05-Python基础4
Posted zwnsyw
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了05-Python基础4相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本节大纲:
- 模块介绍
- time &datetime模块
- random
- os
- sys
- shutil
- json & picle
- shelve
- xml处理
- yaml处理
- configparser
- hashlib
- subprocess
- logging模块
- re正则表达式
模块,用一砣代码实现了某个功能的代码集合。
类似于函数式编程和面向过程编程,函数式编程则完成一个功能,其他代码用来调用即可,提供了代码的重用性和代码间的耦合。而对于一个复杂的功能来,可能需要多个函数才能完成(函数又可以在不同的.py文件中),n个 .py 文件组成的代码集合就称为模块。
如:os 是系统相关的模块;file是文件操作相关的模块
模块分为三种:
- 自定义模块
- 内置标准模块(又称标准库)
- 开源模块
自定义模块 和开源模块的使用参考 http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/4963027.html
time & datetime模块

1 #_*_coding:utf-8_*_
2 __author__ = \'Alex Li\'
3
4 import time
5
6
7 # print(time.clock()) #返回处理器时间,3.3开始已废弃 , 改成了time.process_time()测量处理器运算时间,不包括sleep时间,不稳定,mac上测不出来
8 # print(time.altzone) #返回与utc时间的时间差,以秒计算\\
9 # print(time.asctime()) #返回时间格式"Fri Aug 19 11:14:16 2016",
10 # print(time.localtime()) #返回本地时间 的struct time对象格式
11 # print(time.gmtime(time.time()-800000)) #返回utc时间的struc时间对象格式
12
13 # print(time.asctime(time.localtime())) #返回时间格式"Fri Aug 19 11:14:16 2016",
14 #print(time.ctime()) #返回Fri Aug 19 12:38:29 2016 格式, 同上
15
16
17
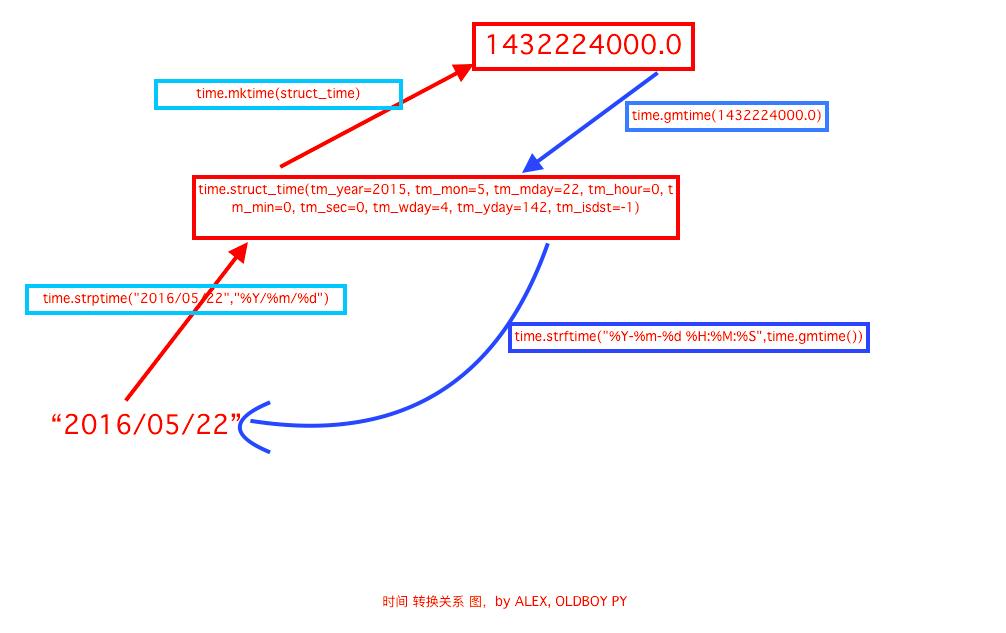
18 # 日期字符串 转成 时间戳
19 # string_2_struct = time.strptime("2016/05/22","%Y/%m/%d") #将 日期字符串 转成 struct时间对象格式
20 # print(string_2_struct)
21 # #
22 # struct_2_stamp = time.mktime(string_2_struct) #将struct时间对象转成时间戳
23 # print(struct_2_stamp)
24
25
26
27 #将时间戳转为字符串格式
28 # print(time.gmtime(time.time()-86640)) #将utc时间戳转换成struct_time格式
29 # print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.gmtime()) ) #将utc struct_time格式转成指定的字符串格式
30
31
32
33
34
35 #时间加减
36 import datetime
37
38 # print(datetime.datetime.now()) #返回 2016-08-19 12:47:03.941925
39 #print(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time()) ) # 时间戳直接转成日期格式 2016-08-19
40 # print(datetime.datetime.now() )
41 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(3)) #当前时间+3天
42 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(-3)) #当前时间-3天
43 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=3)) #当前时间+3小时
44 # print(datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(minutes=30)) #当前时间+30分
45
46
47 #
48 # c_time = datetime.datetime.now()
49 # print(c_time.replace(minute=3,hour=2)) #时间替换
| Directive | Meaning | Notes |
|---|---|---|
%a |
Locale’s abbreviated weekday name. | |
%A |
Locale’s full weekday name. | |
%b |
Locale’s abbreviated month name. | |
%B |
Locale’s full month name. | |
%c |
Locale’s appropriate date and time representation. | |
%d |
Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31]. | |
%H |
Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23]. | |
%I |
Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12]. | |
%j |
Day of the year as a decimal number [001,366]. | |
%m |
Month as a decimal number [01,12]. | |
%M |
Minute as a decimal number [00,59]. | |
%p |
Locale’s equivalent of either AM or PM. | (1) |
%S |
Second as a decimal number [00,61]. | (2) |
%U |
Week number of the year (Sunday as the first day of the week) as a decimal number [00,53]. All days in a new year preceding the first Sunday are considered to be in week 0. | (3) |
%w |
Weekday as a decimal number [0(Sunday),6]. | |
%W |
Week number of the year (Monday as the first day of the week) as a decimal number [00,53]. All days in a new year preceding the first Monday are considered to be in week 0. | (3) |
%x |
