2. OpenCV-Python——阈值平滑处理形态学操作
Posted 红叶楠木
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2. OpenCV-Python——阈值平滑处理形态学操作相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、阈值
ret, dst = cv2.threshold(src, thresh, maxval, type)
-
src: 输入图,只能输入单通道图像,通常来说为灰度图
-
dst: 输出图
- ret: 返回阈值的数值
-
thresh: 阈值
-
maxval: 当像素值超过了阈值(或者小于阈值,根据type来决定),所赋予的值
-
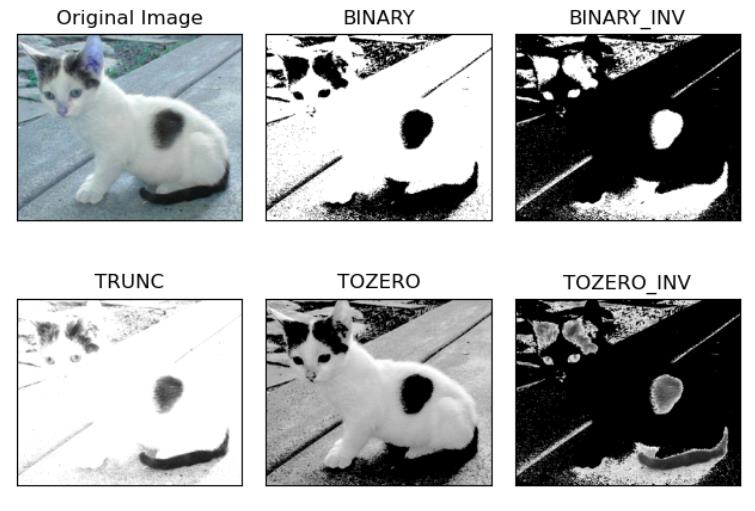
type:二值化操作的类型,包含以下5种类型: cv2.THRESH_BINARY;cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV; cv2.THRESH_TRUNC; cv2.THRESH_TOZERO;cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV
-
cv2.THRESH_BINARY 超过阈值部分取maxval(最大值),否则取0
-
cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV THRESH_BINARY的反转
-
cv2.THRESH_TRUNC 大于阈值部分设为阈值,否则不变
-
cv2.THRESH_TOZERO 大于阈值部分不改变,否则设为0
-
cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV THRESH_TOZERO的反转
1 # *******************阈值**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 5 img = cv2.imread(\'cat.jpg\') # 读取图像 6 img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 灰度化 7 8 ret, thresh1 = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) 9 ret, thresh2 = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV) 10 ret, thresh3 = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_TRUNC) 11 ret, thresh4 = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_TOZERO) 12 ret, thresh5 = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV) 13 14 titles = [\'Original Image\', \'BINARY\', \'BINARY_INV\', \'TRUNC\', \'TOZERO\', \'TOZERO_INV\'] 15 images = [img, thresh1, thresh2, thresh3, thresh4, thresh5] 16 17 for i in range(6): 18 plt.subplot(2, 3, i + 1), plt.imshow(images[i], \'gray\') 19 plt.title(titles[i]) 20 plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) 21 plt.show() 22 # *******************阈值**********************结束
二、平滑处理
1 # *******************平滑处理**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import numpy as np 4 # import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 img = cv2.imread(\'lenaNoise.png\') 7 8 # cv2.imshow(\'img\', img) 9 # cv2.waitKey(0) 10 # cv2.destroyAllWindows() 11 12 # 均值滤波 13 # 简单的平均卷积操作 14 blur = cv2.blur(img, (3, 3)) # 3*3的卷积核 15 16 # cv2.imshow(\'blur\', blur) 17 # cv2.waitKey(0) 18 # cv2.destroyAllWindows() 19 20 # 