vite 基础一网打尽
Posted wanglei1900
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了vite 基础一网打尽相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
vite
Webpack和Vite都是现代化的前端构建工具,它们的主要区别在于构建速度和开发体验。Webpack是一个功能强大的构建工具,它可以处理各种类型的文件,但是在构建大型项目时,它的构建速度可能会变慢
1. vite.config.ts 项目基础配置
/*
- defineConfig 是一个函数,它接受一个函数作为参数,该函数返回一个 UserConfig 对象,该对象描述了项目的配置。
- loadEnv 是一个函数,它接受两个参数:mode 和 cwd。mode 是一个字符串,表示当前的构建模式(例如 development 或 production),cwd 是一个字符串,表示当前工作目录的路径。loadEnv 函数返回一个对象,该对象包含了当前环境的所有变量。
- ConfigEnv 是一个类型别名,它描述了 Vite 构建工具的配置环境。
- UserConfig 是一个类型别名,它描述了 Vite 构建工具的用户配置。
- command参数 是启动vite的命令(dev/serve 或 build),可以用来配置不同场景。
- mode参数 据当前工作目录中的 `mode` 加载相应的 .env 文件.
- ssrBuild参数 SSR 构建(ssrBuild)实验属性vite2无,vite3才有
*/
import defineConfig, loadEnv, ConfigEnv, UserConfig from "vite";
export default defineConfig(( command, mode, ssrBuild : ConfigEnv): UserConfig =>
// ...
)
2. defineConfig函数的配置项接口UserConfig
可以对暴露的defineConfig函数的配置项有个大概的了解
export declare interface UserConfig
/**
* 项目根目录。可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对于配置文件本身的路径。
* @default process.cwd()
*/
root?: string;
/**
* 在开发或生产环境中提供服务时的基本公共路径。
* @default \'/\'
*/
base?: string;
/**
* 用作纯静态资源的目录。此目录中的文件将原样提供服务并复制到构建的 dist 目录中,而不进行转换。
* 值可以是绝对文件系统路径或相对于 <root> 的路径。
*
* 将其设置为 `false` 或空字符串以禁用将静态资源复制到构建的 dist 目录中。
* @default \'public\'
*/
publicDir?: string | false;
/**
* 保存缓存文件的目录。此目录中的文件是预打包的依赖项或由 vite 生成的其他缓存文件,可以提高性能。
* 您可以使用 `--force` 标志或手动删除目录以重新生成缓存文件。
* 值可以是绝对文件系统路径或相对于 <root> 的路径。
* 在未检测到 `package.json` 时默认为 `.vite`。
* @default \'node_modules/.vite\'
*/
cacheDir?: string;
/**
* 显式设置要运行的模式。这将覆盖每个命令的默认模式,并可以被命令行 --mode 选项覆盖。
*/
mode?: string;
/**
* 定义全局变量替换。
* 条目将在开发期间在 `window` 上定义,并在构建期间替换。
*/
define?: Record<string, any>;
/**
* 要使用的 vite 插件数组。
*/
plugins?: PluginOption[];
/**
* 配置解析器
*/
resolve?: ResolveOptions &
alias?: AliasOptions;
;
/**
* 与 CSS 相关的选项(预处理器和 CSS 模块)
*/
css?: CSSOptions;
/**
* JSON 加载选项
*/
json?: JsonOptions;
/**
* 传递给 esbuild 的转换选项。
* 或将其设置为 `false` 以禁用 esbuild。
*/
esbuild?: ESBuildOptions | false;
/**
* 指定要视为静态资源的其他 picomatch 模式。
*/
assetsInclude?: string | RegExp | (string | RegExp)[];
/**
* 服务器特定选项,例如主机、端口、https...
*/
server?: ServerOptions;
/**
* 构建特定选项
*/
build?: BuildOptions;
/**
* 预览特定选项,例如主机、端口、https...
*/
preview?: PreviewOptions;
/**
* 依赖项优化选项
*/
optimizeDeps?: DepOptimizationOptions;
/* 从此版本中排除:ssr */
/**
* 日志级别。
* 默认值:\'info\'
*/
logLevel?: LogLevel;
/**
* 自定义日志记录器。
*/
customLogger?: Logger;
/**
* 默认值:true
*/
clearScreen?: boolean;
/**
* 环境文件目录。可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对于配置文件本身的路径。
* @default root
*/
envDir?: string;
/**
* 以 `envPrefix` 开头的环境变量将通过 import.meta.env 在客户端源代码中公开。
* @default \'VITE_\'
*/
envPrefix?: string | string[];
/**
* 导入别名
* @deprecated 请改用 `resolve.alias`
*/
alias?: AliasOptions;
/**
* 强制 Vite 始终将列出的依赖项解析为相同的副本(从项目根目录)。
* @deprecated 请改用 `resolve.dedupe`
*/
dedupe?: string[];
/**
* Worker bundle 选项
*/
worker?:
/**
* Worker bundle 的输出格式
* @default \'iife\'
*/
format?: \'es\' | \'iife\';
/**
* 适用于 worker bundle 的 Vite 插件
*/
plugins?: PluginOption[];
/**
* 用于构建 worker bundle 的 Rollup 选项
*/
rollupOptions?: Omit<RollupOptions, \'plugins\' | \'input\' | \'onwarn\' | \'preserveEntrySignatures\'>;
;
3. vite.config.ts中进行场景切换和使用环境变量
export default defineConfig(( command, mode, ssrBuild : ConfigEnv): UserConfig =>
// 如果配置文件需要基于(dev/serve 或 build)命令或者不同的 模式 来决定选项,亦或者是一个 SSR 构建(ssrBuild)
console.log(\'mode:\', mode); // mode: \'development\'
console.log(\'command:\', command); // command: \'serve\'
if (command === \'serve\')
return
// dev 独有配置
else
// command === \'build\'
return
// build 独有配置
/*
根据当前工作目录中的 `mode` 加载 .env 文件
第二个参数:process.cwd()表示返回运行当前脚本的工作目录的路径(current work directory)
设置第三个参数为 \'\' 来加载所有环境变量,而不管是否有 `VITE_` 前缀。
*/
const env = loadEnv(mode, process.cwd(),\'\');
console.log(\'env:\', env);
/*
ViteEnv 是一个接口,它描述了 Vite 构建工具的环境变量配置。具体来说,ViteEnv 包含了以下属性:
- VITE_API_URL:一个字符串类型的属性,表示 API 的基础 URL。
- VITE_PORT:一个数字类型的属性,表示 Vite 服务器的端口号。
- VITE_OPEN:一个布尔类型的属性,表示是否在启动 Vite 服务器时自动打开浏览器。
- VITE_GLOB_APP_TITLE:一个字符串类型的属性,表示应用程序的标题。
- VITE_DROP_CONSOLE:一个布尔类型的属性,表示是否在生产模式下删除控制台输出。
- VITE_PROXY_URL:一个字符串类型的属性,表示代理服务器的 URL。
- VITE_BUILD_GZIP:一个布尔类型的属性,表示是否在构建时启用 Gzip 压缩。
- VITE_REPORT:一个布尔类型的属性,表示是否在构建时生成报告。
env
VITE_API_URL: \'/api\',
VITE_PORT: \'3301\',
VITE_OPEN: \'true\',
VITE_GLOB_APP_TITLE: \'Hooks-Admin\',
VITE_DROP_CONSOLE: \'true\'
VITE_USER_NODE_ENV: \'development\',
VITE_BUILD_GZIP: \'false\',
VITE_REPORT: \'false\',
*/
)
4. 项目中使用环境变量
4.1 环境变量
Vite 在一个特殊的 import.meta.env 对象上暴露环境变量
以下变量在所有情况下都能直接使用,其余环境变量需考虑对应加载的环境文件。
- import.meta.env.MODE: string 应用运行的模式。
- import.meta.env.BASE_URL: string 部署应用时的基本 URL。他由base 配置项决定。
- import.meta.env.PROD: boolean 应用是否运行在生产环境。
