Spring IOC
Posted MeltSky
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring IOC相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1 .SpringIoc
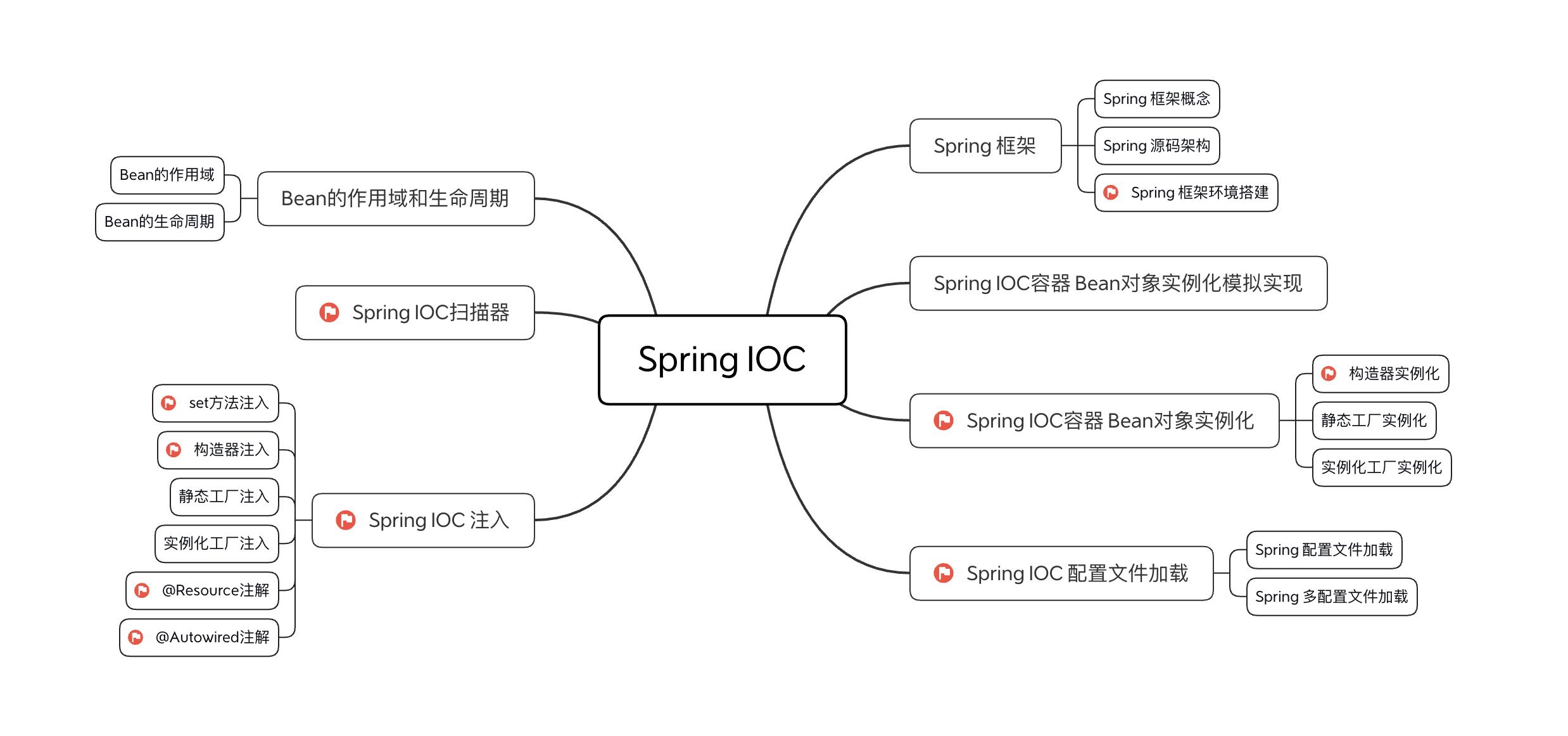
2 Spring框架
2.1 Spring框架概念
Spring 是众多开源java项目中的一员,基于分层的javaEE应用一站式轻量级开源框架,主要核心是
IOC(控制反转/依赖注入)与 AOP(面向切面)两大技术,实现项目在开发过程中的轻松解耦,提高项
目的开发效率。
在项目中引入 Spring 立即可以带来下面的好处 降低组件之间的耦合度,实现软件各层之间的解耦。可
以使用容器提供的众多服务,如:事务管理服务、消息服务等等。当我们使用容器管理事务时,开发人
员就不再需要手工控制事务.也不需处理复杂的事务传播。 容器提供单例模式支持,开发人员不再需要自
己编写实现代码。 容器提供了AOP技术,利用它很容易实现如权限拦截、运行期监控等功能。
2.2 Spring 源码架构
Spring 总共大约有20个模块,由1300多个不同的文件构成。而这些组件被分别整合在核心容器
(Core Container)、Aop(Aspect Oriented Programming)和设备支持(Instrmentation)、数据
访问及集成(Data Access/Integeration)、Web、报文发送(Messaging)、测试6个模块集合中。
-
核心容器:Spring-beans 和 Spring-core 模块是 Spring 框架的核心模块,包含控制反转
(Inversion of Control, IoC)和依赖注入(Dependency Injection, DI),核心容器提供 Spring 框
架的基本功能。核心容器的主要组件是 BeanFactory,工厂模式的实现。BeanFactory 使用控制反
转(IOC) 思想将应用程序的配置和依赖性规范与实际的应用程序代码分开。
Spring 上下文Spring Context:Spring 上下文是一个配置文件,向 Spring 框架提供上下文信息。
Spring 上下文包括企业服务,例如 JNDI、EJB、电子邮件、国际化、校验和调度功能。
Spring-Expression 模块是统一表达式语言(unified EL)的扩展模块,可以查询、管理运行中的对
象,同时也方便的可以调用对象方法、操作数组、集合等。它的语法类似于传统EL,但提供了额外
的功能,最出色的要数函数调用和简单字符串的模板函数。
-
Spring-AOP:Spring-aop是Spring的另一个核心模块, 在Spring中,他是以JVM的动态代理技术为
基础,然后设计出了一系列的Aop横切实现,比如前置通知、返回通知、异常通知等。通过其配置
管理特性,Spring AOP 模块直接将面向切面的编程功能集成到了 Spring 框架中。所以,可以很容
易地使 Spring 框架管理的任何对象支持 AOP。
-
Spring Data Access(数据访问):由Spring-jdbc、Spring-tx、Spring-orm、Spring-jms和Spring
oxm 5个模块组成 Spring-jdbc 模块是 Spring 提供的JDBC抽象框架的主要实现模块,用于简化
Spring JDBC。
Spring-tx 模块是SpringJDBC事务控制实现模块。使用Spring框架,它对事务做了很好的封装,通
过它的Aop配置,可以灵活的配置在任何一层。
Spring-Orm 模块是ORM框架支持模块,主要集成 hibernate, Java Persistence API (JPA) 和 Java
Data Objects (JDO) 用于资源管理、数据访问对象(DAO)的实现和事务策略。
Spring-Jms 模块(Java Messaging Service)能够发送和接受信息。Spring-Oxm 模块主要提供一个抽象层以支撑 OXM(OXM 是 Object-to-XML-Mapping 的缩写,它
是一个O/M-mapper,将java对象映射成 XML 数据,或者将 XML 数据映射成 java 对象),例
如:JAXB, Castor, XMLBeans, JiBX 和 XStream 等。
-
Web 模块:由Spring-web、Spring-webmvc、Spring-websocket和Spring-webmvc-portlet 4个
模块组成,Web 上下文模块建立在应用程序上下文模块之上,为基于 Web 的应用程序提供了上下
文。Web 模块还简化了处理多部分请求以及将请求参数绑定到域对象的工作。
