python04-列表推导式元组字典
Posted libotao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python04-列表推导式元组字典相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、列表推导式:如:list02=[value+1 for value in list01 if value>10] ,得到list01中所有大于10的数,然后分别加1,形成新的列表list02
1 """ 2 列表推导式 3 练习:exercise01.py 4 """ 5 6 # 将list01中所有元素,增加1以后存入list02中. 7 list01 = [5, 56, 6, 7, 7, 8, 19] 8 # list02 = [] 9 # for item in list01: 10 # list02.append(item + 1) 11 list02 = [item + 1 for item in list01] 12 print(list02) 13 # 将list01中大于10元素,增加1以后存入list02中. 14 # list02 = [] 15 # for item in list01: 16 # if item >10: 17 # list02.append(item + 1) 18 list02 = [item + 1 for item in list01 if item > 10]
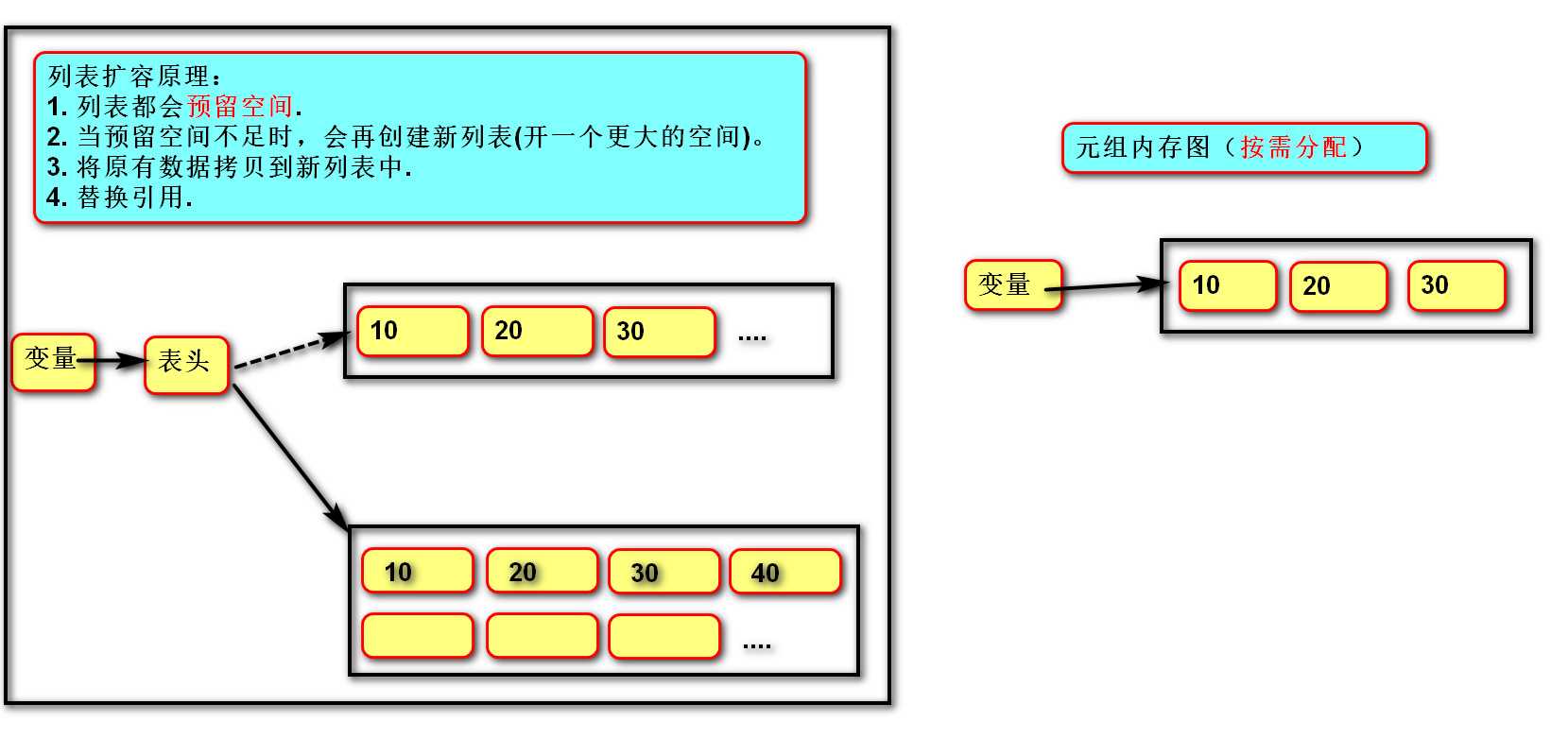
二、元组:不可变 固定大小,但是可以转换成列表
1 """ 2 元组 3 基础操作 4 练习:exercise02.py 5 exercise03.py 6 """ 7 # 1. 创建元组 8 # 空 9 tuple01 = () 10 11 # 具有默认值 12 tuple01 = (1, 2, 3) 13 14 # 列表 --> 元组 15 tuple01 = tuple(["a", "b"]) 16 print(tuple01) #输出 (a,b) 17 # 元组 --> 列表 18 list01 = list(tuple01) 19 print(list01) #输出["a","b"] 20 21 # 如果元组只有一个元素 22 # tuple02 = (100) 23 # print(type(tuple02))# int 24 25 tuple02 = (100,) 26 print(type(tuple02)) # tuple 27 28 # 不能变化 29 # tuple02[0] = 10 30 31 # 2. 获取元素(索引 切片) 32 tuple03 = ("a", "b", "c", "d") 33 e01 = tuple03[1] 34 print(type(e01)) # str 35 36 e02 = tuple03[-2:] 37 print(type(e02)) # tuple 38 39 # 可以直接将元组赋值给多个变量 40 tuper04 = (100, 200) 41 a, b = tuper04 42 print(a) 43 print(b) 44 45 # 3. 遍历元素 46 # 正向 47 for item in tuper04: 48 print(item) 49 50 # 反向 51 # 1 0 52 for i in range(len(tuper04) - 1, -1, -1): 53 print(tuper04[i])
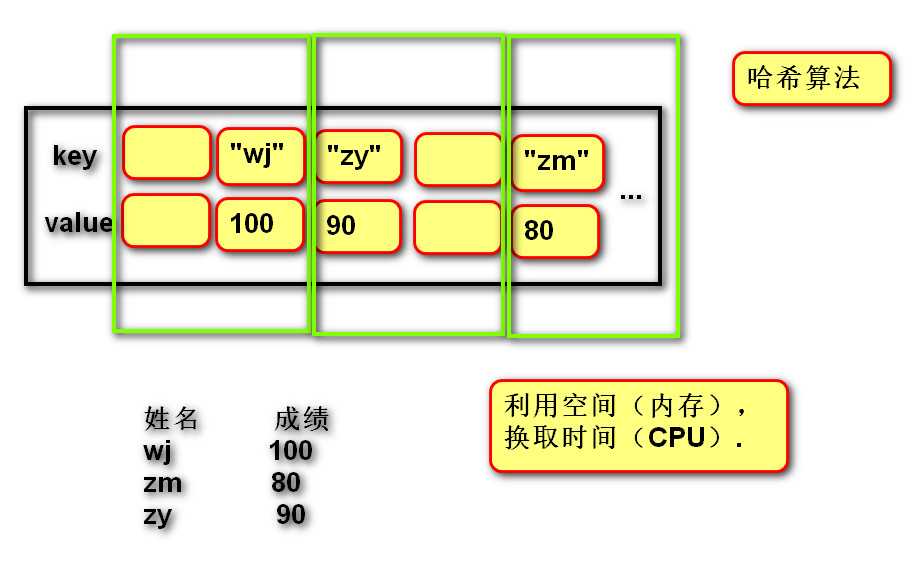
三、字典:无序、占内存 、键值对,根据键读取速度快
