Python Machine Learning
Posted 1直在路上1
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python Machine Learning相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Chapter 3:A Tour of Machine Learning Classifiers Using Scikit-learn
3.1:Training a perceptron via scikit-learn
from sklearn import datasets
import numpy as np
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, [2, 3]]
y = iris.target
np.unique(y)
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
#从150个样本中随机抽取30%的样本作为test_data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3, random_state=0)
#数据归一化
#StandardScaler estimated the parameters μ(sample mean) and (standard deviation)
#(x - mean)/ (standard deviation)
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
sc.fit(X_train)
X_train_std = sc.transform(X_train)
X_test_std = sc.transform(X_test)
#Perceptron分类
#eta0 is equivalent to the learning rate
from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
ppn = Perceptron(n_iter=40, eta0=0.1, random_state=0)
ppn.fit(X_train_std, y_train)
y_pred = ppn.predict(X_test_std)
#y_test != y_pred
\'\'\'
array([False, False, False, False, False, False, False, False, False,
False, True, False, False, False, False, False, False, False,
False, False, False, False, False, False, False, False, False,
False, True, False, False, False, False, False, False, True,
False, True, False, False, False, False, False, False, False])
\'\'\'
print(\'Misclassified samples: %d\' % (y_test != y_pred).sum())
#Misclassified samples: 4
#Thus, the misclassification error on the test dataset is 0.089 or 8.9 percent (4/45)
#the metrics module:performance metrics
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
print(\'Accuracy: %.2f\' % accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
#Accuracy:0.91
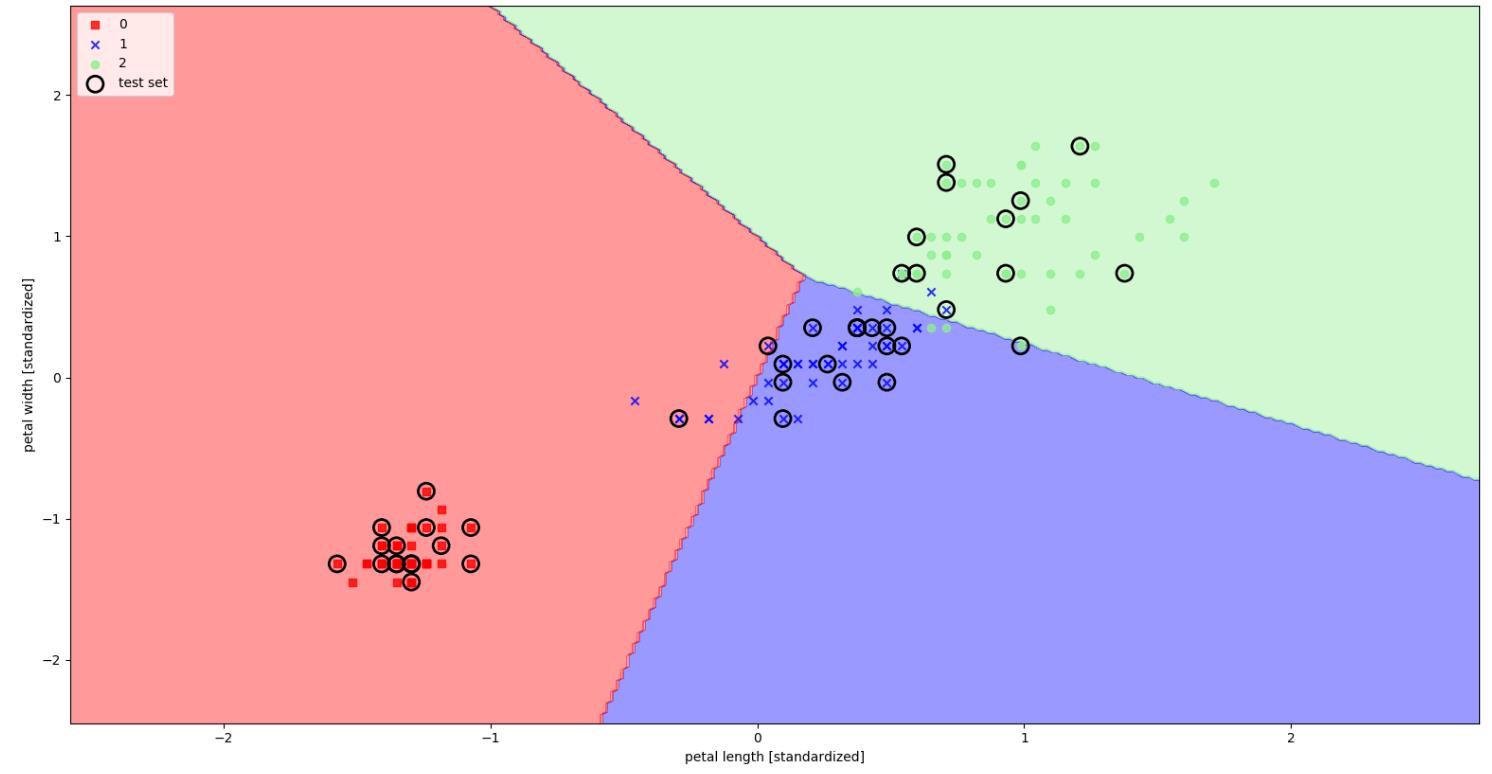
#plot_decision_regions:visualize how well it separates the different flower samples
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, test_idx=None, resolution=0.02):
#setup marker generator and color map
markers = (\'s\', \'x\', \'o\', \'^\', \'v\')
