[Typescript] ts-toolbelt F.Narrow preserve the exactly data for function arguement
Posted Answer1215
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[Typescript] ts-toolbelt F.Narrow preserve the exactly data for function arguement相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Example code:
interface Fruit
name: string;
price: number;
export const wrapFruit = <TFruits extends Fruit[]>(fruits: TFruits) =>
const getFruit = (name: unknown): unknown =>
return fruits.find((fruit) => fruit.name === name);
;
return
getFruit,
;
;
const fruits = wrapFruit([
name: \'apple\',
price: 1,
,
name: \'banana\',
price: 2,
,
]);
The wrapFruit function has following types:
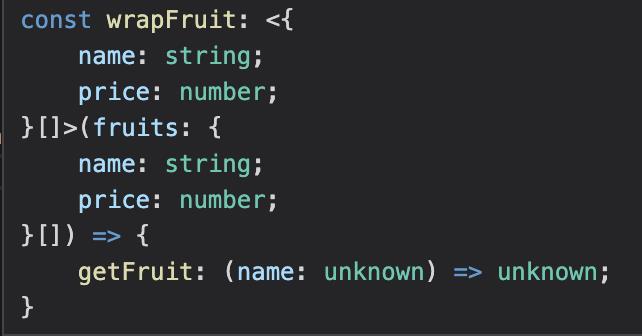
We saw that <name: string, price: nunmber> which is not what we want.
We want:
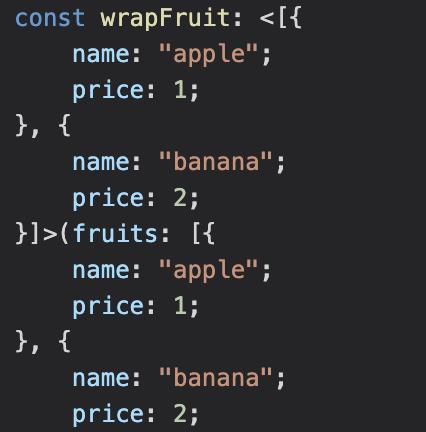
To do that we need to use the F.Narrowtype helper from \'ts-toolbelt\'
export const wrapFruit = <TFruits extends Fruit[]>(fruits: F.Narrow<TFruits>) =>
const getFruit = (name: unknown): unknown =>
return fruits.find((fruit) => fruit.name === name);
;
return
getFruit,
;
;
Narrow:
export declare type Try<A1 extends any, A2 extends any, Catch = never> = A1 extends A2 ? A1 : Catch;
export declare type Narrowable = string | number | bigint | boolean;
export declare type NarrowRaw<A> = (A extends [] ? [] : never) | (A extends Narrowable ? A : never) | (
[K in keyof A]: A[K] extends Function ? A[K] : NarrowRaw<A[K]>;
);
declare type Narrow<A extends any> = Try<A, [], NarrowRaw<A>>;
function fn<T>(inputs: T)
fn([name: \'apple\', price: 1])
With Typescript V5.0, there will be a <const T> https://devblogs.microsoft.com/typescript/announcing-typescript-5-0-beta/#const-type-parameters
Which doing pretty much the same thing as F.Narrow.
Another appraoch
interface Fruit
name: string;
price: number;
export const wrapFruit = <const T extends Fruit>(fruits: T[]) =>
const getFruit = <TName extends T[\'name\']>(name: TName) =>
return fruits.find((fruit) => fruit.name === name) as Extract<T, name: TName>;
;
return
getFruit,
;
;
const fruits = wrapFruit([
name: "apple",
price: 1,
,
name: "banana",
price: 2,
,
]);
const banana = fruits.getFruit("banana");
const apple = fruits.getFruit("apple");
// @ts-expect-error
const notAllowed = fruits.getFruit("not-allowed");
type tests = [
Expect<Equal<typeof apple, readonly name: "apple"; readonly price: 1 >>,
Expect<Equal<typeof banana, readonly name: "banana"; readonly price: 2 >>
];
TypeScript入门学习之路
TypeScript学习之路
TypeScript学习之路
安装typescript环境
npm install -g typescript
查看版本
tsc -v
typescript起步
1、新建hello.ts
const hello : string = "Hello World!"
