JAVA面向对象程序设计_PTA题目集04-06总结分析
Posted psychewind
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JAVA面向对象程序设计_PTA题目集04-06总结分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言:
JAVA_BLOG_PTA题目集4-6_总结分析
题目集四:
知识点:大体如预备知识,即:通过查询Java API文档,了解Scanner类中nextLine()等方法、String类中split()等方法、Integer类中parseInt()等方法的用法,了解LocalDate类中of()、isAfter()、isBefore()、until()等方法的使用规则,了解ChronoUnit类中DAYS、WEEKS、MONTHS等单位的用法。另加上题目一难度较大的类间设计与方法使用。
题量:适中,时间开得相对较短但是勉强写得下来。
难度:菜单计价程序难度较大,其余题目难度偏低。但是在看见最后一题的预备知识提要之间写得崎岖艰辛,希望下次可以把它放到整个题目集的前言或者第一题的须知。
题目集五:
知识点:正则表达式、字符串、类间聚合设计。
题量:适中,写下来比题目集四轻松。
难度:正则表达式训练难度不大,但是这属于记忆量较大的新知识,上手比较慢,但是找到对应的公式后写起来很快。末两题在一开始对于这种高聚合调用有点无从下手,试了两次上手了就还好,算法和之前的差不多,之前没做出来的日期差这次写出来了,总体上过得去。
题目集六:
知识点:技术上,类的设计,类间关系的处理。方法上,把题目变成填空题。一些微妙的算法。
题量:只有一题。
难度:老师原话,难度较大,预计代码行数1000+,需用时20h+。后更新准确数据为1700+行往上,个人用时,只作粗略估计,远不止20h……
设计与分析:
04-7-1
(源码稀巴烂所以只作分析……)
分析:(事后再来看。当时居然连Main以外的类都没写出来,蠢得没下限啊这是。)
增删查都是ArrayList,返回类型是ArrayList的new一开始就少了个<>,识别就在数组里遍历一遍查找对照,多桌菜循环加对首字符串的判断。写了0671再来看这个真的蠢得……
05-7-5
源码数据:

类图:

源码:
//package _05_5__; import java.util.*; public class Main public static void main(String[] args) Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int year1, month1, day1; int year2, month2, day2; int number = in.nextInt(); if(number < 1 || number > 3) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); else if (number == 1) //下n天 year1 = in.nextInt(); month1 = in.nextInt(); day1 = in.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year1, month1, day1); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); else int m = in.nextInt(); System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); else if (number == 2) //前n天 year1 = in.nextInt(); month1 = in.nextInt(); day1 = in.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year1, month1, day1); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) //检查日期是否合法 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); else int n = in.nextInt(); if(n < 0) //日期越界情况 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); else //两天之间相差的天数 year1 = in.nextInt(); month1 = in.nextInt(); day1 = in.nextInt(); year2 = in.nextInt(); month2 = in.nextInt(); day2 = in.nextInt(); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year1, month1, day1); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(year2, month2, day2); if (!fromDate.checkInputValidity() || !toDate.checkInputValidity()) //检查日期的合法性 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); else System.out.println(fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); //package _05_5__; class Year private int value; public Year() public Year(int value) this.value = value; public int getValue() return value; public void setValue(int value) this.value = value; //判断是否为闰年 public boolean isLeapYear() if((value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0) || value % 400 == 0) return true; else return false; //校验数据合法性 public boolean validate() if(value < 1900 || value > 2050) return false; else return true; //年份加一 public void yearIncrease() value++; //年份减一 public void yearReduction() value--; //package _05_5__; class Month private int value; private Year year; public Month() public Month(int yearValue, int monthValue) this.value = monthValue; this.year = new Year(yearValue); public int getValue() return value; public void setValue(int value) this.value = value; public Year getYear() return year; public void setYear(Year year) this.year = year; //月份复位(1) public void resetMin() value = 1; //月份设置为12 public void resetMax() value = 12; //检验数据合法性 public boolean validate() if(value < 1 || value > 12) return false; else return true; //月份加一 public void monthIncrement() value ++; //月份减一 public void monthReduction() value --; //package _05_5__; class Day private int value; private Month month; private int[] mon_maxnum =31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31; public Day() public Day(int yearValue, int monthValue, int dayValue) this.month = new Month(yearValue,monthValue); this.value = dayValue; public int getValue() return value; public void setValue(int value) this.value = value; public Month getMonth() return month; public void setMonth(Month month) this.month = month; //日期复位1 public void resetMin() value = 1; //日期设为本月最大值 public void resetMax() if(this.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[1] = 29; value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue() - 1]; //校验数据合法性 public boolean validate() if(this.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[1] = 29; if (value < 1 || value > mon_maxnum[month.getValue() - 1]) return false; else return true; //日期加一 public void dayIncrement() value ++; //日期减一 public void dayReduction() value --; //package _05_5__; class DateUtil private Day day; public DateUtil() public DateUtil(int d, int m, int y) this.day = new Day(d, m, y); public Day getDay() return day; public void setDay(Day d) this.day = d; //检验数据是否合法 public boolean checkInputValidity() if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().validate() && this.getDay().getMonth().validate() && day.validate()) return true; else return false; //比较两个日期的大小 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() < this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return false; else if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && date.getDay().getMonth().getValue() < this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return false; else if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && date.