-
报文发送:即Spring-messaging模块。
Spring-messaging是Spring4 新加入的一个模块,主要职责是为Spring 框架集成一些基础的报文
传送应用。
-
单元测试:即Spring-test模块。Spring-test模块主要为测试提供支持
2.3 Spring框架环境搭建
2.3.1. 环境要求
JDK 版本:
JDK 1.7 及以上版本Spring版本:
Spring 5.x版本2.3.2. 新建 Maven 项目
-
创建 Maven 的普通 Java 项目

-
设置项目的坐标、名称、工作空间
-
设置项目的 Maven 环境
2.3.3 调整项目环境
1.修改JDK版本
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>-
修改单元测试 JUnit 版本
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>-
build标签中的pluginManagement标签
<!--删除build标签中的pluginManagement标签-->
<build>
</build>2.3.4 添加 Spring 框架的依赖坐标
Maven仓库:https://mvnrepository.com/
<!-- 添加Spring框架的核心依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>2.3.5 编写Bean对象
package com.xxxx.service;
public class UserService
public void test()
System.out.println("Hello Spring!");
2.3.6 添加Spring配置文件
-
在项目的src下创建文件夹 resources(Alt+insert)
-
将 resources 标记为资源目录
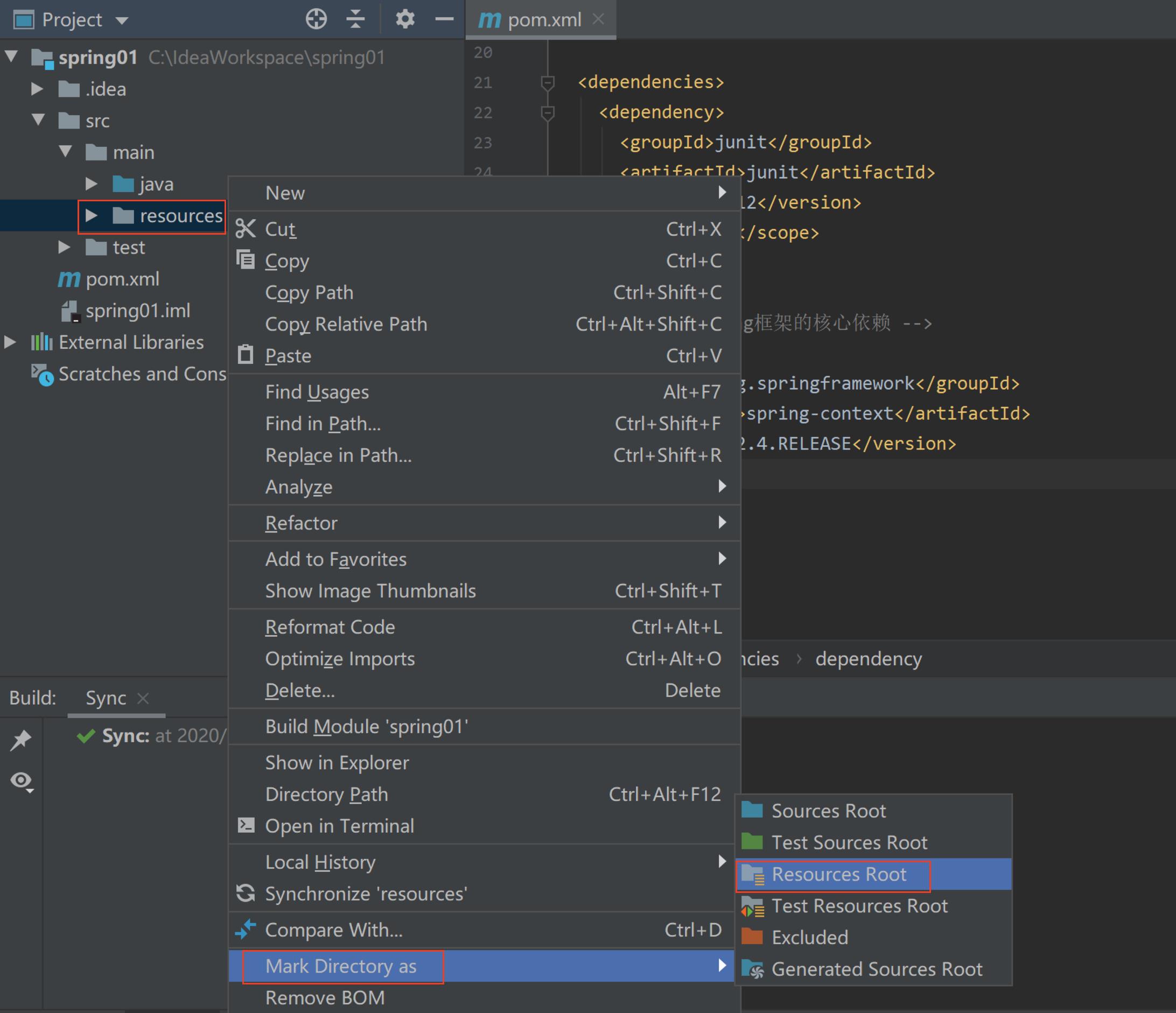
-
在 src\\main\\resources 目录下新建 spring.xml 文件,并拷贝官网文档提供的模板内容到 xml 中。
配置 bean 到 xml 中,把对应 bean 纳入到 Spring 容器来管理
spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
xmlns 即 xml namespace xml使用的命名空间
xmlns:xsi 即xml schema instance xml 遵守的具体规范
xsi:schemaLocation 本文档xml遵守的规范 官方指定
-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService"></bean>
</beans>4.在 spring.xml 中配置 Bean 对象
<!--
id:bean对象的id,唯一标识。一般是Bean对象的名称的首字母小写
class:bean对象的类路径
-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService"></bean>2.3.7. 加载配置文件,获取实例化对象
package com.xxxx;
import com.xxxx.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App
public static void main(String[] args)
// 获取Spring上下文环境 (加载配置文件)
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
// 通过getBean方法得到Spring容器中实例化好的Bean对象 (实例化Bean对象)
// userService代表的是配置文件中bean标签的id属性值
UserService userService = (UserService) ac.getBean("userService");
// 调用方法 (使用实例化对象)
userService.test();
3 Spring IOC 容器 Bean对象实例化模拟
思路:
-
定义Bean 工厂接口,提供获取bean方法
-
定义Bean工厂接口实现类,解析配置文件,实例化Bean对象
-
实现获取Bean方法
3.1 定义 Bean 属性对象
package com.xxx.spring;
/**
* Bean属性对象
* 用来存放配置文件中bean标签对应的id和class属性
*/
public class MyBean
private String id; //bean标签的id属性值
private String clazz; //bean标签的class属性值