方框滤波 21 # 基本和均值一样,可以选择归一化,不做归一化容易越界溢出 22 box = cv2.boxFilter(img,-1,(3,3), normalize=True) # -1表示在颜色通道上保持一致 23 24 # cv2.imshow(\'box\', box) 25 # cv2.waitKey(0) 26 # cv2.destroyAllWindows() 27 28 # 高斯滤波 29 # 高斯模糊的卷积核里的数值是满足高斯分布,相当于更重视中间的 30 aussian = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (5, 5), 1) 31 32 # cv2.imshow(\'aussian\', aussian) 33 # cv2.waitKey(0) 34 # cv2.destroyAllWindows() 35 36 # 中值滤波 37 # 相当于用中值代替 38 median = cv2.medianBlur(img, 5) # 中值滤波 39 40 # cv2.imshow(\'median\', median) 41 # cv2.waitKey(0) 42 # cv2.destroyAllWindows() 43 44 # 展示所有的滤波结果 45 res = np.hstack((blur,aussian,median)) # vstack为垂直方向 46 #print (res) 47 cv2.imshow(\'median vs average\', res) 48 cv2.waitKey(0) 49 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 50 # *******************平滑处理**********************结束
三、形态学操作
1、腐蚀操作
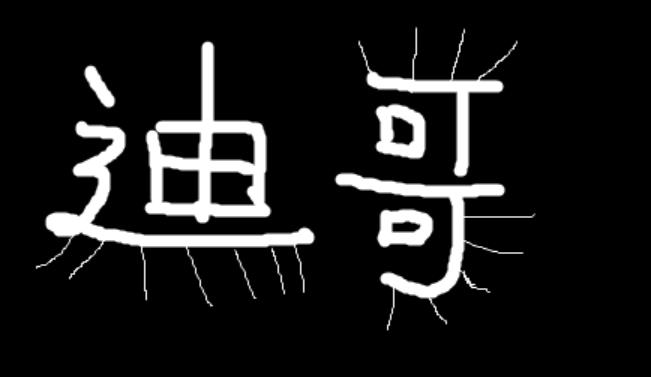
1 # *******************形态学-腐蚀**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 img = cv2.imread(\'dige.png\') 6 7 cv2.imshow(\'img\', img) 8 cv2.waitKey(0) 9 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 10 11 kernel = np.ones((3,3),np.uint8) 12 erosion = cv2.erode(img,kernel,iterations = 1) # irerations迭代次数 13 14 cv2.imshow(\'erosion\', erosion) 15 cv2.waitKey(0) 16 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 17 # *******************形态学-腐蚀**********************结束
2、膨胀操作
1 # *******************形态学-膨胀**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 img = cv2.imread(\'dige.png\') 6 cv2.imshow(\'img\', img) 7 cv2.waitKey(0) 8 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 9 10 # 先腐蚀 11 kernel = np.ones((3,3),np.uint8) 12 erosion = cv2.erode(img,kernel,iterations = 1) 13 # 后膨胀 14 kernel = np.ones((3,3),np.uint8) 15 dige_dilate = cv2.dilate(erosion,kernel,iterations = 1) 16 17 cv2.imshow(\'dilate\', dige_dilate) 18 cv2.waitKey(0) 19 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 20 # *******************形态学-膨胀**********************结束
3、开运算与闭运算
