLen1) else: a =int(inputLen2)-int(inputLen1) countPoint = lenWords ** int(inputLen1) for n in range(a): countPoint +=(lenWords**(int(inputLen1)+n+1)) countOut=countPoint inputLen2 =int(inputLen2)+1 n =0 runTrue =round(countPoint/100, 2) x =runTrue runDic =-1 while True: InputRun =input("估算字典体积大小==%.5f"%(countPoint*13/(1024**3))+"GB,是否要继续生成?(Y/N):{}{}".format(‘x5F‘*5,‘x08‘*5)) if InputRun ==‘n‘ or InputRun ==‘N‘ or InputRun ==‘No‘ or InputRun ==‘no‘: break elif InputRun ==‘‘ or InputRun ==‘y‘ or InputRun ==‘Y‘ or InputRun ==‘Yes‘ or InputRun ==‘yes‘: runDic *=-1 break else: print("输入有误请重新输入!!!!") if runDic ==1: dic=open(‘Jue字典.txt‘, ‘w+‘) for num in range(int(inputLen1), int(inputLen2)): keys = its.product(inputWords, repeat=num) for key in keys: if n >runTrue: x +=runTrue y =round(x*(100/countPoint)) z =int(y/(100/50)) print(‘x0D‘ + ‘x2A‘ * z + str(y) + ‘%x20‘, end=‘‘) n=0 dic.write("".join(key) + " ") n += 1 dic.close() print("x0A已经成功生成字典文件,名为"Jue字典.txt".") time.sleep(1) print("字典体积大小==%.5f" % (countPoint * 13 / (1024 ** 3)) + "GB") time.sleep(1) else: print("x0A虽然已经取消了生成,但是你也别太嚣张了靓仔.") time.sleep(1.5) print("x0A感谢你的使用,破解愉快!握着玫瑰的屠夫 QQ:2472674814.") time.sleep(5)
手机号补全

#author :握着玫瑰的屠夫 #date :2020.10.11 #contact :QQ 2472674814 #project :creat dictionaries #130******37 import itertools as its import time print(‘生成器只需要用后输入两段号码即可自动枚举.‘) print(‘列如:输入前段号码为137,后段为30.那么就会生成批量6位数并且合并前后段‘) print(‘列如:前后段都不输入那么就会生成11位数的枚举。x0A‘) inputS =input("请输入前部分已知手机号,如果不知道请按Enter:{}{}".format("x5F"*8, "x08"*8)) inputE =input("请输入后部分已知手机号,如果不知道请按Enter:{}{}".format("x5F"*8, "x08"*8)) words="0123456789" lenWords =len(words) lenStart =11-len(inputS)-len(inputE) lenEnd =lenStart+1 countPoint =lenWords**lenStart n =0 runTrue =round(countPoint/100, 2) x =runTrue runDic =-1 while True: InputRun =input("估算字典体积大小==%.5f"%(countPoint*13/(1024**3))+"GB,是否要继续生成?(Y/N):{}{}".format(‘x5F‘*5,‘x08‘*5)) if InputRun ==‘n‘ or InputRun ==‘N‘ or InputRun ==‘No‘ or InputRun ==‘no‘: break elif InputRun ==‘‘ or InputRun ==‘y‘ or InputRun ==‘Y‘ or InputRun ==‘Yes‘ or InputRun ==‘yes‘: runDic *=-1 break else: print("输入有误请重新输入!!!!") if runDic ==1: dic=open(‘Jue手机号补全.txt‘, ‘w+‘) for num in range(lenStart, lenEnd): keys = its.product(words, repeat=num) for key in keys: if n >runTrue: x +=runTrue y =round(x*(100/countPoint)) z =int(y/(100/50)) print(‘x0D‘+‘x2A‘*z + str(y)+‘%x20‘, end=‘‘) n=0 dic.write("".join(inputS)) dic.write("".join(key)) dic.write("".join(inputE)+‘x0A‘) n += 1 dic.close() print("x0A已经成功生成字典文件,名为"Jue手机号补全.txt".") time.sleep(1) print("字典体积大小==%.5f"%(countPoint*13/(1024**3))+"GB") time.sleep(1) else: print("x0A你已经取消生成字典,请不要太嚣张.") time.sleep(1.5) print("x0A感谢你的使用,破解愉快!握着玫瑰的屠夫 QQ:2472674814.") time.sleep(5)
WINDOWS下批量搜索图片GPS
python -m pip install exifread
python依赖安装 exifread

#author :Jue #date :2020.10.11 #contact :QQ 2472674814 #project :creat dictionaries from tkinter import * from tkinter.filedialog import askdirectory import time import exifread import os LOG_LINE_NUM =0 DATA_LINE_NUM =0 class MY_GUI(): def __init__(self, init_window_name, path1,path2): self.dir_path = {‘path1‘: ‘‘, ‘path2‘: ‘‘} self.path1 =path1;self.path2 =path2 self.countList =[] self.countPathFile =[] self.dataOUT =[] self.logOUT =[] self.logOUT2 =[] self.runLogOUT1 =-1 self.runLogOUT2 =-1 self.init_window_name =init_window_name self.sys_width = self.init_window_name.winfo_screenwidth() # 获得系统分辨率 self.sys_height = self.init_window_name.winfo_screenheight() self.screen_width = 800 #窗口的分辨率值 self.screen_height = 720 self.size = (‘%dx%d+%d+%d‘ % (self.screen_width, self.screen_height, ((self.sys_width - self.screen_width) / 2), (self.sys_height - self.screen_height) / 2)) # 居中 self.init_window_name.title("{}绝x20x20QQ:2472674814".format("x2A"*int(self.screen_width/12))) # 窗口名 #self.init_window_name.resizable(0, 0) # 固定窗口,禁止拖拉 # 定义窗口弹出时的默认展示位置 self.init_window_name.geometry(‘%s‘ % (self.size)) self.init_window_name["bg"] = "#000000" # 窗口背景色,其他背景色见:blog.csdn.net/chl0000/article/details/7657887 self.init_window_name.attributes("-alpha",0.9) #虚化,值越小虚化程度越高 #标签 self.Label1 =Label(self.init_window_name,width=10, text="目标路径1:") self.Label1.grid(row=0, column=0) self.Label2 = Label(self.init_window_name, width=10, text="目标路径2:") self.Label2.grid(row=1, column=0) self.Label3 = Label(self.init_window_name, width=10, height=2,text="输出内容:") self.Label3.grid(row=3, column=1) self.Label4 = Label(self.init_window_name, width=10, height=1,text="日记:") self.Label4.grid(row=15, column=0) #路径文本0框 self.Entry1 =Entry(self.init_window_name, width=int(self.screen_width/7-27),textvariable=self.path1) self.Entry1.grid(row=0, column=1) self.Entry2 = Entry(self.init_window_name, width=int(self.screen_width/7-27),textvariable=self.path2) self.Entry2.grid(row=1, column=1) self.Entry3 = Entry(self.init_window_name, width=int(self.screen_width/7.5-20),bg=‘#000000‘) self.Entry3.grid(row=2, column=1) #信息输出文本框 self.data_Text = Text(self.init_window_name, width=int(self.screen_width/8), bg=‘#87CEEB‘, height=int(self.screen_height/30)) self.data_Text.grid(row=4, column=0, rowspan=10, columnspan=10) #日记输出文本框 self.log_data_Text = Text(self.init_window_name, width=int(self.screen_width/7.3), bg=‘#FFB6C1‘, height=int(self.screen_height/55)) self.log_data_Text.grid(row=16, column=0, columnspan=10) #按钮 self.Button1 =Button(self.init_window_name, text ="照片路径1", bg="lightblue", width=15, command=self.selectPath1) self.Button1.grid(row = 0, column =2) self.Button2 = Button(self.init_window_name, text="照片路径2", bg="#228B22", width=15, command=self.selectPath2) self.Button2.grid(row=1, column=2) self.Button3 = Button(self.init_window_name, text="开始搜索", bg="#DC143C", width=15, height=4, command=self.openPicture) self.Button3.grid(row=14, column=1) # 获取当前时间 def get_current_time(self): current_time = time.strftime(‘%Y-%m-%d_%H:%M:%S‘,time.localtime(time.time())) return current_time def getPictureList(self, dir1, dir2): list =[‘.png‘, ‘.jpg‘, ‘.jpeg‘, ‘.bmp‘, ‘.rwa‘] #list = [‘.png‘, ‘.jpg‘, ‘.jpeg‘, ‘.bmp‘, ‘.rwa‘, ‘.tlf‘, ‘.gif‘, ‘.tga‘, ‘.exif‘, #‘.fpx‘, ‘.svg‘, ‘.psd‘, ‘.cdr‘, ‘.pcd‘, ‘.dxf‘, ‘.ufo‘, ‘.eps‘, ‘.ai‘, #‘.hdri‘, ‘.wmf‘, ‘.flic‘, ‘.emf‘, ‘.ico‘, ‘avif‘, #‘.png‘, ‘.jpg‘, ‘.jpeg‘, ‘.bmp‘, ‘.rwa‘] outList1 =[] outList2 =[] temp_list =[] on_off =-1 count_c ="" picList1 =dir1 picList2 =dir2 for i in picList1: for ii in i[-5::]: if ii == ‘.‘: temp_list.append(‘.‘) on_off *=-1 elif on_off == 1: temp_list.append(ii) on_off *=-1 for c in temp_list: count_c+=c temp_list =[] if count_c in list: outList1.append(i) count_c ="" on_off =-1 for i2 in picList2: for ii2 in i2[-5::]: if ii2 == ‘.‘: temp_list.append(‘.