Python 拼接字符串的几种方式
Posted 悲欢自饮
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python 拼接字符串的几种方式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在学习Python(3x)的过程中,在拼接字符串的时候遇到了些问题,所以抽点时间整理一下Python 拼接字符串的几种方式。
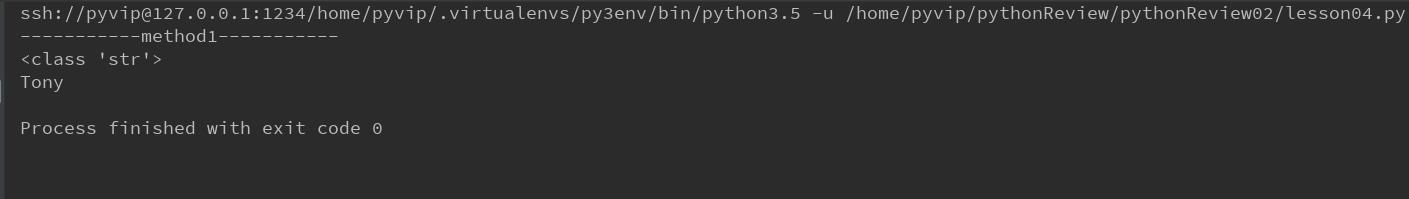
方式1,使用加号(+)连接,使用加号连接各个变量或者元素必须是字符串类型(<class \'str\'>)
例如:
str_name1 = \'To\' str_name2 = \'ny\' str_name = str_name1 + str_name2 print(str_name)
输出结果:
我是学C#出身的,把c#编程习惯用到了Python 上面,于是就出现了下面的代码
number=34 print(\'这个数是:\'+number)
编译通过运行才发现行不通,出现了一下错误。
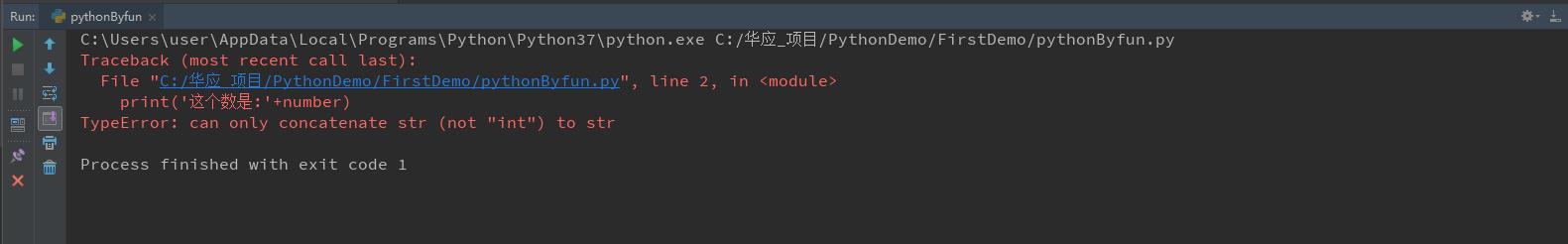
突然就懵了。
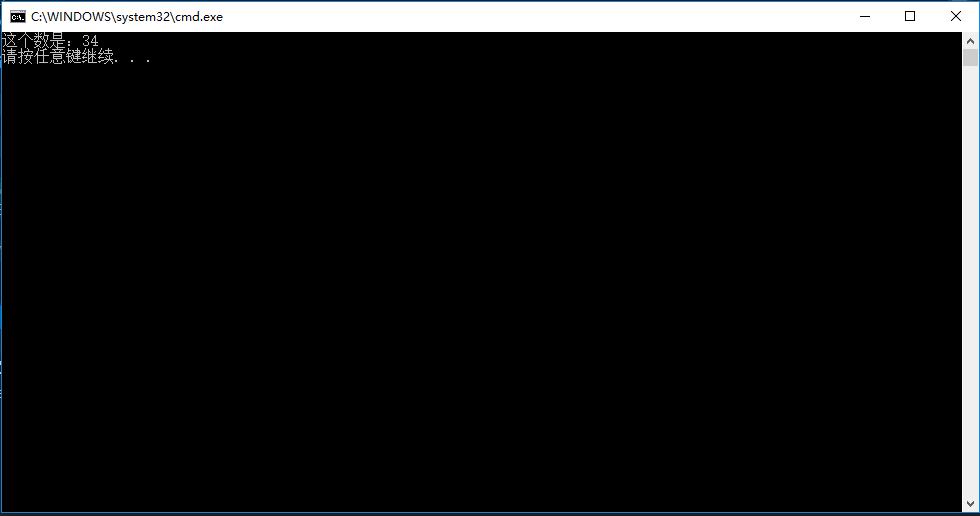
C#代码
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //c# 字符串使用"+"拼接 int num = 34; Console.WriteLine("这个数是:"+num); } }
编译通过,执行结果如下
修改Python 代码:
number=34
print(\'这个数是:\'+str(number))
方式三:使用.joiin(iterable) 拼接
print(\'-----------method3-----------\')
# method3 使用join拼接字符串
# str.join(iterable)
# 可join的条件 join(iterable) iterable 可迭代的, 如果列表(list)为 非嵌套列表,列表元素为字符串(str)类型,
# 序列类型,散列类型 都可以作为参数传入
# eg(1):
list_good_night = [\'晚\', \'上\', \'好\', \'!\']
str_night = \'\'.join(list_good_night)
print(str_night)
# eg(2):
# 拼接前缀 (\'拼接前缀\').join(iterable)
str_night1 = \'------>\'.join(list_good_night)
print(str_night1)
# eg(3) 拼接 iterable = 字典 key,value 必须字符串 默认拼接key 的列表
dict_name = {\'key1\': \'value1\', \'key2\': \'value2\'}
str_key = \',\'.join(dict_name)
# 拼接value 的列表
str_value = \',\'.join(dict_name.values())
print(str_key)
