实验3 控制语句与组合数据类型应用编程
Posted zz666666
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了实验3 控制语句与组合数据类型应用编程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
实验任务1
编译源代码
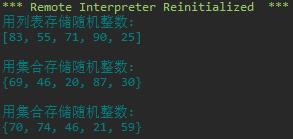
#task1.py import random print(\'用列表存储随机整数: \') lst = [random.randint(0, 100) for i in range(5)] print(lst) print(\'\\n用集合存储随机整数: \') s1 = random.randint(0, 100) for i in range(5) print(s1) print(\'\\n用集合存储随机整数: \') s2 = set() while len(s2) < 5: s2.add(random.randint(0, 100)) print(s2)
运行结果截图
实验任务2
task2_1.py
编译源代码
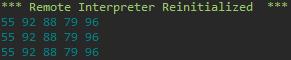
#task2_1.py #列表遍历 lst = [55,92,88,79,96] #遍历方式1:使用while + 索引 i = 0 while i < len(lst): print(lst[i],end = \' \') i += 1 print() #遍历方式2:使用for + 索引 for i in range(len(lst)): print(lst[i],end = \' \') print() #遍历方式3:使用for...in for i in lst: print(i,end = \' \') print()
运行结果截图
task2_2.py
编译源代码
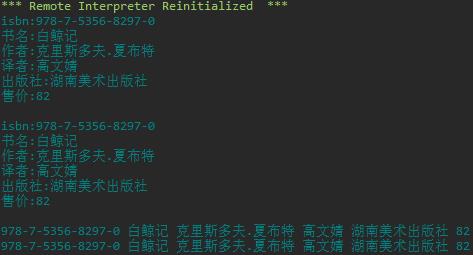
#task2_2.py #字典遍历 book_info = \'isbn\':\'978-7-5356-8297-0\', \'书名\':\'白鲸记\', \'作者\':\'克里斯多夫.夏布特\', \'译者\':\'高文婧\', \'出版社\':\'湖南美术出版社\', \'售价\':82 #遍历key-value对:实现方式1 for key,value in book_info.items(): print(f\'key:value\') print() #遍历key-value对:实现方式2 for item in book_info.items(): print(f\'item[0]:item[1]\') print() #遍历值:实现方式1 for value in book_info.values(): print(value,end = \' \') print() #遍历值:实现方式2 for key in book_info.keys(): print(book_info[key],end = \' \')
运行结果截图
task2_3.py
编译源代码
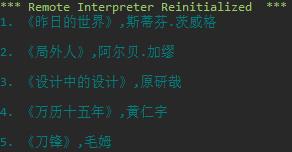
#task2_3.py book_infos = [\'书名\': \'昨日的世界\', \'作者\': \'斯蒂芬.茨威格\', \'书名\': \'局外人\', \'作者\': \'阿尔贝.加缪\', \'书名\': \'设计中的设计\', \'作者\': \'原研哉\', \'书名\': \'万历十五年\', \'作者\': \'黄仁宇\', \'书名\': \'刀锋\', \'作者\': \'毛姆\' ] for i in range(1,6): print(f\'i.\',end = \' \') lst = [] for value in book_infos[i-1].values(): lst.append(value) for x in range(2): if x == 0: print(f\'《lst[x]》\',end = \',\') else: print(f\'lst[x]\') print()