console.log(hello)
2、通过 tsc 命令编译
tsc hello.ts
3、此时路径下会生成一个hello.js文件
var hello = "Hello World!";
console.log(hello);
4、node hello.js打开或者引入xxx.html浏览器打开查看

typescript开发工具vscode自动编译.ts文件
1、创建 tsconfig.json 文件 cmd后执行命令 tsc --init 生成配置文件

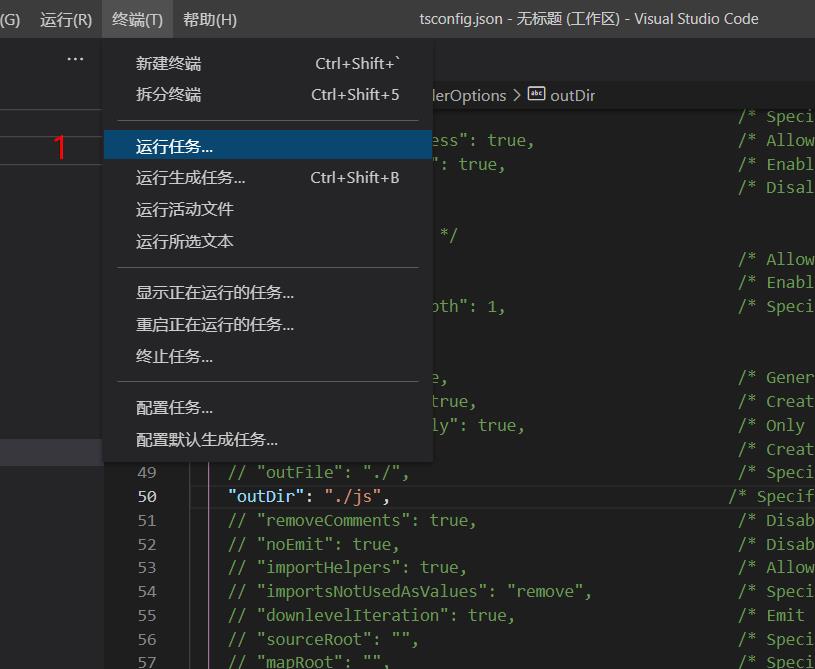

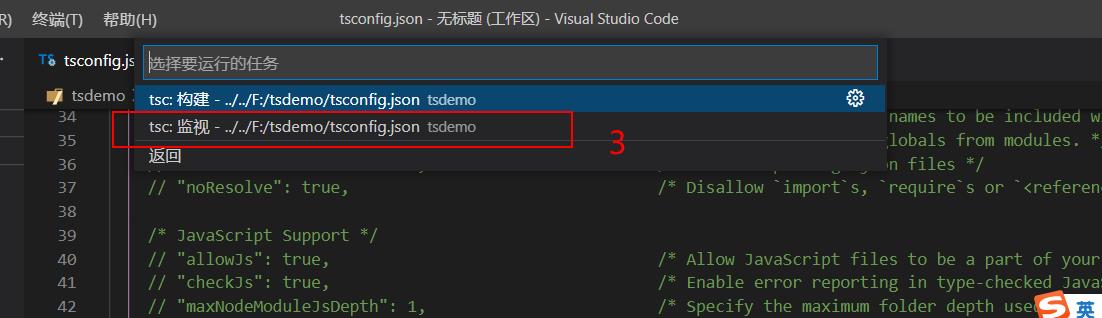
然后就可以自动编译.ts文件
typescript中的数据类型
// typescript中为了使编写代码更加规范 有利于维护 增加了类型校验
/*
布尔类型 boolean
数字类型 number
字符串类型 string
数组类型 array
元祖类型 tuple
枚举类型 enum
任意类型 any
null 和undefined
void类型
never类型
*/
// 布尔类型 boolean
var flag: boolean = true
flag = false
// 数字类型 number
var num: number = 123
console.log(num);
// 字符串类型 string
let str: string = 'fqniu'
console.log(str);
// 数组类型 array
// 第一种定义
let arr1: number[] = [1, 2, 3, 4]
console.log(arr1);
let arr2: string[] = ['1', '2', '3', '4']
console.log(arr2);
// 第二种定义
let arr3: Array<number> = [1, 2, 3, 4]
let arr4: Array<string> = ['1', '2', '3', '4']
// 第三种定义
let arr5: any[] = [1, 2, '3', 4, true]
// 元祖类型 tuple (定义数组的一种方式)
let arr7: [string, number, boolean] = ['fqniu', 25, true]
// 枚举类型 enum
enum Flag success = 1, error = -1
let fs: Flag = Flag.success
let fe: Flag = Flag.error
console.log(fs, fe); // 1 -1
enum Color red, blue, yellow // 如果这里默认不赋值的话打印的是索引值 0 1 2
let c: Color = Color.yellow
console.log(c); // 2
enum Color1 red, blue = 5, yellow // 如果这里默认不赋值的话打印的是索引值 0 1 2
let cr: Color1 = Color1.red
let cb: Color1 = Color1.blue
let cy: Color1 = Color1.yellow
console.log(cr); // 0
