Kaggle上使用Tensorboard
Posted 镜花月-冷月
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Kaggle上使用Tensorboard相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
 Kaggle上使用Tensorboard
Kaggle上使用Tensorboard
Kaggle上使用Tensorboard
1. 前言
- 想在Kaggle上使用Tensorboard,找了一圈。
- 参考了Kaggle上的一个Code:Tensorboard on Kaggle
- 但发现有些变化,Code中用到的内网穿透工具Ngrok需要加一个Token,所以需要注册一个
Ngrok账号,免费获取一个通道的Token。
2. Kaggle上使用Tensorboard
2.1. 方法一
- 其实直接把在Kaggle上跑出来的Tensorboard日志文件下载到本地,在本地启动Tensorboard即可查看。
- 当然,这里主要讲在线的方法。
2.2. 方法二
- 在线使用Tensorboard
2.2.1. 获取一个Ngrok的免费通道
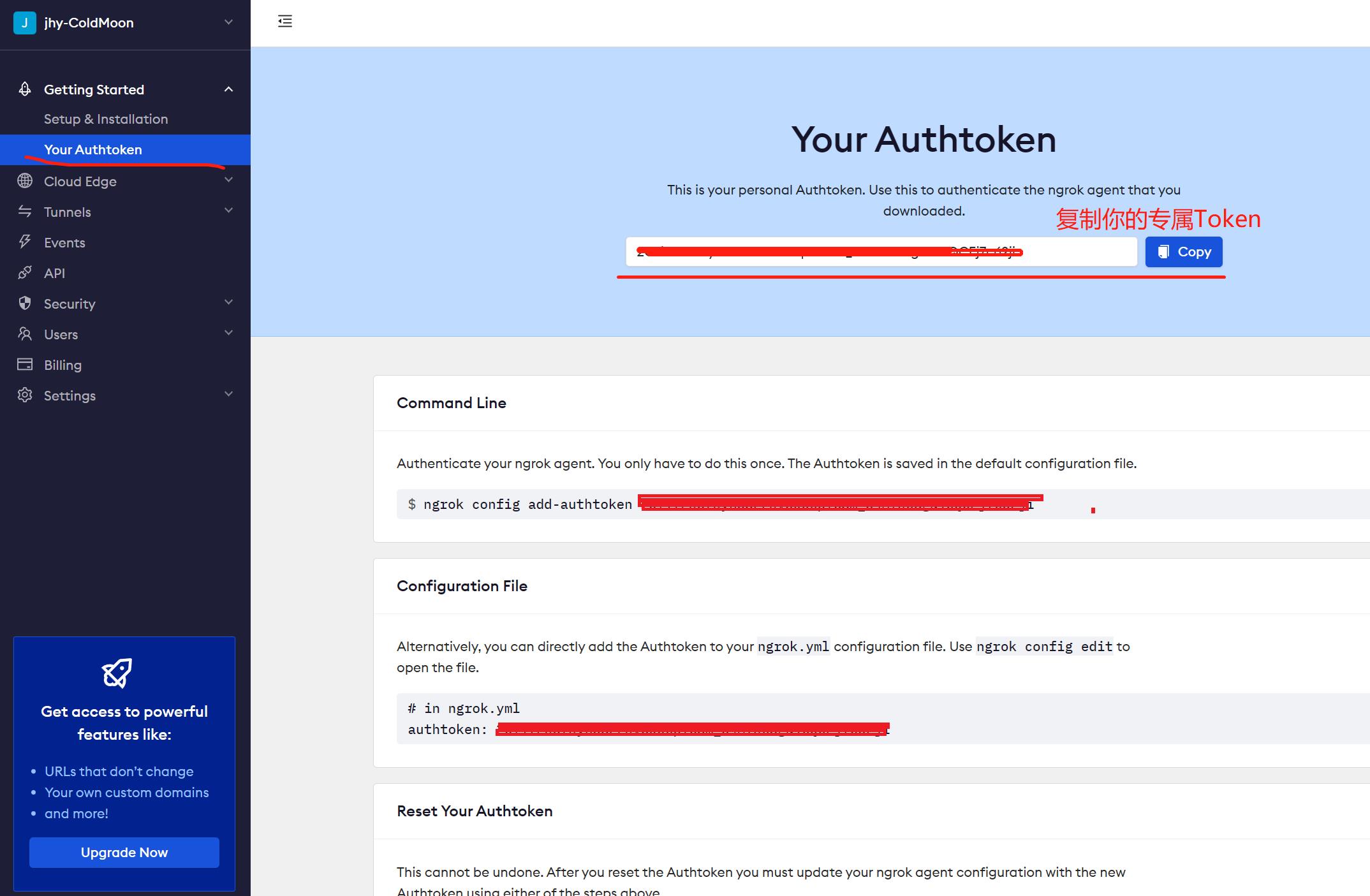
- 访问Ngrok,注册一个账号并登录
- 登录后界面如下,复制并保存你的Token
2.2.2. 调试运行代码
- 主要参考Kaggle上的一个Code:Tensorboard on Kaggle
- 建议分段运行,以避免中间出错,全部重新运行一次
- 以下代码在Kaggle的Notebook中运行
(1) 环境准备
import tensorflow as tf # This is how we import tf
# Clear any logs from previous runs
# 清除以前运行的所有日志
!rm -rf ./logs/
!mkdir ./logs/
(2) 启动Tensorboard
