Python获取Linux或Windows系统的基本信息
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python获取Linux或Windows系统的基本信息相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前段时间写了一篇博文名为《利用Python脚本获取Windows和Linux的系统版本信息》,本篇博文利用这篇文章中的知识提供一个增强版本的获取信息的Python脚本。执行后,看起来就像登录Ubuntu Linux系统时提示的motd信息一样,可以看到:
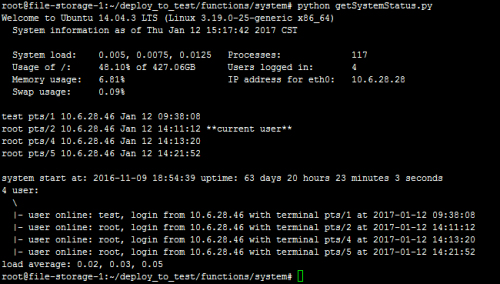
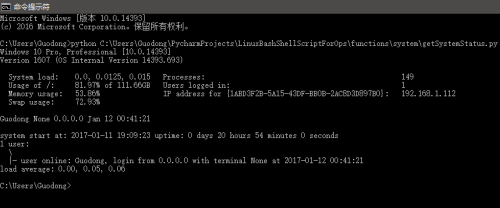
系统的类型、发行版本(具体信息)、内核版本等
当前系统的时间、时区
系统每一个CPU核心的负载和CPU整体负载
进程数量
根分区的磁盘空间,Windows下默认C盘
登录的用户总数和每一个登录到系统的用户的信息
内存和交换分区的利用率
默认网卡的IP地址
系统启动时间和已运行时间
运行截图如下:
(1)Linux下截图:
(2)Windows下截图:
Python代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
# encoding: utf-8
# -*- coding: utf8 -*-
"""
Created by PyCharm.
File: LinuxBashShellScriptForOps:getSystemStatus.py
User: Guodong
Create Date: 2016/8/18
Create Time: 15:32
"""
import platform
import psutil
import subprocess
import os
import sys
import time
import re
import prettytable
mswindows = (sys.platform == "win32") # learning from ‘subprocess‘ module
linux = (sys.platform == "linux2")
def getLocalIP():
import netifaces
routingNicName = netifaces.gateways()[‘default‘][netifaces.AF_INET][1]
for interface in netifaces.interfaces():
if interface == routingNicName:
try:
routingIPAddr = netifaces.ifaddresses(interface)[netifaces.AF_INET][0][‘addr‘]
return interface, routingIPAddr
except KeyError:
pass
def getUser():
if linux:
proc_obj = subprocess.Popen(r‘tty‘, shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.STDOUT)
tty = proc_obj.communicate()[0]
else:
tty = []
user_object = psutil.users()
for login in user_object:
username, login_tty, login_host, login_time = [suser for suser in login]
print username, login_tty, login_host, time.strftime(‘%b %d %H:%M:%S‘, time.localtime(login_time)),
if login_tty in tty:
print ‘**current user**‘
else:
print
def getTimeZone():
return time.strftime("%Z", time.gmtime())
def getTimeNow():
now = time.strftime(‘%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y %Z‘, time.localtime(time.time()))
return now
def printHeader():
if linux:
try:
with open(‘/etc/issue‘) as f:
content = f.read().strip()
output_list = re.split(r‘ \\‘, content)
linux_type = list(output_list)[0]
except IOError:
pass
else:
if linux_type is not None:
return "Welcome to %s (%s %s %s)\n System information as of %s" % (
linux_type, platform.system(), platform.release(), platform.machine(), getTimeNow()
)
else:
return
if mswindows:
def get_system_encoding():
import codecs
import locale
"""
The encoding of the default system locale but falls back to the given
fallback encoding if the encoding is unsupported by python or could
not be determined. See tickets #10335 and #5846
"""
try:
encoding = locale.getdefaultlocale()[1] or ‘ascii‘
codecs.lookup(encoding)
except Exception:
encoding = ‘ascii‘
return encoding
DEFAULT_LOCALE_ENCODING = get_system_encoding()
import _winreg
try:
reg_key = _winreg.OpenKey(_winreg.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, "SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows NT\\CurrentVersion")
if reg_key:
ProductName = _winreg.QueryValueEx(reg_key, "ProductName")[0] or None
EditionId = _winreg.QueryValueEx(reg_key, "EditionId")[0] or None
ReleaseId = _winreg.QueryValueEx(reg_key, "ReleaseId")[0] or None
BuildLabEx = _winreg.QueryValueEx(reg_key, "BuildLabEx")[0][:9] or None
return "%s, %s [%s]\r\nVersion %s (OS Internal Version %s)" % (
ProductName, EditionId, platform.version(), ReleaseId, BuildLabEx)
except Exception as e:
print e.message.decode(DEFAULT_LOCALE_ENCODING)
def getHostname():
return platform.node()
def getCPU():
return [x / 100.0 for x in psutil.cpu_percent(interval=0, percpu=True)]
def getLoadAverage():
if linux:
import multiprocessing
k = 1.0
k /= multiprocessing.cpu_count()
if os.path.exists(‘/proc/loadavg‘):
return [float(open(‘/proc/loadavg‘).read().split()[x]) * k for x in range(3)]
else:
tokens = subprocess.check_output([‘uptime‘]).split()
return [float(x.strip(‘,‘)) * k for x in tokens[-3:]]
if mswindows:
# print psutil.cpu_percent()
# print psutil.cpu_times_percent()
# print psutil.cpu_times()
# print psutil.cpu_stats()
return "%.2f%%" % psutil.cpu_percent()
def getMemory():
v = psutil.virtual_memory()
return {
‘used‘: v.total - v.available,