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() && date.getDay().getValue() < this.getDay().getValue()) return false; else return true; //判定两个日期是否相等 public boolean equalDates(DateUtil date) if (this.getDay().getValue() == date.getDay().getValue() && this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getValue() && this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return true; else return false; //日期值格式化 public String showDate() return this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() + "-" + this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() + "-" + this.getDay().getValue(); //求下n天 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) int[] mon_maxnum = new int[]0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31; for (; n > 0; n--) if (day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else mon_maxnum[2] = 28; if (day.getValue() > mon_maxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()] - 1) if (day.getMonth().getValue() < 12) day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); day.resetMin(); else day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrease(); day.getMonth().resetMin(); day.resetMin(); else day.dayIncrement(); return new DateUtil(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(), day.getMonth().getValue(), day.getValue()); //求前n天 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) for (; n > 0; n--) if (day.getValue() > 1) day.dayReduction(); else if (day.getMonth().getValue() == 1) day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); day.getMonth().resetMax(); day.resetMax(); else day.getMonth().monthReduction(); day.resetMax(); return new DateUtil(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(), day.getMonth().getValue(), day.getValue()); private static int[] mon = //几个月之间的天数和 0, 31, 59, 90, 120, 151, 181, 212, 243, 273, 304, 334; //求两个日期之间的天数 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) DateUtil date1 = this; DateUtil date2 = date; if (this.equalDates(date)) //如果两天的日期相等 return 0; else if (!this.compareDates(date)) //如果日期大小不对 date1 = date; date2 = this; int[] mon_nummax = 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31; int i = 0, j = 0, days = 0; if(date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() < date2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() - 1) for (i = date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() + 1; i < date2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); i++) //两个日期之间有完整的间隔年,其日期数 days = days + 365; if (new Year(i).isLeapYear()) days++; if (date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && date1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == date2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) //年份相同,月份相同,日不同 days = days + (date2.getDay().getValue() - date1.getDay().getValue()); else if (date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && date1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() < date2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) //年份相同,月份不同 if (date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear())//是闰年 mon_nummax[1] = 29; days = days + mon_nummax[date1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1] - date1.getDay().getValue();//小日期该月剩余的天数 days = days + date2.getDay().getValue();//大日期的天数 for (j = date1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() + 1; j <= date2.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1; j++)//月份天数和 days += mon_nummax[j - 1]; //date1<date2 else if (date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && date1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() > date2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) //年份相同,月份不同 if (date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear())//是闰年 mon_nummax[1] = 29; days = days + mon_nummax[date2.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1] - date2.getDay().getValue();//小日期该月剩余的天数 days = days + date1.getDay().getValue();//大日期的天数 for (j = date2.getDay().getMonth().getValue() + 1; j <= date1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1; j++)//月份天数和 days += mon_nummax[j - 1]; //date1>date2 else if (date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() != date2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) //年份不同 days = days + mon_nummax[date1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1] - date1.getDay().getValue();//小日期在该月剩余的天数 days = days + date2.getDay().getValue();//大日期在该月已经过的天数 for (j = date1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() + 1; j <= 12; j++)//小日期在该年剩余的天数 days = days + mon_nummax[j - 1]; for (j = date2.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1; j > 0; j--)//大日期在该年已经过的天数 days = days + mon_nummax[j - 1]; if (date1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() && date1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() <= 2)//如果小日期该年为闰年且该天在1月或2月 days++; if (date2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() && date2.getDay().getMonth().getValue() > 2)//如果大日期该年为闰年且该天在1月或2月后 days++; return days;
分析:按照题给类图搭起框架,发现相对难写的不是算法,是各种调用。算法按之前的改了改,新写出来的日期差的逻辑是:先判断日期是否同样,同样返回零即零天,不同则进算法,分多层判断年、月、日的大小,按有无整年差整月差和碎天数来加日期。做这题体验了一把模块化的清晰也感受到了高耦合的离谱和诡异。这题耦合度真的太高,类图生成出来直接是链式,好夸张。
05-7-6
源码数据:

类图:
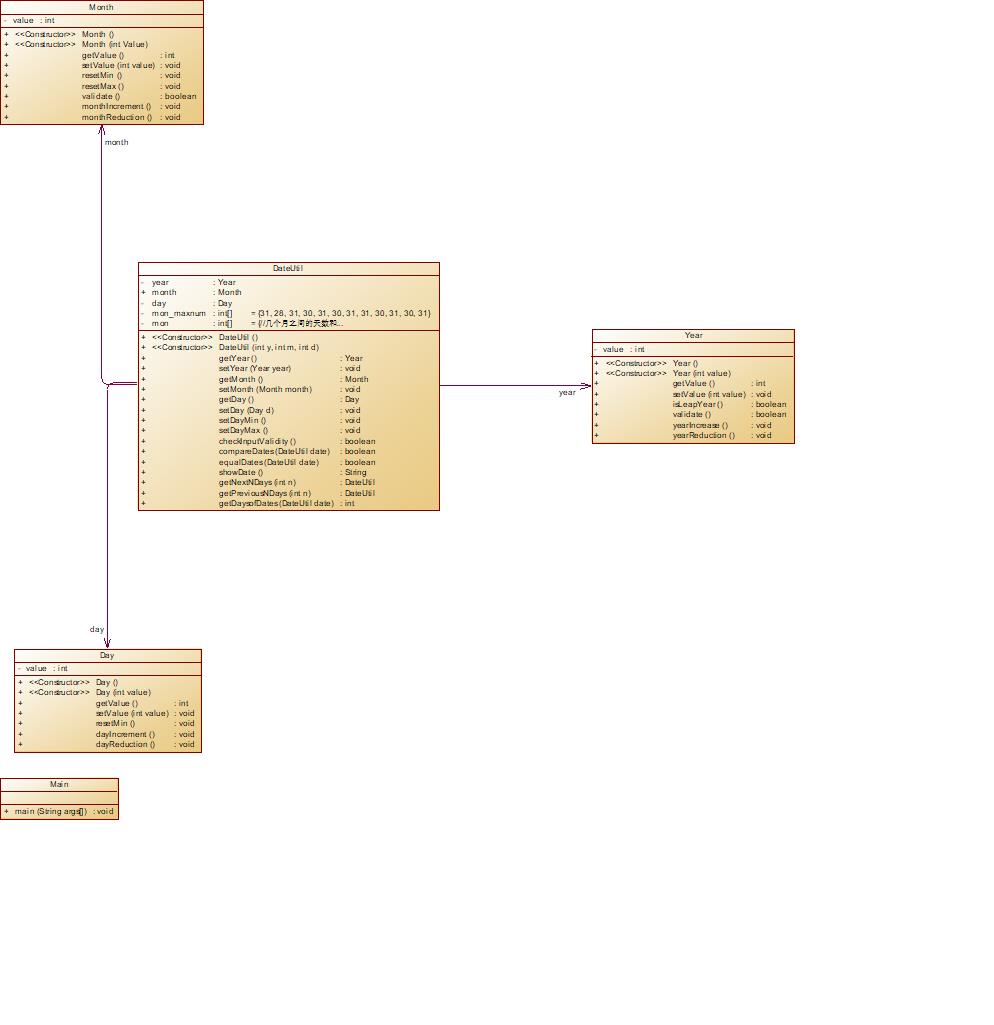
源码:
//package _05_6__; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main public static void main(String[] args) Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int year1, month1, day1; int year2, month2, day2; int number = in.nextInt(); if(number < 1 || number > 3) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); else if (number == 1) //下n天 year1 = in.nextInt(); month1 = in.nextInt(); day1 = in.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year1, month1, day1); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); else int m = in.nextInt(); System.out.println(year1 + "-" + month1 + "-" + day1 + " next " + m + " days is:" +date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); else if (number == 2) //前n天 year1 = in.nextInt(); month1 = in.nextInt(); day1 = in.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year1, month1, day1); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) //检查日期是否合法 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); else int n = in.nextInt(); if(n < 0) //日期越界情况 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); System.out.println(year1 + "-" + month1 + "-" + day1 + " previous " + n + " days is:" +date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); else //两天之间相差的天数 year1 = in.nextInt(); month1 = in.nextInt(); day1 = in.nextInt(); year2 = in.nextInt(); month2 = in.nextInt(); day2 = in.nextInt(); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year1, month1, day1); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(year2, month2, day2); if (!fromDate.checkInputValidity() || !toDate.checkInputValidity()) //检查日期的合法性 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); else System.out.println("The days between " + year1 + "-" + month1 + "-" + day1 + " and " + year2 + "-" + month2 + "-" + day2 + " are:" + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); //package _05_6__; class Year private int value; public