print(str_value)
执行结果:

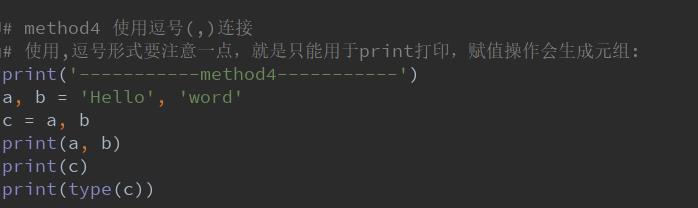
方式四:使用逗号(,)拼接
# method4 使用逗号(,)连接 # 使用,逗号形式要注意一点,就是只能用于print打印,赋值操作会生成元组: print(\'-----------method4-----------\') a, b = \'Hello\', \'word\' c = a, b print(a, b) print(c) print(type(c))
输出结果:
方式五:直接拼接
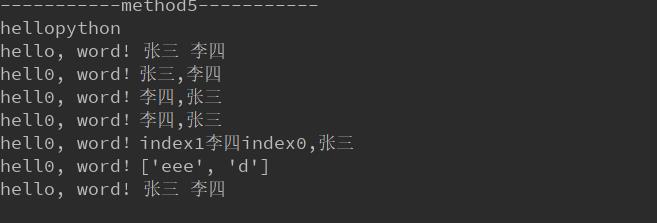
# mehon5 直接连接 print(\'-----------method5-----------\') print(\'hello\'\'python\')
方式六:format 拼接
# mehon5 直接连接
print(\'-----------method5-----------\')
print(\'hello\'\'python\')
# methon6 format 拼接 str.format(args,**kwargs)
# eg(1) {} 充当占位符
str_word = \'hello, word! {} {}\'.format(\'张三\', \'李四\')
print(str_word)
# eg(2) {[index]} 按索引位置填充 .format([0]=value1, [1]= value1},)
str_word_index0 = \'hell0, word!{0},{1}\'.format(\'张三\', \'李四\')
str_word_index1 = \'hell0, word!{1},{0}\'.format(\'张三\', \'李四\')
print(str_word_index0)
print(str_word_index1)
# eg(3) {[keyword]}
str_word_keyword = \'hell0, word!{a},{b}\'.format(b=\'张三\', a=\'李四\')
print(str_word_keyword)
# eg(4) {[keyword,indec]} keyword 放在最后
str_word1 = \'hell0, word!{1}{a}{0},{b}\'.format(\'index0\', \'index1\', b=\'张三\', a=\'李四\')
print(str_word1)
# eg(5) format 参数类型不限,当为元祖,列表,集合,字典时输出
str_word2 = \'hell0, word!{b}\'.format(b=[\'eee\', \'d\'])
print(str_word2)
# eg(6) 作为函数使用
str_word3 = \'hello, word! {} {}\'.format
word = str_word3(\'张三\', \'李四\')
print(word)
输出结果:
以上是关于Python 拼接字符串的几种方式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章