Python数据可视化库-Matplotlib
Posted tianqizhi
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python数据可视化库-Matplotlib相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
折线图绘制:

import pandas as pd unrate = pd.read_csv(‘unrate.csv‘) unrate[‘DATE‘] = pd.to_datetime(unrate[‘DATE‘])#可将1948/1/1时间格式转换为1948-01-01 print(unrate.head(12))
结果:

DATE VALUE
0 1948-01-01 3.4
1 1948-02-01 3.8
2 1948-03-01 4.0
3 1948-04-01 3.9
4 1948-05-01 3.5
5 1948-06-01 3.6
6 1948-07-01 3.6
7 1948-08-01 3.9
8 1948-09-01 3.8
9 1948-10-01 3.7
10 1948-11-01 3.8
11 1948-12-01 4.0
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #%matplotlib inline #Using the different pyplot functions, we can create, customize, and display a plot. For example, we can use 2 functions to : plt.plot() plt.show()
结果:
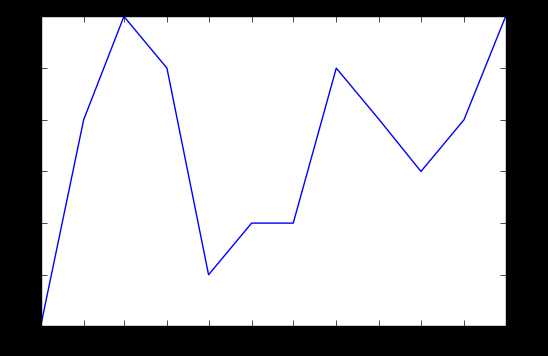
first_twelve = unrate[0:12] plt.plot(first_twelve[‘DATE‘], first_twelve[‘VALUE‘]) plt.show()
结果:
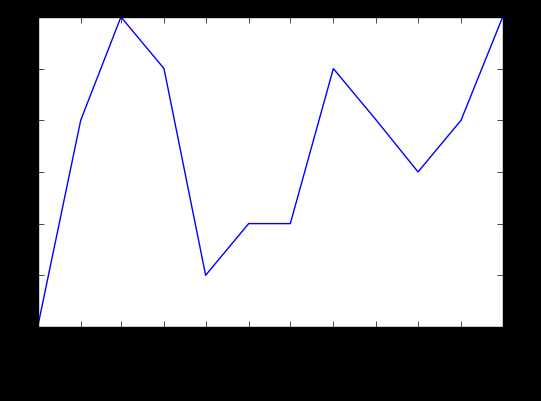
#While the y-axis looks fine, the x-axis tick labels are too close together and are unreadable #We can rotate the x-axis tick labels by 90 degrees so they don‘t overlap #We can specify degrees of rotation using a float or integer value. plt.plot(first_twelve[‘DATE‘], first_twelve[‘VALUE‘]) plt.xticks(rotation=45)#指定x轴标注的角度,这里选的为45度 #print help(plt.xticks) plt.show()
结果:
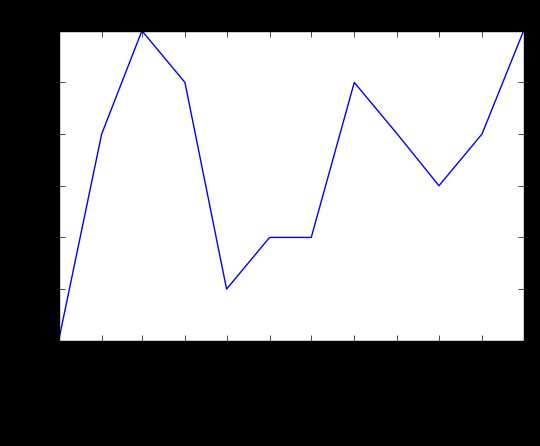