public MyBean()
public MyBean(String id, String clazz)
this.id = id;
this.clazz = clazz;
public String getId()
return id;
public void setId(String id)
this.id = id;
public String getClazz()
return clazz;
public void setClazz(String clazz)
this.clazz = clazz;
3.2. 添加 dom4j 坐标依赖
<!--引入dom4j依赖-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/dom4j/dom4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>1.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/jaxen/jaxen -->
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxen</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
<version>1.1.6</version>
</dependency>
3.3. 准备自定义配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans>
<!--设置JavaBean对应的bean标签-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxx.dao.UserDao"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxx.service.UserService"></bean>
</beans>
3.4. 定义 Bean 工厂接口
package com.xxx.spring;
/**
* Bean 工厂接口定义
*/
public interface MyFactory
//通过id属性值获取对象
public Object getBean(String id);
3.5.定义Bean接口的实现类
package com.xxx.spring;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.XPath;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 模拟Spring的实现
* 1.通过带参构造器得到对应的配置文件
* 2.通过dom4j解析配置文件(xml文件),得到list集合(存放bean标签的id和class属性值)
* 3.通过反射得到对应的实例化对象,放置在map对象中(遍历list集合,通过获取对应的class属性,利用Class.forName(class).newIntance())
* 4.通过id属性值获取指定的实例化对象
*/
public class MyClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements MyFactory
private List<MyBean> beanList; //存放从配置文件文件中获取到的bean标签的信息(myBean代表的就是每一个bean标签)
private Map<String ,Object> beanMap =new HashMap<>(); //存放实例化好的对象,通过id获取对应的对象
//1.通过带参构造器得到对应的配置文件
public MyClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String fileName)
// 2.通过dom4j解析配置文件(xml文件),得到list集合
this.parseXml(fileName);
//3.通过反射得到对应的实例化对象
this.instanceBean();
/**
* 通过dom4j解析配置文件(xml文件),得到list集合
* 1.获取解析器
* 2.获取配置文件的URL
* 3.通过解析器解析配置文件(xml文件)
* 4.通过XPath语法解析,获取beans标签下的所有bean标签
* 5.通过指定的解析语法解析文档对象,返回元素集合
* 6.判断元素集合是否为空
* 7.如果元素集合不为空,遍历集合
* 8.获取bean标签元素属性(id和class属性值)
* 9.获取MyBean对象,将id和class属性值设置到对象中,再将对象设置到MyBean的集合中