运行结果截图
实验任务3
编译源代码
text = \'\'\'The Zen of Python, by Tim Peters Beautiful is better than ugly. Explicit is better than implicit. Simple is better than complex. Complex is better than complicated. Flat is better than nested. Sparse is better than dense. Readability counts. Special cases aren\'t special enough to break the rules. Although practicality beats purity. Errors should never pass silently. Unless explicitly silenced. In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess. There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it. Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you\'re Dutch. Now is better than never. Although never is often better than *right* now. If the implementation is hard to explain, it\'s a bad idea. If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea. Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let\'s do more of those! \'\'\' x = text.lower() D = for i in range(97,123): D[x.count(chr(i))] = chr(i) y = sorted(D, reverse = True) for i in y: print(f\'D[i]:i\')
运行结果截图
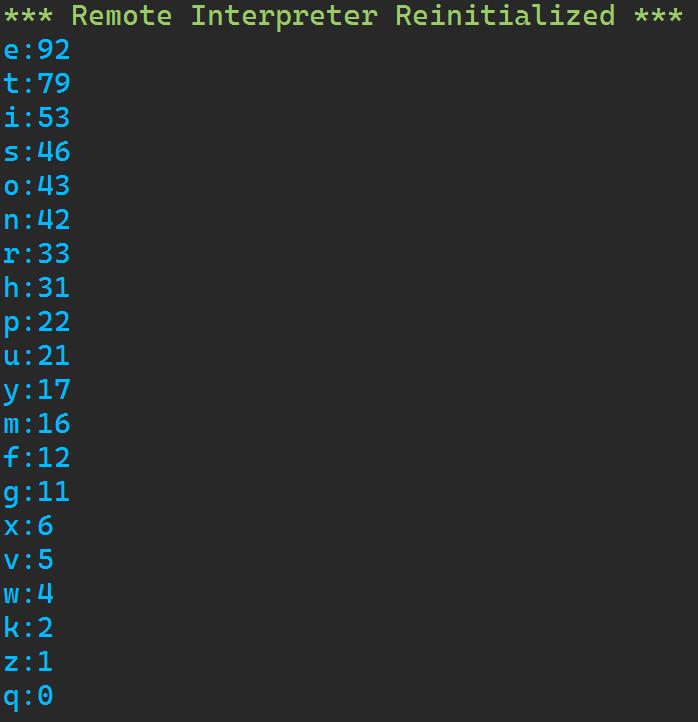
实验任务4
编译源代码
code_majors=8326:\'地信类\', 8329:\'计算机类\', 8330:\'气科类\', 8336:\'防灾工程\', 8345:\'海洋科学\', 8382:\'气象工程\' a = \'专业代号信息\' print(a.center(20,\'-\')) for key, value in code_majors.items(): print(f\'key:value\') b = \'学生专业查询\' print(b.center(20,\'-\')) while True: x = input(\'请输入学号:\') if x ==\'#\': print("查询结束") break else: y = int(x[4:8]) if y in code_majors: print(f\'专业是:code_majors[y]\') else: print("不在这些专业中")
运行结果截图
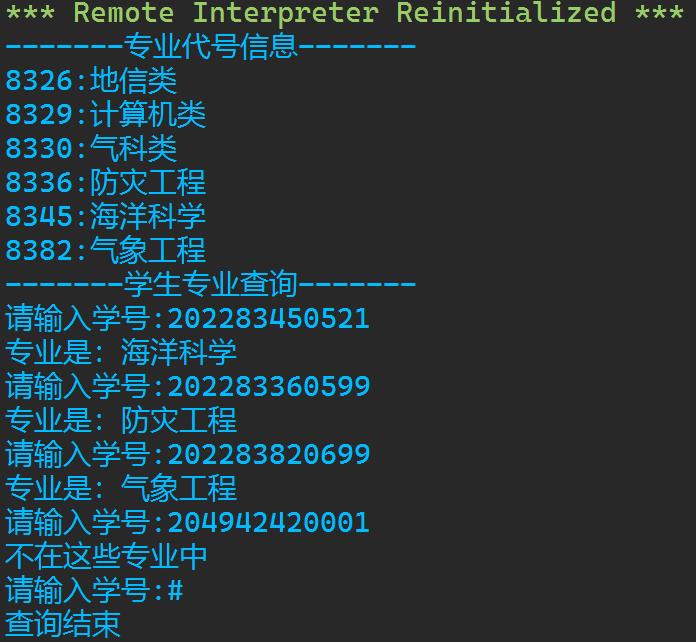
实验任务5
编译源代码