#xlabel(): accepts a string value, which gets set as the x-axis label. #ylabel(): accepts a string value, which is set as the y-axis label. #title(): accepts a string value, which is set as the plot title. plt.plot(first_twelve[‘DATE‘], first_twelve[‘VALUE‘]) plt.xticks(rotation=90) plt.xlabel(‘Month‘) plt.ylabel(‘Unemployment Rate‘) plt.title(‘Monthly Unemployment Trends, 1948‘) plt.show()
结果:
子图操作:
#add_subplot(first,second,index) first means number of Row,second means number of Column. import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig = plt.figure()#规定画图区间(画图域) ax1 = fig.add_subplot(3,2,1) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(3,2,2) ax3 = fig.add_subplot(3,2,6) plt.show()
结果:
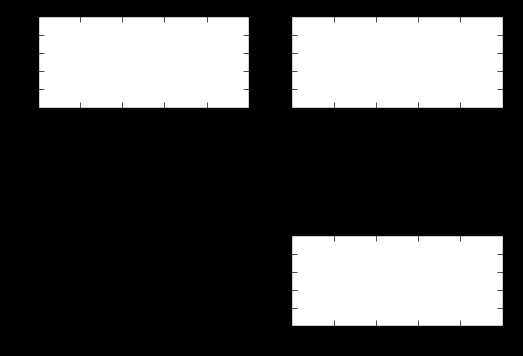
import numpy as np fig = plt.figure() #fig = plt.figure(figsize=(3, 3))#figsize指定图的长和宽 ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2,1,1) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(2,1,2) ax1.plot(np.random.randint(1,5,5), np.arange(5)) ax2.plot(np.arange(10)*3, np.arange(10)) plt.show()
结果:
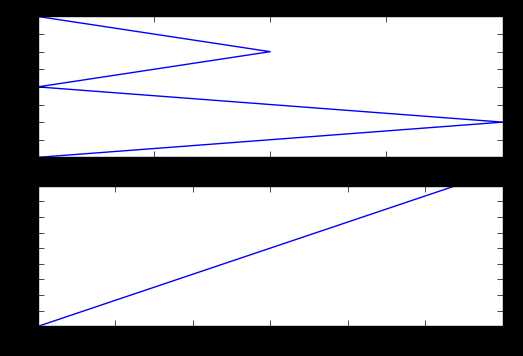
unrate[‘MONTH‘] = unrate[‘DATE‘].dt.month unrate[‘MONTH‘] = unrate[‘DATE‘].dt.month fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,3)) #同一个图中画出两条线 plt.plot(unrate[0:12][‘MONTH‘], unrate[0:12][‘VALUE‘], c=‘red‘)#c的值可以用小写或缩写或rgb颜色通道值也可以 plt.plot(unrate[12:24][‘MONTH‘], unrate[12:24][‘VALUE‘], c=‘blue‘) plt.show()
