PTA题集4-6总结
Posted BR-boru
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了PTA题集4-6总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一,前言
题集四主要考察了arraylist数组的运用,面向对象的封装性,运用数组高效率去重以及运用数组的一些自带方法解决问题,题量较小,除了7-1之外,其它题目难度较低。除此之外,7-6要求我们自主学习Scanner类中nextLine()等方法、String类中split()等方法、Integer类中parseInt()等方法的用法,了解LocalDate类中of()、isAfter()、isBefore()、until()等方法的使用规则,了解ChronoUnit类中DAYS、WEEKS、MONTHS等单位的用法。7-1是菜单计价程序的开始,但是我没做完,时间有点不够。做这次题集我花了很多时间。
题集五主要考察了正则表达式的简单运用,聚合关系,题目难点在于日期类设计聚合一,日期类设计聚合二,题量较小,难度较低,是这两次作业里面比较轻松的了。做这次题集没有花费我多长时间。
题集六只有一个题目,就是菜单计价程序-4,这个题目我没有写出来,我只写了700多行代码,只拿了一点点分,我感觉最难的就是输入数据的处理和输出结果很难搞,太多异常处理,没有一点头绪,做的时候又静不下心来,导致浪费了很多时间没有做出来。
二,设计与分析
题集四7-1菜单计价程序
题目要求写一个菜单计价程序,这题的细节很多,所以难度偏大,在对用户正常点菜的需求下,还需要满足代点菜的特殊要求。除此之外,还有一些输入异常的错误需要进行判断,时间段的限制与折扣。写好这题需要正确的辨别各种类之间的关系以及输入异常的先后关系,以及对输入的正常数据进行处理。题目已经给了一些类的设计模板,按照题目已给的类再设计其他的类。在我的设计代码中只写了Dish,Menu,Record,Order,Table以及Main类。我觉得这一题的要注意的点在于代点菜总价钱的计算设计,因为带点菜的价格计算在当前这一桌,总价不一定等于当前桌上的菜的价格之和。还有就是计算折扣,这里可以用Calendar类里面的方法去求某天是星期几,题目并没有限制,这是我所设计的代码逆生成的类图。
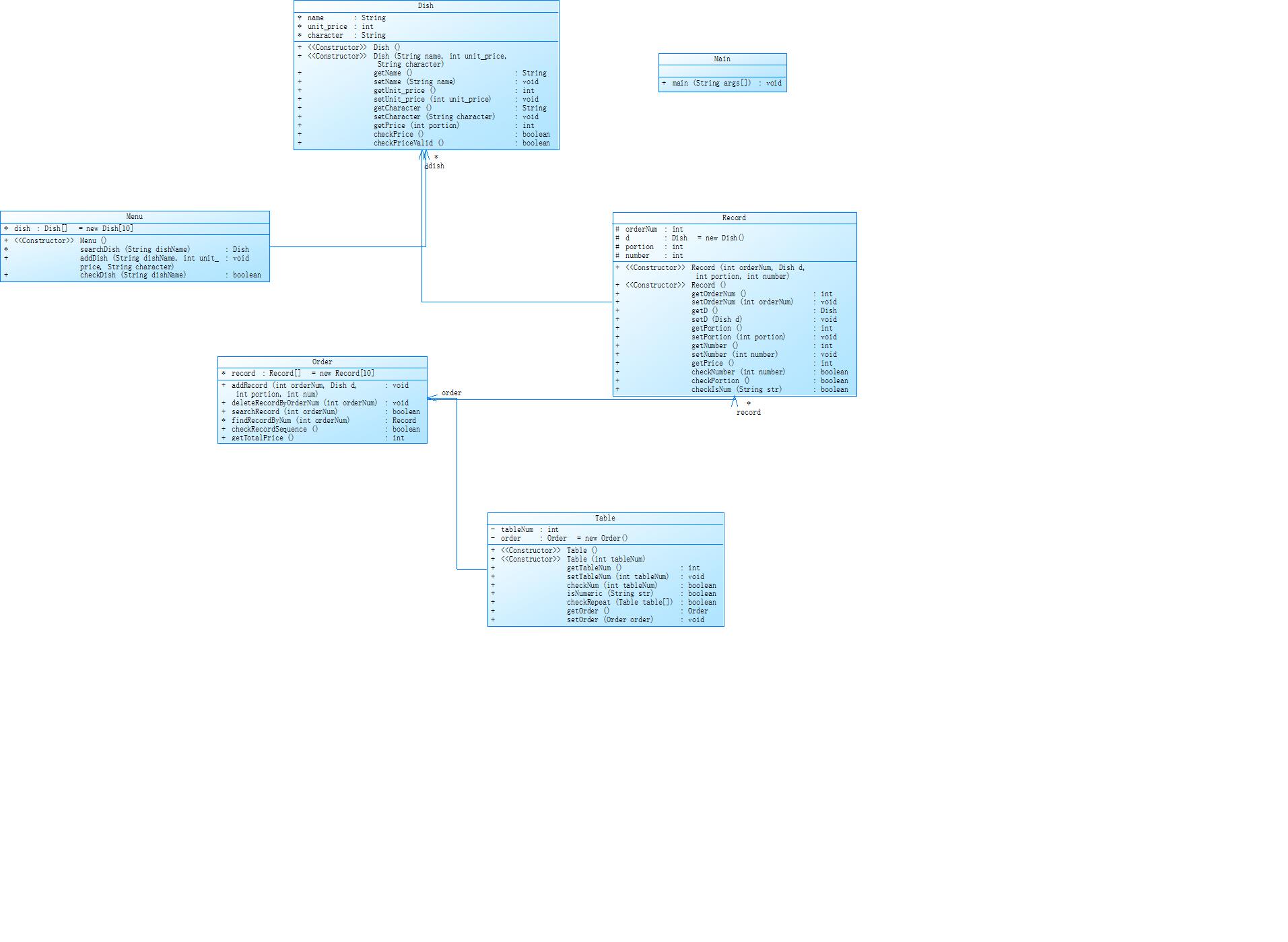
题集四7-4
单词统计与排序
从键盘录入一段英文文本(句子之间的标点符号只包括“,”或“.”,单词之间、单词与标点之间都以" "分割。
要求:按照每个单词的长度由高到低输出各个单词(重复单词只输出一次),如果单词长度相同,则按照单词的首字母顺序(不区分大小写,首字母相同的比较第二个字母,以此类推)升序输出。
做这道题时我一开始尝试用split方法将英文文本中的“,”,“.”,“ ”都去掉,返回一个字符串数组,再用冒泡排序的方法去做,但是我当时不知道怎么去删除重复的字符串数组,尝试了几种方法都没有用,然后又想用arraylist中的方法中有删除的简单方法,结果自己又不会怎样将String类型的数组转换成Array List类型的数组,属实是做不了了,之后就用了另一种方法去做,具体代码如下:


import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Main public static void main(String[] args) Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String str = input.nextLine(); ArrayList <String> list= new ArrayList<>(); String segment=""; int i=0,j=0,k=0; for(i=0;i<str.length();i++) if(str.charAt(i)==\' \') list.add(segment); segment="";//每次添加完,都要归零 else if(str.charAt(i)==\'.\'||str.charAt(i)==\',\') list.add(segment); segment=""; i++;//向后走一步,因为有空格 else segment=segment+str.charAt(i); //删除重复元素 for(i=0;i<list.size()-1;i++) for(j=i+1;j<list.size();j++) if(list.get(i).equals(list.get(j))) list.remove(j); j--;//一删一减,j不变 //按照长度冒泡排序 for(i=0;i<list.size()-1;i++) for(j=0;j<list.size()-1-i;j++) if(list.get(j).length()<list.get(j+1).length()) segment=list.get(j); list.set(j,list.get(j+1)); list.set(j+1,segment); else if(list.get(j).length()==list.get(j+1).length()) if(list.get(j).compareToIgnoreCase(list.get(j+1))>0) //不区分大小写 segment=list.get(j); list.set(j,list.get(j+1)); list.set(j+1,segment); for(i=0;i<list.size();i++) System.out.println(list.get(i));
这段代码就是先处理掉文本中的非英文字符,在删除重复元素,最后在排序。去除非英文字符时,采用的是一个一个英文字符添加到单词的临时储存变量中,直到碰见“,”,“.”,“ ”,停止,才将单词加入数组,之后再清空临时变量。之后就是去重和排序操作了,非常的简单粗暴。由于ArrayList数组的删除,添加等操作都较为方便,代码几乎没啥难度。
题集五7-5日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
1.设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] 。题目设计要求DateUtil聚合于Day,Day聚合于Month,Month聚合于Year。在做这个题目时,主要的难度便是设计类与类之间的聚合关系,具体的日期算法之前便已经设计过,这里可以直接拿过来用,稍作修改即可。编写代码实现功能时通过DateUtil中的Day类型的属性去调用Day类中的方法以及Month类型的属性,再用Month类型的属性去调用Month中的方法以及Year类型的属性,再用Year类型的属性去调用调用Year的方法。我开始做这个题目有一点让我迷惑的点是DateUtil类,Day类,Month类,Year的类的有参构造方法,刚开始看类图的时候还没反应过来,不知道这些方法传这些参数是为啥,之后整个代码快写完了才想明白,这些构造方法是连着写的。这个题目的算法已经设计过了,由于类中的属性都是私有的,将算法中的直接引用改为属性的get方法即可。还有一个问题就是判断输入日期数据是否合法没有写好,没有判断输入的月份是否大于12或小于1,因为判断日期输入是否正确是要用每月最大天数数组的,导致数组越界异常。具体代码以及sourceMonitor生成图如下:


import java.util.Scanner; public class Main public static void main(String[] args) Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());//转化输入数据 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year,month,day);//创建对象 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); else if (choice == 2) // test getPreviousNDays method int n = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());//转化输入数据 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year,month,day);//创建对象 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); n = input.nextInt(); if (n < 0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); else if (choice == 3) //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());//转化输入数据 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year,month,day);//创建对象 DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear,anotherMonth,anotherDay);//创建对象 if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println(fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); class DateUtil private Day day;//日期对象 public DateUtil() //无参构造 public DateUtil(int y,int m,int d) //有参构造 this.day = new Day(y,m,d); public Day getDay() //day的get return day; public void setDay(Day day) //day的set this.day = day; public String showDate()//输出形式 String str=day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+day.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+day.getValue(); return str; public boolean checkInputValidity()//检查输入日期是否正确 boolean result=false; if(day.validate()&&day.getMonth().validate()&&day.getMonth().getYear().validate()) result=true; return result; public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date)//比较两日期大小 boolean result=false; if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()>date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) result=true; else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) result=true; else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()&&this.getDay().getValue()>date.getDay().getValue()) result=true; return result; public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date)//检查两日期是否相等 boolean result=true; if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()!=date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) result=false; else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()!=date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) result=false; else if(this.getDay().getValue()!=date.getDay().getValue()) result=false; return result; public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n)//求下N天 int[] mon_maxnum= 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31; while(n>365)//大于一年时 if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2)//判断该年是否为闰年 if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) n=n-366; this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); else n=n-365; this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>2) this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();//判断下一年是否为闰年 if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) n=n-366; else n=n-365; for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//小于一年时 this.getDay().dayIncrement(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear())//判断该年是否为闰年 mon_maxnum[1]=29; else mon_maxnum[1]=28; if(this.getDay().getValue()>mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1]) this.getDay().getMonth().monthIncrement();//月份进位 this.getDay().reseMin(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>12) this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();//年份进位 this.getDay().getMonth().reseMin(); return this; public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n)//求前N天 int[] mon_maxnum= 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31; while(n>365)//大于一年时 if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>2) if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear())//判断该年是否为闰年 this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); n=n-366; else