import random lucky_day=random.randint(1,31) print(f\'猜猜2023年5月哪一天会是你的lucky daychr(0x1f609)\') guess=int(input(\'你有三次机会,猜吧(1~31):\')) flag=0 while lucky_day!=guess: if guess>lucky_day: print(\'猜晚了,你的lucky day已经过了\') elif guess<lucky_day: print(\'猜早了,你的lucky day还没到呢\') elif guess==lucky_day: break flag+=1 if flag==3: break guess=int(input(\'再猜(1~31):\')) if flag<3: print(f\'哇,猜中了chr(0x1f923)\') elif flag==3: print(f\'哇哦,次数用光啦。\\n偷偷告诉你,5月你的lucky day是lucky_day号。good luckchr(0x1f60a)\')
运行结果截图
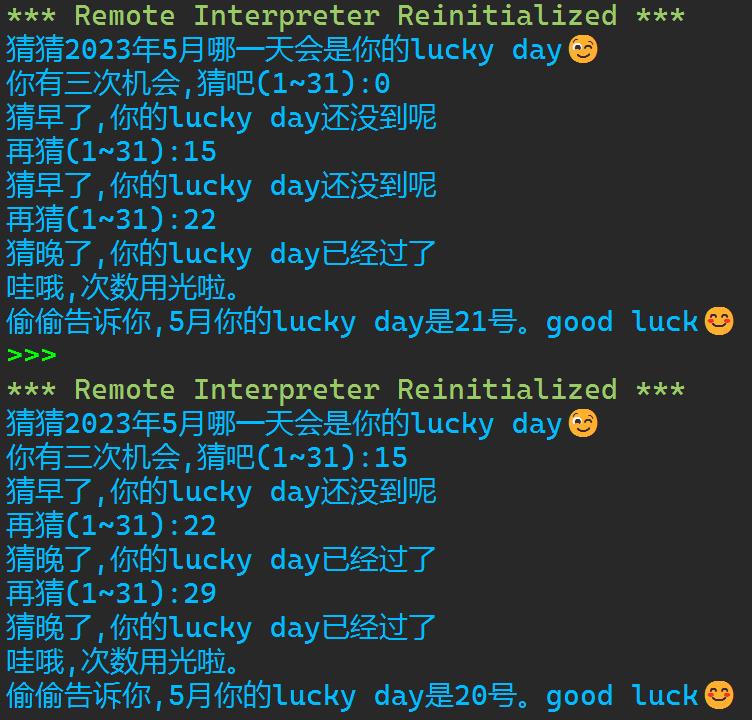
实验任务6
编译源代码
datas = \'2049777001\': [\'篮球\', \'羽毛球\', \'美食\', \'漫画\'], \'2049777002\': [\'音乐\', \'旅行\'], \'2049777003\': [\'马拉松\', \'健身\', \'游戏\'], \'2049777004\': [], \'2049777005\': [\'足球\', \'阅读\'], \'2049777006\': [\'发呆\', \'闲逛\'], \'2049777007\': [], \'2049777008\': [\'书法\', \'电影\'], \'2049777009\': [\'音乐\', \'阅读\', \'电影\', \'漫画\'], \'2049777010\': [\'数学\', \'推理\', \'音乐\', \'旅行\'] x = datas.values() y = for i in x: for j in i: if j in y: y[j] += 1 else: y[j] = 1 y_new = list(zip(y.values(), y.keys())) z = sorted(y_new, reverse = True) for i in z: print(f\'i[1]:i[0]\')
运行结果截图
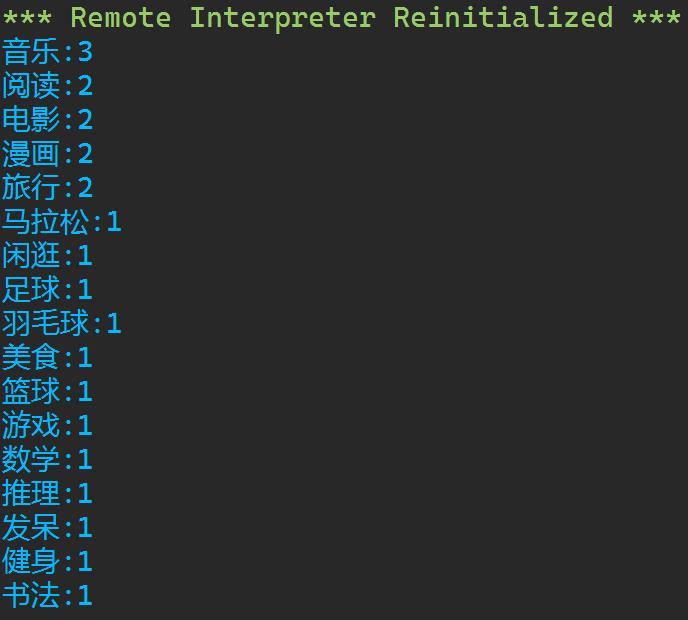
实验任务7
编译源代码
""" 家用电器销售系统 v1.3 """ #欢迎信息 print(\'欢迎使用家用电器销售系统!\') #商品数据初始化 products = [ [\'0001\',\'电视机\',\'海尔\',5999.00,20], [\'0002\',\'冰箱\',\'西门子\',6998.00,15], [\'0003\',\'洗衣机\',\'小天鹅\',1999.00,10], [\'0004\',\'空调\',\'格力\',3900.00,10], [\'0005\',\'热水器\',\'美的\',688.00,30], [\'0006\',\'笔记本\',\'联想\',5699.00,10], [\'0007\',\'微波炉\',\'苏泊尔\',480.50,33], [\'0008\',\'投影仪\',\'松下\',1250.00,12], [\'0009\',\'吸尘器\',\'飞利浦\',999.00,9] ] #初始化用户购物车 products_cart = [] option = input(\'请选择您的操作;1-查看商品;2-购物;3—查看购物车;其他-结账\') while option in[\'1\', \'2\', \'3\']: if option == \'1\': # 产品信息列表 print(\'产品和价格信息如下:\') print(\':*^48\'.format(\'*\')) print(\':10\'.format(\'编号\'), \':10\'.format(\'名称\'), \':10\'.format(\'品牌\'), \':10\'.format(\'价格\'), \':10\'.format(\'库存数量\')) print(\':-^50\'.format(\'-\')) for i in range(len(products)): print(\':10\'.format(products[i][0]), \':10\'.format(products[i][1]), \':10\'.format(products[i][2]), \':10\'.format(products[i][3]), \':10\'.format(products[i][4])) print(\':-^50\'.format(\'-\')) elif option == \'2\': product_id = input(\'请输入您要购买的产品编号:\') while product_id not in [item[0] for item in products]: product_id = input(\'编号不存在,请重新输入您要购买的产品编号:\') count = int(input(\'请输入您要购买的产品数量:\')) while count > products[int(product_id)-1][4]: count = int(input(\'数量超出库存,请重新输入您要购买的产品数量:\')) # 将所购买的商品加入购物车 if product_id not in [item[0] for item in products_cart]: products_cart.append([product_id,count]) else: for i in range(len(products_cart)): if products_cart[i][0] == product_id: products_cart[i][1]+=count # 更新商品列表 for i in range(len(products)): if products[i][0] == product_id: products[i][4] -= count else: print(\'购物车信息如下:\') print(\':*^48\'.format(\'*\')) print(\':10\'.format(\'编号\'), \':10\'.format(\'购买数量\')) print(\':-^50\'.format(\'-\')) for i in range(len(products_cart)): print(\':10\'.format(products_cart[i][0]), \':6\'.format(products_cart[i][1])) print(\':-^50\'.format(\'-\')) option = input(\'操作成功!请选择你的操作:1-查看商品;2-购物;3-查看购物车;其他-结账\') # 计算金额 if len(products_cart) > 0: amount = 0 for i in range(len(products_cart)): product_index = 0 for j in range(len(products)): if products[j][0] == products_cart[i][0]: product_index = j break price = products[product_index][3] count = products_cart[i][1] amount += price*count if 5000 < amount <= 10000: amount = amount * 0.95 elif 10000 < amount <= 20000: amount = amount * 0.90 elif amount > 20000: amount = amount*0.85 else: amount = amount*1 print(\'购买成功,您需要支付%8.2f元\' % amount) # 退出系统 print(\'谢谢您的光临,下次再见!\')