console.log(cb); // 5
console.log(cy); // 6 取上一个值, blue的值 +1
// 任意类型 any
let numAny: any = 25
numAny = 'fqniu'
numAny = true
console.log(numAny);
// any的用处:获取dom元素节点 操作dom的样式等
// var oBox: any = document.getElementById('box')
// oBox.style.color = 'red'
// null 和undefined
let undef: undefined
console.log(undef);
var nul: null
nul = null
console.log(nul);
// 一个元素可能是 number类型 可能是null 可能是undefined
var ele: number | null | undefined
console.log(ele);
// void类型 typescript 中的void表示没有任何类型 一般用于定义方法的时候 方法没有返回值
function fun(): void
console.log('fun');
fun()
// 有返回值时
function fun1(): number
console.log('fun');
return 123
fun1()
// never类型:其他类型(包括null 和undefined)的子类型,代表从不会出现的值,这意味着声明never的变量只能被never类型所赋值
let error:never
// error = 25 // 报错
// 正确
error = (() =>
throw new Error('错误')
)()
typescript中的函数
// 函数的定义
// js中函数声明定义
function fun1()
// js中匿名函数定义 函数表达式
var fun2 = function ()
// ts中函数声明定义
function fun3(): string
return 'fqniu'
console.log(fun3()); // fqniu
// ts中匿名函数定义 函数表达式
var fun4 = function (): number
return 25
console.log(fun4()); // 25
// 1、函数的传参
function fun5(name: string, age: number): string
return `$name -- $age`
console.log(fun5('fqniu', 25)); // fqniu -- 25
var fun6 = function (name: string, age: number): string
return `$name -- $age`
console.log(fun6('nfq', 22)); // nfq -- 22
// 没有返回值的方法
function fun7(): void
console.log('fun7');
fun7()
// 2、函数的可选参数
// es5里面的方法的实参和形参可以不一样
// 但是ts必须一致,不一样的话可以配置可选参数,注意参数必须配置到参数的最后一个 加?