this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); n=n-365; else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2) this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();//判断前一年年是否为闰年 if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) n=n-366; else n=n-365; for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//小于一年时 this.getDay().dayReduction(); if(this.getDay().getValue()<=0)//判断该年是否为闰年 if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[1]=29; else mon_maxnum[1]=28; this.getDay().getMonth().monthReduction();; if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=0)//往后退一年 this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); this.getDay().getMonth().reseMax(); this.getDay().reseMax(); return this; public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date)//求两日期之间的天数 int gap=0; int[] mon_maxnum= 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31; if(this.compareDates(date))//第一个日期大于第二个,求的方法与求前n天大致一样 while(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()-date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()>=2)//当两个日期相差大于两年时,先减至两年一下再算 if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>2) if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear())//判断该年是否为闰年 gap+=366; else gap+=365; this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2) this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction();//判断前一年是否为闰年 if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) gap+=366; else gap+=365; while(true) if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) break; gap++; this.getDay().dayReduction(); if(this.getDay().getValue()<=0) this.getDay().getMonth().monthReduction(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=0) this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); this.getDay().getMonth().reseMax(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[1]=29; else mon_maxnum[1]=28; this.getDay().reseMax(); else//第一个日期小于第二个,求的方法与求后n天大致一样 while(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()-this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()>=2)//当两个日期相差大于两年时,先减至两年一下再算 if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>2) this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement();//判断后一年是否为闰年 if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) gap+=366; else gap+=365; if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2) if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear())//判断该年是否为闰年 gap+=366; else gap+=365; this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); while(true) if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) break; gap++; this.getDay().dayIncrement(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[1]=29; else mon_maxnum[1]=28; if(this.getDay().getValue()>mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1]) this.getDay().getMonth().monthIncrement(); this.getDay().reseMin(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>12) this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); this.getDay().getMonth().reseMin(); return gap; class Day private int value;//日期 private Month month;//月份对象 private int[] mon_maxnum= 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31;//每月最大天数 public Day() //无参构造 public Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue) //有参构造 this.value=dayValue; this.month=new Month(yearValue,monthValue); public int getValue() //Value的get return value; public void setValue(int value) //value的set this.value = value; public Month getMonth() //month的get return month; public void setMonth(Month month) //month的set this.month = month; public void reseMin() //日期复位 this.value=1; public void reseMax() //日期改为最大值 