运行结果截图
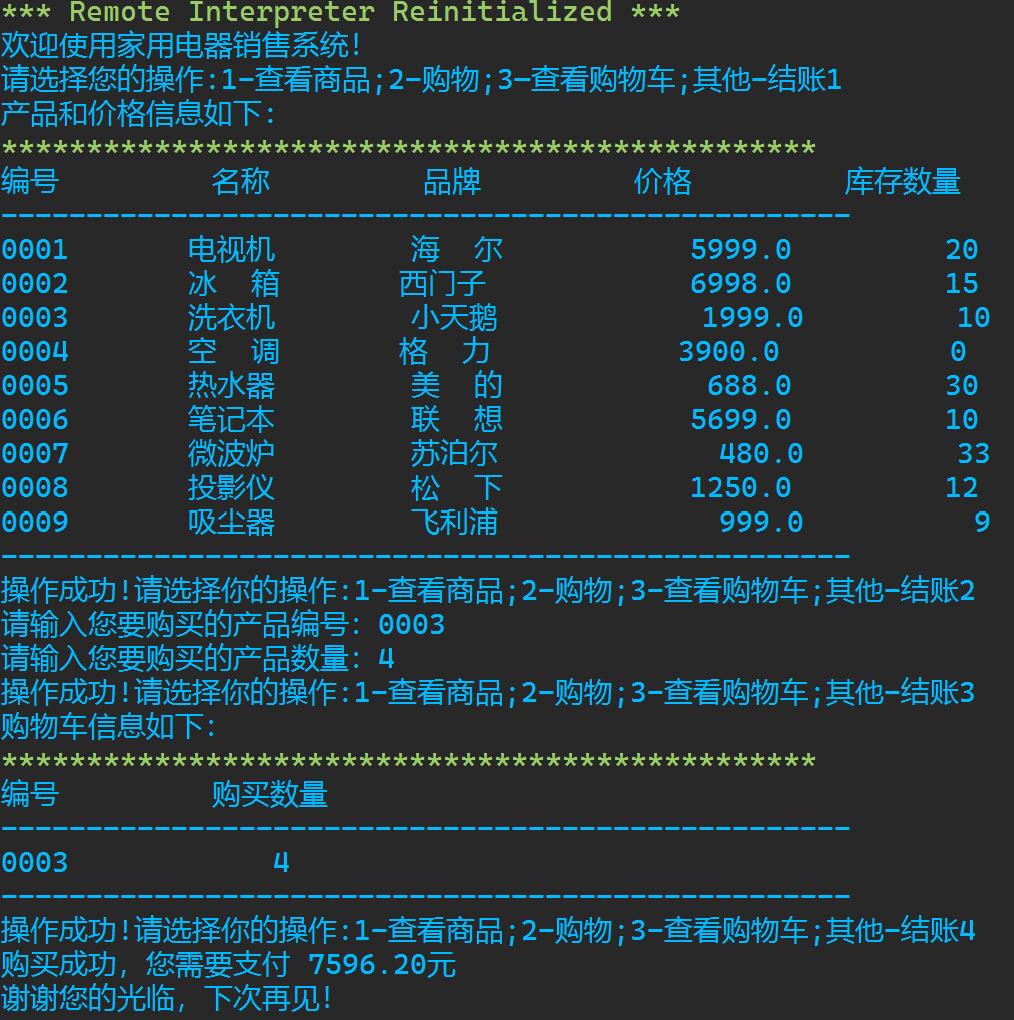
实验任务8
task8_1.py
编译源代码
\'\'\' 家用电器销售系统 v1.4 \'\'\' # 欢迎信息 print(\'欢迎使用家用电器销售系统!\') # 商品数据初始化 products=[ \'id\':\'0001\',\'name\':\'电视机\',\'brand\':\'海尔\',\'price\':5999.00,\'count\':20, \'id\':\'0002\',\'name\':\'冰箱\',\'brand\':\'西门子\',\'price\':6998.00,\'count\':15, \'id\':\'0003\',\'name\':\'洗衣机\',\'brand\':\'小天鹅\',\'price\':1999.00,\'count\':10, \'id\':\'0004\',\'name\':\'空调\',\'brand\':\'格力\',\'price\':3900.00,\'count\':0, \'id\':\'0005\',\'name\':\'热水器\',\'brand\':\'格力\',\'price\':688.00,\'count\':30, \'id\':\'0006\',\'name\':\'笔记本\',\'brand\':\'联想\',\'price\':5699.00,\'count\':10, \'id\':\'0007\',\'name\':\'微波炉\',\'brand\':\'苏泊尔\',\'price\':580.00,\'count\':33, \'id\':\'0008\',\'name\':\'投影仪\',\'brand\':\'松下\',\'price\':1250.00,\'count\':12, \'id\':\'0009\',\'name\':\'吸尘器\',\'brand\':\'飞利浦\',\'price\':999.00,\'count\':9, ] # 初始化用户购物车 products_cart = [] option = input(\'请选择您的操作:1-查看商品;2-购物;3-查看购物车;其他-结账\') while option in [\'1\', \'2\', \'3\']: if option == \'1\': # 产品信息列表 print(\'产品和价格信息如下:\') print(f\'"":*>48s\') print(f\'"编号":10s"名称":10s"品牌":10s"价格":10s"库存数量":10s\') print(f\'"":->50s\') for i in range(len(products)): print(\':10\'.format(products[i][\'id\']),\':10\'.format(products[i][\'name\']),\':10\'.format(products[i][\'brand\']),\':10\'.format(products[i][\'price\'])) print(f\'"":->50s\') elif option == \'2\': product_id = input(\'请输入您要购买的商品编号:\') while product_id not in [item[\'id\'] for item in products]: product_id = input(\'编号不存在,请重新输入您要购买的产品编号:\') count = int(input(\'请输入您要购买的产品数量:\')) while count > products[int(product_id)-1][\'count\']: count = int(input(\'数量超出库存,请重新输入您要购买的产品数量:\')) # 将所购买的产品加入购物车 if product_id not in [item[\'id\'] for item in products_cart]: products_cart.append(\'id\':product_id,\'count\':count) else: for i in range(len(products_cart)): if products_cart[i].get(\'id\') == product_id: products_cart[i][\'count\'] += count # 更新商品列表 for i in range(len(products)): if products[i][\'id\'] == product_id: products[i][\'count\'] -= count else: print(\'购物车信息如下\') print(f\'"":*>48s\') print(f\'"编号":10s"购买数量":10s\') print(f\'"":->50s\') for i in range(len(products_cart)): print(\':10\'.format(products_cart[i][\'id\']),\':6\'.format(products_cart[i][\'count\'])) print(f\'"":->50s\') option=input(\'操作成功!请选择您的操作:1-查看商品;2-购物;3-查看购物车;其他-结账\') # 计算金额 if len(products_cart)>0: amount=0 for i in range(len(products_cart)): product_index = 0 for j in range(len(products)): if products[j][\'id\'] == products_cart[i][\'id\']: product_index = j break price = products[product_index][\'price\'] count = products_cart[i][\'count\'] amount += price*count if 5000 < amount <= 10000: amount = amount*0.95 elif 10000 < amount < 20000: amount = amount*0.90 elif amount > 20000: amount = amount*0.85 else: amount = amount*1 print(\'购买成功,您需要支付%8.2f\'%amount) # 退出系统 print(\'谢谢您的光临,下次再见!\')
运行结果截图
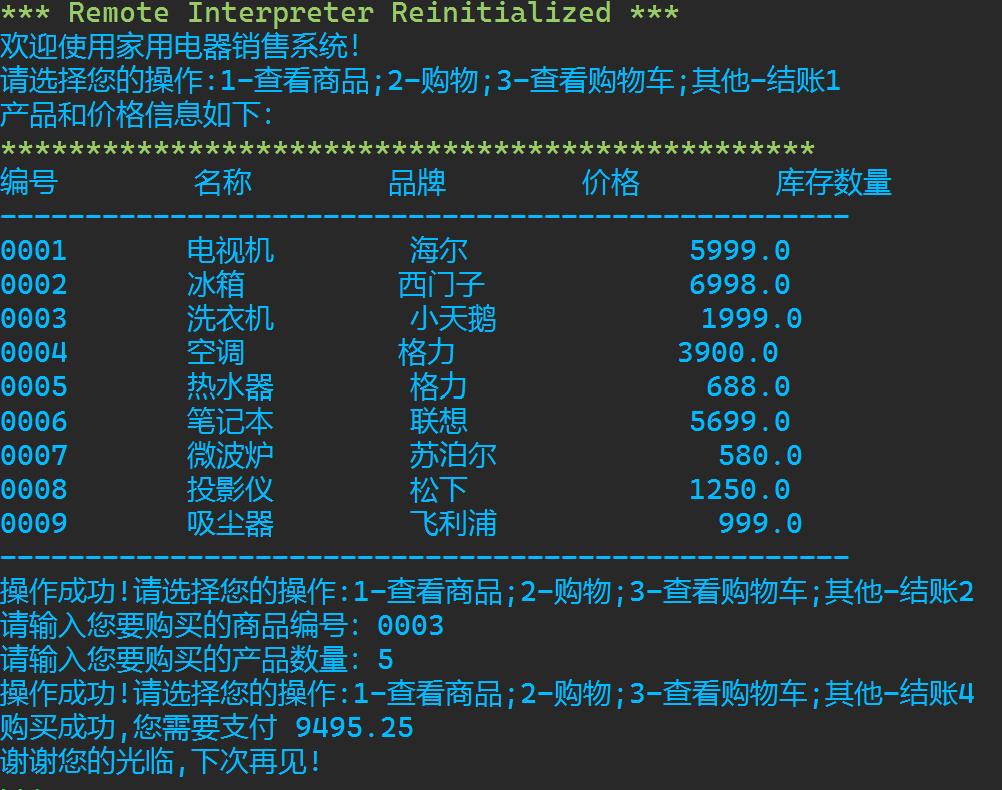
task8_2.py
编译源代码
\'\'\' 家用电器销售系统 v1.4 \'\'\' # 欢迎信息 print(\'欢迎使用家用电器销售系统!