- import.meta.env.DEV: boolean 应用是否运行在开发环境 (永远与 import.meta.env.PROD相反)。
- import.meta.env.SSR: boolean 应用是否运行在 server 上。
4.2 .env文件
vite根据环境模式加载对应的环境变量
指定模式(.env.production)将会比通用模式的优先级更高(.env)
- .env # 所有情况下都会加载
- .env.local # 所有情况下都会加载,但会被 git 忽略
- .env.[mode] # 只在指定模式下加载
- .env.[mode].local # 只在指定模式下加载,但会被 git 忽略
4.3 环境变量的优先级
- 指定模式的文件(例如 .env.production)会比通用形式的优先级更高(例如 .env)。
- Vite 执行时已经存在的环境变量有最高的优先级(系统变量),不会被 .env 类文件覆盖(例如当终端运行 VITE_SOME_KEY=123 npm run dev)。
- .env 类文件会在 Vite 启动一开始时被加载,而改动会在重启服务器后生效。如果你需要在运行时动态修改环境变量,可以考虑使用 Node.js 的 process.env 对象来实现。
- 加载的环境变量也会通过 import.meta.env 以字符串形式读取。为了防止意外地将一些环境变量泄漏到客户端,只有以 VITE_ 为前缀的变量才会暴露给经过 vite 处理的代码,所以VITE_的变量不应该包含任何敏感细腻。
- 敏感变量应该放到.env.*.local中,并在git中设置忽略。
4.4 智能提示
随着在 .env[mode] 文件中自定义了越来越多的环境变量,你可能想要在代码中获取这些以 VITE_ 为前缀的用户自定义环境变量的 TypeScript 智能提示。
// src 目录下创建一个 env.d.ts 文件,接着按下面这样增加 ImportMetaEnv 的定义
/// <reference types="vite/client" />
// typescrite 智能提示读取import.meta.env里的变量
interface ImportMetaEnv
readonly VITE_APP_TITLE: string
readonly VITE_PORT: string
readonly VITE_API_URL: string
readonly VITE_OPEN: string
// 更多环境变量...
interface ImportMeta
readonly env: ImportMetaEnv
// 解决.ts文件识别不了.vue文件
declare module \'*.vue\'
import type DefineComponent from \'vue\'
const component: DefineComponent<, , any>
export default **component**
4.5 HTML中环境变量的替换
Vite 还支持在 HTML 文件中替换环境变量。import.meta.env 中的任何属性都可以通过特殊的 %ENV_NAME% 语法在 HTML 文件中使用:
<h1>Vite is running in %MODE%</h1>
<p>Using data from %VITE_API_URL%</p>
如果环境变量在 import.meta.env 中不存在,比如不存在的 %NON_EXISTENT%,则会将被忽略而不被替换,这与 JS 中的 import.meta.env.NON_EXISTENT 不同,JS 中会被替换为 undefined。
5. 配置项
5.1 resolve.alias
这将创建一个名为@的别名,指向当前文件所在目录下的src目录。请注意,您需要在webpack配置文件中引入Node.js的path模块,以便使用path.resolve()方法来创建绝对路径。
resolve:
alias:
"@": resolve(__dirname, "./src")
,
5.2 css.preprocessorOptions
指定传递给 CSS 预处理器的选项。文件扩展名用作选项的键。每个预处理器支持的选项可以在它们各自的文档中找到
css:
preprocessorOptions:
// additionalData属性设置了一个名为$injectedColor的变量,它的值为orange。这个变量可以在SCSS文件中使用。
scss:
additionalData: `$injectedColor: orange;`,
,
// dditionalData属性设置了一个@import语句,它导入了一个名为var.less的文件。这个文件中可能包含一些变量或混合器,可以在LESS文件中使用。
less:
additionalData: `@import "@/styles/var.less";`
,
// 仅支持 define,可以作为对象传递
styl:
define:
$specialColor: new stylus.nodes.RGBA(51, 197, 255, 1),
,
,
,
,
5.3 esbuild
- pure: 安全删除调试
- target:指定编译后的 JavaScript 代码的目标运行环境。默认为当前 Node.js 版本。
- jsxFactory 和 jsxFragment:指定 JSX 语法中的 createElement 函数和 Fragment 组件。默认为 React.createElement 和 React.Fragment。
- jsxInject: 自动为每一个文件注入jsx helper。例如:jsxInject:
import React from \'react\', - define:定义全局常量,可以在代码中使用。例如,define: \'process.env.NODE_ENV\': JSON.stringify(mode) 可以将 process.env.NODE_ENV 定义为当前的环境变量 mode。
- minify:是否启用代码压缩。默认为 true。
- keepNames:是否保留函数和变量的名称。默认为 false。
- tsconfig:指定 TypeScript 配置文件的路径。默认为 tsconfig.json。
- loader:自定义文件加载器。例如,loader: \'.svg\': \'file\' 可以将 SVG 文件加载为文件路径。
esbuild:
pure: ["console.log", "debugger"],
target: "es2015",
jsxFactory: "h",
jsxFragment: "Fragment",
define:
"process.env.NODE_ENV": JSON.stringify(mode),
"process.env.BASE_URL": JSON.stringify(base),
,
minify: false,
keepNames: true,
tsconfig: "tsconfig.json",
loader:
".svg": "file",
,
,
5.4 server
- host:指定服务器监听的主机名。默认为 "localhost"。如果将此设置为 0.0.0.0 或者 true,允许外部访问。
- port:指定服务器监听的端口号。默认为 3000。
- https:是否启用 HTTPS。默认为 false。
- open:是否在启动服务器时自动打开浏览器。默认为 false。如果你想在你喜欢的某个浏览器打开该开发服务器,你可以设置环境变量 process.env.BROWSER (例如 firefox)
- cors:是否启用跨域资源共享。默认为 false。
- strictPort:是否启用严格的端口检查。默认为 false。
- proxy:配置代理服务器。例如,proxy: \'/api\': \'http://localhost:8080\' 可以将 /api 路径下的请求代理到 http://localhost:8080。
- hmr:配置模块热替换。例如,hmr: overlay: false 可以禁用热更新时的错误提示。
- watch:配置文件监听。例如,watch: disableGlobbing: true 可以禁用文件名通配符。
- middleware:配置自定义中间件。例如,middleware: [myMiddleware] 可以添加一个自定义中间件函数 myMiddleware。
server:
host: "localhost",
port: 8080,
https: true,
open: true,
cors: true,
strictPort: true,
proxy:
"/api": "http://localhost:3000", // 定代理服务器的地址。
changeOrigin: true, // 是否改变请求头中的 Origin 字段。默认为 false。
rewrite: path => path.replace(/^\\/api/, "") // 重写请求路径。例如,path => path.replace(/^\\/api/, "") 可以将 /api 前缀去掉。
,
hmr:
overlay: false, // 模块热替换禁用了错误提示
,
watch:
usePolling: true, // 文件监听使用了轮询方式
,
middleware: [myMiddleware], //自定义中间件函数 myMiddleware 被添加到了中间件数组中。
,
5.5 build
- outDir:指定输出目录,默认为dist。
- assetsDir:指定静态资源目录,默认为assets。
- assetsInlineLimit:指定资源内联的最大大小,单位为字节,默认为4096。
- cssCodeSplit:指定是否将CSS代码拆分为单独的文件,默认为true。
- minify:指定是否压缩代码,默认:\'esbuild\'。boolean | \'terser\' | \'esbuild\'
- sourcemap:指定是否生成sourcemap,默认为false。
- chunkSizeWarningLimit:规定触发警告的 chunk 大小。(以 kbs 为单位)。
- rollupOptions:指定传递给Rollup的选项,例如input、output、plugins等。
- terserOptions:指定传递给Terser的选项,例如compress、mangle等。
build:
outDir: \'dist\',
assetsDir: \'assets\',
cssCodeSplit: true,
minify: \'esbuild\',
sourcemap: false,