if(this.month.getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[1]=29; else mon_maxnum[1]=28; this.value=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]; public boolean validate() //检查日期是否合法 boolean result=false; if(month.getValue()==2&&month.getYear().isLeapYear()) if(this.value<=29&&this.value>=1) result=true; else if(month.getValue()<=0||month.getValue()>12) result=false; else if(this.value<=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]&&this.value>=1) result=true; return result; public void dayIncrement() //日期加一天 this.value=this.value+1; public void dayReduction() //日期减一天 this.value=this.value-1; class Month private int value;//月份 private Year year;//年的对象 public Month() //无参构造 public Month(int yearValue,int monthValue) //有参构造 this.value=monthValue; this.year=new Year(yearValue); public int getValue() //value的get return value; public void setValue(int value) //value的set this.value = value; public Year getYear() //year对象的get return year; public void setYear(Year year) //year的对象set this.year = year; public void reseMin() //月份复位 this.value=1; public void reseMax() //月份设置为最大 this.value=12; public boolean validate() //检查月份是否正确 boolean result=false; if(this.value>=1&&this.value<=12) result=true; return result; public void monthIncrement() //月份加一 this.value=this.value+1; public void monthReduction() //月份减一 this.value=this.value-1; class Year private int value;//年份 public Year() //无参构造 public Year(int value) //有参构造 this.value=value; public int getValue() //value的get return value; public void setValue(int value) //value的set this.value = value; public boolean isLeapYear()//闰年判断 boolean result=false; if((value%4==0&&value%100!=0)||value%400==0) result=true; return result; public boolean validate() //年份合法判断 boolean result=false; if(value<=2050&&value>=1900) result=true; return result; public void yearIncrement() //年份加一 this.value=this.value+1; public void yearReduction() //年份减一 this.value=this.value-1;

题集五7-6日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
7-6与7-5代码大致相同,也要求改为聚合关系,只不过是DateUtil聚合Day,Month,Year这三个类。根据类图,DateUtil拥有这三个类的类型的属性,可以直接调用通过这三个属性调用这些类中的方法,然后在DateUtil中完成各种对日期的操作,我感觉这道题要比7-5简单一些,从类图上看这个7-6类图7-5类图少了一些东西,比如并没有让我i们设计判断输入天数是否正确的方法,测的时候也没有测试点检测,原因可能是每个月的最大天数数组在DateUtil中定义成了私有属性,类图中也没有这个数组的get方法,所以就没有考虑。具体代码以及sourceMonitor生成图如下:


import java.util.Scanner; public class Main public static void main(String[] args) Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); System.out.print(date.getYear().getValue() + "-" + date.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " next " + m + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); else if (choice == 2) // test getPreviousNDays method int n = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); n = input.nextInt(); if (n < 0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); System.out.print( date.getYear().getValue() + "-" + date.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " previous " + n + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); else if (choice == 3) //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); class DateUtil private Day day;////创建对象 private Month month; private Year year; private int[] mon_maxnum= 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31; public DateUtil() //无参构造 public DateUtil(int y,int m,int d) //有参构造 this.day=new Day(d); this.month=new Month(m); this.year=new Year(y); public Day getDay() return day; public void setDay(Day day) this.day = day; public Month getMonth() return month; public void setMonth(Month month) this.month = month; public Year getYear() return year; public void setYear(Year year) this.year = year; public String showDate()//输出形式 String str=year.getValue()+"-"+month.getValue()+"-"+day.getValue(); return str; public void setDayMin() day.setValue(1); public void setDayMax() day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]); public boolean checkInputValidity()//检查输入日期是否正确 boolean result=false; if(month.validate()&&year.validate()) result=true; return result; public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date)//比较两日期大小 boolean result=false; if(this.getYear().getValue()>date.getYear().getValue()) result=true; else if(this.getYear().getValue()==date.getYear().getValue()&&this.getMonth().getValue()>date.getMonth().getValue()) result=true; else if(this.getYear().getValue()==date.getYear().getValue()&&this.getMonth().getValue()==date.getMonth().getValue()&&this.getDay().getValue()>date.getDay().getValue()) result=true; return result; public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date)//检查两日期是否相等 boolean result=true; if(this.getYear().getValue()!=date.getYear().getValue()) result=false; else if(this.getMonth().getValue()!=date.getMonth().getValue()) result=false; else if(this.getDay().getValue()!=date.getDay().getValue()) result=false; return result; public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n)//求下N天 while(n>365)//大于一年时 if(this.getMonth().getValue()<=2)//判断该年是否为闰年 if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) n=n-366; this.getYear().yearIncrement(); else n=n-365; this.getYear().yearIncrement(); else if(this.getMonth().getValue()>2) this.getYear().yearIncrement();//判断下一年是否为闰年 if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) n=n-366; else n=n-365; for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//小于一年时 this.getDay().dayIncrement(); if(this.getYear().isLeapYear())//判断该年是否为闰年 this.mon_maxnum[1]=29; else this.mon_maxnum[1]=28; if(this.getDay().getValue()>this.mon_maxnum[this.getMonth().getValue()-1]) this.getMonth().monthIncrement();//月份进位 this.setDayMin(); if(this.getMonth().getValue()>12) this.getYear().yearIncrement();//年份进位 this.getMonth().reseMin(); return this; public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n)//求前N天 while(n>365)//大于一年时 if(this.getMonth().getValue()>2) if(this.getYear().isLeapYear())//判断该年是否为闰年 this.getYear().yearReduction(); n=n-366; else this.getYear().yearReduction(); n=n-365; else if(this.getMonth().getValue()<=2) this.getYear().yearReduction();//判断前一年年是否为闰年 if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) n=n-366; else n=n-365; for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//小于一年时 this.getDay().dayReduction(); if(this.getDay().getValue()<=0)//判断该年是否为闰年 if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) this.mon_maxnum[1]=29; else this.mon_maxnum[1]=28; this.getMonth().monthReduction();; if(this.getMonth().getValue()<=0)//往后退一年 this.getYear().yearReduction(); this.getMonth().reseMax(); this.setDayMax(); return this; public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date)//求两日期之间的天数 int gap=0; if(this.compareDates(date))//第一个日期大于第二个,求的方法与求前n天大致一样 while(this.getYear().getValue()-date.getYear().getValue()>=2) if(this.getMonth().getValue()>2) if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) gap+=366; else gap+=365; this.getYear().yearReduction(); if(this.getMonth().getValue()<=2) this.getYear().yearReduction(); if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) gap+=366; else gap+=365; while(true) if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) break; gap++; this.getDay().dayReduction(); if(this.getDay().getValue()<=0) this.getMonth().monthReduction(); if(this.getMonth().getValue()<=0) this.getYear().yearReduction(); this.getMonth().reseMax(); if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) this.mon_maxnum[1]=29; else