‘free‘: v.available,
‘total‘: v.total,
‘percent‘: v.percent,
}
def getVirtualMemory():
v = psutil.swap_memory()
return {
‘used‘: v.used,
‘free‘: v.free,
‘total‘: v.total,
‘percent‘: v.percent
}
def getUptime():
uptime_file = "/proc/uptime"
if os.path.exists(uptime_file):
with open(uptime_file, ‘r‘) as f:
return f.read().split(‘ ‘)[0].strip("\n")
else:
return time.time() - psutil.boot_time()
def getUptime2():
boot_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime(psutil.boot_time()))
print "system start at: %s" % boot_time,
uptime_total_seconds = time.time() - psutil.boot_time()
uptime_days = int(uptime_total_seconds / 24 / 60 / 60)
uptime_hours = int(uptime_total_seconds / 60 / 60 % 24)
uptime_minutes = int(uptime_total_seconds / 60 % 60)
uptime_seconds = int(uptime_total_seconds % 60)
print "uptime: %d days %d hours %d minutes %d seconds" % (uptime_days, uptime_hours, uptime_minutes, uptime_seconds)
user_number = len(psutil.users())
print "%d user:" % user_number
print " \\"
for user_tuple in psutil.users():
user_name = user_tuple[0]
user_terminal = user_tuple[1]
user_host = user_tuple[2]
user_login_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime(user_tuple[3]))
print " |- user online: %s, login from %s with terminal %s at %s" % (
user_name, user_host, user_terminal, user_login_time)
cpu_count = psutil.cpu_count()
try:
with open(‘/proc/loadavg‘, ‘r‘) as f:
loadavg_c = f.read().split(‘ ‘)
loadavg = dict()
if loadavg_c is not None:
loadavg[‘lavg_1‘] = loadavg_c[0]
loadavg[‘lavg_5‘] = loadavg_c[1]
loadavg[‘lavg_15‘] = loadavg_c[2]
loadavg[‘nr‘] = loadavg_c[3]
loadavg[‘last_pid‘] = loadavg_c[4]
print "load average: %s, %s, %s" % (loadavg[‘lavg_1‘], loadavg[‘lavg_5‘], loadavg[‘lavg_15‘])
if float(loadavg[‘lavg_15‘]) > cpu_count:
print "Note: cpu 15 min load is high!"
if float(loadavg[‘lavg_5‘]) > cpu_count:
print "Note: cpu 5 min load is high!"
if float(loadavg[‘lavg_1‘]) > cpu_count:
print "Note: cpu 1 min load is high!"
except IOError:
pass
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
header = printHeader()
print header
print
system_load = str(getLoadAverage()).strip("[]")
user_logged_in = len(psutil.users())
info_of_root_partition = psutil.disk_usage("/")
percent_of_root_partition_usage = "%.2f%%" % (
float(info_of_root_partition.used) * 100 / float(info_of_root_partition.total))
total_size_of_root_partition = "%.2f" % (float(psutil.disk_usage("/").total / 1024) / 1024 / 1024)
memory_info = getMemory()
memory_usage = "%.2f%%" % (float(memory_info[‘used‘]) * 100 / float(memory_info[‘total‘]))
swap_info = getVirtualMemory()
swap_usage = "%.2f%%" % (float(swap_info[‘used‘]) * 100 / float(swap_info[‘total‘]))
local_ip_address = getLocalIP()
table = prettytable.PrettyTable(border=False, header=False, left_padding_width=2)
table.field_names = ["key1", "value1", "key2", "value2"]
table.add_row(["System load:", system_load, "Processes:", len(list(psutil.process_iter()))])
table.add_row(["Usage of /:", "%s of %sGB" % (percent_of_root_partition_usage, total_size_of_root_partition),
"Users logged in:", user_logged_in])
table.add_row(["Memory usage:", memory_usage, "IP address for %s:" % local_ip_address[0], local_ip_address[1]])
table.add_row(["Swap usage:", swap_usage, "", ""])
for field in table.field_names:
table.align[field] = "l"
print table.get_string()
print
getUser()
print
getUptime2()注:脚本内容可以通过GitHub获取,https://github.com/DingGuodong/LinuxBashShellScriptForOps/blob/master/functions/system/getSystemStatus.py,欢迎star、fork。
已知存在问题:
暂时未实现获取Windows下网卡的中文可视名称
Windows下的tty名称默认为None,暂时没有设置对用户友好的显示
Ubuntu Linux上motd信息的用户登录数量显示为同一用户同一个IP的多个用户视为同一用户,脚本中视为不同用户
首次运行可能需要安装依赖的地方库,如psutil、platform、prettytable、netifaces等,请使用easy_install、pip、conda等安装。
其他的因为时间原因未指出和未实现的问题,欢迎在文章下面评论留言和在GitHub上提issue
tag:Python、Linux系统信息、Windows系统信息
--end--
本文出自 “通信,我的最爱” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://dgd2010.blog.51cto.com/1539422/1891468
以上是关于Python获取Linux或Windows系统的基本信息的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
利用Python脚本获取Windows和Linux的系统版本信息
在 Linux 中从 Java 或 Python 访问扫描器(或者其他的,如果它有技术动机的话)(但 Windows 会很好)
python使用psutil获取系统(Windows Linux)所有运行进程信息实战:CPU时间内存使用量内存占用率PID名称创建时间等;