# Download Ngrok to tunnel the tensorboard port to an external port
# 下载 Ngrok 以将 tensorboard 端口隧道传输到外部端口
!wget https://bin.equinox.io/c/4VmDzA7iaHb/ngrok-stable-linux-amd64.zip
!unzip ngrok-stable-linux-amd64.zip
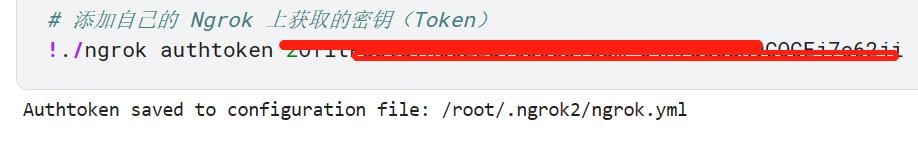
# 添加自己在 Ngrok 上获取的专属Token
!./ngrok authtoken 粘贴你的专属Token
- 注意这一步需要添加自己在 Ngrok 上获取的专属Token
# Run tensorboard as well as Ngrok (for tunneling as non-blocking processes)
# 运行 tensorboard 和 Ngrok(用于作为非阻塞进程的隧道)
import os
import multiprocessing
pool = multiprocessing.Pool(processes = 10)
# --logdir ./logs/ 是 TensorBoard 的日志文件(log)路径
# 你可以修改为你训练时的log保存路径(可以用绝对/相对路径),但相关的代码路径也要记得修改
results_of_processes = [pool.apply_async(os.system, args=(cmd, ), callback = None )
for cmd in [
f"tensorboard --logdir ./logs/ --host 0.0.0.0 --port 6006 &",
"./ngrok http 6006 &"
]]
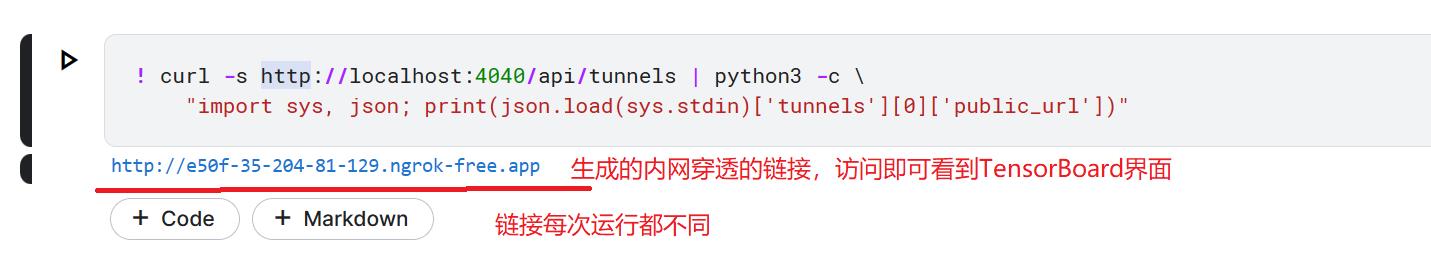
- 获取访问 Tensorload 的
URL,访问生成的URL即可看到 Tensorload 界面 - 但还没有产生日志文件,所以现在还看不到有图形
! curl -s http://localhost:4040/api/tunnels | python3 -c \\