this.mon_maxnum[1]=28; this.setDayMax(); else//第一个日期小于第二个,求的方法与求后n天大致一样 while(date.getYear().getValue()-this.getYear().getValue()>=2) if(this.getMonth().getValue()>2) this.getYear().yearIncrement(); if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) gap+=366; else gap+=365; if(this.getMonth().getValue()<=2) if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) gap+=366; else gap+=365; this.getYear().yearIncrement(); while(true) if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) break; gap++; this.getDay().dayIncrement(); if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) this.mon_maxnum[1]=29; else this.mon_maxnum[1]=28; if(this.getDay().getValue()>this.mon_maxnum[this.getMonth().getValue()-1]) this.getMonth().monthIncrement(); this.setDayMin(); if(this.getMonth().getValue()>12) this.getYear().yearIncrement(); this.getMonth().reseMin(); return gap; class Year private int value;//年份 public Year() //无参构造 public Year(int value) //有参构造 this.value=value; public int getValue() //value的get return value; public void setValue(int value) //value的set this.value = value; public boolean isLeapYear()//判断是否为闰年 boolean result=false; if((value%4==0&&value%100!=0)||value%400==0) result=true; return result; public boolean validate() //判断输入数据是否合法 boolean result=false; if(value<=2020&&value>=1820) result=true; return result; public void yearIncrement() //年份加一 this.value=this.value+1; public void yearReduction() //年份减一 this.value=this.value-1; class Month private int value;//月份 public Month() //无参构造 public Month(int Value) //有参构造 this.value=Value; public int getValue() //value的get return value; public void setValue(int value) //value的set this.value = value; public void reseMin() //月份设置最小值 this.value=1; public void reseMax() //月份设计最大值 this.value=12; public boolean validate() //判断输入数据是否合法 boolean result=false; if(this.value>=1&&this.value<=12) result=true; return result; public void monthIncrement() //月份加一 this.value=this.value+1; public void monthReduction() //月份减一 this.value=this.value-1; class Day private int value;//天数 public Day() //无参构造 public Day(int Value) //有参构造 this.value=Value; public int getValue() //value的get return value; public void setValue(int value) //value的set this.value = value; public void dayIncrement() //天数加一 this.value=this.value+1; public void dayReduction() //天数减一 this.value=this.value-1;

题集六7-1菜单计价程序-4
这个菜单要比之前的那个难很多,尤其是其中的输入异常判断,输入异常的判断有很多,要输出很多异常报错,既要考虑异常输出的先后顺序,还要考虑因为某个异常会忽略其他异常的输出。同时还要考虑在桌号相同的时候,看时间是否在同一时间段,来判断是不是同一记录,再进行计算价格。在数据处理上,新增了特色菜这个菜系,也就代表着之前的所有菜价加在一起再算折扣的后的总价方法要改,改成同类型的菜价格相加再去乘以折扣。同时,这个题目的输入数据判断可以用正则表达式进行初步判断,在进行接下来的操作。在这次的7-4中,新加了很多功能,我就将原先Table类中的一些功能拿了出来,我觉得Table类的功能太多,新增了Date类和Restaurant类,用于实现一些功能,减少Table类的职责,这是我所写的代码设计类图,不知道为什么我的powerdesigner逆生成类图不会有依赖关系。

三,踩坑心得
1.不管是在做什么题目时,先把题目要求看清楚,再去做,因为这个原因,导致我题集六的题目没做好,题目没有看明白,我一开始题集四7-1的代点菜设计是对的,但是我自己在做7-4是没有仔细看题,以为输出每一桌的总价钱是直接跟在每一桌的点菜记录后面,导致改掉了原来题集四7-1的输出设计,最后这个题目只做出来一点异常处理,直到题目时间截止后,我才发现我看错题目了。
2.注意所用的类的方法放回的数据类型,以及是否会返回负数,如:long weeks = date1.until(date2, ChronoUnit.WEEKS);这里weeks是可以为负数的,以及要用long类型的数据接收。
3.在做题集五7-5时要写一个方法判断输入日期数据是否合法没有写好,没有判断输入的月份是否大于12或小于1,因为判断日期输入是否正确是要用每月最大天数数组的,导致数组越界异常,这里判断异常时应该先判断年份是否异常,再判断月份是否异常,最后判断日期是否正常。
4.写菜单计价程序时,因为用到了对象数组,有时只给了对象数组一部分元素申请空间,但是在查找元素的时候,还是用简单的for循环去写,但这样那些未申请空间的数组成员都为空,就会出现对象为空的异常报错空,当然这也与我不会用Arraylist数组有关,ArrayList数组的大小不固定,可随时扩充,再配合for-each
作业10-异常 java
1. 本周学习总结
1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结异常相关内容。
2. 书面作业
本次PTA作业题集异常
1. 常用异常
结合题集题目7-1回答
1.1 自己以前编写的代码中经常出现什么异常、需要捕获吗(为什么)?应如何避免?