1 # *******************形态学-开运算与闭运算**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 # 开:先腐蚀,再膨胀 6 img = cv2.imread(\'dige.png\') 7 8 kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.uint8) 9 opening = cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel) 10 11 cv2.imshow(\'opening\', opening) 12 cv2.waitKey(0) 13 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 14 15 # 闭:先膨胀,再腐蚀 16 img = cv2.imread(\'dige.png\') 17 18 kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.uint8) 19 closing = cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel) 20 21 cv2.imshow(\'closing\', closing) 22 cv2.waitKey(0) 23 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 24 # *******************形态学-开运算与闭运算**********************结束
4、梯度运算
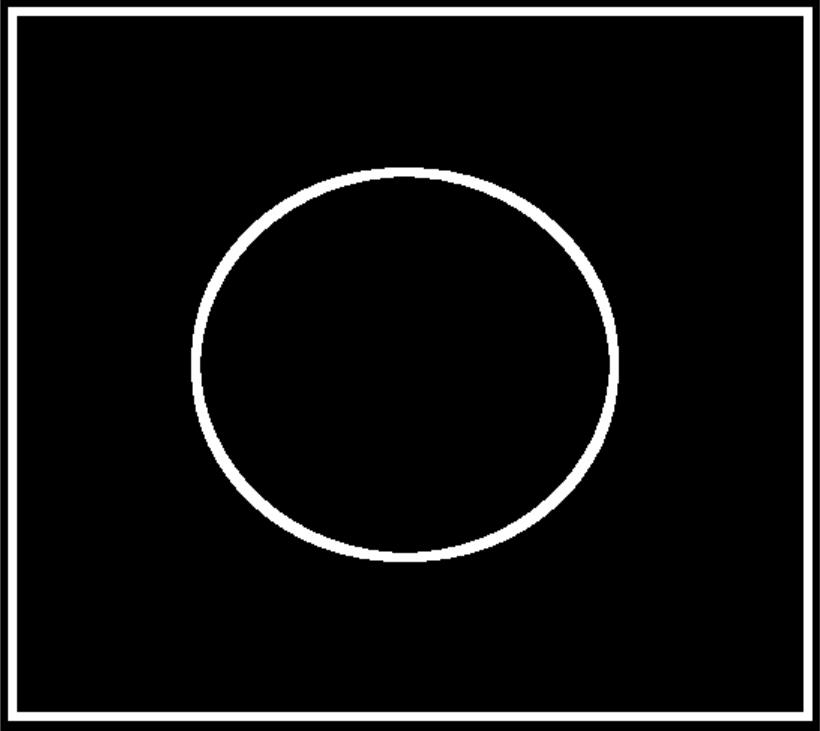
1 # *******************形态学-梯度运算**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 # 梯度=膨胀-腐蚀 6 pie = cv2.imread(\'pie.png\') 7 kernel = np.ones((7,7),np.uint8) 8 #--------------------------------------------------------- 9 dilate = cv2.dilate(pie,kernel,iterations = 5) 10 erosion = cv2.erode(pie,kernel,iterations = 5) 11 12 res = np.hstack((dilate,erosion)) # 显示分别膨胀和腐蚀的结果 13 cv2.imshow(\'res\', res) 14 cv2.waitKey(0) 15 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 16 17 #--------------------------------------------------------- 18 gradient = cv2.morphologyEx(pie, cv2.MORPH_GRADIENT, kernel) # 梯度运算 19 cv2.imshow(\'gradient\', gradient) 20 cv2.waitKey(0) 21 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 22 # *******************形态学-梯度运算**********************结束
5、礼帽与黑帽
- 礼帽 = 原始输入-开运算结果
- 黑帽 = 闭运算-原始输入
1 # *******************形态学-礼帽与黑帽**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 #------------------------------------------------------- 6 #礼帽 7 img = cv2.imread(\'dige.png\') 8 cv2.imshow(\'image\',img) 9 kernel = np.ones((7,7),np.uint8) 10 tophat = cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_TOPHAT, kernel) 11 cv2.imshow(\'tophat\', tophat) 12 cv2.waitKey(0) 13 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 14 15 #------------------------------------------------------- 16 #黑帽 17 img = cv2.imread(\'dige.png\') 18 kernel = np.ones((7,7),np.uint8) 19 blackhat = cv2.morphologyEx(img,cv2.MORPH_BLACKHAT, kernel) 20 cv2.imshow(\'blackhat \', blackhat ) 21 cv2.waitKey(0) 22 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 23 # *******************形态学-礼帽与黑帽**********************结束


以上是关于2. OpenCV-Python——阈值平滑处理形态学操作的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章