Year() public Year(int value) this.value = value; public int getValue() return value; public void setValue(int value) this.value = value; //判断是否为闰年 public boolean isLeapYear() if((value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0) || value % 400 == 0) return true; else return false; //校验数据合法性 public boolean validate() if(value < 1820 || value > 2020) return false; else return true; //年份加一 public void yearIncrease() value++; //年份减一 public void yearReduction() value--; //package _05_6__; class Month private int value; public Month() public Month(int Value) this.value = Value; public int getValue() return value; public void setValue(int value) this.value = value; //月份复位(1) public void resetMin() value = 1; //月份设置为12 public void resetMax() value = 12; //检验数据合法性 public boolean validate() if(value < 1 || value > 12) return false; else return true; //月份加一 public void monthIncrement() value ++; //月份减一 public void monthReduction() value --; //package _05_6__; class Day private int value; //private int[] mon_maxnum =31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31; public Day() public Day(int value) this.value = value; public int getValue() return value; public void setValue(int value) this.value = value; //日期复位1 public void resetMin() value = 1; //日期加一 public void dayIncrement() value ++; //日期减一 public void dayReduction() value --; //package _05_6__; class DateUtil private Year year; public Month month; private Day day; private int[] mon_maxnum =31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31; public DateUtil() public DateUtil(int y, int m, int d) this.year = new Year(y); this.month = new Month(m); this.day = new Day(d); public Year getYear() return year; public void setYear(Year year) this.year = year; public Month getMonth() return month; public void setMonth(Month month) this.month = month; public Day getDay() return day; public void setDay(Day d) this.day = d; public void setDayMin() day.setValue(1); //日期设为本月最大值 public void setDayMax() if(this.getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[1] = 29; day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue() - 1]); //检验数据是否合法 public boolean checkInputValidity() if (this.getYear().validate() && this.getMonth().validate()) return true; else return false; //比较两个日期的大小 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) if (date.getYear().getValue() < this.getYear().getValue())//不同年 return false; else if (date.getYear().getValue() == this.getYear().getValue() && date.getMonth().getValue() < this.getMonth().getValue()) return false;//同年不同月 else if (date.getYear().getValue() == this.getYear().getValue() && date.getMonth().getValue() == this.getMonth().getValue() && date.getDay().getValue() < this.getDay().getValue())//同年同月日期一小于二 return false; else return true; //判定两个日期是否相等 public boolean equalDates(DateUtil date) if (this.getDay().getValue() == date.getDay().getValue() && this.getMonth().getValue() == date.getMonth().getValue() && this.getYear().getValue() == date.getYear().getValue()) return true; else return false; //日期值格式化 public String showDate() return this.getYear().getValue() + "-" + this.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + this.getDay().getValue(); //求下n天 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) int[] mon_maxnum = new int[]0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31; for (; n > 0; n--) if (year.isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else mon_maxnum[2] = 28; if (day.getValue() > mon_maxnum[month.getValue()] - 1) if (month.getValue() < 12) month.monthIncrement(); day.resetMin(); else year.yearIncrease(); month.resetMin(); day.resetMin(); else day.dayIncrement(); return new DateUtil(year.getValue(), month.getValue(), day.getValue()); //求前n天 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) for (; n > 0; n--) if (day.getValue() > 1) day.dayReduction(); else if (month.getValue() == 1) year.yearReduction(); month.resetMax(); setDayMax(); else month.monthReduction(); setDayMax(); return new DateUtil(year.getValue(), month.getValue(), day.getValue()); int[] mon = //几个月之间的天数和 0, 31, 59, 90, 120, 151, 181, 212, 243, 273, 304, 334; //求两个日期之间的天数 //求两个日期之间的天数 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) DateUtil date1 = this; DateUtil date2 = date; if (this.equalDates(date)) //如果两天的日期相等 return 0; else if (!this.compareDates(date)) //如果日期大小不对 date1 = date; date2 = this; int[] mon_nummax = 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31; int i = 0, j = 0, days = 0; if(date1.year.getValue() < date2.year.getValue() - 1) for (i = date1.year.getValue() + 1; i < date2.year.getValue(); i++) //两个日期之间有完整的间隔年,其日期数 days = days + 365; if (new Year(i).isLeapYear()) days++; if (date1.year.getValue() == date2.year.getValue() && date1.month.getValue() == date2.month.getValue()) //年份相同,月份相同,日不同 days = days + (date2.getDay().getValue() - date1.getDay().getValue()); else if (date1.year.getValue() == date2.year.getValue() && date1.month.getValue() < date2.month.getValue()) //年份相同,月份不同 if (date1.year.isLeapYear())//是闰年 mon_nummax[1] = 29; days = days + mon_nummax[date1.month.getValue() - 1] - date1.getDay().getValue();//小日期该月剩余的天数 days = days + date2.getDay().getValue();//大日期的天数 for (j = date1.month.getValue() + 1; j <= date2.month.getValue() - 1; j++)//月份天数和 days += mon_nummax[j - 1]; //date1<date2 else if (date1.year.getValue() == date2.year.getValue() && date1.month.getValue() > date2.month.getValue()) //年份相同,月份不同 if (date1.year.isLeapYear())//是闰年 mon_nummax[1] = 29; days = days + mon_nummax[date2.month.getValue() - 1] - date2.getDay().getValue();//小日期该月剩余的天数 days = days + date1.getDay().getValue();//大日期的天数 for (j = date2.month.getValue() + 1; j <= date1.month.getValue() - 1; j++)//月份天数和 days += mon_nummax[j - 1]; //date1>date2 else if (date1.year.getValue() != date2.year.getValue()) //年份不同 days = days + mon_nummax[date1.month.getValue() - 1] - date1.getDay().getValue();//小日期在该月剩余的天数 days = days + date2.getDay().getValue();//大日期在该月已经过的天数 for (j = date1.month.getValue() + 1; j <= 12; j++)//小日期在该年剩余的天数 days = days + mon_nummax[j - 1]; for (j = date2.month.getValue() - 1; j > 0; j--)//大日期在该年已经过的天数 days = days + mon_nummax[j - 1]; if (date1.year.isLeapYear() && date1.month.getValue() <= 2)//如果小日期该年为闰年且该天在1月或2月 days++; if (date2.year.isLeapYear() && date2.month.getValue() > 2)//如果大日期该年为闰年且该天在1月或2月后 days++; return days;