chunkSizeWarningLimit: 1500,
rollupOptions:
input:
main: \'./src/main.js\',
secondary: \'./src/secondary.js\'
,
output:
entryFileNames: \'[name]-[hash].js\',
chunkFileNames: \'[name]-[hash].js\',
assetFileNames: \'[name]-[hash].[ext]\'
,
plugins: [
// 添加rollup插件
// Static resource classification and packaging
chunkFileNames: "assets/js/[name]-[hash].js",
entryFileNames: "assets/js/[name]-[hash].js",
assetFileNames: "assets/[ext]/[name]-[hash].[ext]"
]
,
// terserOptions:
// compress:
// drop_console: true,
// drop_debugger: true
// ,
// mangle: true
//
5.6 plugins
需要用到的插件数组
- react():用于在Vite中使用React。
- createHtmlPlugin():用于生成HTML文件并注入数据。
- createSvgIconsPlugin():用于导入SVG图标。
- eslintPlugin():用于在开发过程中进行ESLint检查。
- visualizer():用于生成包预览。
- viteCompression():用于压缩生成的文件。
- @vitejs/plugin-vue:用于在Vue应用程序中使用单文件组件。
- @vitejs/plugin-react-refresh:用于在React应用程序中启用热重载。
- @vitejs/plugin-legacy:用于在旧版浏览器中使用ES5代码。
- @vitejs/plugin-json:用于导入JSON文件。
- @vitejs/plugin-commonjs:用于将CommonJS模块转换为ES模块。
- @vitejs/plugin-node-resolve:用于解析Node.js模块。
- @vitejs/plugin-eslint:用于在开发过程中进行ESLint检查。
- @vitejs/plugin-svg:用于导入SVG文件。
- @vitejs/plugin-image:用于导入图像文件。
6.示例
/*
- defineConfig 是一个函数,它接受一个函数作为参数,该函数返回一个 UserConfig 对象,该对象描述了项目的配置。
- loadEnv 是一个函数,它接受两个参数:mode 和 cwd。mode 是一个字符串,表示当前的构建模式(例如 development 或 production),cwd 是一个字符串,表示当前工作目录的路径。loadEnv 函数返回一个对象,该对象包含了当前环境的所有变量。
- ConfigEnv 是一个类型别名,它描述了 Vite 构建工具的配置环境。
- UserConfig 是一个类型别名,它描述了 Vite 构建工具的用户配置。
*/
import defineConfig, loadEnv, ConfigEnv, UserConfig from "vite";
import react from "@vitejs/plugin-react";
import resolve from "path";
import wrapperEnv from "./src/utils/getEnv";
import visualizer from "rollup-plugin-visualizer";
import createHtmlPlugin from "vite-plugin-html";
import viteCompression from "vite-plugin-compression";
import eslintPlugin from "vite-plugin-eslint";
import createSvgIconsPlugin from "vite-plugin-svg-icons";
// @see: https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig((mode: ConfigEnv): UserConfig =>
console.log(\'mode\', mode);
/*
mode 23:15:28
mode: \'development\',
command: \'serve\'
*/
/*
根据当前工作目录中的 `mode` 加载 .env 文件
第二个参数:process.cwd()表示返回运行当前脚本的工作目录的路径(current work directory)
设置第三个参数为 \'\' 来加载所有环境变量,而不管是否有 `VITE_` 前缀。
*/
const env = loadEnv(mode.mode, process.cwd());
const viteEnv = wrapperEnv(env);
console.log(\'env\', env);
/*
ViteEnv 是一个接口,它描述了 Vite 构建工具的环境变量配置。具体来说,ViteEnv 包含了以下属性:
- VITE_API_URL:一个字符串类型的属性,表示 API 的基础 URL。
- VITE_PORT:一个数字类型的属性,表示 Vite 服务器的端口号。
- VITE_OPEN:一个布尔类型的属性,表示是否在启动 Vite 服务器时自动打开浏览器。
- VITE_GLOB_APP_TITLE:一个字符串类型的属性,表示应用程序的标题。
- VITE_DROP_CONSOLE:一个布尔类型的属性,表示是否在生产模式下删除控制台输出。
- VITE_PROXY_URL:一个字符串类型的属性,表示代理服务器的 URL。
- VITE_BUILD_GZIP:一个布尔类型的属性,表示是否在构建时启用 Gzip 压缩。
- VITE_REPORT:一个布尔类型的属性,表示是否在构建时生成报告。
env 23:22:04
VITE_API_URL: \'/api\',
VITE_PORT: \'3301\',
VITE_OPEN: \'true\',
VITE_GLOB_APP_TITLE: \'Hooks-Admin\',
VITE_DROP_CONSOLE: \'true\'
VITE_USER_NODE_ENV: \'development\',
VITE_BUILD_GZIP: \'false\',
VITE_REPORT: \'false\',
*/
return
// base: "/",
// alias config
resolve:
alias:
"@": resolve(__dirname, "./src")
,
// global css
css:
preprocessorOptions:
less:
// modifyVars:
// "primary-color": "#1DA57A",
// ,
javascriptEnabled: true,
additionalData: `@import "@/styles/var.less";`
,
// server config
server:
host: "0.0.0.0", // 服务器主机名,如果允许外部访问,可设置为"0.0.0.0"
port: viteEnv.VITE_PORT,
open: viteEnv.VITE_OPEN,
cors: true,
// https: false,
// 代理跨域(mock 不需要配置,这里只是个事列)
proxy:
"/api":
target: "https://mock.mengxuegu.com/mock/62abda3212c1416424630a45", // easymock
changeOrigin: true,
rewrite: path => path.replace(/^\\/api/, "")
,
// plugins
plugins: [
react(),
createHtmlPlugin(
inject:
data:
title: viteEnv.VITE_GLOB_APP_TITLE
),
// * 使用 svg 图标
createSvgIconsPlugin(
iconDirs: [resolve(process.cwd(), "src/assets/icons")],
symbolId: "icon-[dir]-[name]"
),
// * EsLint 报错信息显示在浏览器界面上
eslintPlugin(),
// * 是否生成包预览
viteEnv.VITE_REPORT && visualizer(),
// * gzip compress
viteEnv.VITE_BUILD_GZIP &&
viteCompression(
verbose: true,
disable: false,
threshold: 10240,
algorithm: "gzip",
ext: ".gz"
)
],
esbuild:
pure: viteEnv.VITE_DROP_CONSOLE ? ["console.log", "debugger"] : []
,
// build configure
build:
outDir: "dist",
// esbuild 打包更快,但是不能去除 console.log,去除 console 使用 terser 模式
minify: "esbuild",
// minify: "terser",
// terserOptions:
// compress:
// drop_console: viteEnv.VITE_DROP_CONSOLE,
// drop_debugger: true
//
// ,
rollupOptions:
output:
// Static resource classification and packaging
chunkFileNames: "assets/js/[name]-[hash].js",
entryFileNames: "assets/js/[name]-[hash].js",
assetFileNames: "assets/[ext]/[name]-[hash].[ext]"
;
);Vue3 的基础使用(详细)
一、Vite创建Vue3 项目
npm init vite@latest vue3-ts-vite -- --template vue
创建成功后用npm install命令安装依赖运行项目