‘) on_off *= -1 elif on_off == 1: temp_list.append(ii2) on_off *= -1 for c in temp_list: count_c += c temp_list = [] if count_c in list: outList2.append(i2) count_c = "" if outList1: self.countList =outList1 else: A="照片路径1:{}未能找到有效图片路径,请重新选择{}".format(‘x21‘*5,‘x21‘*5)+‘x0A‘ self.runLogOUT1*=-1 self.logOUT2.append(A) if outList2: if self.countList: for c_list2 in outList2: self.countList.append(c_list2) else: self.countList =outList2 else: A="照片路径2:{}未能找到有效图片路径,请重新选择{}".format(‘x21‘*5,‘x21‘*5)+‘x0A‘ self.runLogOUT2*=-1 self.logOUT2.append(A) #print(self.countList) #print(len(self.countList)) #time.sleep(1) #图片打开搜索GPS信息 def openPicture(self): # 获取目录所有文件 f1 = self.dir_path[‘path1‘] f2 = self.dir_path[‘path2‘] file_add1 =[] file_add2 =[] for root, dirs, file_1 in os.walk(f1): if file_1: for p_f in file_1: a = root +‘/‘+ p_f file_add1.append(a) for root, dirs, file_2 in os.walk(f2): if file_2: for p_f in file_2: a = root +‘/‘+ p_f file_add2.append(a) # file_1 当前路径下所有非目录子文件 # dirs 当前路径下所有子目录 # root 当前目录路径 self.getPictureList(file_add1, file_add2) for times in range(len(self.countList)): with open(self.countList[times], ‘rb‘) as f: exif_dict = exifread.process_file(f) mPATH ="{}".format("x2A" * 5)+"第x20"+str(times+1)+",x20张图片x20照片地址:"+self.countList[times]+‘x0A‘ #print(mPATH) #print(‘拍摄时间:‘, exif_dict[‘EXIF DateTimeOriginal‘]) #print(‘照相机制造商:‘, exif_dict[‘Image Make‘]) #print(‘照相机型号:‘, exif_dict[‘Image Model‘]) #print(‘相片尺寸: ‘, exif_dict[‘EXIF ExifImageWidth‘], exif_dict[‘EXIF ExifImageLength‘]) # 经度 try: lon_ref = exif_dict["GPS GPSLongitudeRef"].printable lon = exif_dict["GPS GPSLongitude"].printable[1:-1].replace(" ", "").replace("/", ",").split(",") lon = float(lon[0]) + float(lon[1]) / 60 + float(lon[2]) / float(lon[3]) / 3600 if lon_ref != "E": lon = lon * (-1) # 纬度 lat_ref = exif_dict["GPS GPSLatitudeRef"].printable lat = exif_dict["GPS GPSLatitude"].printable[1:-1].replace(" ", "").replace("/", ",").split(",") lat = float(lat[0]) + float(lat[1]) / 60 + float(lat[2]) / float(lat[3]) / 3600 if lat_ref != "N": lat = lat * (-1) # for key in exif_dict: # print("%s %s" % (key, exif_dict[key])) mx =(lat, lon) mGPS ="照片经纬:>>>>>>>"+str(mx)+‘x0Ax0A‘ #print(mGPS) mTRUE =‘{}成功获得GPS{}‘.format("x2A" * 4, "x2A" * 4) #print(mTRUE) # 打印当前时间 current_time = self.get_current_time() logmsg_in = (str(current_time) + "x20") mDATE = "搜索生成时间: " + logmsg_in + ‘x0A‘ mDATA =mDATE+mPATH+mTRUE+mGPS mlogIn = "第 " + str(times + 1) + " 图片,执行时间:" + logmsg_in + mTRUE + "照片地址: " + self.countList[times] + ‘x0A‘ self.logOUT.append(mlogIn) self.dataOUT.append(mDATA) except Exception as e: mFALSE =‘{}获取GPS失败{}‘.format("x21" * 4, "x21" * 4) current_time = self.get_current_time() logmsg_in = (str(current_time) + "x20") mlogIn ="第 "+str(times+1)+" 图片,执行时间:"+logmsg_in+mFALSE+"照片地址: "+self.countList[times]+‘x0A‘ self.logOUT.append(mlogIn) with open(‘GPS数据存储.txt‘, ‘a+‘) as f: for dataKey in self.dataOUT: f.write(dataKey) f.flush() f.close() readList =open(‘GPS数据存储.txt‘, ‘r‘) if readList: lenRead =len(readList.readlines()) if lenRead >=100: f =open(‘GPS数据存储.txt‘, ‘w‘) f.write(‘‘) f.flush() f.close() with open(‘GPS日记存储.txt‘, ‘a+‘) as f: for logKey in self.logOUT: f.write(logKey) f.flush() f.close() readList = open(‘GPS日记存储.txt‘, ‘r‘) if readList: lenRead = len(readList.readlines()) if lenRead >= 1000: f = open(‘GPS日记存储.txt‘, ‘w‘) f.write(‘‘) f.flush() f.close() self.write_dataText(self.dataOUT) self.write_logText(self.logOUT, self.logOUT2) self.logOUT =[] self.logOUT2 =[] self.dataOUT =[] self.countList = [] #动态打印数据。。。。 def write_dataText(self, dataOUT): global DATA_LINE_NUM dataout =dataOUT if dataout: for data in dataout: if DATA_LINE_NUM <=7: self.data_Text.insert(END, data) DATA_LINE_NUM +=1 else: self.data_Text.delete(1.0, END) self.data_Text.insert(END, data) DATA_LINE_NUM =1 # 动态打印日记数据。。。。 def write_logText(self, logOUT, logOUT2): global LOG_LINE_NUM logout =logOUT logout2 =logOUT2 if self.logOUT2: for log2 in logout2: self.log_data_Text.insert(END, log2) LOG_LINE_NUM += 1 if LOG_LINE_NUM >= 11: self.log_data_Text.delete(1.0, END) self.log_data_Text.insert(END, log2) LOG_LINE_NUM =1 if self.runLogOUT1 ==1: self.runLogOUT1*=-1 elif self.runLogOUT2 ==1: self.runLogOUT2*=-1 if logout: for log in logout: if LOG_LINE_NUM <= 11: self.log_data_Text.insert(END, log) LOG_LINE_NUM += 1 else: self.log_data_Text.delete(1.0, END) self.log_data_Text.insert(END, log) LOG_LINE_NUM = 1 def selectPath1(self): path_ = askdirectory() self.path1.set(path_) self.dir_path[‘path1‘] = path_ def selectPath2(self): path_ = askdirectory() self.path2.set(path_) self.dir_path[‘path2‘] =path_ def runGui(): init_window =Tk() path2 =StringVar() path1 =StringVar() MY_GUI(init_window, path1, path2) init_window.mainloop() runGui()
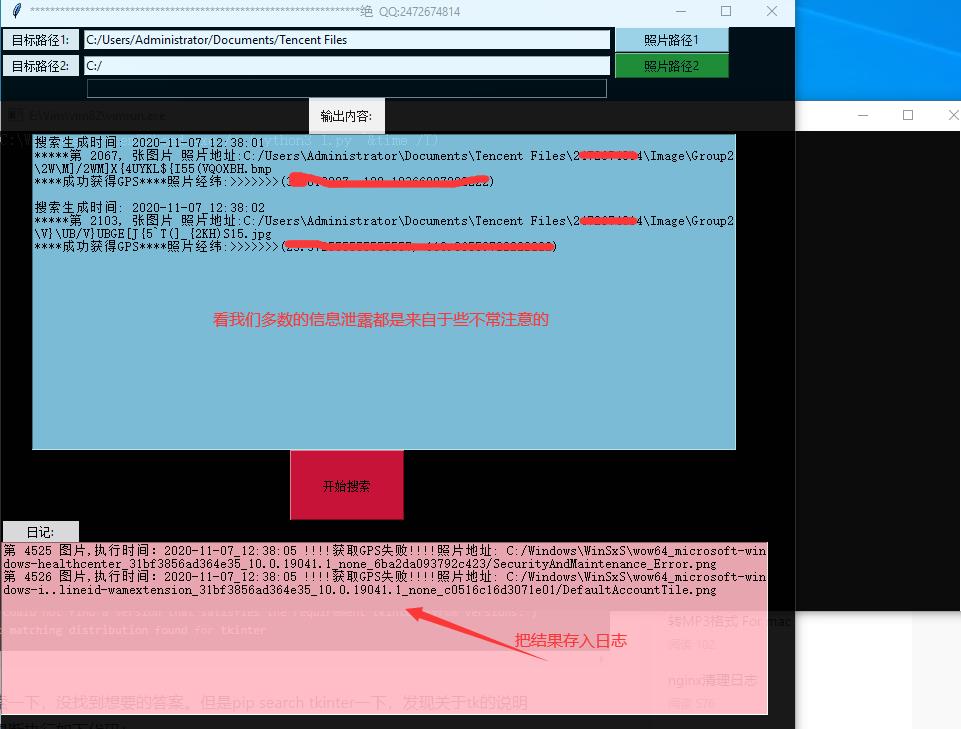