Locale’s appropriate date representation. | |
%X |
Locale’s appropriate time representation. | |
%y |
Year without century as a decimal number [00,99]. | |
%Y |
Year with century as a decimal number. | |
%z |
Time zone offset indicating a positive or negative time difference from UTC/GMT of the form +HHMM or -HHMM, where H represents decimal hour digits and M represents decimal minute digits [-23:59, +23:59]. | |
%Z |
Time zone name (no characters if no time zone exists). | |
%% |
A literal \'%\' character. |
random模块
随机数
|
1
2
3
4
|
mport randomprint random.random()print random.randint(1,2)print random.randrange(1,10) |
生成随机验证码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import randomcheckcode = \'\'for i in range(4): current = random.randrange(0,4) if current != i: temp = chr(random.randint(65,90)) else: temp = random.randint(0,9) checkcode += str(temp)print checkcode |
OS模块
提供对操作系统进行调用的接口
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cdos.curdir 返回当前目录: (\'.\')os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:(\'..\')os.makedirs(\'dirname1/dirname2\') 可生成多层递归目录os.removedirs(\'dirname1\') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推os.mkdir(\'dirname\') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirnameos.rmdir(\'dirname\') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirnameos.listdir(\'dirname\') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印os.remove() 删除一个文件os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录os.stat(\'path/filename\') 获取文件/目录信息os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\\\",Linux下为"/"os.linesep 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\\t\\n",Linux下为"\\n"os.pathsep 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串os.name 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->\'nt\'; Linux->\'posix\'os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示os.environ 获取系统环境变量os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回Falseos.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回Trueos.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回Falseos.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回Falseos.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间 |
更多猛击这里
sys模块
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0)sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息sys.maxint 最大的Int值sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称sys.stdout.write(\'please:\')val = sys.stdin.readline()[:-1] |
shutil 模块
直接参考 http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/4963027.html
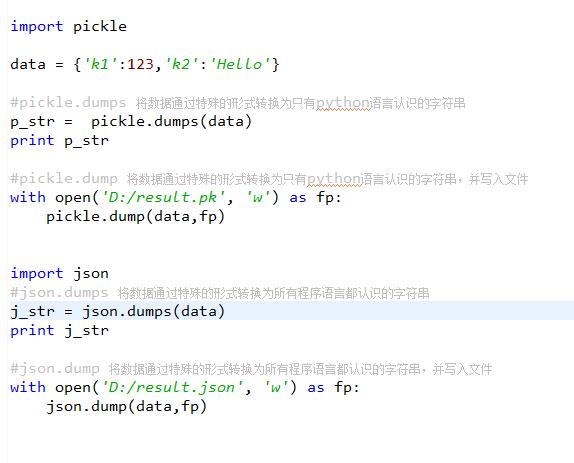
json & pickle 模块
用于序列化的两个模块
- json,用于字符串 和 python数据类型间进行转换
- pickle,用于python特有的类型 和 python的数据类型间进行转换
Json模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
pickle模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
shelve 模块
shelve模块是一个简单的k,v将内存数据通过文件持久化的模块,可以持久化任何pickle可支持的python数据格式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
import shelved = shelve.open(\'shelve_test\') #打开一个文件class Test(object): def __init__(self,n): self.n = nt = Test(123) t2 = Test(123334)name = ["alex","rain","test"]d["test"] = name #持久化列表d["t1"] = t #持久化类d["t2"] = t2d.close() |
xml处理模块
xml是实现不同语言或程序之间进行数据交换的协议,跟json差不多,但json使用起来更简单,不过,古时候,在json还没诞生的黑暗年代,大家只能选择用xml呀,至今很多传统公司如金融行业的很多系统的接口还主要是xml。
xml的格式如下,就是通过<>节点来区别数据结构的:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