vue3+vite初始化项目的基础结构

启动成功的页面

二、Vue3基本语法
1、定义全局变量
<template>
<h1>msg</h1>
<div>
<a href="https://vitejs.dev" target="_blank">
<img src="/vite.svg" class="logo" alt="Vite logo" />
</a>
<a href="https://vuejs.org/" target="_blank">
<img src="./assets/vue.svg" class="logo vue" alt="Vue logo" />
</a>
</div>
<HelloWorld msg="Vite + Vue" />
</template>
<script setup>
// This starter template is using Vue 3 <script setup> SFCs
// Check out https://vuejs.org/api/sfc-script-setup.html#script-setup
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
let msg = "定义全局变量"
</script>
<style scoped>
.logo
height: 6em;
padding: 1.5em;
will-change: filter;
.logo:hover
filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #646cffaa);
.logo.vue:hover
filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #42b883aa);
</style>
在<script setup>中定义的变量为全局变量,可以全局使用。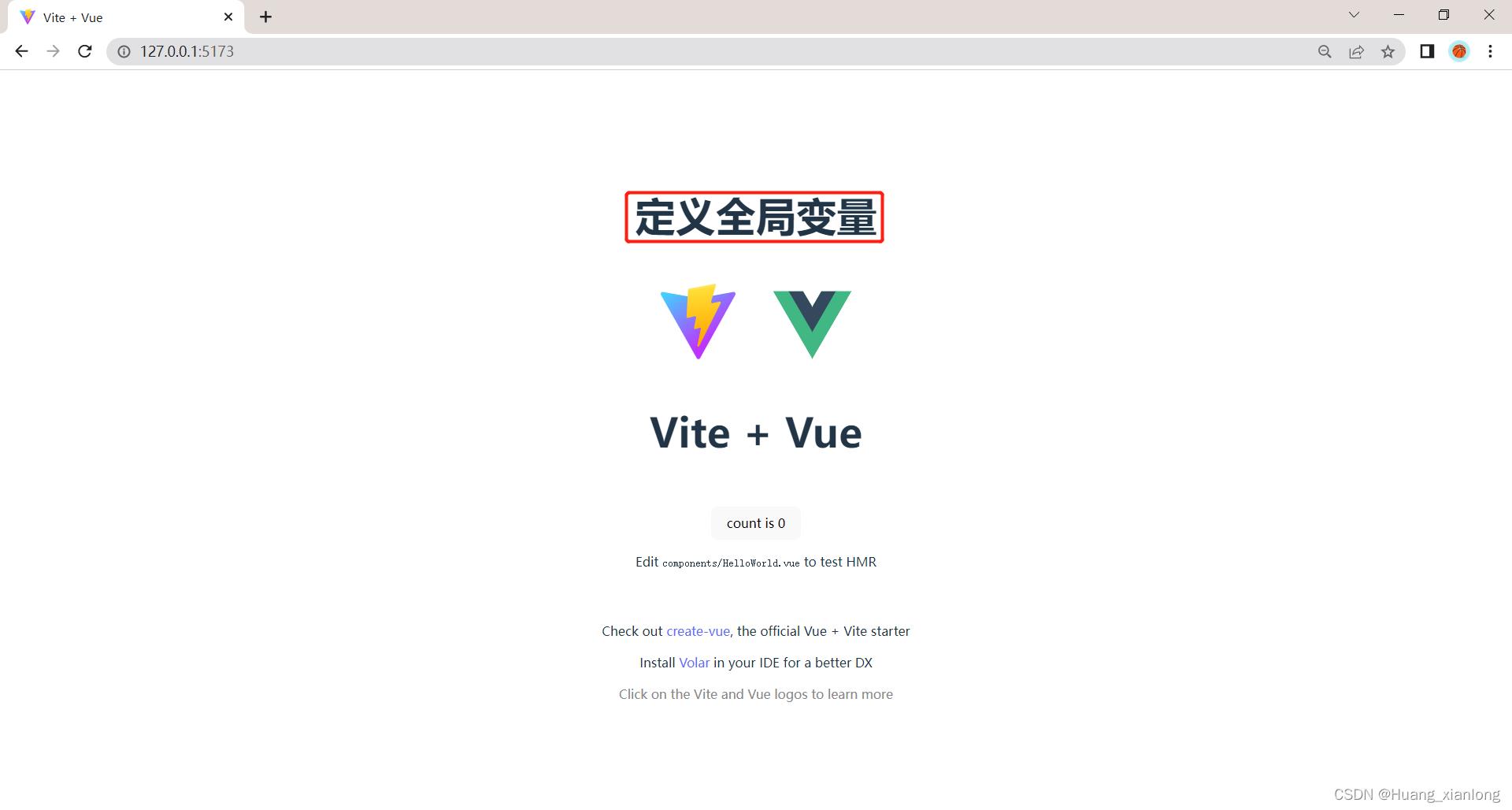
2、定义函数
翻转字符串函数
<template>
<h1>msg</h1>
<h1>reMsg(msg)</h1>
<div>
<a href="https://vitejs.dev" target="_blank">
<img src="/vite.svg" class="logo" alt="Vite logo" />
</a>
<a href="https://vuejs.org/" target="_blank">
<img src="./assets/vue.svg" class="logo vue" alt="Vue logo" />
</a>
</div>
<HelloWorld msg="Vite + Vue" />
</template>
<script setup>
// This starter template is using Vue 3 <script setup> SFCs
// Check out https://vuejs.org/api/sfc-script-setup.html#script-setup
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
let msg = "定义全局变量"
function reMsg(val)
return val.split('').reverse().join('')
</script>
<style scoped>
.logo
height: 6em;
padding: 1.5em;
will-change: filter;
.logo:hover
filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #646cffaa);
.logo.vue:hover
filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #42b883aa);
</style>

3、定义响应式ref
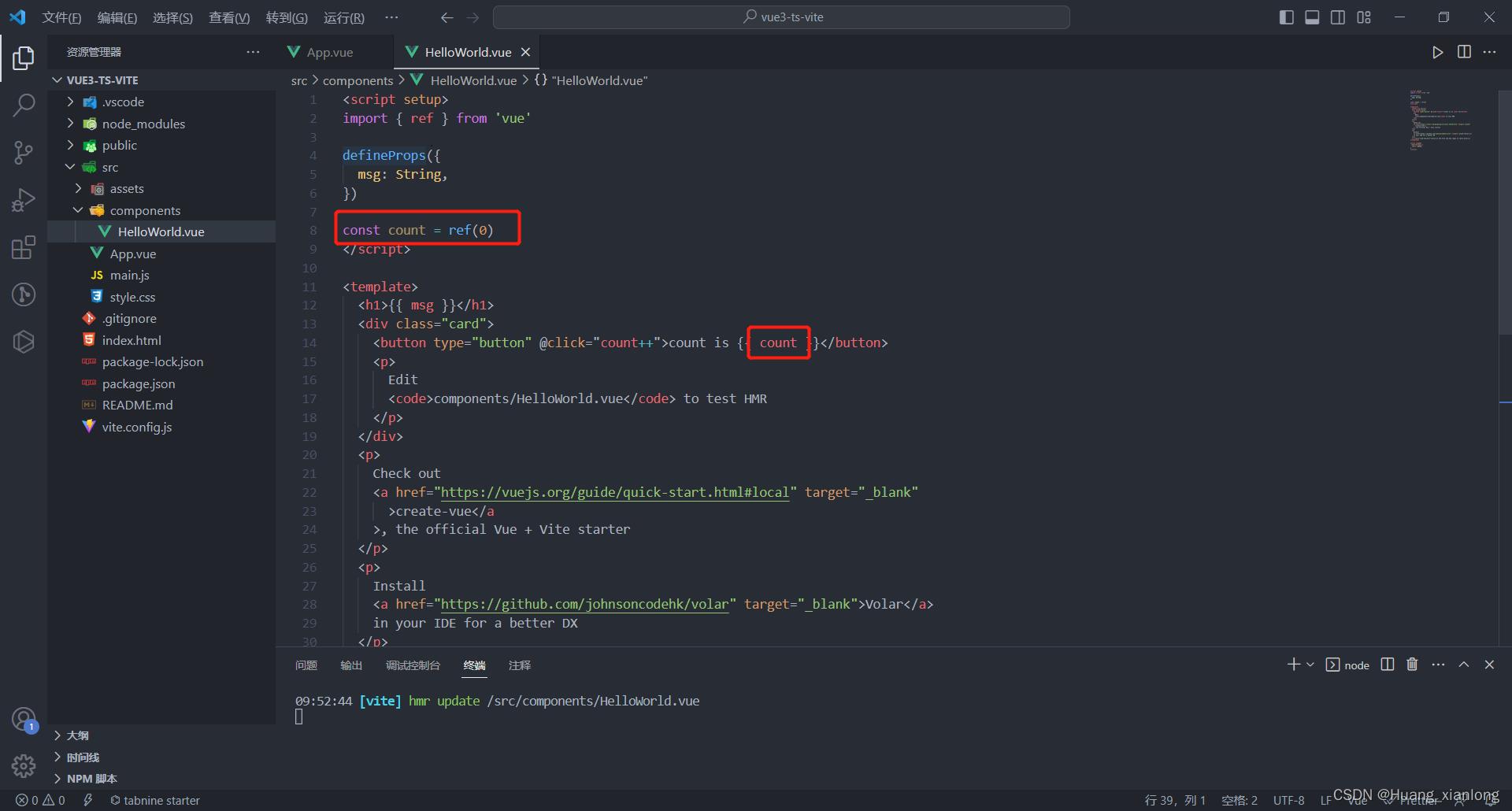
在vue3中想要数据具有响应性,就需要用ref来创建响应式对象。
<template>
<h1>msg</h1>
<h1>reMsg(msg)</h1>
<button @click="setMsg">点击修改</button>
<div>
<a href="https://vitejs.dev" target="_blank">
<img src="/vite.svg" class="logo" alt="Vite logo" />
</a>
<a href="https://vuejs.org/" target="_blank">
<img src="./assets/vue.svg" class="logo vue" alt="Vue logo" />
</a>
</div>
<HelloWorld msg="Vite + Vue" />
</template>
<script setup>
// This starter template is using Vue 3 <script setup> SFCs
// Check out https://vuejs.org/api/sfc-script-setup.html#script-setup
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
import ref from 'vue'
//通过 ref 创建响应式对象
let msg = ref("定义全局变量")
function reMsg(val)
return val.split('').reverse().join('')
function setMsg()
msg.value = "ref创建响应式对象"
</script>
<style scoped>
.logo
height: 6em;
padding: 1.5em;
will-change: filter;
.logo:hover
filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #646cffaa);
.logo.vue:hover
filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #42b883aa);
</style>

