Python编程小白的第一本python(循环与判断)
Posted daijux
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python编程小白的第一本python(循环与判断)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
| 逻辑控制与循环
True & False 这一小节的内容都会在命令行/终端环境里输入代码
比较运算的一些小问题:
字符串的比较。其实就是对比左右两边的字符串是否完全一致。Python中有着严格的大小写区分。
不同类型的对象不能使用 <,>,>=,<=进行比较,但是却可以使用 == 和 !=,例如字符串和数字。需要注意的是,浮点和整数虽然是不同类型,但是不影响比较运算
布尔类型的比较。True等同1,False等同0
成员运算符与身份运算符
成员运算符和身份运算符的关键词是 in 与 is。
1.in 和 not in
把 in 放在两个对象中间的含义是,测试前者是否存在于 in 后面的集合中。表示归属关系的布尔运算符号
(1)先介绍一个简单易懂的集合类型——列表(List)
album = [] // 创建一个链表 album = [‘Black Star‘,‘David Bowie‘,25,True] # 创建一个非空列表 album.append(‘new song‘) # 向列表中添加元素,会自动排列到列表尾部 print(album[0],album[-1]) # 打印列表中第一个和最后一个元素
(2)接下来我们用 in 来测试字符串‘Black Star‘ 是否在列表 album 中。如果存在将会显示True
‘Black Star‘ in album
2.is 和 is not
它们是表示身份鉴别的布尔运算符
在Python中任何一个对象都要满足身份(Identity)、类型(Type)、值(Value)这三个点,缺一不可。is 操作符号就是来进行身份的对比的。
the_Eddie = ‘Eddie‘ name = ‘Eddie‘ the_Eddie == name the_Eddie is name # 返回 True
3.bool()函数
其实在Python中任何对象都可判断其布尔值,除了0、None和所有空的序列与集合(列表、字典、集合)布尔值为False之外,其它的都为True,可以使用函数bool()来进行判别。
当你想设定一个变量,但又没想好它应该等于什么值时,就可以设置成None
4.布尔运算符
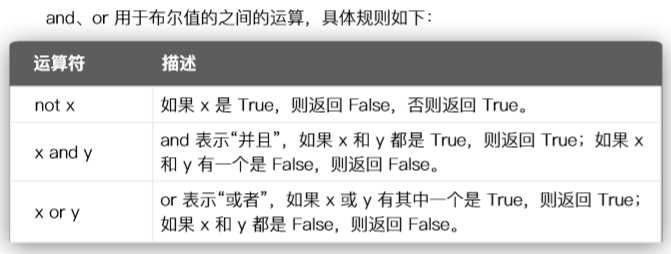
| 条件控制
条件控制其实就是 if...else 的使用
结合函数来创建一个猜密码的函数
def account_login(): password = input(‘Password:‘) if password == ‘12345‘: print(‘Login success!‘) else: print(‘Wrong password or invalid input!‘) account_login() account_login()
多条件判断,还是用刚才的函数,增加一个重置密码的功能
password_list = [‘*#*#‘,‘12345‘] def account_login(): password = input(‘Password:‘) password_correct = password == password_list[-1] password_reset = password == password_list[0] if password_correct: print(‘Login success!‘) elif password_reset: new_passowrd = input(‘Enter a new passowrd:‘) password_list.append(new_passowrd) print(‘Your password has changed successfully!‘) account_login() else: print(‘Wrong password or invalid input!‘) account_login() account_login()
| 循环
1.for循环
for every_letter in ‘Hello world‘: print(every_letter)
for num in range(1,11): # 不包含11,因此实际范围是1~10
print(str(num) + ‘ + 1 =‘,num+1)
range函数,可以得到一个具有连续整数的序列
现在我们将 for 和 if 语句结合起来
songsList = [‘Holy Diver‘, ‘Thunderstruck‘, ‘Rebel Rebel‘] for song in songsList: if song == ‘Holy Diver‘: print(song,‘- Dio‘) elif song == ‘Thunderstruck‘: print(song,‘ -AC/DC‘) elif song == ‘Rebel Rebel‘: print(song,‘ - David Bowie‘)
2.while循环
注:在终端或者命令行中按 Ctrl + C 停止运行,在PyCharm中则按红色的X停止
1).break 让循环停下的第一种方式:
count = 0 while True: print(‘Repeat this line !‘) count = count + 1 if count == 5: break
2).改变循环条件
password_list = [‘*#*#‘,‘12345‘] def account_login(): tries = 3 while tries > 0: password = input(‘Password:‘) password_correct = password == password_list[-1] password_reset = password == password_list[0] if password_correct: print(‘Login success!‘) elif password_reset: new_passowrd = input(‘Enter a new passowrd:‘) password_list.append(new_passowrd) print(‘Your password has changed successfully!‘) account_login() else: print(‘Wrong password or invalid input!‘) tries = tries - 1 print(tries, ‘times left‘) else: print(‘Your account has been suspended‘) account_login()
| 练习题
1、设计一个函数,在桌面上创建10个文本,以数字1-10给它们命名
for i in range(1,11): file = open(‘C:/Users/asus/Desktop/{}.txt‘.format(i),‘w‘)
# 答案
def text_creation():
path = ‘/Users/Hou/Desktop/w/‘
for name in range(1,11):
with open(path + str(name) + ‘ .txt‘,‘w‘) as
text.write(str(name))
text.close()
print(‘Done‘)
text_creation()
2、设计一个复利计算函数 invest()
def invest(amount, rate, time): for i in range(1, time): print(‘year {}‘.format(i), amount + amount * rate * i * 1.0) return 0 invest(100,0.05,8)
# 答案
def invest(amount, rate, time):
print("principal amount:{}".format(amount))
for t in range(1, time + 1):
amount = amount * (1 + rate)
print("year {}: ${}".format(t, amount))
invest(100, .05, 8)
invest(2000, .025, 5)
3、打印1~100内的偶数
for i in range(1,51): print(i*2)
# 答案
def even_print():
for i in range(1,101):
if i % 2 == 0:
print(i)
even_print()
以上是关于Python编程小白的第一本python(循环与判断)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章