Python 字符串
Posted evilsnake
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python 字符串相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一:创建字符串
创建字符串很简单,只为变量分配一个值即可
创建字符串的方式::
1):使用单引号包含的\'abc\'
2):使用双引号包含的"abd"
3):使用3个单引号\'\'\'abc\'\'\'
4):使用三个双引号 """abc"""
1 result = \'abc\'
2 print("单引号::", result, "type::", type(result))
3
4 result = "abc"
5 print("双引号:", result, "type::", type(result))
6
7 result = \'\'\'abc\'\'\'
8 print("3个单引号::", result, "type::", type(result))
9
10 result = """abc"""
11 print("3个双引号::", result, "type::", type(result))
输出结果::
单引号:: abc type:: <class \'str\'>
双引号: abc type:: <class \'str\'>
3个单引号:: abc type:: <class \'str\'>
3个双引号:: abc type:: <class \'str\'>
二:Python的转义字符
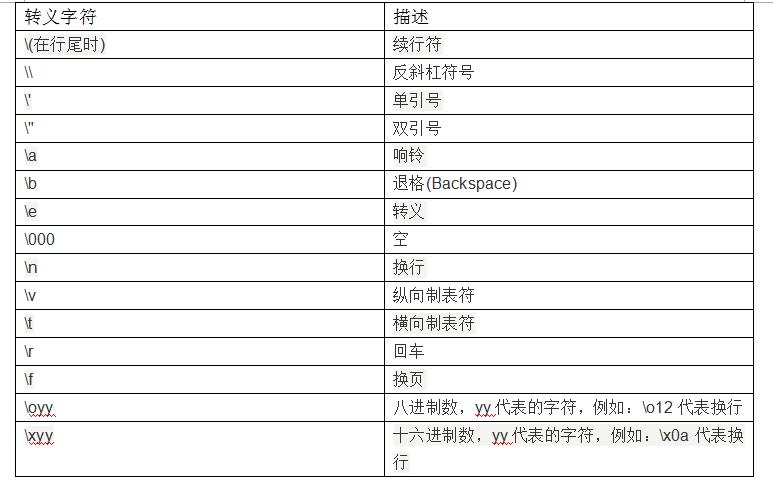
result = "abc\\\'def"
print("转义字符01::", result)
result = "abc\\tdef"
print("转义字符02::", result)
输出结果::
转义字符01:: abc\'def
转义字符02:: abc def
三:原始字符串
使用单引号包含的r\'abc\'
使用双引号包含的r"abd"
使用3个单引号r\'\'\'abc\'\'\'
使用三个双引号 r"""abc"""
# 例如我想输出:我是 \\n Lucy这样的原始字符串
result = "我是 \\n Lucy"
print(result)
# 这样输出的就不是我们想要的原始字符串,但是我们可以使用转义字符实现
result = "我是 \\\\n Lucy"
print(result)
# 除此之外,我们也可以这样来实现
result = r"我是 \\n Lucy"
print(result)
1 # 三个双引号可以跨行书写
2 result = """hello
3 world
4 happy
5 day
6 """
7 print(result)
输出结果为:
hello
world
happy
day
# 使用小括号可以实现连行符的作用
result = "hello \\
world"
print(result)
result = ("hello "
"world")
print(result)
输出结果为:
hello world
hello world
# 三引号还可以用于注释
"""
这是多行注释,用三个双引号
这是多行注释,用三个双引号
这是多行注释,用三个双引号
"""
四:字符串的一般操作
1)字符串的拼接
1 result = "hello" + "world"
2 print("字符串的拼接01:: ", result)
3
4 # 直接把两个字符串写在一起,但是不能加换行
5 result = "happy every" "day"
6 print("字符串拼接02:: ", result)
7
8 # 格式化字符串
9 result = "how are %s"%"you"
10 print("字符串拼接03:: ", result)
11
12 # 重复输出字符串
13 print("字符串拼接04:: ", "hello\\t"*4)
输出结果为:
字符串的拼接01:: helloworld
字符串拼接02:: happy everyday
字符串拼接03:: how are you
字符串拼接04:: hello hello hello hello
2)字符串的切片
# 获取字符串中的某个片段
# 获取某个字符
# 获取一个字符串片段
01:# 获取某个字符
# name[下标]
# 下标 字符串中每个字符的编号就像座位编号一样
# 注意:1)下标越界的问题
# 2)负数下标 如果为负数,则从尾部开始定位 最后一个字符为-1
1 name = "abcdefg"
2 print("字符串:: ", name)
3
4 print("字符串切片:: ", name[3])
5
6 print("字符串切片:: ", name[-1])
7 print("字符串切片:: ", name[-2])
输出结果为::
字符串:: abcdefg
字符串切片:: d
字符串切片:: g
字符串切片:: f
02::获取一个字符串片段
# name[起始:结束:步长]
# 获取范围:[起始,结束) 起始包含 结束不包含
# 注意::
# 1):默认值 起始默认值:0 结束默认值:len(name) 整个字符串的长度 步长默认值:1
# 2):获取顺序:步长 > 0 从左边到右边 步长 < 0 从右往左 注意:不能从头部跳到尾部,或者从尾部跳到头部
1 name = "hello world"
2 print("获取字符串片段01:: ", name[0:3])
3
4 #默认值
5 print("获取字符串片段02:: ", name[::])