vue3项目初始化的HelloWorld.vue的count数值变化的原理也是因为用了ref来创建响应式对象。

4、响应式reactive
ref允许我们创建一个任意类型的响应式的ref对象,在使用时需要带上.value。在模板中使用ref对象时,假如ref位于顶层,就不需要使用value,它会自动解包,但如果ref对象是作为一个属性声明于对象之中,在模板中进行运算时仍然要使用.value。
通常使用reactive()来创建一个响应式的对象或数组,这样的对象或数组状态都是默认深层响应式的,无论嵌套多深,都能跟踪到。但他也有局限性,就是只对对象类型有效,对基本数据类型无效,并且假如用一个新对象替换了原来的旧对象,那么原来的旧对象会失去响应性。

 点击相应的按钮都能改变数据并显示
点击相应的按钮都能改变数据并显示

两者区别:
1、ref多用来定义基本数据类型(也可以定义对象,内部会自动通过reactive转为代理对象),而 reactive只能用来定义对象数组类型;
2、ref操作数据需要.value,reactive操作数据不需要.value;
3、ref通过Object.defineProperty()的get和set来实现响应式, reactive通过Proxy来实现响应式,并通过Reflect操作源对象内部的数据。
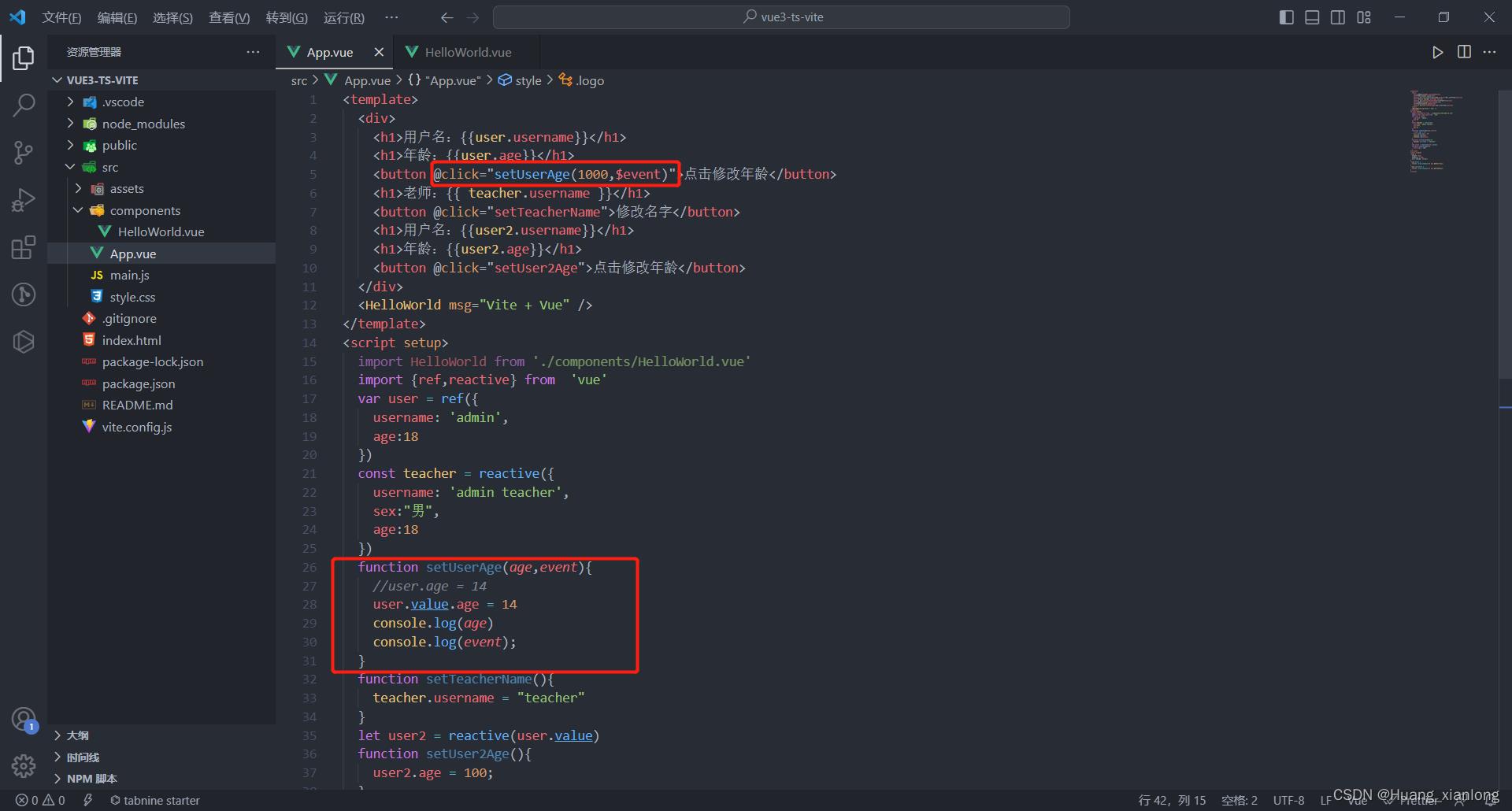
5、Vue3事件对象与传递参数
Vue3事件对象与传递参数与普通函数的定义和使用一致。