* @param fileName
*/
private void parseXml(String fileName)
//1.获取解析器
SAXReader saxReader =new SAXReader();
//2.获取配置文件的URL
URL url =this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(fileName);
try
//3.通过解析器解析配置文件(xml文件)
Document document =saxReader.read(url);
// 4.通过XPath语法解析,获取beans标签下的所有bean标签
XPath xPath =document.createXPath("beans/bean");
//5.通过指定的解析语法解析文档对象,返回元素集合
List<Element> elementList =xPath.selectNodes(document);
//6.判断元素集合是否为空
if (elementList !=null && elementList.size()>0)
//实例化beanList
beanList =new ArrayList<>();
//7.如果元素集合不为空,遍历集合
for(Element el:elementList)
//8.获取bean标签元素属性(id和class属性值)
String id =el.attributeValue("id");
String clazz =el.attributeValue("class");
//9.获取MyBean对象,将id和class属性值设置到对象中,再将对象设置到MyBean的集合中
MyBean myBean =new MyBean(id,clazz);
beanList.add(myBean);
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
/**
* 通过反射得到对应的实例化对象,放置在map对象中
* 1.判断对象集合是否为空,如果不为空,则遍历集合,获取对象的id和class
* 2.通过类的全路径名 反射 得到实例化对象 Class.forName(class).newInstance();
* 3.将对应的id和实例化的bean对象设置到map对象
*/
private void instanceBean()
//1.判断对象集合是否为空,如果不为空,则遍历集合,获取对象的id和class
if (beanList !=null &&beanList.size()>0)
for (MyBean bean :beanList)
String id =bean.getId();
String clazz =bean.getClazz();
try
//2.通过类的全路径名 反射 得到实例化对象 Class.forName(class).newInstance();
Object object =Class.forName(clazz).newInstance();
//3.将对应的id和实例化的bean对象设置到map对象
beanMap.put(id,object);
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
/**
* 通过id获取对应的map对象中的value值(实例化好bean对象)
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object getBean(String id)
Object object = beanMap.get(id);
return object;
3.6. 测试自定义 IOC 容器
1.创建与配置文件中对应的Bean对象
UserService.java
package com.xxx.service;
public class UserService
public void test()
System.out.println("userService test...");
UserDao.java
package com.xxx.dao;
public class UserDao
public void test()
System.out.println("userDao test...");
2.测试是否可以获取实例化的Bean对象
package com.xxx;
import com.xxx.dao.UserDao;
import com.xxx.service.UserService;
import com.xxx.spring.MyClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.xxx.spring.MyFactory;
/**
* Hello world!