1.2 什么样的异常要求用户一定要使用捕获处理?
2. 处理异常使你的程序更加健壮
题集题目7-2
2.1 实验总结。并回答:怎么样才能让你的程序更加健壮?
3. throw与throws
题集题目7-3
阅读Integer.parsetInt源代码
3.1 Integer.parsetInt一开始就有大量的抛出异常的代码,这种做法有什么好处?
3.2 结合自己编写的程序与3.1,分析自己编写的方法抛出异常时一般需要传递给调用者一些什么信息?
4. 用异常改进ArrayIntegerStack
题集题目6-3
4.1 结合6-3代码,回答使用抛出异常的方式代表程序运行时出错有什么好处?比单纯的返回错误值,有何优点?
4.2 如果一个方法内部的内码抛出的是RuntimeException类型的异常,那么方法声明是否应该使用throws关键字,如果使用throws关键字声明该方法抛出的异常,能给我们带来什么好处吗?
5. 函数题-多种异常的捕获
题集题目6-1
5.1 结合6-1代码,回答:一个try块中如果可能抛出多种异常,且异常之间可能有继承关系,捕获时需要注意些什么?
5.2 一个try块中如果可能抛出多种异常,使用Java8的多重异常捕获语法需要注意些什么?
6. 为如下代码加上异常处理
byte[] content = null;
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("testfis.txt");
int bytesAvailabe = fis.available();//获得该文件可用的字节数
if(bytesAvailabe>0){
content = new byte[bytesAvailabe];//创建可容纳文件大小的数组
fis.read(content);//将文件内容读入数组
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(content));//打印数组内容6.1 改正代码,并增加如下功能。当找不到文件时,需提示用户找不到文件xxx,请重新输入文件名,然后尝试重新打开。 如果是其他异常则提示打开或读取文件失败!。
注1:里面有多个方法均可能抛出异常。
功能2:需要添加finally关闭文件。无论上面的代码是否产生异常,总要提示关闭文件ing。如果关闭文件失败,提示关闭文件失败!
6.2 结合题集6-2代码,要将什么样操作放在finally块?为什么?使用finally关闭资源需要注意一些什么?
6.3 使用Java7中的try-with-resources来改写上述代码实现自动关闭资源。简述这种方法有何好处?
7. 面向对象设计作业-图书馆管理系统(分组完成,每组不超过3个同学)
登录lib.jmu.edu.cn,对图书进行搜索。然后登录图书馆信息系统,查看我的图书馆。如果让你实现一个图书借阅系统,尝试使用面向对象建模。
7.1 该系统的使用者有谁?
7.2 主要功能模块(不要太多)及每个模块的负责人。下周每个人要提交自己负责的模块代码及运行视频。
7.3 该系统的主要的类设计及类图(可用)
7.4 你准备如何存储图书信息、解决信息、读者信息等。
3.码云及PTA
题目集:异常
3.1. 码云代码提交记录
在码云的项目中,依次选择“统计-Commits历史-设置时间段”, 然后搜索并截图
3.2 截图PTA题集完成情况图
需要有两张图(1. 排名图。2.PTA提交列表图)
3.3 统计本周完成的代码量
需要将每周的代码统计情况融合到一张表中。
以上是关于PTA题集4-6总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章