分析:0575的迭代,改了类间关系,一开始看两版类图笔者才疏学浅没太大感觉,写起来,0575你这样设计在公司会被开了的吧。算法一模一样所以不提,类间设计图给得很清晰很舒服,照着填空真的轻松设计类是真累……一个这版没过上版过了的测试点,debug了,没de出来……错,在改。
06-7-1
源码数据:

类图:
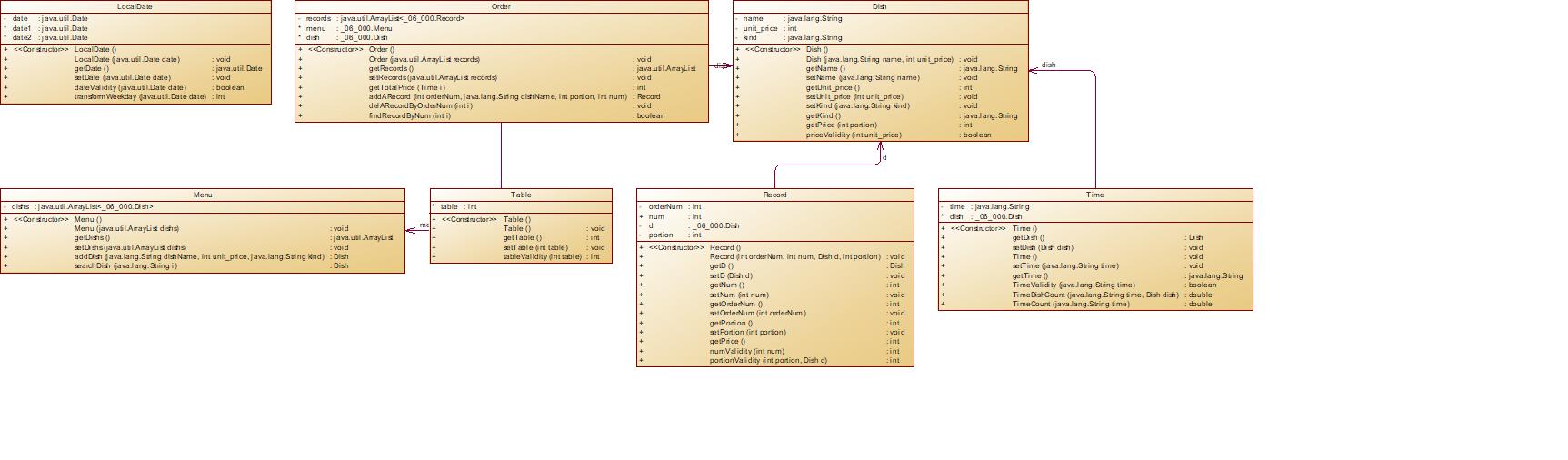
源码:
package _06_000; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.*; public class Main public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); Dish dish = new Dish(); LocalDate localDate = new LocalDate(); Menu menu = new Menu(); Order order = new Order(); Record record = new Record(); Table table = new Table(); Time time = new Time(); //只输出WrongFormat的单独拎出来判断,终止进程System.exit(0) String[] ordermenu = new String[100];//序号最多五十五,但是还有别的信息 int i = 0; boolean flag1 = true; while (true) String information = in.nextLine();//暂时存放每行信息 if (information.equals("end")) //end一单结尾 break; ordermenu[i] = information;//每一行一个信息存进数组 i ++; int pause = 0; boolean flag0 = false; //每一道菜品记录于菜谱 for(int j = 0; j < ordermenu.length; j ++) if(ordermenu[j].split(" ")[0].equals("table")) flag0 = true; if (flag0) pause = j;//结束菜谱输入,暂停,下个循环以此为起始点 break; else dish.setName(ordermenu[j].split(" ")[0]);//分割后第零个小字符串是名字 //判断是否为浮点数:转化为字符数组,看有没有小数点 char[] CheckChar; boolean flag2 = true; for (int p = 0; p < ordermenu[j].split(" ")[1].length(); p ++) CheckChar = ordermenu[j].split(" ")[1].toCharArray(); if(CheckChar[0] == \'0\') System.out.println("wrong format"); System.exit(0); else if(CheckChar[p] == \'.\') flag2 = false; break; if(!flag2) System.out.println("wrong format"); break; else dish.setUnit_price(Integer.parseInt(ordermenu[j].split(" ")[1]));//价格 //有些没有T,那里是空,就会数组越界 if(ordermenu[j].split(" ").length == 2) dish.setKind("N"); else if(ordermenu[j].split(" ").length == 3) dish.setKind("T");//特色菜 if(!dish.priceValidity(dish.getUnit_price())) System.out.println(dish.getName() + " price out of range " + dish.getUnit_price()); menu.addDish(dish.getName(), dish.getUnit_price(), dish.getKind());//添加进菜谱里 //每次以table为开始的一桌点菜, for (int j = pause; j < ordermenu.length; j ++) //j-table // 时间日期格式不对输出错误后直接终止,先判断 for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) if(ordermenu[j] == null) break; else if(ordermenu[j].split(" ")[3].split("/")[k].length() > 2 || ordermenu[j].split(" ")[3].split("/")[k].length() < 1) System.out.println("wrong format"); System.exit(0); //时间格式错误直接结束 if(ordermenu[j] == null) break; else time.setTime(ordermenu[j].split(" ")[3]);//输入时间 if(!time.TimeValidity(time.getTime())) System.out.println("table" + table.getTable() + "out of opening hours"); //不在营业时间 //字符串转日期 SimpleDateFormat datestring = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd"); for(int k = 1; k < 3; k ++) if((ordermenu[j].split(" ")[2].split("/")[k].length() > 2 || ordermenu[j].split(" ")[2].split("/")[k].length() < 1) || ordermenu[j].split(" ")[2].split("/")[0].length() != 4) System.out.println("wrong format"); System.exit(0); //日期格式错误直接结束 localDate.setDate(datestring.parse(ordermenu[j].split(" ")[2])); ///时间区域????? if(localDate.dateValidity(localDate.getDate())) System.out.println("not a valid time period"); //日期非法 if(ordermenu[pause].split(" ")[0].equals("table"))//第一个词是table if(Character.isDigit(ordermenu[j].split(" ")[1].charAt(0)))//桌号输入第一个数是数字 table.setTable(Integer.parseInt(ordermenu[j].split(" ")[1]));//桌号 if(table.tableValidity(table.getTable()) == 0)// System.out.println(table + "table num out of range"); else if(ordermenu[j].split(" ")[1].startsWith("0")) System.out.println("wrong format"); System.exit(0); else System.out.println("table " + table.getTable() + ": "); else System.out.println("wrong format"); System.exit(0); else System.out.println("wrong format");//不是table //table行输入结束,开始点菜 for (int k = pause + 1; k < ordermenu.length; k ++, j ++) if (ordermenu[k] == null) break; else record.setOrderNum(Integer.parseInt(ordermenu[k].split(" ")[0]));//序号 //序号必须从小到大"record serial number sequence error"————待 if (ordermenu[k].split(" ")[1].equals("delete")) if (order.findRecordByNum(Integer.parseInt(ordermenu[k].split(" ")[0]))) //序号不存在 System.out.println("delete error");//删除记录序号不存在 else order.delARecordByOrderNum(record.getOrderNum()); if (ordermenu[k].equals(ordermenu[k + 1])) System.out.println("deduplication " + ordermenu[k].split(" ")[0]); //重复删除 //输入删除 else if (menu.searchDish(ordermenu[k].split(" ")[1]). getName().equals(ordermenu[k].split(" ")[1])) record.setD(menu.searchDish(ordermenu[k].split(" ")[1]));//点菜 if(record.portionValidity(record.getPortion()) == -1) //份额为两位 System.out.println("wrong format"); System.exit(0); record.setPortion(Integer.parseInt(ordermenu[k].split(" ")[2]));//份额 if(ordermenu[k].split(" ")[3].startsWith("0")) //份数以0开头 System.out.println("wrong format"); System.exit(0); record.setNum(Integer.parseInt(ordermenu[k].split(" ")[3]));//份数 // order.addARecord(record.getOrderNum(), record.getD().getName(), // record.getPortion(), record.getNum()); if (record.numValidity(record.getNum()) == 0) System.out.println(record.getOrderNum() + " num out of range " + record.getNum()); //份数合法性 if (record.portionValidity(record.getPortion()) == 0) System.out.println(record.getOrderNum() + " portion out of range " + record.getPortion()); //份额数据合法性????? if (record.numValidity(record.getNum()) == 1 && record.portionValidity(record.getPortion()) == 1) System.out.println(record.getOrderNum() + " " + record.getD().getName() + " " + record.getD().getUnit_price() * record.getNum()); //输入的是菜谱里有的菜 else System.out.println("wrong format"); System.exit(0); //————应该只输出wrongformat if (ordermenu[k].split(" ")[0].equals("end")) break; System.out.printf("table %d: %d %.0f", table.getTable(), order.getTotalPrice(time), order.getTotalPrice(time) * time.TimeCount(time.getTime(), dish)); static class LocalDate private Date date = new Date();//eg.2023/15/16 //private String date; Date date1 = new Date(2022, 1,1); Date date2 = new Date(2023,12,31); public LocalDate() // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub public void LocalDate(Date date) this.date = date; public Date getDate() return date; public void setDate(Date date) this.date = date; public boolean dateValidity(Date date) if (date.after(date1) && date.before(date2)) return true; else return false; public int transformWeekday(Date date) //日期转换为周几 int[] weekDays = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7; Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); cal.setTime(date); int weekday = cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK) - 1; if (weekday < 0) weekday = 0; return weekDays[weekday]; //菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。 