*
*/
public class App
public static void main( String[] args )
//得到工厂的实现对象
MyFactory factory =new MyClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
//得到对应的实例化对象
UserDao userDao = (UserDao) factory.getBean("userDao");
userDao.test();
UserService userService = (UserService) factory.getBean("userService");
userService.test();
Spring 容器在启动的时候 读取xml配置信息,并对配置的 bean 进行实例化(这里模拟的比较简
单,仅用于帮助大家理解),同时通过上下文对象提供的 getBean() 方法拿到我们配置的 bean 对
象,从而实现外部容器自动化维护并创建 bean 的效果。
4. Spring IOC 配置文件加载
4.1. Spring配置文件加载
spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
xmlns 即 xml namespace xml使用的命名空间
xmlns:xsi 即xml schema instance xml 遵守的具体规范
xsi:schemaLocation 本文档xml遵守的规范 官方指定
-->
<!--
id:bean对象的id,唯一标识。一般是Bean对象的名称的首字母小写
class:bean对象的类路径(包名加类名)
-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxx.service.UserService">
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
</beans>4.1.1 根据相对路径加载资源
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");4.1.2 根据绝对路径加载资源(了解)
ApplicationContext ac = new
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("C:/IdeaWorkspace/spring01/src/main/resources/spring.xml");
4.2. Spring 多配置文件加载
Spring 框架启动时可以加载多个配置文件到环境中。对于比较复杂的项目,可能对应的配置文件有多
个,项目在启动部署时会将多个配置文件同时加载进来。
service.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService"></bean>
</beans>dao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao"></bean>
</beans>4.2.1. 可变参数,传入多个文件名
// 同时加载多个资源文件
ApplicationContext ac = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml","dao.xml");
4.2.2. 通过总的配置文件import其他配置文件
spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--通过import导入其他配置文件-->
<import resource="beans.xml"></import>
<import resource="spring.xml"></import>
</beans>加载时只需加载总的配置文件即可
// 加载总的资源文件
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
5.Spring IOC容器Bean 对象实例化
5.1. 构造器实例化
注:通过默认构造器创建 空构造方法必须存在 否则创建失败
1.设置配置文件 spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
构造器实例化
对应Bean对象需要提供空构造
-->
<bean id="typeDao" class="com.xxx.dao.TypeDao"></bean>
</beans>2.获取实例化对象
package com.xxx.test;
import com.xxx.dao.TypeDao;
import com.xxx.service.UserService;
import com.xxx.service.UserService02;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* IOC容器Bean对象的实例化方式
* 1.构造器实例化 (Bean对象需要提供空构造)
*/
public class Starter03
public static void main(String[] args)
BeanFactory factory =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring02.xml");
TypeDao typeDao = (TypeDao) factory.getBean("typeDao");
typeDao.test();
5.2.静态工厂实例化(了解)
注:
要有该工厂类及工厂方法
工厂方法为静态的
1.定义静态工厂类
package com.xxx.factory;
import com.xxx.service.TypeService;
import sun.reflect.generics.tree.TypeSignature;
/**
* 定义静态工厂类
*
*/
public class StaticFactory
/**
* 定义对应的静态方法
* @return
*/
public static TypeService createService()
return new TypeService();
2.设置配置文件 spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
静态工厂实例化
1.定义工厂类及对应的静态方法
2.配置bean对象对应的工厂类及静态方法
id:需要被实例化的bean对象的id
class:静态工厂类的路径
factory-method:静态工厂类中实例化bean对象的静态方法
-->
<bean id="typeService" class="com.xxx.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="createService"></bean>
</beans>3.获取实例化对象
//静态工厂实例化
TypeService typeService = (TypeService) factory.getBean("typeService");
typeService.test();当我们指定Spring使用静态工厂方法来创建Bean实例时,Spring将先解析配置文件,并根据配
置文件指定的信息,通过反射调用静态工厂类的静态工厂方法,并将该静态工厂方法的返回值作为Bean实例,