function fun8(name: string, age?: number): string
if (age)
return `$name -- $age`
else
return `$name -- 保密`
console.log(fun8('fqniu')); // fqniu -- 保密
console.log(fun8('fqniu', 25)); // fqniu -- 25
// 3、默认参数
// es5里面没办法设置默认参数,es6和ts可以设置默认参数
function fun9(name: string, age = 20): string
if (age)
return `$name -- $age`
else
return `$name -- 保密`
console.log(fun9('fqniu')); // fqniu -- 20
console.log(fun9('fqniu', 25)); // fqniu -- 25
// 4、剩余参数
function sum1(a: number, b: number, c: number, d: number): number
return a + b + c + d
console.log(sum1(1, 2, 3, 4)); // 10
function sum2(...result: number[]): number
var sum = 0
for (var i = 0; i < result.length; i++)
sum += result[i]
return sum
console.log(sum2(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)); // 21
// 5、函数的重载
// Java中方法的重载,是指的两个或者多个同名函数,但是他们的参数不一样,这时会出现函数重载的情况
// ts中的重载:通过为同一个函数提供多个函数类型定义来实现多种功能的目的
function getInfo(name: string): string;
function getInfo(age: number): string;
function getInfo(str: any): any
if (typeof str === 'string')
return '我叫 ' + str
else
return '我的年龄是' + str
console.log(getInfo('fqniu'));
console.log(getInfo(22));
// 6、箭头函数
// this指向上下文
setTimeout(() =>
console.log('fqniu ws');
, 2000);
typescript中类的定义
// ts中类的定义
class Person
name: string; //属性 前面省略public关键词
constructor(name: string) // 构造函数 实例化类的时候触发的方法
this.name = name;
fun(): void
console.log('fun', this.name);
getName(): string
return this.name
setName(name: string): void
this.name = name
var p = new Person('fqniu')
console.log(p.name); // fqniu
console.log(p.getName()); //fqniu
p.setName('niuniu')
console.log(p.getName()); // niuniu
继承
javascript中的继承
function Person()
this.name = 'fqniu' /*属性*/
this.age = 25
this.fun = function ()
console.log(this.name + this.age);
var p = new Person()
console.log(p.name);
p.fun()
// 原型链上的属性会被多个实例共享,但是构造函数不会
Person.prototype.sex = '男'
Person.prototype.work = function ()
console.log(this.name + '敲代码');
p.work()
// 添加静态方法
Person.getInfo = function ()
console.log('我是静态方法');
Person.getInfo()
// es中的继承 继承Person类
// 1、对象冒充实现继承
function Web1()
Person.call(this) //对象冒充实现继承
var web1 = new Web1()
web1.fun() // 对象冒充实现继承构造函数中的属性和方法
// web.work() // 报错 index.html:48 Uncaught TypeError: web.work is not a function 但是没办法继承原型链上的属性和方法
// 2、原型链实现继承
function Web2()
Web2.prototype = new Person() // 原型链实现继承
var web2 = new Web2()
console.log(web2.name); // fqniu
web2.fun() // fqniu25
web2.work() // fqniu敲代码
// 原型链实现继承好处:既可以继承构造函数中的属性和方法,也可以继承原型链上的方法
// 原型链实现继承的问题? 当实例化子类的时候,没办法给父类传参
function Person1(name, age)
this.name = name /*属性*/
this.age = age
this.fun = function ()
console.log(this.name + this.age);
function Web3(name, age)
Web3.prototype = new Person1() // 原型链实现继承
var web3 = new Web3('nfq', 25)
console.log(web3.name); // undefined 因为实例化子类的时候,没办法给父类传参
// 组合继承模式
function Person2(name, age)
this.name = name /*属性*/
this.age = age
this.fun = function ()
console.log(this.name + this.age);
Person2.prototype.sex = '男'
Person2.prototype.work = function ()
console.log(this.name + '敲代码');
function Web4(name, age)
Person2.call(this, name, age) // 对象冒充继承,实例化子类可以给父类传参
Web4.prototype = new Person2() // 原型链实现继承
// 或者
// Web4.prototype = Person2.prototype
var web4 = new Web4('nfq', 25)
console.log(web4.name); // nfq
web4.fun() // nfq25
web4.work() // nfq敲代码
typescript中的继承
// ts中实现继承 extends、 super
class Person
name: string; //属性 前面省略public关键词
constructor(name: string) // 构造函数 实例化类的时候触发的方法
this.name = name;
fun(): void
console.log('fun', this.name);
getName(): string
return this.name
setName(name: string): void
this.name = name
class Web extends Person
constructor(name: string)
super(name) // 初始化父类的构造函数
work(): void
console.log(`$this.name在敲代码`);
// fun(): void
// console.log('fun - 子类', this.name);
//
var w = new Web('fqniu')
w.fun() // fun fqniu
w.work() // fqniu在敲代码
// 类里面的修饰符 typescript里面定义属性的时候提供了三种修饰符
/*
public:公有 —— 在当前类里面、子类、类外面都可以访问
protected:保护类型 —— 在当前类里面,子类都可以访问,在类外部无法访问
provite:私有 —— 只有当前类里面访问,子类、类外部都无法访问
属以上是关于[Typescript] ts-toolbelt F.Narrow preserve the exactly data for function arguement的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章