static class Dish private String name;//菜品名称 private int unit_price; //单价 private String kind;//是否是特色菜 //Time time = new Time(); public Dish() public void Dish(String name, int unit_price) this.name = name; this.unit_price = unit_price; public String getName() return name; public void setName(String name) this.name = name; public int getUnit_price() return unit_price; public void setUnit_price(int unit_price) this.unit_price = unit_price; public void setKind(String kind) this.kind = kind; public String getKind() return kind; public int getPrice(int portion) //一个菜确定大小和时间后的单价 if(portion == 2) unit_price = (int) (Math.ceil(unit_price * 1.5)); else if(portion == 3) unit_price = (int) (Math.ceil(unit_price * 2.0)); return unit_price; //计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) public boolean priceValidity(int unit_price) if (unit_price <= 0 || unit_price >= 300) return false; else return true; //菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。 static class Menu //Dish[] dish; private ArrayList<Dish> dishs = new ArrayList<Di第一次博客:PTA题目集1-3总结
第一次博客:PTA题目集1-3总结前言:JAVA是一门非常好的语言,因其面向对象的思想,在解决问题时思路与上学期学习的C语言截然不同,但是其优势也是显然易见的,特别是在写大型程序时其面向对象的思想,可以让人思路清晰。
这次PTA中三个“菜单计价”的题目让刚刚学习JAVA的我感到无力,但是在一阵磕磕碰碰之后终于还是解决了问题,以下是对题目的一些分析与总结:这几次的题目量以及难度按老师的说法是和上一届比简单了许多,但是突然使用一种新的编程语言和编程方式进行编程还是相当困难的。
题目概述:
第一次:虽然有9题但是总的来说题目不算难并没有用到“类”的思想,其主要目的是让我们熟悉JAVA语言的基本使用,以及各种类库的基本使用。
以下是各题的知识点考察:
知识储备:1.使用Scanner输入以及System.out输出 2.不同类型的变量的定义以及输入 3.类库的简单使用。
7-1 身体质量指数(BMI)测算 7-2 长度质量计量单位换算 7-4 房产税费计算2022 7-5 游戏角色选择:考察简单的输入(注意:输入为浮点型)以及条件判断(if—else)和输出。
7-3 奇数求和:考察在循环中进行输入和判断以及求合操作。
7-6 学号识别 7-9 二进制数值提取:考察(String)字符串操作类(substring,length,charAt)的使用。
7-8 巴比伦法求平方根近似值:考察(Math)类(abs)求绝对值的使用的使用。
7-7 判断三角形类型:考察判断的嵌套(分好类可以打的很漂亮)以及浮点类型数比较(需要设定精度)。
第二次:从这次开始上难度了!!!蔡老师开始向你展示JAVA的限额,但是困难总是伴随着成长,那些打不倒你的,只会使你变的更加强大;
知识储备:1.对类与方法的基础使用 2.日期类的简单使用 3简单算法的使用 4类型转换。
这里可以窥见面向对象思想的雏形,特别是“菜单计价1,2”以及“7-3 jmu-java-日期类的基本使用”,还有那阴间的测试点折磨的我痛不欲生,还好我是 一个阳光开朗大男孩,在连续问了七八个大佬后终于还是做出来了。下面简单分析7-3,7-4 剩下两个为菜单系列后面会统一分析
7-3 jmu-java-日期类的基本使用
难度:中等。
考察对JAVA日期类的使用(Date、DateFormat、Calendar)都可以,其实真正难的是这题的类需要自己进行设计对于一个JAVA小白来说这简直就是”难于上青天“,且因为阴间的测试点,即使你的代码过了所有的测试点(例如:2022-10--1,如果使用字符串分割函数就会少一位导致后续判断失误)但是可能提交后一分也拿不到,而因为当时没有学习正则表达式,所以对输入的正确的判断变的十分困难——需要判断长度,是否为数字以及时间是否合法为此我还特意写了一个类。下面是我使用的(Calendar)以及正则表达式。
class 判断日期
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();//父类引用指向子类对象,右边的方法返回一个子类对象
void 日期(int year,int month,int day)
c.set(year,month-1,day);//设置时间
int a=c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR);
int b=c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
int d=c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
//星期天为1
if(d==1)
d=7;
else
d-=1;
System.out.printf("%04d-%02d-%02d是当年第%d天,当月第%d天,当周第%d天.\\n",year,month,day,a,b,d);
// 2021-02-28是当年第59天,当月第28天,当周第7天.
class 比较日期大小
Calendar c1 = Calendar.getInstance();//日期1
Calendar c2 = Calendar.getInstance();//日期2
void 比较(int year1,int month1,int day1,int year2,int month2,int day2)
c1.set(year1,month1-1,day1);
c2.set(year2,month2-1,day2);
int days = ((int)(c2.getTime().getTime()/1000)-(int)(c1.getTime().getTime()/1000))/3600/24;
System.out.printf("%d-%02d-%02d与%d-%02d-%02d之间相差%d天,所在月份相差%d,所在年份相差%d.\\n",year2,month2,day2,year1,month1,day1,days,month2-month1,year2-year1);
//2020-01-02与2019-08-01之间相差154天,所在月份相差-7,所在年份相差1.
注:输入月份要-1,因为(calendar)的月份是从第0月开始的,以及其星期天为第1天,所有需要进行转换操作
正则表达式:
String timeRegex2 = "([-9][[91[0-9[2[-91][0-9][0-9161][919-9121[910913(1((([5[18101(191][201013[01]))|*+"(146911)1)(01[0912]2101010)(2()01091010~1010)((-9]2)(0[48][2468]048][13579]126])[+(181][4161481][35791]3]0)))02\\29)$";
//写的有点麻烦不知可否简化
注:使用这个两行就可以解决问题
7-4 小明走格子:
难度:中等。
这题找到规律其实计算并不困难(走到第n格的方法数等于走到前四格的方法数的总和)我使用了递归,但是难的是解决运行超时的问题,这让我想到可以使用记忆化搜索(其原理为将之前的运算结果进行储存,使函数不会进行重复计算);
//b用于储存数据
static int[] b=new int[10009];
//d用于记忆化搜索//1为以有数据
static boolean[] d=new boolean[10009];//当d[n]为true时说明a[n]已经有数据不用重复进行运算
static int dfs(int x)
if(x==0)
return 1;
else if(x==1)
return 1;
else if(x==2)
return 2;
else if(x==3)
return 4;
else if(x==4)
return 8;
else
if(d[x])
return b[x];
else
d[x]=true;
b[x]=dfs(x-1)+dfs(x-2)+dfs(x-3)+dfs(x-4);
return b[x];
但是遗憾的是即使使用了记忆化搜索还是有一个测试点不能通过(出题老师把运行时卡的太死了),无奈只能求助于网络,其原因为使用(scanner)进行输入效率很低,应当改用(BufferedReader)进行输入,下面附上相应代码;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;BufferedReader in=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n=0;
tryn = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
注意:确实非常麻烦但是其效率是(scannre)的两倍,以后有运行时问题可以考虑使用。
第三次:这次可谓是时间紧任务重,6天7题实在是有点困难不过相对与上一次这次每题(第1题除外)的平均代码量远小于上一次,其主要考察方向为集合以及各种方法的使用(即运行时问题为主要问题),做的时候一定要切记不能使用暴力求解!!!像我这样一个上学期C语言算法没有好好学的就深受其害。所有的这次的方法都是网上即学即用,只能说:CSDN YYDS。
知识储备:1.对集合有基本认识(没有学习的话会带上痛苦面具) 2.一些算法基本知识(所有语言的算法都是互通的) 3.对封装性有基本认识(类,属性,方法的公有与私有)。
7-2 有重复的数据:使用双循环明显是不明智的,这里建议使用sort或MAP判重 因为只需要判断是否重复不需要将原输入进行处理后输出所以无论是使用那一种都十分的方便。下面是我使用的sort 其原理为将数组使用二分法进行快速排序,之后只需要判断每一个元素与其下一个元素是否相等即可(一重循环)。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main
public static void main(String[] args)
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n;
数据处理 b=new 数据处理();
n=in.nextInt();
int[] a=new int[n];
boolean flag=true;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
a[i]=in.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a);//排序
b.排序(a);
b.查重(a);
if(flag)
System.out.println("NO");
else
System.out.println("YES");
class 数据处理
int[] 排序(int[] a)
Arrays.sort(a);
return a;
boolean 查重(int[] a)
for(int i=0;i<len-1;i++)
if(a[i]==a[i+1])
return false;
return true;
看似完美但是我忽略了一个重要的问题(内存),于是我带上了痛苦面具,在一番深思熟虑后我发现了问题所在每次无论是使用“数据处理”中的 “排序” 还是“查重”方法都要开一个与a[]等大的数组导致内存超限。于是乎我将 “数据处理”类并入main中解决了这因为画蛇添足导致的问题。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main
public static void main(String[] args)
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n;
// 数据处理 b=new 数据处理();
n=in.nextInt();
int[] a=new int[n];
boolean flag=true;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
a[i]=in.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a);//排序
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)
if(a[i]==a[i+1])
flag= false;
break;
if(flag)
System.out.println("NO");
else
System.out.println("YES");
事实证明不要整花活!!!