6、Vue3计算属性
6.1引入computed将计算的结果进行缓存,防止多次调用损失性能
<template>
<div>
<h1>msg</h1>
<h1> reMsg </h1>
<h1> reMsg </h1>
<h1> reMsg </h1>
<button @click="setMsg('itred',$event)"></button>
</div>
<HelloWorld msg="Vite + Vue" />
</template>
<script setup>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
import ref,computed,reactive from 'vue'
let msg = reactive("计算属性computed")
function setMsg(value,event)
msg.value = value
console.log(value)
console.log(event)
const reMsg = computed( function ()
console.log(123)
return msg.split("").reverse().join("")
)
</script>
<style scoped>
.logo
height: 6em;
padding: 1.5em;
will-change: filter;
.logo:hover
filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #646cffaa);
.logo.vue:hover
filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #42b883aa);
</style> 我们可以发现虽然调用了三遍,但是函数只执行了一次。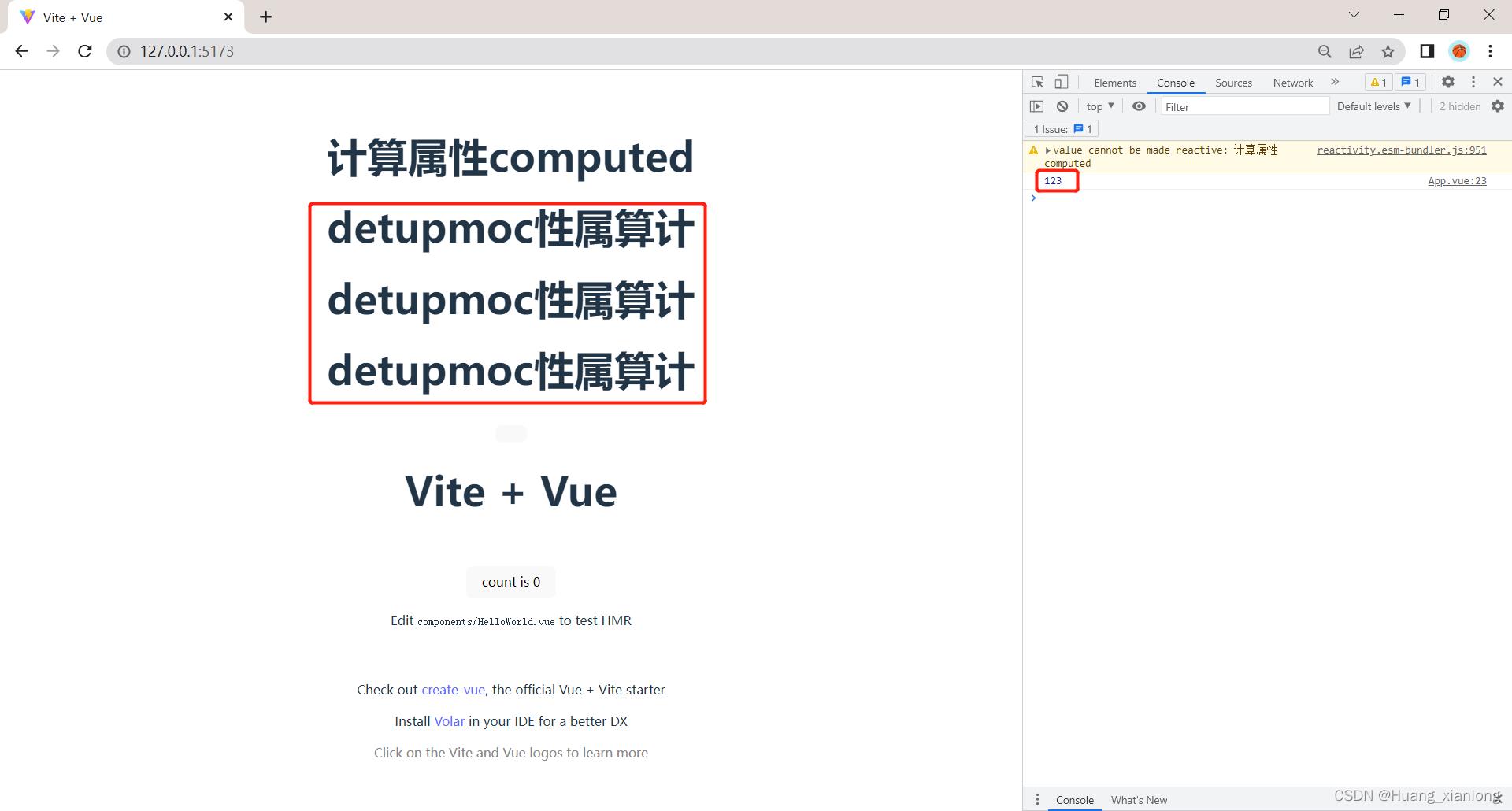
6.2 设置值和修改值
<template>
<div>
<h1> msg </h1>
<h1> reMsg </h1>
<h1> reMsg </h1>
<h1> reMsg </h1>
<button @click="setMsg('methods', $event)">修改内容</button>
<button @click="setReMsg">修改计算属性reMsg</button>
</div>
<HelloWorld msg="Vite + Vue" />
</template>
<script setup>
import HelloWorld from "./components/HelloWorld.vue";
import ref, computed from "vue";
let msg = ref("计算属性computed");
function setMsg(value, event)
msg.value = value;
console.log("methods");
const reMsg = computed(
get: () =>
console.log("get");
return msg.value.split("").reverse().join("");
,
set: (value) =>
console.log("set");
msg.value = value.split("").reverse().join("");
,
);
function setReMsg()
reMsg.value = "computed";
</script>
<style scoped>
.logo
height: 6em;
padding: 1.5em;
will-change: filter;
.logo:hover
filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #646cffaa);
.logo.vue:hover
filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #42b883aa);
</style>
reMsg默认加载的时候调用了get方法

点击修改计算属性reMsg的时候调用set方法后又调用get方法。
7、Vue3监听数据变化



监听对象



7.2、多个数据监听
同时监听多个数据
// 同时监听mes和user.name
watch([msg, () => user.name], (newValue, oldValue) =>
console.log("newValue", newValue);
console.log("oldValue", oldValue);
);

8、Vue3常见指令与样式
<template>
<div>
<h1>msg</h1>
<h1 v-bind:class="classname"></h1>
<h1 :class="classname"></h1>
</div>
<HelloWorld msg="Vite + Vue" />
</template>
<script setup>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
import ref, computed, watch, reactive from 'vue'
let msg = ref("Vue3")
let classname = ref('box bgRed')
</script>
<style scoped>
.box
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
.bgRed
background-color: red;
</style>
8.2、id
<template>
<div>
<h1>msg</h1>
<h1 v-bind:class="classname"></h1>
<h1 :class="classname"></h1>
<h1 :id="box"></h1>
</div>
<HelloWorld msg="Vite + Vue" />
</template>
<script setup>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
import ref, computed, watch, reactive from 'vue'
let msg = ref("Vue3")
let classname = ref('box bgRed')
let box = ref('box')
</script>
<style scoped>
.box
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
.bgRed
background-color: red;
#box
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
</style>
8.3、title
<template>
<div>
<h1>msg</h1>
<h1 v-bind:class="classname"></h1>
<h1 :title="desc" :class="classname"></h1>
<h1 :id="box"></h1>
</div>
<HelloWorld msg="Vite + Vue" />
</template>
<script setup>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
import ref, computed, watch, reactive from 'vue'
let msg = ref("Vue3")
let classname = ref('box bgRed')
let box = ref('box')
let desc = ref("这是一个box")
</script>
<style scoped>
.box
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
.bgRed
background-color: red;
#box
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
</style>title设置后鼠标放到该元素上会显示设置的内容