6 print("字符串的长度:: ", len(name))
7 print(name[0:len(name):1])
8
9 # 步长
10 print("获取字符串片段03:: ", name[0:len(name):2])
11
12 print("获取字符串片段04:: ", name[len(name):0:-1])
13
14 print("获取字符串片段05:: ", name[-1:-4:-1])
输出结果为::
获取字符串片段01:: hel
获取字符串片段02:: hello world
字符串的长度:: 11
hello world
获取字符串片段03:: hlowrd
获取字符串片段04:: dlrow olle
获取字符串片段05:: dlr
03:字符串更新
1 # 你可以截取字符串的一部分并与其他字段拼接
2 name = "hello world"
3 print("已更新字符串:: ", name[:4]+"Lucu")
输出结果为::
已更新字符串:: hellLucu
五:字符串常用的一些函数
1):查找计算类的函数
# len Python内建函数
# 作用 方法返回对象(字符串、列表、元组等)长度或项目个数。
# 语法 len( s )
# 参数 s -- 对象。
# 返回值
# 整型
# 返回对象长度
1 name = "runnoob"
2 print("字符串的字符个数:: ", len(name))
3
4 # len计算的是字符串的字符个数,而不是所占的内存长度
5 name = "我是HL"
6 print("字符串的字符个数:: ", len(name))
7
8 # 转义字符也是仅仅作为一个字符来计算的
9 name = "我是HL\\n"
10 print("字符串的字符个数:: ", len(name))
输出结果为::
字符串的字符个数:: 7
字符串的字符个数:: 4
字符串的字符个数:: 5
# find() 方法检测字符串中是否包含子字符串 str ,如果指定 beg(开始) 和 end(结束) 范围,则检查是否包含在指定范围内,
# 如果指定范围内如果包含指定索引值,返回的是索引值在字符串中的起始位置。如果不包含索引值,返回-1。
# find()方法语法:
# str.find(str, beg=0, end=len(string))
# 参数
# str -- 指定检索的字符串
# beg -- 开始索引,默认为0。可以省略
# end -- 结束索引,默认为字符串的长度。可以省略
# 返回值
# 如果包含子字符串返回开始的索引值,否则返回-1。
1 str1 = "hello example wow"
2 str2 = "exam"
3 print("find()01::", str1.find(str2))
4 print("find()02::", str1.find(str2, 5))
5 print("find()03::", str1.find(str2, 9))
6
7 info = \'abca\'
8 print("find()04::", info.find(\'a\'))
9 print("find()05::", info.find(\'a\', 1))
输出结果为::
find()01:: 6
find()02:: 6
find()03:: -1
find()04:: 0
find()05:: 3
# rfind() 返回字符串最后一次出现的位置,如果没有匹配项则返回-1
# rfind()方法语法:
# str.rfind(str, beg=0 end=len(string))
# 参数
# str -- 查找的字符串
# beg -- 开始查找的位置,默认为0
# end -- 结束查找位置,默认为字符串的长度。
# 返回值
# 返回字符串最后一次出现的位置,如果没有匹配项则返回-1。
1 str1 = "this is really a string example,is there"
2 str2 = "is"
3
4 print("rfind()::", str1.rfind(str2))
5 print("rfind()::", str1.rfind(str2, 0, 10))
输出结果为::
rfind():: 32
rfind():: 5
# index() 方法检测字符串中是否包含子字符串 str ,如果指定 beg(开始) 和 end(结束) 范围,
# 则检查是否包含在指定范围内,该方法与 python find()方法一样,只不过如果str不在 string中会报一个异常
# index()方法语法:
# str.index(str, beg=0, end=len(string))
# 参数:
# str -- 指定检索的字符串
# beg -- 开始索引,默认为0。
# end -- 结束索引,默认为字符串的长度。
# 返回值:
# 如果包含子字符串返回开始的索引值,否则抛出异常。
1 str1 = "hello world"
2 str2 = "lo"
3
4 print("index()01:: ", str1.index(str2))
输出结果为:
index()01:: 3
str1 = "hello world"
str2 = "lo"
print("index()02:: ", str1.index(str2, 4))
此时就会报错输出::
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "StringFunction.py", line 80, in <module>
print("index()02:: ", str1.index(str2, 4))