结果:
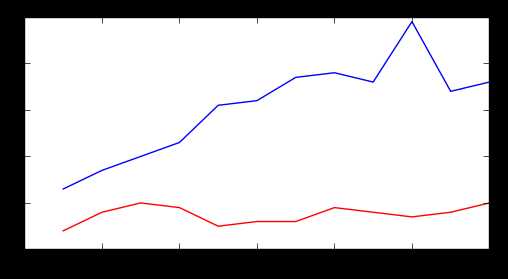
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
colors = [‘red‘, ‘blue‘, ‘green‘, ‘orange‘, ‘black‘]
for i in range(5):
start_index = i*12
end_index = (i+1)*12
subset = unrate[start_index:end_index]
plt.plot(subset[‘MONTH‘], subset[‘VALUE‘], c=colors[i])
plt.show()
结果:
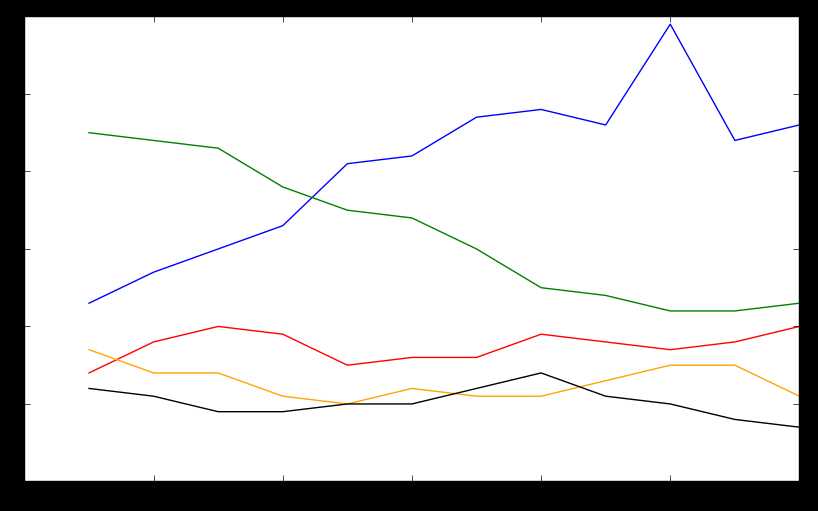
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
colors = [‘red‘, ‘blue‘, ‘green‘, ‘orange‘, ‘black‘]
for i in range(5):
start_index = i*12
end_index = (i+1)*12
subset = unrate[start_index:end_index]
label = str(1948 + i)
plt.plot(subset[‘MONTH‘], subset[‘VALUE‘], c=colors[i], label=label)
plt.legend(loc=‘best‘)#显示label loc指的是label所放置位置,best是自动选择最好位置
#print help(plt.legend)
plt.show()
结果:
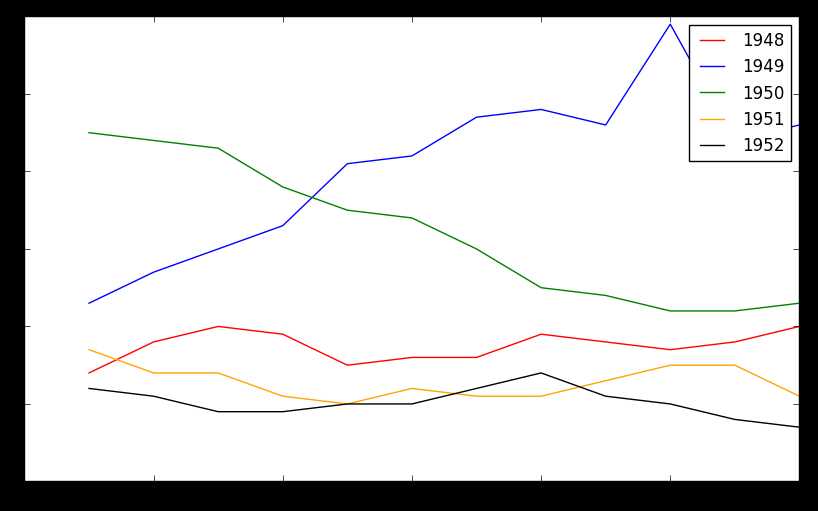
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
colors = [‘red‘, ‘blue‘, ‘green‘, ‘orange‘, ‘black‘]
for i in range(5):
start_index = i*12
end_index = (i+1)*12
subset = unrate[start_index:end_index]
label = str(1948 + i)
plt.plot(subset[‘MONTH‘], subset[‘VALUE‘], c=colors[i], label=label)
plt.legend(loc=‘upper left‘)
plt.xlabel(‘Month, Integer‘)
plt.ylabel(‘Unemployment Rate, Percent‘)
plt.title(‘Monthly Unemployment Trends, 1948-1952‘)
plt.show()
结果:
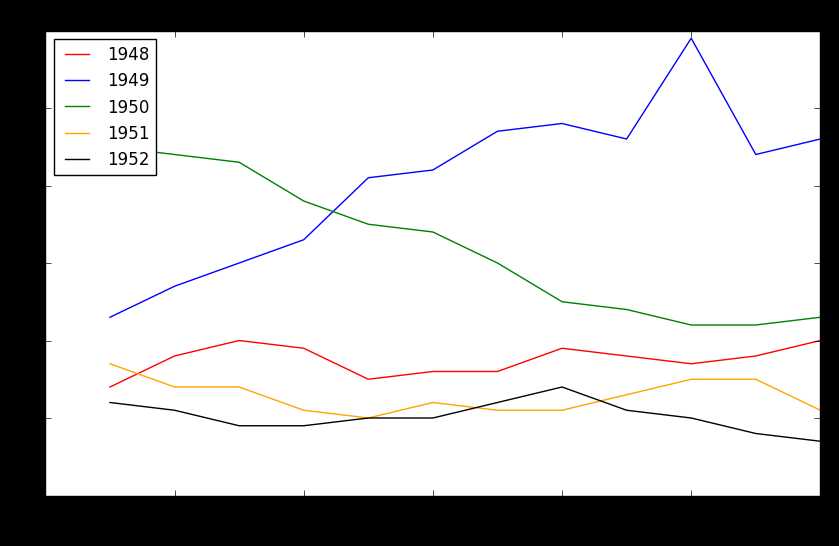
条形图与散点图:
以上是关于Python数据可视化库-Matplotlib的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