7-3 去掉重复的数据:这题就是7-2plus,要求去除重复数据并输出,明显是不能使用sort了,但是观察数据为数字所以可以考虑使用数组标记法(多开一个标记数组,输入a[i],b[a[i]]++,这样子只需要检测b[a[i]]是否为1,即可判断是否需要进行输出 )但是容易爆内存。所以这里我选择使用LinkedHashSet为什么不能使用Set呢???因为题目要求按原来的数据进行输出而Set,HashSet内存放的数据都是无序的(与输入顺序不同)而LinkedHashSet内部的数据是有序的(与输入顺序相同)下面是基本使用方法。
//定义
Set<String> set = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
//添加元素
set.add(a);
//使用迭代器输出
Iterator<String> iter = set.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext())
System.out.print(" "+iter.next()); //输出是有序的
7-4 单词统计与排序 一个典型的自定义排序问题,但是在输入处理这块就把我难住了,同时使用"," " " "."进行字符串分割,直接a=in.nextLine();String[] arr = a.split(" |,|.");当两个分割标志同时出现时会有多余字符出现如输入样例中同时有“,和 空格”会导致数组中会有一个空格多余而导致大错误。所以我先使用空格进行分割,之后使用循环遍历所有字符去除"."和","(注:千万不能先排序,然后在输出的时候去除"."和",",这样子的话"hello."将会和"hello"被视为相同的字符串)某个大聪明(指我自己)犯了这种低级错误。
如果是C语言的话我会用sort重构compare函数进行排序然后进行去重,当然JAVA也可以怎么做,但是我想试试集合TreeSet重构排序解决问题。下面是ThreeSet的简单使用以及重载函数的写法
//定义:
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<String>(new SortDescending());//使用自定义排序
//添加元素
set.add(b);
//重载比较方法
class SortDescending implements Comparator //自定义排序
@Override//重载方法标志
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2)
String s1 = (String) o1;
String s2 = (String) o2;
if(s1.length()>s2.length())//按长度比较
return -1;
else if(s1.length()<s2.length())
return 1;
else //长度相等
return s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2);//按字典序比较//不分大小写
7-5 面向对象编程(封装性):考察构造方法的使用,难度偏低,唯一要注意的点是:写了有参构造方法会覆盖掉原来自带的无参构造方法,所以需要再手写一个无参构造方法以保证可以使用无参构造方法构造对象
7-6 GPS测绘中度分秒转换:这个题目主要考察格式化输出,但是如果全部采用格式化输出 "秒" 将不能保持与输入位数相等,所以解题思路为“度”“分”“秒”使用普通输出方式进行输出(print),结果使用格式输出(printf)以控制6位小数。
7-7 判断两个日期的先后,计算间隔天数、周数:这题的方法在 第二次作业7-3 jmu-java-日期类的基本使用 中讲过这里就不再赘述了,但是有一点值得注意的是如果使用的是(Date、DateFormat)类进行求解,因为其时间输入格式要求所以应当将输入转换为统一格式(2022-6-6>>2022-06-06)。
菜单系列
这是蔡老师对我们全体学生的爱,麻婆豆腐 12 油淋生菜 9 想必所有同学都以及烂熟于心了吧。按老师的说法,这比上一届的三角形简单一些,而且蔡老师贴心的为我们先写好了框架,我们最重要做的是对类中方法的调度,作为一个初学JAVA的新手,这过于复杂的题目曾一度让我想要放弃,无数次非零返回,答案错误,段错误,让我带上了痛苦面具,不过在鏖战了几天几夜之后我还是勉强将其做了出来。下面我将一一介绍这三座大山的不同难度以及特点。
知识储备:1.对JAVA类初步认识 2.类的设计 3.类中方法的设计 4.对象的使用
菜单计价程序-1 这是这个系列的第一题难度当然是比不上后面俩题,但是正所谓万事开头难,这复杂的类间关系,和我那浅薄的知识量,CPU烧了!!!不过通过这题我对JAVA类的创建和调度已经算是初窥门径,所有没有压力就没有动力,人的潜能是被逼出来的。
过程非常的简单用户输入点菜,计价,输出,计算总价,要是不用面向对象的思想,使用面向过程的方法我很快就可以将其写成,但是使用面向对象我就不行了,下面我简单介绍一下我认为得各个类的作用和类间的调度与交流。
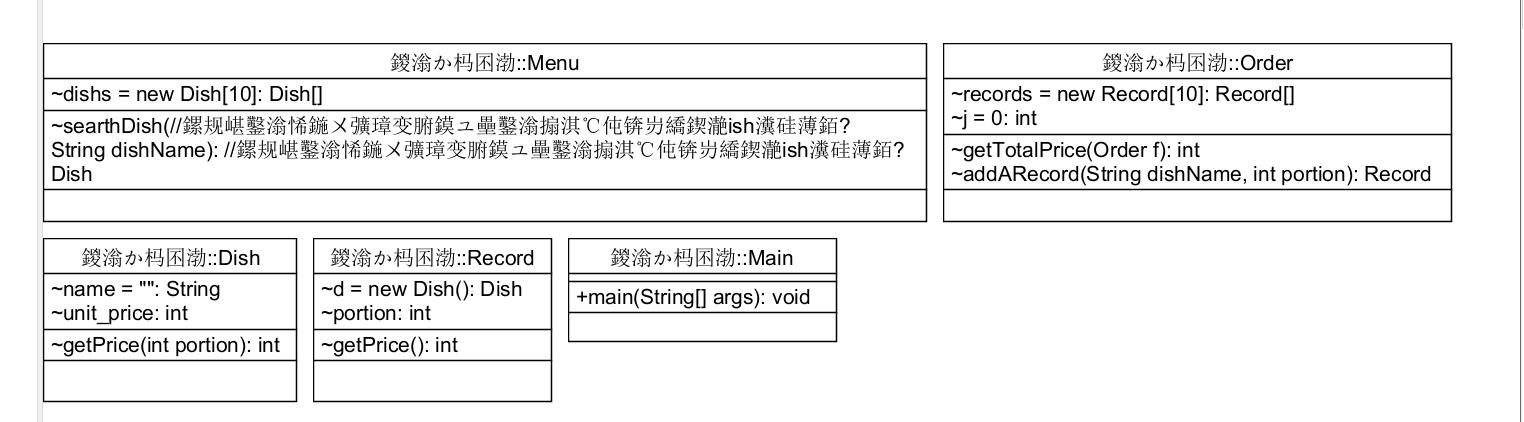