在这个过程中,Spring不再负责创建Bean实例,Bean实例是由用户提供的静态工厂方法提供的。
5.3. 实例化工厂实例化(了解)
注:
工厂方法为非静态方法
需要配置工厂bean,并在业务bean中配置factory-bean,factory-method属性
1.定义工厂类
package com.xxx.factory;
import com.xxx.controller.TypeController;
/**
* 定义实例化工厂
*/
public class InstanceFactory
/**
* 定义实例化方法
* @return
*/
public TypeController createTypeController()
return new TypeController();
2.设置配置文件 spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
实例化工厂
1.定义工厂类及对应的方法
2.配置工厂对象
3.配置bean对象对应的工厂对象及工厂方法
factory-bean:工厂对象对应的id属性值
factory-method:工厂类中的方法
-->
<!--工厂对象-->
<bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.xxx.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean>
<!--bean对象-->
<bean id="typeController" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="createTypeController"></bean>
</beans>
3.获取实例化对象
package com.xxx.test;
import com.xxx.controller.TypeController;
import com.xxx.dao.TypeDao;
import com.xxx.service.TypeService;
import com.xxx.service.UserService;
import com.xxx.service.UserService02;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* IOC容器Bean对象的实例化方式
* 1.构造器实例化 (Bean对象需要提供空构造)
* 2.静态工厂实例化(了解)
* 3.实例化工厂(了解)
*/
public class Starter03
public static void main(String[] args)
BeanFactory factory =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring02.xml");
//构造器实现
TypeDao typeDao = (TypeDao) factory.getBean("typeDao");
typeDao.test();
//静态工厂实例化
TypeService typeService = (TypeService) factory.getBean("typeService");
typeService.test();
//实例化工厂
TypeController typeController = (TypeController) factory.getBean("typeController");
typeController.test();
5.4. Spring三种实例化Bean的方式比较
方式一:通过bean的缺省构造函数创建,当各个bean的业务逻辑相互比较独立的时候或者和外界
关联较少的时候可以使用。
方式二:利用静态factory方法创建,可以统一管理各个bean的创建,如各个bean在创建之前需要
相同的初始化处理,则可用这个factory方法险进行统一的处理等等。
方式三:利用实例化factory方法创建,即将factory方法也作为了业务bean来控制,1可用于集成
其他框架的bean创建管理方法,2能够使bean和factory的角色互换。
开发中项目一般使用一种方式实例化bean,项目开发基本采用第一种方式,交给Spring托管,使用
时直接拿来使用即可。另外两种了解
6. Spring IOC 注入
手动实例化与外部引入
图一:
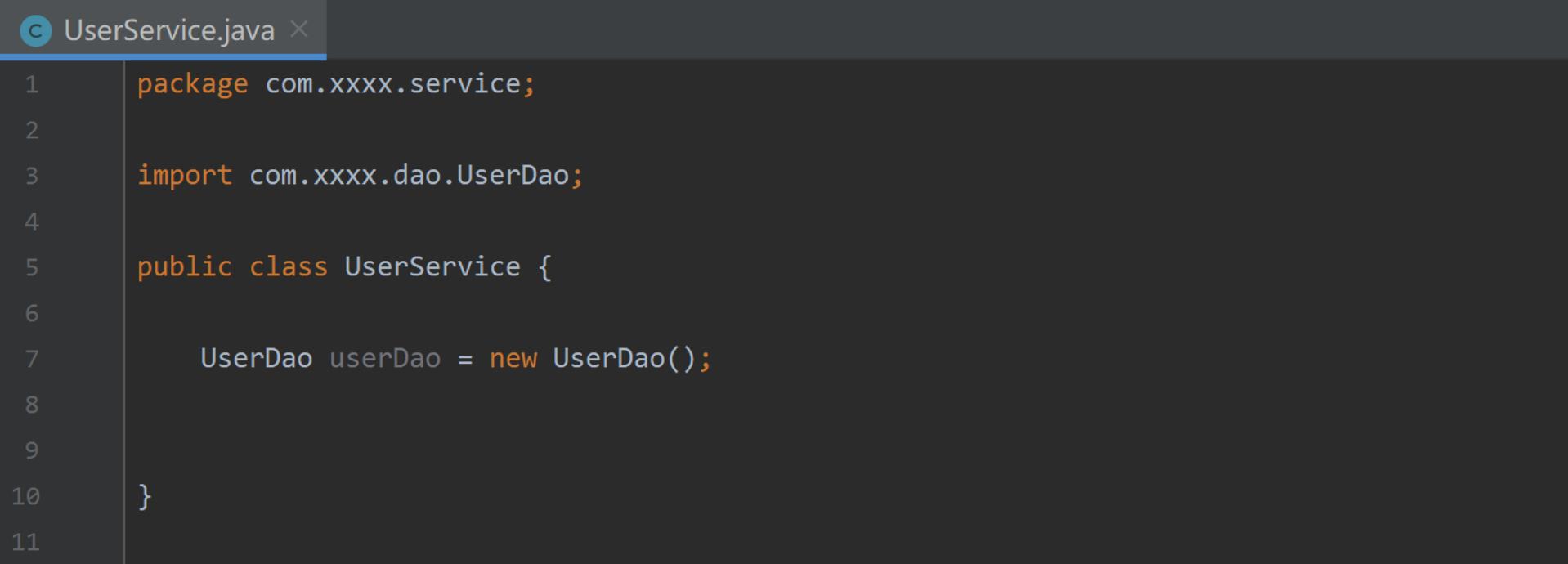
图二:

对比发现:图二中对于 UserDao 对象的创建并没有像图一那样主动的去实例化,而是通过带参方法
形式将UserDao 传入过来,从而实现 UserService 对UserDao类 的依赖。
而实际创建对象的幕后对象即是交给了外部来创建。
6.1. Spring IOC手动装配(注入)
Spring 支持的注入方式共有四种:set 注入、构造器注入、静态工厂注入、实例化工厂注入。
6.1.1. set方法注入
注:
属性字段需要提供set方法
四种方式,推荐使用set方法注入
6.1.1.1. 业务对象 JavaBean
1.属性字段提供set方法
package com.xxx.service;
import com.xxx.dao.UserDao;
public class UserService
//手动实例化
//private UserDao userDao =new UserDao();
//业务逻辑对象 javabean对象,提供set方法注入
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao)
this.userDao = userDao;
public void test()
System.out.println("UserService test...");
userDao.test();
2.配置文件的bean标签设置property标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
Set方法注入
通过property属性注入
name:bean对象中属性字段的名称
ref:指定bean标签的id属性值
-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxx.service.UserService">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"></property>
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxx.dao.UserDao"></bean>
</beans>
6.1.1.2. 常用对象和基本类型
1.属性字段提供set方法
public class UserService
// 常用对象String set注入(提供set方法)
private String host;
public void setHost(String host)
this.host = host;
// 基本类型Integer set注入(提供set方法)
private Integer port;
public void setPort(Integer port)
this.port = port;
2.配置文件的bean标签设置property标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