<?xml version="1.0"?><data> <country name="Liechtenstein"> <rank updated="yes">2</rank> <year>2008</year> <gdppc>141100</gdppc> <neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/> <neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/> </country> <country name="Singapore"> <rank updated="yes">5</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>59900</gdppc> <neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/> </country> <country name="Panama"> <rank updated="yes">69</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>13600</gdppc> <neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/> <neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/> </country></data> |
xml协议在各个语言里的都 是支持的,在python中可以用以下模块操作xml
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ETtree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml")root = tree.getroot()print(root.tag)#遍历xml文档for child in root: print(child.tag, child.attrib) for i in child: print(i.tag,i.text)#只遍历year 节点for node in root.iter(\'year\'): print(node.tag,node.text) |
修改和删除xml文档内容
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ETtree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml")root = tree.getroot()#修改for node in root.iter(\'year\'): new_year = int(node.text) + 1 node.text = str(new_year) node.set("updated","yes")tree.write("xmltest.xml")#删除nodefor country in root.findall(\'country\'): rank = int(country.find(\'rank\').text) if rank > 50: root.remove(country)tree.write(\'output.xml\') |
自己创建xml文档
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ETnew_xml = ET.Element("namelist")name = ET.SubElement(new_xml,"name",attrib={"enrolled":"yes"})age = ET.SubElement(name,"age",attrib={"checked":"no"})sex = ET.SubElement(name,"sex")sex.text = \'33\'name2 = ET.SubElement(new_xml,"name",attrib={"enrolled":"no"})age = ET.SubElement(name2,"age")age.text = \'19\'et = ET.ElementTree(new_xml) #生成文档对象et.write("test.xml", encoding="utf-8",xml_declaration=True)ET.dump(new_xml) #打印生成的格式 |
PyYAML模块
Python也可以很容易的处理ymal文档格式,只不过需要安装一个模块,参考文档:http://pyyaml.org/wiki/PyYAMLDocumentation
ConfigParser模块
用于生成和修改常见配置文档,当前模块的名称在 python 3.x 版本中变更为 configparser。
来看一个好多软件的常见文档格式如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
[DEFAULT]ServerAliveInterval = 45Compression = yesCompressionLevel = 9ForwardX11 = yes[bitbucket.org]User = hg[topsecret.server.com]Port = 50022ForwardX11 = no |
如果想用python生成一个这样的文档怎么做呢?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import configparserconfig = configparser.ConfigParser()config["DEFAULT"] = {\'ServerAliveInterval\': \'45\', \'Compression\': \'yes\', \'CompressionLevel\': \'9\'}config[\'bitbucket.org\'] = {}config[\'bitbucket.org\'][\'User\'] = \'hg\'config[\'topsecret.server.com\'] = {}topsecret = config[\'topsecret.server.com\']topsecret[\'Host Port\'] = \'50022\' # mutates the parsertopsecret[\'ForwardX11\'] = \'no\' # same hereconfig[\'DEFAULT\'][\'ForwardX11\'] = \'yes\'with open(\'example.ini\', \'w\') as configfile: config.write(configfile) |
写完了还可以再读出来哈。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
>>> import configparser>>> config = configparser.ConfigParser()>>> config.sections()[]>>> config.read(\'example.ini\')[\'example.ini\']>>> config.sections()[\'bitbucket.org\', \'topsecret.server.com\']>>> \'bitbucket.org\' in configTrue>>> \'bytebong.com\' in configFalse>>> config[\'bitbucket.org\'][\'User\']\'hg\'>>> config[\'DEFAULT\'][\'Compression\']\'yes\'>>> topsecret = config[\'topsecret.server.com\']>>> topsecret[\'ForwardX11\']\'no\'>>> topsecret[< |