\') # 商品数据初始化 products=[ \'id\':\'0001\',\'name\':\'电视机\',\'brand\':\'海尔\',\'price\':5999.00,\'count\':20, \'id\':\'0002\',\'name\':\'冰箱\',\'brand\':\'西门子\',\'price\':6998.00,\'count\':15, \'id\':\'0003\',\'name\':\'洗衣机\',\'brand\':\'小天鹅\',\'price\':1999.00,\'count\':10, \'id\':\'0004\',\'name\':\'空调\',\'brand\':\'格力\',\'price\':3900.00,\'count\':0, \'id\':\'0005\',\'name\':\'热水器\',\'brand\':\'格力\',\'price\':688.00,\'count\':30, \'id\':\'0006\',\'name\':\'笔记本\',\'brand\':\'联想\',\'price\':5699.00,\'count\':10, \'id\':\'0007\',\'name\':\'微波炉\',\'brand\':\'苏泊尔\',\'price\':580.00,\'count\':33, \'id\':\'0008\',\'name\':\'投影仪\',\'brand\':\'松下\',\'price\':1250.00,\'count\':12, \'id\':\'0009\',\'name\':\'吸尘器\',\'brand\':\'飞利浦\',\'price\':999.00,\'count\':9, ] # 初始化用户购物车 products_cart = [] option = input(\'请选择您的操作:1-查看商品;2-购物;3-查看购物车;其他-结账\') while option in [\'1\', \'2\', \'3\']: if option == \'1\': # 产品信息列表 print(\'产品和价格信息如下:\') print(f\'"":*>48s\') print(f\'"编号":10s"名称":10s"品牌":10s"价格":10s"库存数量":10s\') print(f\'"":->50s\') for i in range(len(products)): print(\':10\'.format(products[i][\'id\']),\':10\'.format(products[i][\'name\']),\':10\'.format(products[i][\'brand\']),\':10\'.format(products[i][\'price\'])) print(f\'"":->50s\') elif option == \'2\': product_id = input(\'请输入您要购买的商品编号:\') while product_id not in [item[\'id\'] for item in products]: product_id = input(\'编号不存在,请重新输入您要购买的产品编号:\') count = int(input(\'请输入您要购买的产品数量:\')) while count > products[int(product_id)-1][\'count\']: count = int(input(\'数量超出库存,请重新输入您要购买的产品数量:\')) # 将所购买的产品加入购物车 if product_id not in [item[\'id\'] for item in products_cart]: products_cart.append(\'id\':product_id,\'count\':count) else: for i in range(len(products_cart)): if products_cart[i].get(\'id\') == product_id: products_cart[i][\'count\'] += count # 更新商品列表 for i in range(len(products)): if products[i][\'id\'] == product_id: products[i][\'count\'] -= count