1 """ 2 字典 3 15:35 上课 4 练习:exercise04.py 5 """ 6 # 1. 创建 7 # 空 8 dict01 = {} 9 dict01 = dict() 10 # 默认值 11 dict01 = {"wj": 100, "zm": 80, "zr": 90} 12 dict01 = dict([("a", "b"), ("c", "d")]) 13 print(dict01) 14 15 # 2. 查找元素(根据key查找value) 16 print(dict01["a"]) 17 # 如果key不存在,查找时会错误. 18 if "qtx" in dict01: # 如果存在key 19 print(dict01["qtx"]) 20 21 # 3. 修改元素(之前存在key) 22 dict01["a"] = "BB" 23 24 # 4. 添加(之前不存在key) 25 dict01["e"] = "f" 26 27 # 5. 删除 28 del dict01["a"] 29 30 print(dict01) 31 # 6. 遍历(获取字典中所有元素) 32 33 # 遍历字典,获取key 34 for key in dict01:#默认获取的是键 35 print(key) 36 print(dict01[key]) 37 38 # 遍历字典,获取value 39 for value in dict01.values(): 40 print(value) 41 42 # 遍历字典,获取键值对key value(元组). 43 # for item in dict01.items(): 44 # print(item[0]) 45 # print(item[1]) 46 47 for k, v in dict01.items(): 48 print(k) 49 print(v)
四、字典列表嵌套比较
""" 总结: 存储多个学生信息(姓名,年龄,成绩,性别)的多种方式 1. exercise05字典内嵌列表: { "张无忌":[28,100,"男"], } 2. exercise06字典内嵌字典: { "张无忌":{"age":28,"score":100,"sex":"男"}, } 3. exercise07列表内嵌字典: [ {"name":"张无忌","age":28,"score":100,"sex":"男"}, ] 4. 列表内嵌列表 [ ["张无忌",28,100男], ] 选择策略:根据具体需求,结合优缺点,综合考虑(两害相权取其轻). 字典: 优点:根据键获取值,读取速度快; 代码可读性相对列表更高(根据键获取与根据索引获取). 缺点:内存占用大; 获取值只能根据键,不灵活. 列表: 优点:根据索引/切片,获取元素更灵活. 相比字典占内存更小。 缺点:通过索引获取,如果信息较多,可读性不高. """ """ 练习:在控制台中录入多个人的多个喜好,输入空字符停止. 例如:请输入姓名: 请输入第1个喜好: 请输入第2个喜好: ... 请输入姓名: ... 最后在控制台打印所有人的所有喜好. [ {“无忌”:[赵敏,周芷若,小赵]} ] list_person_bobby = [] while True: name = input("请输入姓名:") if name == "": break dict_person = {name:[]} list_person_bobby.append(dict_person) while True: bobby = input("请输入喜好:") if bobby == "": break dict_person[name].append(bobby) """ """ { “无忌”:[赵敏,周芷若,小赵] } """ dict_person_bobby = {} while True: name = input("请输入姓名:") if name == "": break dict_person_bobby[name] = [] while True: bobby = input("请输入喜好:") if bobby == "": break dict_person_bobby[name].append(bobby) for name, list_bobby in dict_person_bobby.items(): print("%s喜欢:" % name) for item in list_bobby: print(item)
以上是关于python04-列表推导式元组字典的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章