colors = (\'red\', \'blue\', \'lightgreen\', \'black\', \'cyan\')
cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))])
# plot the decision surface
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() -1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() -1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution), np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution))
Z = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T)
Z = Z.reshape(xx1.shape)
plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap=cmap)
plt.xlim(xx1.min(), xx1.max())
plt.ylim(xx2.min(), xx2.max())
# plot all samples
for idx, c1 in enumerate(np.unique(y)):
print idx,c1
plt.scatter(x=X[y == c1, 0], y=X[y == c1, 1], alpha=0.8, c=cmap(idx),marker=markers[idx],label=c1)
#highlight test samples
if test_idx :
X_test, y_test = X[test_idx, :], y[test_idx]
#把 corlor 设置为空,通过edgecolors来控制颜色
plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0],X_test[:, 1], color=\'\',edgecolors=\'black\', alpha=1.0, linewidths=2, marker=\'o\',s=150, label=\'test set\')
X_combined_std = np.vstack((X_train_std, X_test_std))
y_combined = np.hstack((y_train, y_test))
plot_decision_regions(X=X_combined_std, y=y_combined, classifier=ppn, test_idx=range(105,150))
plt.xlabel(\'petal length [standardized]\')
plt.ylabel(\'petal width [standardized]\')
plt.legend(loc=\'upper left\')
plt.show()
3.2 Training a logistic regression model with scikit-learn
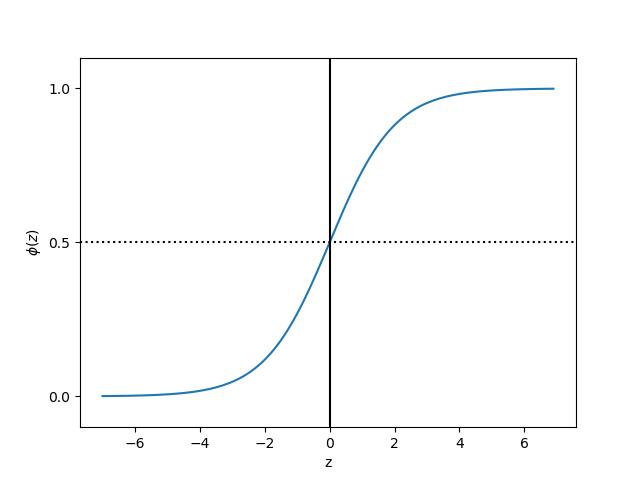
sigmoid function:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(z):
return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z))
z = np.arange(-7, 7, 0.1)
phi_z = sigmoid(z)
plt.plot(z, phi_z)
plt.axvline(0.0, color=\'k\')
plt.axhspan(0.0, 1.0, facecolor=\'1.0\', alpha=1.0, ls=\'dotted\')
plt.axhline(y=0.5, ls=\'dotted\', color=\'k\')
plt.yticks([0.0, 0.5, 1.0])
plt.ylim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.xlabel(\'z\')
plt.ylabel(\'$\\phi (z)$\')
plt.show()
以上是关于Python Machine Learning的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章