else: print(\'购物车信息如下\') print(f\'"":*>48s\') print(f\'"编号":10s"购买数量":10s\') print(f\'"":->50s\') for i in range(len(products_cart)): print(\':10\'.format(products_cart[i][\'id\']),\':6\'.format(products_cart[i][\'count\'])) print(f\'"":->50s\') option=input(\'操作成功!请选择您的操作:1-查看商品;2-购物;3-查看购物车;其他-结账\') # 计算金额 if len(products_cart)>0: amount=0 for i in range(len(products_cart)): product_index = 0 for j in range(len(products)): if products[j][\'id\'] == products_cart[i][\'id\']: product_index = j break price = products[product_index][\'price\'] count = products_cart[i][\'count\'] amount += price*count if 5000 < amount <= 10000: amount = amount*0.95 elif 10000 < amount < 20000: amount = amount*0.90 elif amount > 20000: amount = amount*0.85 else: amount = amount*1 print(\'购买成功,您需要支付%8.2f\'%amount) # 退出系统 print(\'谢谢您的光临,下次再见!\')
运行结果截图
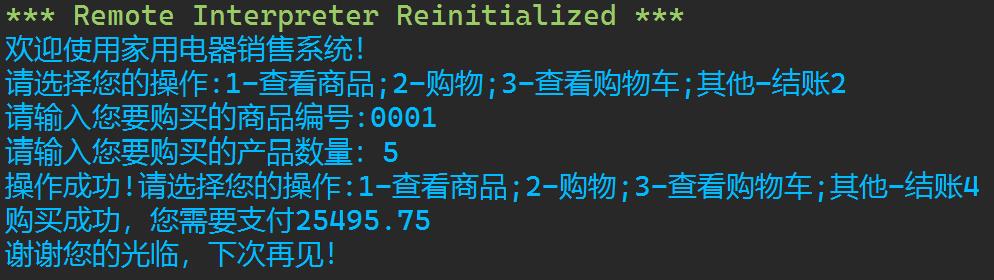
实验六附加:PL/SQL编程基础
实验六附加:PL/SQL编程基础(1)
实验目的
-
熟悉掌握PL/SQL编程中的变量定义语句
-
熟悉掌握PL/SQL编程中的条件语句和循环语句等流程控制语句。
-
能熟练使用上述基本语句编写PL/SQL代码完成指定的数据处理功能。
实验内容
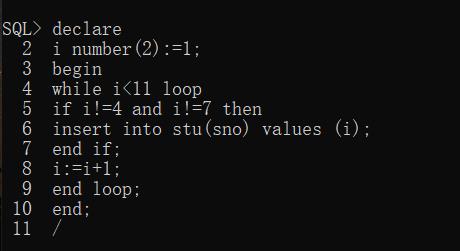
1、创建一个表stu,该表只有一个字段sno 类型是number(2),编写一个块,向stu表中添加数字1到10,但不包括4和7。
(1)创建表格。
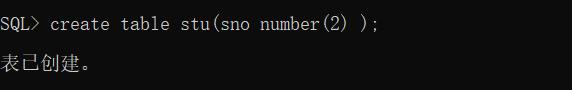
(2)使用PL/SQL块向stu表中添加数据。
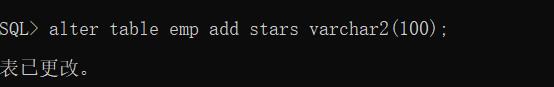
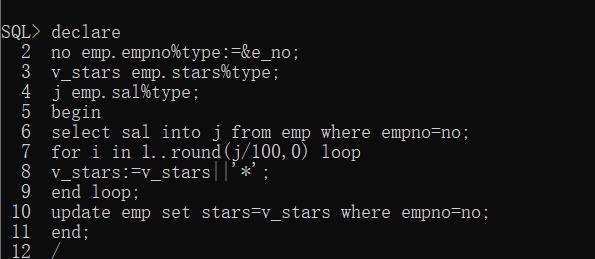
2、为Scott用户下的emp表增加一个列stars,类型为VARCHAR2(100)。创建一个PL/SQL块,通过输入任意员工编号(&e_no),根据员工的工资计算他能获得的星号’*’数量,每100元奖励一个星号,按四舍五入处理(使用函数round)。并根据员工所获得的星号数量n,形成由n个星号组成的字符串,写入emp表的stars列。
例如:若输入7369,PL/SQL块能向emp表中编号为7369的员工的starts列添加8个’’,对编号为7369的员工工资和星级查询时,显示结果如下*:
(1) 为emp表增加一个列stars。
(2) 使用PL/SQL块向emp表中某个员工的starts列添加’*’号。
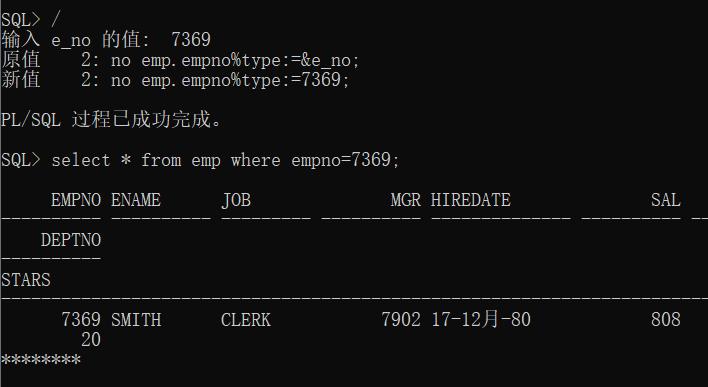
以上是关于实验3 控制语句与组合数据类型应用编程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