8.4、富文本显示
<template>
<div>
<h1>msg</h1>
<h1 v-bind:class="classname"></h1>
<h1 :title="desc" :class="classname"></h1>
<h1 :id="box"></h1>
<span>无富文本显示</span>
<div class="content">html</div>
<span>富文本显示</span>
<div class="content" v-html="html"></div>
</div>
<HelloWorld msg="Vite + Vue" />
</template>
<script setup>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
import ref, computed, watch, reactive from 'vue'
let msg = ref("Vue3")
let classname = ref('box bgRed')
let box = ref('box')
let desc = ref("这是一个box")
let html = ref("<h1>这是HTML的内容</h1>")
</script>
<style scoped>
.box
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
.bgRed
background-color: red;
#box
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
</style>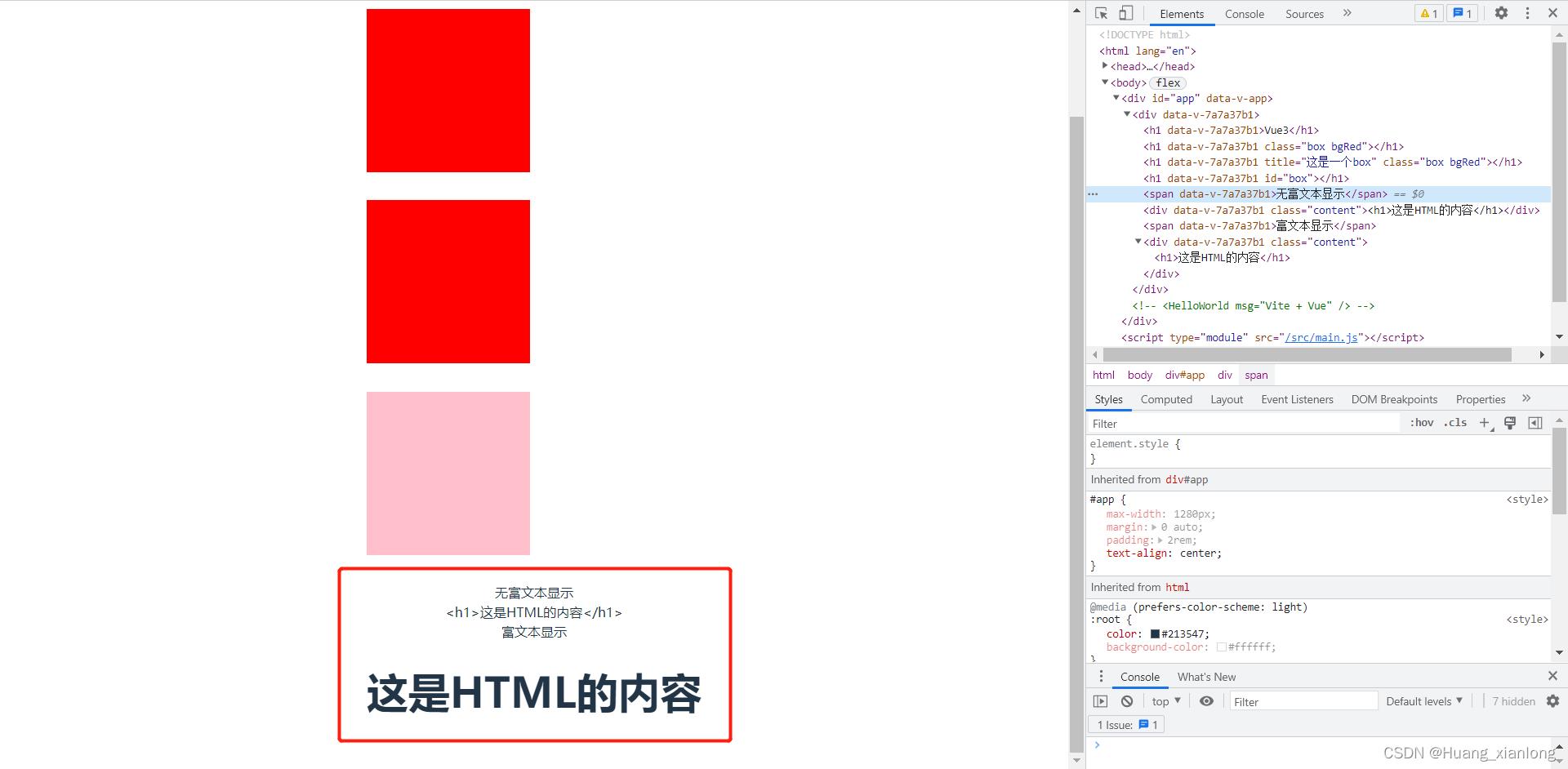
8.5、点击事件
监听点击事件

 8.6、点击切换样式
8.6、点击切换样式



8.7、:style
使用:style写的样式为行内样式


9、Vue父子组件数据传递Props


9.2 设置父组件给子组件传递数据



10、Vue3自定义事件
10.1 定义子组件在父组件当中引用(父组件的数据传递给子组件)
子组件当中定义事件
// 子组件
<template>
<h1 @click="sendRead">
<span>
props.num
</span>
---------
<span>
props.title
</span>
<br />
article
<span>
props.article.num
</span>
---------
<span>
props.article.title
</span>
</h1>
</template>
<script setup>
import defineProps, defineEmits from "vue";
const props = defineProps(
num: Number,
title: String,
article: Object,
);
const emit = defineEmits(["finishRead", "reading"]);
function sendRead()
emit("finishRead");
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
父组件接受事件
// 父组件
<template>
<div>
<ListItem
:num="article.num"
:title="article.title"
:article="article"
></ListItem>
<h1>列表循环</h1>
<ListItem
:num="item.num"
:title="item.title"
:article="item"
v-for="item in articleList"
:key="item.num"
@finishRead="changeTitle(item)"
>
</ListItem>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import ListItem from "./components/ListItem.vue";
import reactive from "vue";
let article = reactive(
num: 10,
title: "定义propss",
);
let articleList = reactive([
num: 10,
title: "定义propss1",
,
num: 11,
title: "定义propss2",
,
]);
function changeTitle(item)
console.log(item);
item.title += "【已读】";
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>点击前

点击后

10.2 定义子组件在父组件当中引用(子组件的数据传递给父组件)

11、Vue3路由
vue的vue-router是基于路由和组件的,路由用于设定访问路径, 将路径和组件映射起来,在vue-router的单页面应用中, 页面的路径的改变就是组件的切换。
11.1 安装路由
npm install vue-router@411.2 路由的使用步骤和基本使用流程

路由的基本使用流程
router.js
// history模式
import
createRouter,
createWebHashHistory,
from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../pages/Home.vue'
import About from '../pages/About.vue'
const routes = [
// 路由的默认路径
path:'/',
redirect:"/home"
,
path: '/home',
component: Home
,
path: '/about',
component: About
,
]
// 创建路由对象
const router = createRouter(
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes
)
export default router;
main.js
import
createApp
from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app')
App.js
<template>
<div>
<router-link to="/home">home</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">about</router-link>
<keep-alive>
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default
name: "App",
components: ,
;
</script>
<style>
</style>
11.3 路由懒加载
如果我们能把不同路由对应的组件分割成不同的代码块,然后当路由被访问的时候才加载对应组件,这样就会更加高效;
这里可以使用webpack的分包知识,而Vue Router默认就支持动态来导入组件;
这是因为component可以传入一个组件,也可以接收一个函数,该函数 需要放回一个Promise;
而import函数就是返回一个Promise;
const routes = [
path: '/',
redirect: "/home"
,
path: '/home',
component: () => import('../pages/Home.vue')
,
path: '/about',
component: () => import('../pages/About.vue')
,
]我们会发现分包是没有一个很明确的名称的,其实webpack从3.x开始支持对分包进行命名(chunk name):
const routes = [
path: '/',
redirect: "/home"
,
path: '/home',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName:"home-chunk"*/'../pages/Home.vue')
,
path: '/about',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName:"about-chunk"*/'../pages/About.vue')
,
]11.4 动态路由基本匹配
很多时候我们需要将给定匹配模式的路由映射到同一个组件:
在Vue Router中,我们可以在路径中使用一个动态字段来实现,我们称之为 路径参数
path: “/user/:id”,
component: () => import(’…/pages/user.vue’)
在router-link中进行如下跳转:
<router-link to="/user/123">user</router-link>
获取路由的值
在setup中,我们要使用 vue-router库给我们提供的一个hook useRoute;
<template>
<div> route.params </div>
</template>
<script>
import useRoute from "vue-router";
export default
setup()
const route = useRoute();
return route ;
,
;
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
</style>
NotFound
对于哪些没有匹配到的路由,我们通常会匹配到固定的某个页面
- 比如NotFound的错误页面中,这个时候我们可编写一个动态路由用于匹配所有的页面;
path: '/:pathMatch(.*)',
component: () => import('../pages/NotFound.vue')
我们可以通过 $route.params.pathMatch获取到传入的参数:
$route.params.pathMatch
匹配规则加*
*我在/:pathMatch(.*)后面又加了一个 ;
path: '/:pathMatch(.*)*',
component: () => import('../pages/NotFound.vue')
路由的嵌套
顾名思义是子路由,界面里面还有界面
path: '/home',
component: () => import( /* webpackChunkName:"home-chunk"*/ '../pages/Home.vue'),
children: [
path:'',
redirect:'/home/product'
,
path:'product',
component:()=>import('../pages/HomeProduct.vue')
]
,
代码的页面跳转
有时候我们希望通过代码来完成页面的跳转,比如点击的是一个按钮
junpToProfile()
this.$router.push('/profile')
当然,我们也可以传入一个对象
junpToProfile()
this.$router.push(
path:'/profile'
)
如果是在setup中编写 的代码,那么我们需要通过useRouter来获取
const router = useRouter()
const junpToProfile = () =>
router.replace('/profile')
query方式的参数
setup()
const router = useRouter();
const jumpTo = () =>
router.push(
path: "/about",
query:
name: "fuck",
,
);
;
return jumpTo;
,
在界面中通过 $route.query 来获取参数:
$route.query
替换当前的位置
使用push的特点是压入一个新的页面,那么在用户点击返回时,上一个页面还可以回退,但是如果我们希望当前
页面是一个替换操作,那么可以使用replace:
<router-link to="/home/product" replace="">子界面</router-link>
页面的前进后退