ValueError: substring not found
# rindex() 返回子字符串 str 在字符串中最后出现的位置,
# 如果没有匹配的字符串会报异常,你可以指定可选参数[beg:end]设置查找的区间
# rindex()方法语法:
# str.rindex(str, beg=0 end=len(string))
# 参数:
# str -- 查找的字符串
# beg -- 开始查找的位置,默认为0
# end -- 结束查找位置,默认为字符串的长度。
# 返回值:
# 返回子字符串 str 在字符串中最后出现的位置,如果没有匹配的字符串会报异常
1 str1 = "this is a string"
2 str2 = "is"
3
4 print("rindex()01:: ", str1.rindex(str2))
输出结果为:
rindex()01:: 5
# count() 方法用于统计字符串里某个字符出现的次数。可选参数为在字符串搜索的开始与结束位置。
# count()方法语法:
# str.count(sub, start= 0,end=len(string))
# 参数::
# sub -- 搜索的子字符串
# start -- 字符串开始搜索的位置。默认为第一个字符,第一个字符索引值为0。
# end -- 字符串中结束搜索的位置。字符中第一个字符的索引为 0。默认为字符串的最后一个位置。
# 返回值::
# 该方法返回子字符串在字符串中出现的次数。
1 str1 = "hello world"
2 str2 = "l"
3 print("count()01:: ", str1.count(str2))
4
5 print("count()02:: ", str1.count(str2, 0, 5))
输出结果为::
count()01:: 3
count()02:: 2
2)字符串转换操作相关的
# replace() 方法把字符串中的 old(旧字符串) 替换成 new(新字符串),
# 如果指定第三个参数max,则替换不超过 max 次。
# replace()方法语法:
# str.replace(old, new[, max])
# 参数::
# old -- 将被替换的子字符串。
# new -- 新字符串,用于替换old子字符串。
# max -- 可选字符串, 替换不超过 max 次
# 返回值::
# 返回字符串中的 old(旧字符串) 替换成 new(新字符串)后生成的新字符串,
# 如果指定第三个参数max,则替换不超过 max 次。
1 str1 = "this is an banana"
2 print("旧的字符串:: ", str1)
3 print("替换的新的字符串:: ", str1.replace("banana", "Mango"))
4
5 print("replace():: ", str1.replace("is", "was"))
6 print("replace():: ", str1.replace("is", "was", 1))
输出结果为::
旧的字符串:: this is an banana
替换的新的字符串:: this is an Mango
replace():: thwas was an banana
replace():: thwas is an banana
# capitalize()将字符串的第一个字母变成大写,其他字母变小写。
# capitalize()方法语法:
# str.capitalize()
# 参数:无
# 返回值::
# 该方法返回一个首字母大写的字符串
1 str1 = "this is a banana"
2 print("str1.capitalize():: ", str1.capitalize())
输出结果为:
str1.capitalize():: This is a banana
# title() 方法返回"标题化"的字符串,就是说所有单词都是以大写开始,
# 其余字母均为小写
# title()方法语法:
# str.title();
# 参数::无
# 返回值::
# 返回"标题化"的字符串,就是说所有单词都是以大写开始。
1 str1 = "this is a mango"
2 print("str1.title():: ", str1.title())
3 # 凡是中间不是字母的都统统算作一个分隔符,分隔符两边的东西都被当做单独的单词来处理,首字母都被转化成大写的
4 str2 = "this is-a*adv-qq&yy"
5 print("str2.title():: ", str2.title())
# lower() 方法转换字符串中所有大写字符为小写。
# lower()方法语法:
# str.lower()
# 参数::无
# 返回值::
# 返回将字符串中所有大写字符转换为小写后生成的字符串。
1 str1 = "Hello World"
2 print("str.lower():: ", str1.lower())
输出结果为:str.lower():: hello world
# upper() 方法将字符串中的小写字母转为大写字母。
# upper()方法语法:
# str.upper()
# 参数::无
# 返回值::
# 返回小写字母转为大写字母的字符串。
1 str1 = "this is an apple"
2 print("str.upper():: ", str1.upper())
输出结果为:
str.upper():: THIS IS AN APPLE
3)字符串填充压缩操作