这里有点小bug,由于时隔比较久,也不影响效率就不修改了。提示:不要目标1和目标2重复一个目录,否则会输出同样结果 也会导致BUG
Pyinstaller打包exe还是比较推荐用这个
核心打包的工具及依赖安装
pip install pyinstaller pip install pywin32
打包python并输出exe格式可执行软件的依赖 Pyinstaller pywin32
http://upx.sourceforge.net/ 官方网,一个能让输出exe格式压缩极小的搭配软件。推荐使用
https://github.com/upx/upx/releases/tag/v3.96 下载地址,有各种系统版本,由于我是做的exe所以选择 upx-3.96-win64.zip
桌面建立Tools把它解压进去就行了 PyInstaller最新版只支持Python2.7
pyinstaller命令解释
| -F --onefile | 产生单个可执行文件 |
| -D --onefile | 产生一个目录(包含多个文件) 作为可执行程序 |
| -a --ascii | 不包含 Unicode 字符集支持 |
| -d --debug | 产生debug版本的可执行文件 |
| -w --windowed --noconsolc | 指定程序运行时不显示命令行窗口(仅对 Windows 有效) |
| -o DIR,--out=DIR | 指定 spec 文件的生成目录。如果没有指定,则默认使用当前目录来生成 spec 文件 |
| -p DIR,--path=DIR | 设置 Python 导入模块的路径(和设置 PYTHONPATH 环境变量的作用相似)。也可使用路径分隔符(Windows 使用分号,Linux 使用冒号)来分隔多个路径 |
| -n NAME,--name=NAME | 指定项目(产生的 spec)名字。如果省略该选项,那么第一个脚本的主文件名将作为 spec 的名字 |
| -i <FILE.ico or FILE.exe,ID or FILE.icns> --icon | 可以把file.ico格式或 file.exe格式的 icons修改软件图标. .exe格式的图片转换会模糊,建议下载icon图 |
| -c --nowindowed, --console | 显示控制台执行 |
| -K, --tk | 在部署时包含 TCL/TK |
| -s --strip | 可执行文件和共享库将run through strip.注意Cygwin的strip往往使普通的win32 Dll无法使用. |
| -X --upx | 如果有UPX安装(执行Configure.py时检测),会压缩执行文件(Windows系统中的DLL也会) |
实例 图形界面
pyinstaller -w -i putty64ssh.exe -F main.py
这里讲下,如果你的项目有一个主文件和几个配置文件组成,在-F 后面输入main.py 主文件即可。它会处理组合到一起
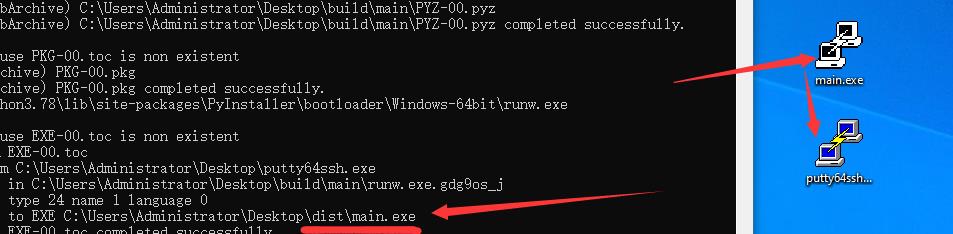
-F就是会生成一个 单个文件 -i exe就会模糊化,建议用 .ico图标。
|
源码大小
|
执行后大小
|
差率
|
|
单个项目:文件12.5KB
|
文件8.17MB
|
约670倍,大了8354KB,
|
对比下putty.exe的大小也才1.12MB python的生存足足8MB ,单个文件输出会影响运行速度,如果想减小这些影响可以-D输出依赖。
pyinstaller -w -i putty64ssh.exe -D main.py
也就是说如果main.exe离开了目录就不能执行,
|
源码大小
|
执行后大小
|
结果
|
|
单个项目:文件12.5KB
|
多个文件:共18.7MB
|
可以看到输出目录后占容量变大了,但是运行速度快了很多
|
压缩exe
pyi-makespec -w -i "putty64ssh.exe" -D main.py
建立main.spec打包管理文件 或pyi-makespec main.py , vim main.spec 编辑生成的main.spec文件,可修改icons或其他信息
pyinstaller --upx-dir "C:UsersAdministratorDesktopToolsupx-3.96-win64" --clean main.spec
--clean 参数是清楚一些残留的,--upx-dir 指的是刚刚你下载解压所存放upx的目录。但都会报错,暂时没去解决。先放一边
|
源码大小
|
执行后大小
|
结果差
|
|
单个项目exe:文件8.17MB
目录:文件18.7MB
|
单个文件:7.05MB
目录:文件10.6MB
|
单文件约减小了1/8
目录压缩:原来大小的56%
|
关于python生成的exe报错
1.在其他电脑使用报错
解决办法:到微软下载 VC2015Redist 就能解决依赖问题
2.upx.exe 在windows压缩报错
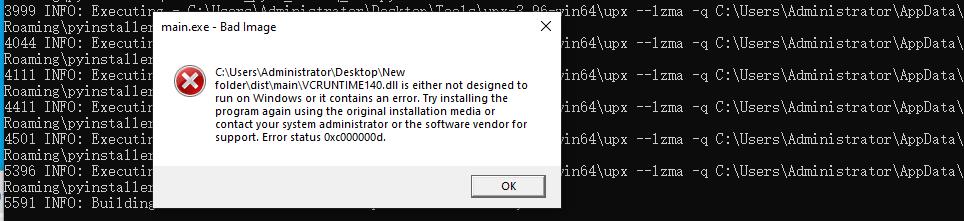
我们可以看到报错的原因在VCRUNTIME140.dll VC运行错误,只要先把正常的 VCRUNTIME140.dll保存起来,压缩完后粘贴即可
目前的解决方案只建立在,目录的方式.