router-link的v-slot
在vue-router3.x的时候,router-link有一个tag属性,可以决定router-link到底渲染成什么元素:
但是在vue-router4.x开始,该属性被移除了;
而给我们提供了更加具有灵活性的v-slot的方式来定制渲染的内容;
我们使用v-slot来作用域插槽来获取内部传给我们的值:
href:解析后的 URL;
route:解析后的规范化的route对象;
navigate:触发导航的函数;
isActive:是否匹配的状态;
isExactActive:是否是精准匹配的状态;
<!-- props: href 跳转的链接 -->
<!-- props: route对象 -->
<!-- props: navigate导航函数 -->
<!-- props: isActive 是否当前处于活跃的状态 -->
<!-- props: isExactActive 是否当前处于精确的活跃状态 -->
<router-link to="/home" v-slot="props">
<p @click="props.navigate"> props.href </p>
<span :class=" active: props.isActive "> props.isActive </span>
<span :class=" active: props.isActive "> props.isExactActive </span>
</router-link>
router-view的v-slot
router-view也提供给我们一个插槽,可以用于 和 组件来包裹你的路由组件:
Component:要渲染的组件;
route:解析出的标准化路由对象;
动态添加路由
某些情况下我们可能需要动态的来添加路由:
如果我们是为route添加一个children路由,那么可以传入对应的name:
// 创建路由对象
const router = createRouter(
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes
)
const categoryA = //接口返回路由信息
path: '/category',
name: 'category',
component: () => category
;
router.addRoute("category",
path: '/child',
name: 'child',
component: () => import('../newpage/child.vue')
)
11.5 动态删除路由
删除路由有以下三种方式:
方式一:添加一个name相同的路由;
方式二:通过removeRoute方法,传入路由的名称;
方式三:通过addRoute方法的返回值回调;
路由导航守卫
vue-router 提供的导航守卫主要用来通过跳转或取消的方式守卫导航。
全局的前置守卫beforeEach是在导航触发时会被回调的:
它有两个参数:to:即将进入的路由Route对象;from:即将离开的路由Route对象;
它有返回值:false:取消当前导航;不返回或者undefined:进行默认导航;
返回一个路由地址:可以是一个string类型的路径;可以是一个对象,对象中包含path、query、params等信息;
可选的第三个参数:next
在Vue2中我们是通过next函数来决定如何进行跳转的;
但是在Vue3中我们是通过返回值来控制的,不再推荐使用next函数,这是因为开发中很容易调用多次next;
router.beforeEach((to, from) =>
console.log('to', to)
console.log('from', from)
if (to.path !== '/about')
const token = localStorage.setItem('token', 'qwer')
if (!token)
return '/about'
)
12、 Vue3中vuex的基本使用
12.1 基本结构
src/store/index.js中,代码如下
// vue3中创建store实例对象的方法createStore()按需引入
import createStore from 'vuex'
export default createStore(
state:
,
mutations:
,
actions:
,
getters:
,
modules:
)
12.2 基本使用
src/store/index.js
import createStore from 'vuex'
export default createStore(
state:
info: 'hello'
,
mutations:
// 定义mutations,用于修改状态(同步)
updateInfo (state, payload)
state.info = payload
,
actions:
// 定义actions,用于修改状态(异步)
// 2秒后更新状态
updateInfo (context, payload)
setTimeout(() =>
context.commit('updateInfo', payload)
, 2000)
,
getters:
// 定义一个getters
formatInfo (state)
return state.info + ' Tom'
,
modules:
)
src/views/Test.vue测试组件中对store中数据的操作与使用
<template>
<div>测试组件</div>
<hr>
<!-- 页面中直接使用渲染时与vue2中的使用方法相同 -->
<div>获取Store中的state、getters: $store.getters.formatInfo</div>
<button @click='handleClick'>点击</button>
</template>
<script>
// 按需引入useStore()方法
import useStore from 'vuex'
export default
name: 'Test',
setup ()
// this.$store.state.info
// Vue3中store类似于Vue2中this.$store
// useStore()方法创建store对象,相当于src/store/index.js中的store实例对象
const store = useStore()
console.log(store.state.info) // hello
// 修改info的值
const handleClick = () =>
// 触发mutations,用于同步修改state的信息
// store.commit('updateInfo', 'nihao')
// 触发actions,用于异步修改state的信息
store.dispatch('updateInfo', 'hi')
return handleClick
</script>
12.3 将store中的数据模块化后的使用
1. 模块化
基于原index.js代码进行改造拆分,假设有两个模块global和user,新建src/store/modules/global.js 、src/store/modules/user.js文件
拆分后代码如下(src/store/modules/global.js)
// 全局store,存放全局使用共享的数据
export default // 注意:全局模块中不需要开启命名空间
state:
,
mutations:
,
actions:
,
getters:
拆分后代码如下(src/store/modules/user.js)
// 用户信息模块(局部模块)
export default
namespaced: true, // 开启命名空间
state ()
return
// 用户信息对象
profile:
id: '',
avatar: '',
nickname: 'yee',
account: '',
mobile: '',
token: ''
,
mutations:
// 定义mutations,用于同步修改状态
updateNickname (state, payload)
state.profile.nickname = payload
,
actions:
// 定义actions,用于异步修改状态
// 2秒后更新状态
updateNickname (context, payload)
setTimeout(() =>
context.commit('updateNickname', payload)
, 2000)
,
getters:
// 定义一个getters
formatNickname (state)
return 'Hi ' + state.profile.nickname
拆分后代码如下(src/store/index.js)
import createStore from 'vuex'
// 全局模块
import global from './modules/global'
// 局部模块
import user from './modules/user'
export default createStore(
// 全局模块
...global,
// 局部模块
modules:
user
)
2.使用
src/views/Test.vue测试组件中对模块化后的store中数据的操作与使用
<template>
<div>测试组件</div>
<hr>
<div>获取Store中user模块的getters: $store.getters['user/formatNickname']</div>
<button @click='handleClick'>点击</button>
</template>
<script>
import useStore from 'vuex'
export default
name: 'Test',
setup ()
// this.$store.state.info
// Vue3中store类似于Vue2中this.$store
const store = useStore()
console.log(store.state.user.profile.nickname)
// 修改nickname的值
const handleClick = () =>
// 触发mutations,用于同步修改user模块state的信息
// store.commit('updateNickname', 'Jackson')
store.dispatch('user/updateNickname', 'Yee')
return handleClick
</script>
以上是关于vite 基础一网打尽的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章