# ljust() 方法返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用空格填充至指定长度的新字符串。
# 如果指定的长度小于原字符串的长度则返回原字符串。
# ljust()方法语法:
# str.ljust(width[, fillchar])
# 参数::
# width -- 指定字符串长度。
# fillchar -- 填充字符,默认为空格。
# 返回值::
# 返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用空格填充至指定长度的新字符串。
# 如果指定的长度小于原字符串的长度则返回原字符串。
1 str1 = "this is a Mango"
2 print("str1.ljust():: ", str1.ljust(20, "-"))
3
4 str1 = "this is a Mango"
5 print("str1.ljust():: ", str1.ljust(8, "-"))
输出结果为:
str1.ljust():: this is a Mango-----
str1.ljust():: this is a Mango
# rjust() 返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串。
# 如果指定的长度小于字符串的长度则返回原字符串。
# rjust()方法语法:
# str.rjust(width[, fillchar])
# 参数::
# width -- 指定填充指定字符后中字符串的总长度.
# fillchar -- 填充的字符,默认为空格
# 返回值::
# 返回一个原字符串右对齐,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串。
# 如果指定的长度小于字符串的长度则返回原字符串
1 str1 = "this is string example"
2 print("str1.rjust():: ", str1.rjust(26, "&"))
输出结果为:
str1.rjust():: &&&&this is string example
# center() 方法返回一个指定的宽度 width 居中的字符串,
# fillchar 为填充的字符,默认为空格。
# center()方法语法:
# str.center(width[, fillchar])
# 参数::
# width -- 字符串的总宽度。
# fillchar -- 填充字符
# 返回值::
# 返回一个指定的宽度 width 居中的字符串,如果 width 小于字符串宽度直接返回字符串,
# 否则使用 fillchar 去填充。
1 str1 = "this is an apple"
2 print("str1.center():: ", str1.center(23, "*"))
输出结果为:
str1.center():: ****this is an apple***
# lstrip() 方法用于截掉字符串左边的空格或指定字符。
# lstrip()方法语法:
# str.lstrip([chars])
# 参数::
# chars --指定截取的字符。
# 返回值::
# 返回截掉字符串左边的空格或指定字符后生成的新字符串。
1 str1 = "*****this is an apple****"
2 print("str1.lstrip():: ", str1.lstrip("*"))
3
4 # 去掉的并不是wo这个字符串,而是\'w\' \'o\'这些字符集
5 str1 = "wwwwoo is hello"
6 print("str1.lstrip():: ", str1.lstrip("wo"))
输出结果:
str1.lstrip():: this is an apple****
str1.lstrip():: is hello
# rstrip() 删除 string 字符串末尾的指定字符(默认为空格).
# rstrip()方法语法:
# str.rstrip([chars])
# 参数::
# chars -- 指定删除的字符(默认为空格)
# 返回值::
# 返回删除 string 字符串末尾的指定字符后生成的新字符串。
1 str1 = " this is an apple "
2 print("str1.rstrip():: ", str1.rstrip()+"|")
3
4 str1 = "*********this is an apple*************"
5 print("str1.rstrip():: ", str1.rstrip("*"))
6
7 # 这样的话是不会移除的
8 str1 = "******this is an apple*******a"
9 print("str1.rstrip():: ", str1.rstrip("*"))
输出结果为:
str1.rstrip():: this is an apple|
str1.rstrip():: *********this is an apple
str1.rstrip():: ******this is an apple*******a
4):字符串分割拼接操作
# split()通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片,如果参数num 有指定值,则仅分隔 num 个子字符串
# split()方法语法:
# str.split(str="", num=string.count(str))
# 参数::
# str -- 分隔符,默认为所有的空字符,包括空格、换行(\\n)、制表符(\\t)等。
# num -- 分割次数。
# 返回值::