缓冲流Demon01
Posted Leizi-go
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了缓冲流Demon01相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
package test2;
import java.io.*;
//缓冲流
public class Demo02
public static void main(String[] args)
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try
fis = new FileInputStream("H:\\\\src.png");
fos = new FileOutputStream("H:\\\\target.png");
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
int readData;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((readData = bis.read()) != -1)
bos.write((char)readData);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("运行时间:" + (end - start));
fos.flush();
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
if (bis != null)
try
bis.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
if (bos != null)
try
bos.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
Java IO流 - 缓冲流的详细使用介绍
文章目录
缓冲流
缓冲流概述
缓冲流介绍:
缓冲流也称为高效流、或者高级流。之前学习的字节流和字符流可以称为原始流。
作用:缓冲流自带缓冲区、可以提高原始字节流、字符流读写数据的性能

缓冲流分为: 字节缓存输入流、字节缓冲输出流、字符缓冲输入流、字符缓冲输出流
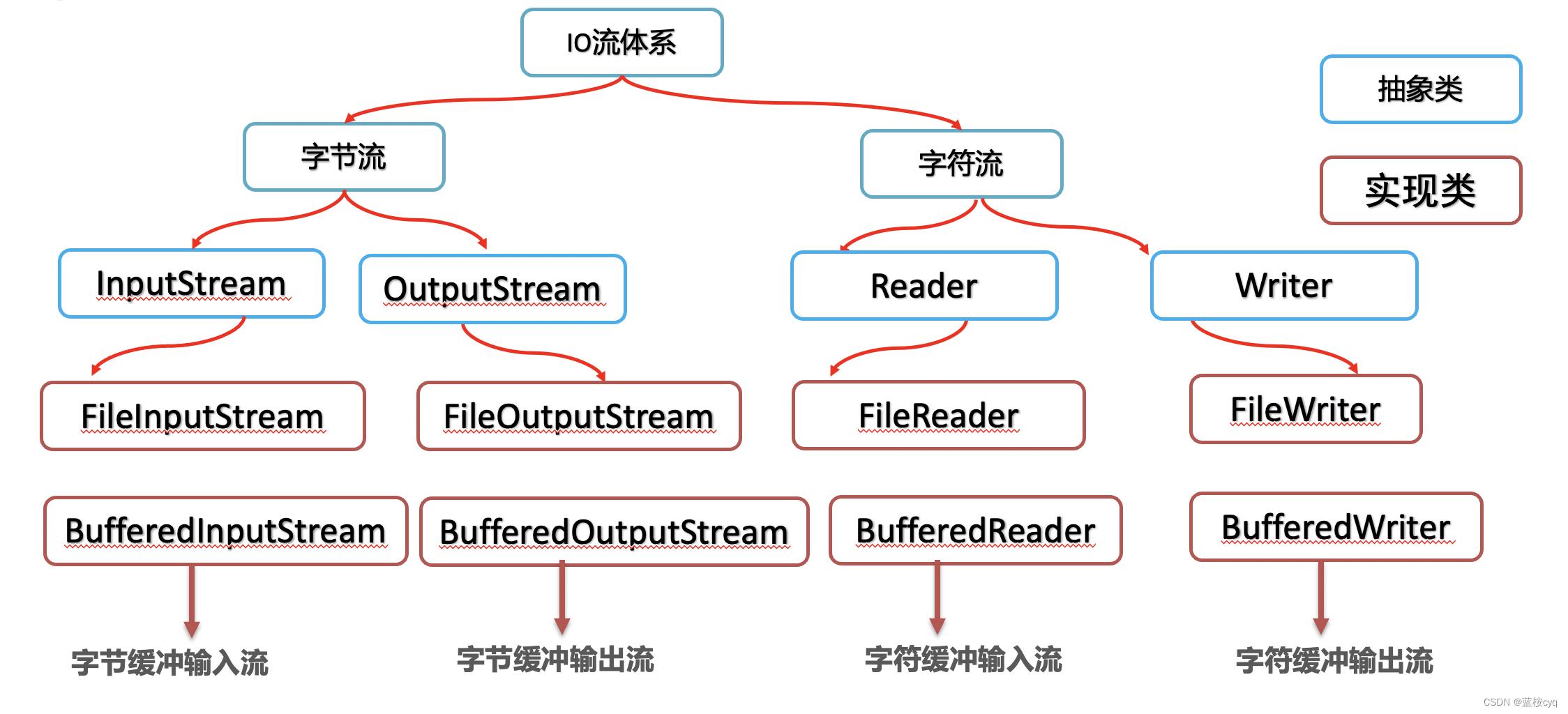
字节缓冲流
字节缓冲输入流:BufferedInputStream,提高字节输入流读取数据的性能,读写功能上与原始流相比并无变化。
字节缓冲输出流:BufferedOutputStream,提高字节输出流读取数据的性能,读写功能上与原始流相比并无变化。
字节缓冲流性能优化原理:
字节缓冲输入流自带了8KB缓冲池,以后我们直接从缓冲池读取数据,所以性能较好。
字节缓冲输出流自带了8KB缓冲池,数据就直接写入到缓冲池中去,写数据性能极高了。
将原始流包装为缓冲流的构造器如下:
| 构造器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BufferedInputStream(InputStream is) | 可以把低级的字节输入流包装成一个高级的缓冲字节输入流管道,从而提高字节输入流读数据的性能 |
| BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream os) | 可以把低级的字节输出流包装成一个高级的缓冲字节输出流,从而提高写数据的性能 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
// 创建原始字节输入流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("/Users/chenyq/Documents/test.txt");
// 创建原始字节输出流
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("/Users/chenyq/Documents/test1.txt");
// 将低级的字节输入流包装为高级的缓存输入流
InputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
// 将低级的字节输出流包装为高级的缓存输出流
OutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);
读写功能和之前原始流的读写并无区别:
public static void main(String[] args)
try (
// 创建原始字节输入流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("/Users/chenyq/Documents/test.txt");
// 创建原始字节输出流
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("/Users/chenyq/Documents/test1.txt");
// 将低级的字节输入流包装为高级的缓存输入流
InputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
// 将低级的字节输出流包装为高级的缓存输出流
OutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);
)
// 文件拷贝: 读写操作
byte[] arr = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(arr)) != -1)
bos.write(arr, 0, len);
catch(Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
字符缓存流
字符缓存输入流
字符缓冲输入流:实现类BufferedReader。