pyi-makespec -w -i "putty64ssh.exe" -D main.py
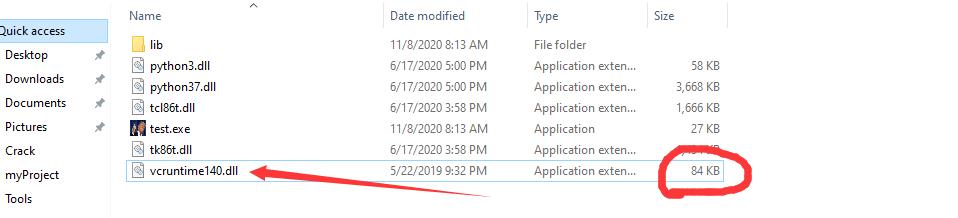
先把这个vcruntine 约84KB的复制好
pyinstaller --upx-dir "C:UsersAdministratorDesktopToolsupx-3.96-win64" --clean main.spec
OK我们可以压缩,我们启动的时候依旧报错vcruntime,这时候把 vcruntime140.dll替换成刚刚我们复制的就OK了。。。
把我们这个打包zip就能上路了
cxfreeze打包exe 支持python3 以及python2
pip install cx-freeze
安装cxfreeze,如果安装不了就去官方https://pypi.org/project/cx_Freeze/4.3.3/#files
在网上找了很多教程都是乱七八糟抓不到重点。最好的办法就是看官方给的指导 cxfreeze --help
cxfreeze命令行
|
-c --compress
|
compress byte code in zip files,压缩zip文件的字节码
|
|
-s --slient
|
suppress all output except warnings and errors, 禁止输出除错误外信息。排除错误用的
|
|
--base-name MAIN
|
--base-name Win32GUI 意思使用图形模式,去掉命令窗口
|
|
--init-script NAME
|
|
|
--target-dir DIR
|
输出目录C:UsersAdministratorDesktopoutput |
|
--target-name NAME
|
输出名称
|
|
--icon NAME.ico
|
替换图标
|

cxfreeze --target-name test --target-dir C:UsersAdministratorDesktopoutput C:UsersAdministratorDesktopmyProjectmain.py --icon F:PhotographICOT.ico --base-name Win32GUI
执行上面View Code代码输出exe名为test 到output 目录,源码main.py, icons图标为T.ico WIN32GUI去除终端窗口
脚本代码修改输出
下载完cx-freeze后会在python目录下的script 产生二个脚本文件 cxfreeze cxfreeze-quickstart.exe, 在myProject里面创建一个setup.py配置文件,然后进行编辑.

__author__ = ‘握着玫瑰的屠夫‘ import sys, os from cx_Freeze import setup, Executable #导入模块的名字 setup Excutable os.environ[‘TCL_LIBRARY‘] = r‘E:Python3.78 cl cl8.6‘ #我的python放在E盘所以是E:python os.environ[‘TK_LIBRARY‘] = r‘E:Python3.78 cl k8.6‘ include_files=[ r‘E:Python3.78DLLs cl86t.dll‘, #需要修改python所在的目录 r‘E:Python3.78DLLs k86t.dll‘ ] base = None # 判断windows系统 if sys.platform == ‘win32‘: base = ‘Win32GUI‘ #设置取消 packages = [] # 动态引入 for dbmodule in [‘win32gui‘, ‘win32api‘, ‘win32con‘, ‘cx_Freeze‘, ‘os‘, ‘tkinter‘, ‘time‘, ‘exifread‘]: try: __import__(dbmodule) except ImportError: pass else: packages.append(dbmodule) options = { ‘build_exe‘: { "packages": packages # 依赖的包 , ‘include_files‘:include_files # 额外添加的文件 可以是文件夹 } } executables = [ Executable( ‘main.py‘ # 源码文件需要修改 , base=base , targetName=‘test.exe‘ # 生成的exe的名称 , icon="Myicon.ico" # 生成的exe的图标 ) ] setup( name=‘测试名‘, version=‘2.1‘, description=‘测试描述‘, options=options, executables=executables )
保存后我们用dos执行下面命令
python setup.py build
我们可以看到main.exe既生成出来,上面代码需要修改否则会出错 都有注释了
python setup.py bdist_msi
打包输出msi格式,安装exe应用
TO THE END
以上是关于Python批量搜索和生成数据脚本,含有打包输出exe和msi的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