1.Dish 菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。没有在主类中直接使用,但是菜单和点菜记录都要依赖于它,其中的getPrice(int portion)方法是于点菜记录中的getPrice()方法对应的。
2.Menu 菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。内有一个Dish类的对象数组用于存菜单内的菜,以及一个Dish类型的方法 searthDish(String dishName)用于配合点菜记录进行查找比对,并返回这道菜(内含有该菜的价格)用于后续计算
3.Record :点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录,配合Menu类里的searthDish(String dishName)和Dish类里的getPrice(int portion)计算菜品的价格
4.Order:订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。 内含Record数组用于储存订单信息,getTotalPrice()/方法/计算订单的总价,addARecord(String dishName,int portion)用于输入
大体流程:循环输入以“end”作为结束标记,使用Order类的addARecord(String dishName,int portion)方法存入订单中,使用循环遍历订单并使用Menu中的 searthDish(String dishName)方法进行比对做出相应的输出,最后使用Order类的getTotalPrice()计算总价。
一些技巧:1.计算要求四舍五入,但是对于本题没有可以直接对“西红柿炒蛋 15”和 “油淋生菜 9”进行特殊处理,即计算结果加1;
2.在点菜时点到菜单没有的菜时searthDish(String dishName)可以返回null,然后通过判断返回值进行相应输出,也可以在返回null前进行输出“菜不存在”。
菜单计价程序-2这比菜单1多加了菜单写入,以及删菜的功能,如果上一题,打的思路清晰,明明白白的话这题就不会很难,由于很多重复的地方所有这里仅讲解不同的部分。
2.Menu 菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。内有一个Dish类的对象数组用于存菜单内的菜,addDish(String dishName,int unit_price)方法用于将输入的菜品存入菜单,以及一个Dish类型的方法 searthDish(String dishName)用于配合点菜记录进行查找比对,并返回这道菜(内含有该菜的价格)用于后续计算。
4.Order:订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。 内含Record数组用于储存订单信息,getTotalPrice()/方法/计算订单的总价,addARecord(String dishName,int portion)用于输入,delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)用于删除订单内的菜品。
大体流程:循环输入以“end”作为结束标记,将输入进行分类,创建菜单时使用Mneu类的addDish(String dishName,int portion)方法储存菜单信息,点菜时使用Order类的addARecord(String dishName,int portion)方法存入订单中,使用循环遍历订单并使用Menu中的 searthDish(String dishName)方法进行比对做出相应的输出,删菜时使用Order类中的delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)方法进行删除并做出相应删除,最后使用Order类的getTotalPrice()计算总价。
一些技巧:1.输入后使用字符串分割函数进行分割(String[] arr = a.split(" ");),之后使用(arr.length)判断数组内元素个数,若为4则为点菜,若为2则判断第二个元素是否 为delete若是则为删菜,否则为加菜到菜谱中。
2.计算要求四舍五入(不能像上面那样投机取巧)因只有五入所以可以直接向上取整((int)Math.ceil(1.0*unit_price*3/2);。
3.删除菜品的时候因为点菜都有编号(且为递增的)所以可以直接与订单数进行比较判断该删除序号是否存在
4.删除菜品的时候可以返回菜品价格之后在计算总价的时候减去,也可以直接将订单中该菜的份数(或价格)改为0。
5.遍历菜单时倒序遍历可以保证读到的是最新的菜信息
菜单计价程序-3在2的基础上加入了,桌,以及待点菜,还有营业时间的判定。感觉一下子就复杂起来了,而且桌类需要我们自己设计,吐槽一下:这题的题目有问题,结束时间应该是21:30,题目上写的是21:00搞的我想跳楼。其他确实没有什么太大的变化,主要就是桌类的设计。下面简单介绍一下我的设计思路。
Table:桌类需要有这一桌的所有信息,所以属性有(
int tablenum;//桌号
String time;//点菜时间