作用:提高字符输入流读取数据的性能,除此之外多了按照行读取数据的功能。
字符缓存输入流构造器如下:
| 构造器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BufferedReader(Reader r) | 可以把低级的字符输入流包装成一个高级的缓冲字符输入流管道,从而提高字符输入流读数据的性能 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
// 创建原始字符输入流
Reader r = new FileReader("/Users/chenyq/Documents/test.txt");
// 将原始字符输入流包装为字符缓存输入流
Reader br = new BufferedReader(r);
字符原始输入流的方法字符缓存输入流同样适用:
public static void main(String[] args)
try (
// 创建原始字符输入流
Reader r = new FileReader("/Users/chenyq/Documents/test.txt");
// 将原始字符输入流包装为字符缓存输入流
Reader br = new BufferedReader(r);
)
// 读取文件
char[] arr = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = br.read(arr)) != -1)
String res = new String(arr, 0, len);
System.out.println(res);
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
字符缓存输入流在原有的方法上新增了方法:
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| readLine() | 读取一行数据, 并返回该行内容的字符串,无行可读返回null |
按行读取: 普通方法
public static void main(String[] args)
try (
Reader r = new FileReader("/Users/chenyq/Documents/test.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(r);
)
// 读取第一行
System.out.println(br.readLine());
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
按行读取: 循环方法
public static void main(String[] args)
try (
Reader r = new FileReader("/Users/chenyq/Documents/test.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(r);
)
String res;
while ((res = br.readLine()) != null)
System.out.println(res);
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
字符缓存输出流:
字符缓冲输出流:实现类BufferedWriter。
作用:提高字符输出流写取数据的性能,除此之外多了换行功能
字符缓存输出流构造器如下:
| 构造器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BufferedWriter(Writer w) | 可以把低级的字符输出流包装成一个高级的缓冲字符输出流管道,从而提高字符输出流写数据的性能 |
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
Writer w = new FileWriter("/Users/chenyq/Documents/test.txt");
// 将原始字符输出流包装为缓冲输出流
Writer bw = new BufferedWriter(w);
字符缓存输出流新增功能:
当然原生输输出流的功能同样可以使用
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| newLine() | 换行操作 |
public static void main(String[] args)
try (
Writer w = new FileWriter("/Users/chenyq/Documents/test.txt", true);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(w);
)
// 定义一个字符数组
char[] arr = '我', '爱', 'C', 'h', 'i', 'n', 'a';
// 定义一个字符串
String str = "我爱学习Java";
// 写入一个字符
bw.write('我');
bw.write(98);
// 换行
bw.newLine();
// 写入一个字符数组
bw.write(arr);
// 换行
bw.newLine();
// 写入字符数组的一部分
bw.write(arr, 1, 3);
// 换行
bw.newLine();
// 写入一个字符串
bw.write(str);
// 换行
bw.newLine();
// 写入一个字符串的一部分
bw.write(str, 0, 4);
// 换行
bw.newLine();
catch (IOException e)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
以上是关于缓冲流Demon01的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章