6.1.1.3. 集合类型和属性对象
1. 属性字段提供set方法
2. 配置文件的bean标签设置property标签
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过property标签手动装配(注入):
Set方法注入
name:bean对象中属性字段的名称
value:具体的值(基本类型 常用对象|日期 集合)
-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService">
<!--常用对象String 注入-->
<property name="host" value="127.0.0.1"/>
<!--基本类型注入-->
<property name="port" value="8080"/>
</bean>
</beans>
6.1.1.3. 集合类型和属性对象
1.属性字段提供set方法
public class UserService
// List集合 set注入(提供set方法)
public List<String> list;
public void setList(List<String> list)
this.list = list;
// Set集合 set注入(提供set方法)
private Set<String> set;
public void setSet(Set<String> set)
this.set = set;
// Map set注入(提供set方法)
private Map<String,Object> map;
public void setMap(Map<String, Object> map)
this.map = map;
// Properties set注入(提供set方法)
private Properties properties;
public void setProperties(Properties properties)
this.properties = properties;
2.配置文件的bean标签设置property标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过property标签手动装配(注入):
Set方法注入
name:bean对象中属性字段的名称
value:具体的值(基本类型 常用对象|日期 集合)
-->
<!--List集合 注入-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>上海</value>
<value>北京</value>
<value>杭州</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--Set集合注入-->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>上海SH</value>
<value>北京BJ</value>
<value>杭州HZ</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--Map注入-->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry>
<key><value>周杰伦</value></key>
<value>我是如此相信</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>林俊杰</value></key>
<value>可惜没如果</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>陈奕迅</value></key>
<value>十年</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--Properties注入-->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="上海">东方明珠</prop>
<prop key="北京">天安门</prop>
<prop key="杭州">西湖</prop>
</props>
</property>
</beans>
6.1.1.4. 测试代码
UserService.java
public class UserService
// 业务对象UserDao set注入(提供set方法)
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao)
this.userDao = userDao;
// 常用对象String set注入(提供set方法)
private String host;
public void setHost(String host)
this.host = host;
// 基本类型Integer set注入(提供set方法)
private Integer port;
public void setPort(Integer port)
this.port = port;
// List集合 set注入(提供set方法)
public List<String> list;
public void setList(List<String> list)
this.list = list;
// List集合输出
public void printList()
list.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// Set集合 set注入(提供set方法)
private Set<String> set;
public void setSet(Set<String> set)
this.set = set;
// Set集合输出
public void printSet()
set.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// Map set注入(提供set方法)
private Map<String,Object> map;
public void setMap(Map<String, Object> map)
this.map = map;
// Map输出
public void printMap()
map.forEach((k,v) -> System.out.println(k + "," + v));
// Properties set注入(提供set方法)
private Properties properties;
public void setProperties(Properties properties)
this.properties = properties;
// Properties输出
public void printProperties()
properties.forEach((k,v) -> System.out.println(k + ","+ v ));
public void test()
System.out.println("UserService Test...");
userDao.test();
studentDao.test();
System.out.println("Host:" + host + ",port:" + port);
// List集合
printList();
// Set集合