int year=0,month=0,day=0,ww=0,hh=0,mm=0,ss=0;
boolean flag=true;//判断时间是否正确
double count=0;//折扣
Order selforder=new Order();//本桌订单),而方法有对时间的处理,判断营业与折扣,计算总价。
大体流程:首先创建一个Table类的数组,循环输入以“end”作为结束标记,将输入进行分类,创建菜单时使用Mneu类的addDish(String dishName,int portion)方法储存菜单信息,加桌的时候将信息存入Table类的数组中的time属性中,点菜时使用Table对象中Order类的addARecord(String dishName,int portion)方法存入订单中(待点菜与其相同),使用循环遍历订单并使用Menu中的 searthDish(String dishName)方法进行比对做出相应的输出,删菜时使用Order类中的delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)方法进行删除并做出相应删除,最后使用Table对象的getTotalPrice()计算总价并做出相应输出。
一些技巧:1.判断是否在营业时间时,可以将Table类中中的count//折扣初始化为0,首先计算折扣,若折扣为0则判断为不在营业设计。
2.四舍五入sum=(int)(sum*count+0.5);用这个就可以了
下面附上我的折扣计算:
void jscount()//运用时间计算折扣
if(ww>=1&&ww<=5)
if(hh>=17&&hh<20)
count=0.8;
else if(hh==20&&mm<30)
count=0.8;
else if(hh==20&&mm==30&&ss==0)
count=0.8;
else if(hh>=11&&hh<=13||hh==10&&mm>=30)
count=0.6;
else if(hh==14&&mm<30)
count=0.6;
else if(hh==14&&mm==30&&ss==0)
count=0.6;
else
if(hh>=10&&hh<=20)
count=1.0;
else if(hh==9&&mm>=30)
count=1.0;
else if(hh==21&&mm<30||hh==21&&mm==30&&ss==0)
count=1.0;
菜单系列踩坑心得(这世上本没有坑,踩的人多了就成了坑)
1.可以去elicpice上测试,但是搞完复制回PTA一定一定要把package删了,以及主类改为Main,会非零返回。
2.使用数组元素时一定要先nuw
3.对象第一次new了之后,无论在那都不要再new了不然会变成null
4.访问数组不能越界,会有段错误
5.只要不是void类型的方法一定要保证所有情况都有返回值,会非零返回
6.不能在定义属性的地方使用方法,如7-1中对菜单的初始化
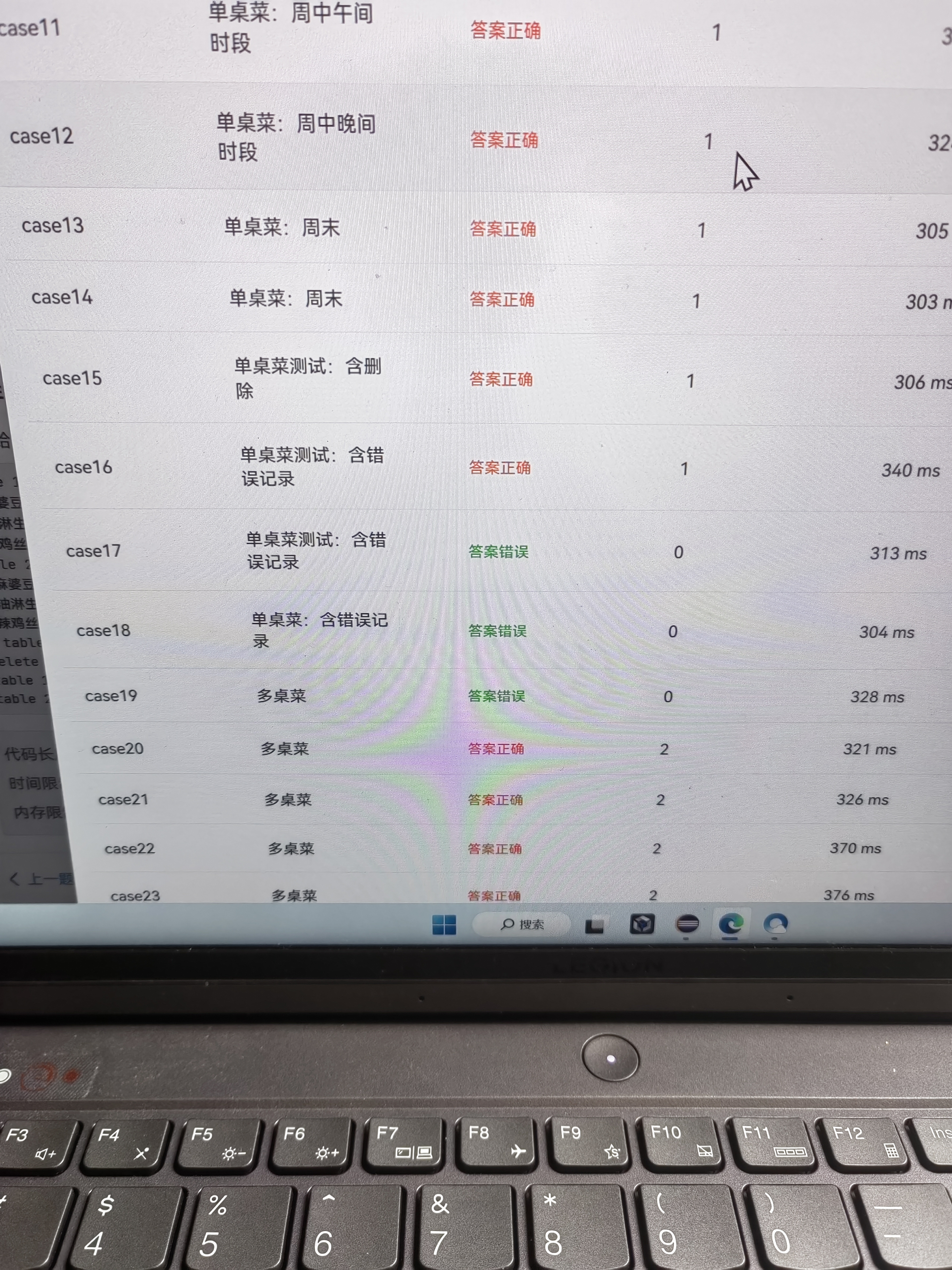
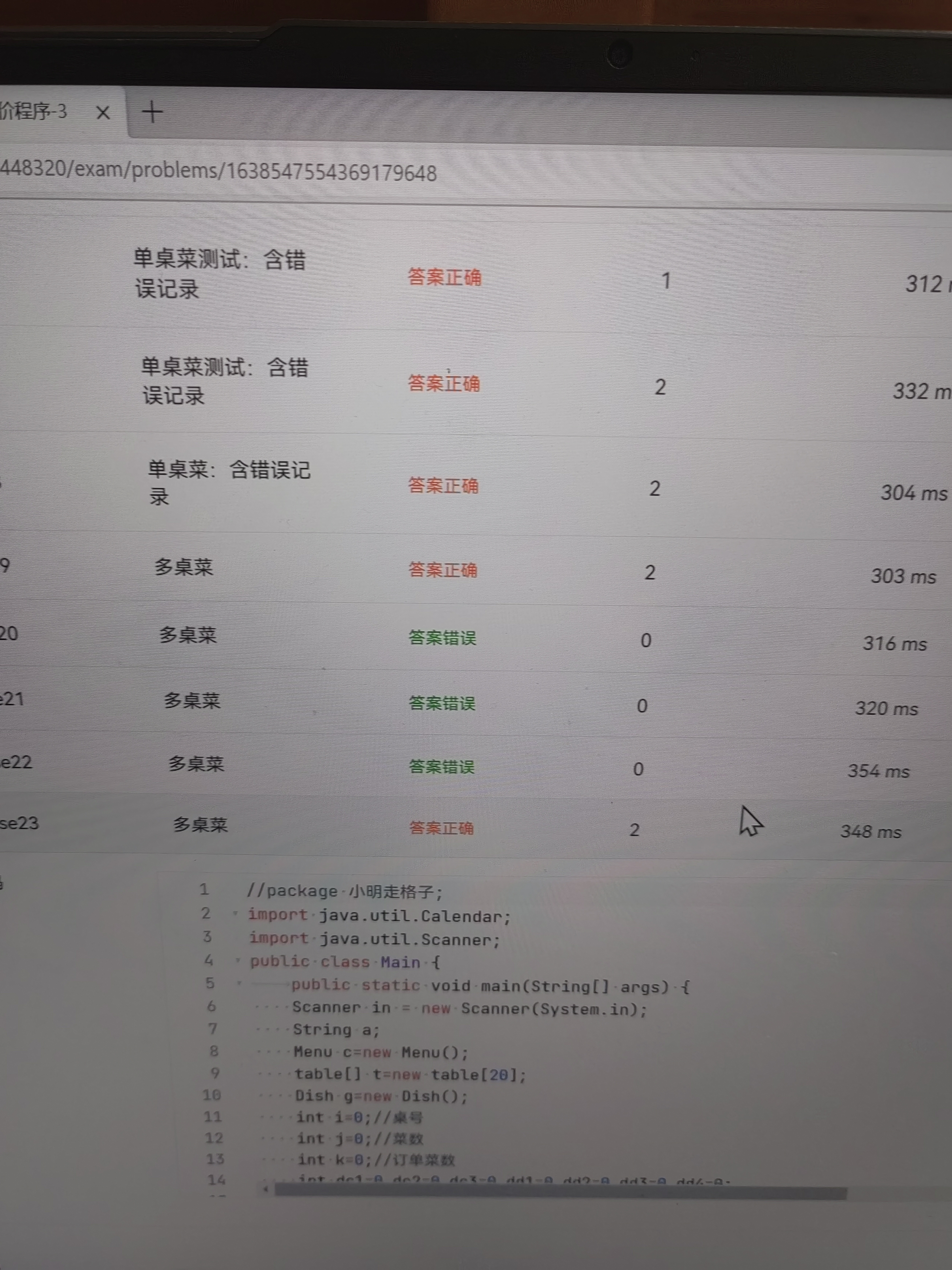
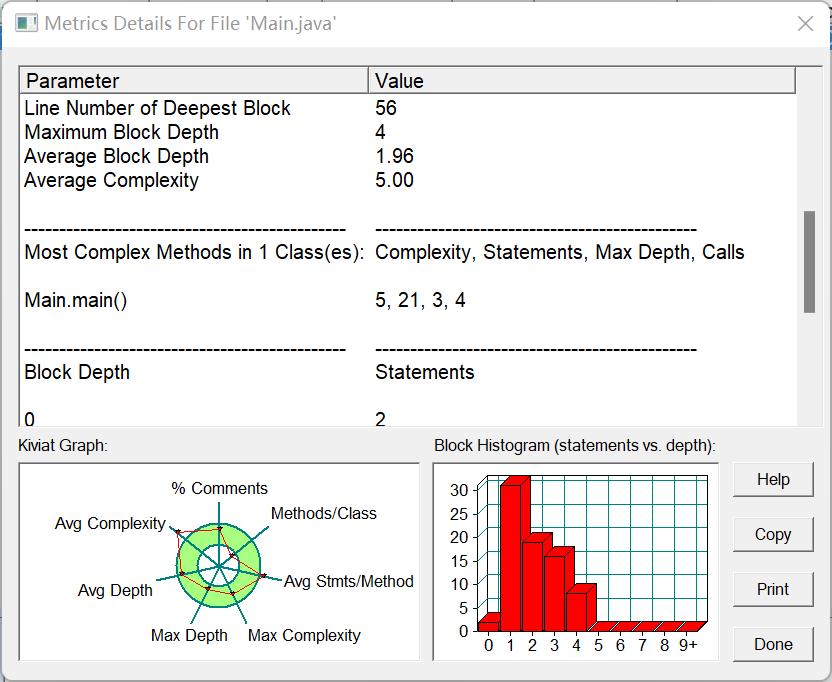
7.一些超时可能是圈复杂度过高,或循环没有出口下面是我的第三个菜单的圈复杂度
8.7-3一定要注意方法的重复执行(对同一道菜算了两次单价),否则会运行超时,好的解决方法是,在Table类中加入sum属性用于计算总价(每次算完单价后直接加)
t[i-1].selforder.addARecord(dd1, dd2, arr[2], dd3,dd4);
g=c.searthDish(arr[2]);
if(g!=null)
t[i-1].selforder.records[k].d=g;
int x=t[i-1].selforder.records[k].getPrice();
//4 table 2 pay for table 1 12
System.out.println(dd2+" table "+i+" pay for table "+dd1+" "+x);
t[i-1].sum+=x;
k++;
总结:
通过这三次PTA大作业,我深刻感受到了,面向对象与面向过程的差别,对类有了一定的认识,题目都不算特别难,但是每一个题目都是一个知识点,特别是菜单系列刚开始的时候无从下手做完后再看看感慨万分,虽然类是老师设计的,但是其中的交流是自己打的,熬了几天大夜虽然很累但是拿满分的那一刻成就感满满。
学到了什么:
1.对类的设计有了一定的了解。
2.对集合有了一定的认知。
3.体会到优秀的框架设计的好处(优秀的架构与细节设计。优秀的含义很广泛,清晰、可读、易维护、易扩展的设计往往是鲁棒的,这样的设计往往很难出现严重的纰漏,因为很多错误已经被规避掉了,即使有错 误,发现、纠正的难度也不会太大)
4.对JAVA报错的修改更加得心应手。
5.对类的封装性有了概念
6.学习了正则表达式的基本使用
对课程的建议
1.每次作业截止之后可以出一下不计分的补题,可以让没有及时解决问题的同学继续尝试。
以上是关于JAVA面向对象程序设计_PTA题目集04-06总结分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章