printSet();
// Map
printMap();
// Properties
printProperties();
spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过property标签手动装配(注入):
Set方法注入
name:bean对象中属性字段的名称
ref:指定bean标签的id属性值
value:具体的值(基本类型 常用对象|日期 集合)
-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService">
<!--业务对象 注入-->
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"/>
<!--常用对象String 注入-->
<property name="host" value="192.168.1.109"/>
<!--基本类型注入-->
<property name="port" value="8080"/>
<!--List集合 注入-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>上海</value>
<value>北京</value>
<value>杭州</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--Set集合注入-->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>上海SH</value>
<value>北京BJ</value>
<value>杭州HZ</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--Map注入-->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry>
<key><value>周杰伦</value></key>
<value>我是如此相信</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>林俊杰</value></key>
<value>可惜没如果</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>陈奕迅</value></key>
<value>十年</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--Properties注入-->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="上海">东方明珠</prop>
<prop key="北京">天安门</prop>
<prop key="杭州">西湖</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
6.1.2 构造器注入
注:
提供带参构造器
6.1.2.1. 单个Bean对象作为参数
java代码
public class UserService
private UserDao userDao; // JavaBean 对象
public UserService(UserDao userDao)
this.userDao = userDao;
public void test()
System.out.println("UserService Test...");
userDao.test();
XML配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过构造器注入:
通过constructor-arg标签进行注入
name:属性名称
ref:指定bean标签的id属性值
-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao" ></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService">
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>6.1.2.1.多个Bean对象作为参数
Java 代码
public class UserService
private UserDao userDao; // JavaBean 对象
private AccountDao accountDao // JavaBean 对象
XML配置
6.1.2.3. Bean对象和常用对象作为参数
Java 代码
public UserService(UserDao userDao, AccountDao accountDao)
this.userDao = userDao;
this.accountDao = accountDao;
public void test()
System.out.println("UserService Test...");
userDao.test();
accountDao.test();
XML配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过构造器注入:
通过constructor-arg标签进行注入
name:属性名称
ref:指定bean标签的id属性值
-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao" ></bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.AccountDao" ></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService">
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>6.1.2.3. Bean对象和常用对象作为参数
Java代码
public class UserService
private UserDao userDao; // JavaBean 对象
private AccountDao accountDao; // JavaBean 对象
private String uname; // 字符串类型
public UserService(UserDao userDao, AccountDao accountDao, String uname)
this.userDao = userDao;
this.accountDao = accountDao;
this.uname = uname;
public void test()
XML配置
6.1.2.4. 循环依赖问题
循环问题产生的原因:
Bean通过构造器注入,之间彼此相互依赖对方导致bean无法实例化。
问题展示:
1. Java 代码
System.out.println("UserService Test...");
userDao.test();
accountDao.test();
System.out.println("uname:" + uname);
XML配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns以上是关于Spring IOC的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章