"import sys, json; print(json.load(sys.stdin)[\'tunnels\'][0][\'public_url\'])"
(3) 创建和训练模型
(x_train, y_train),(x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
def create_model():
return tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(512, activation=\'relu\'),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation=\'softmax\')
])
import datetime
model = create_model()
model.compile(optimizer=\'adam\',
loss=\'sparse_categorical_crossentropy\',
metrics=[\'accuracy\'])
log_dir = "logs/fit/" + datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
tensorboard_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir=log_dir, histogram_freq=1)
model.fit(x=x_train,
y=y_train,
epochs=10,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test),
callbacks=[tensorboard_callback])
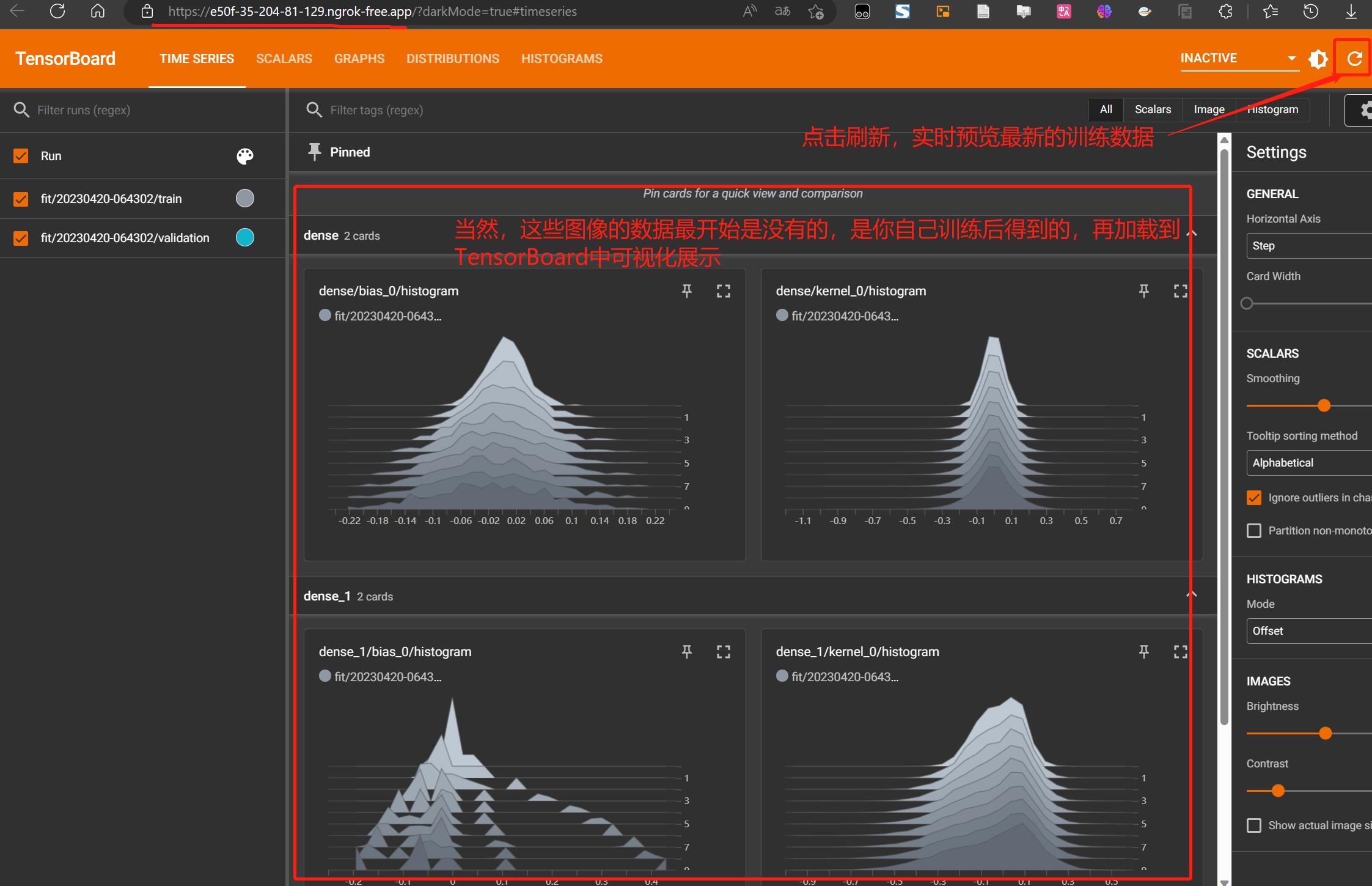
- 产生日志文件后,就可以在打开的 Tensorboard 界面点击刷新,看到实时训练趋势了
到底了
[Kaggle] dogs-vs-cats之建立模型
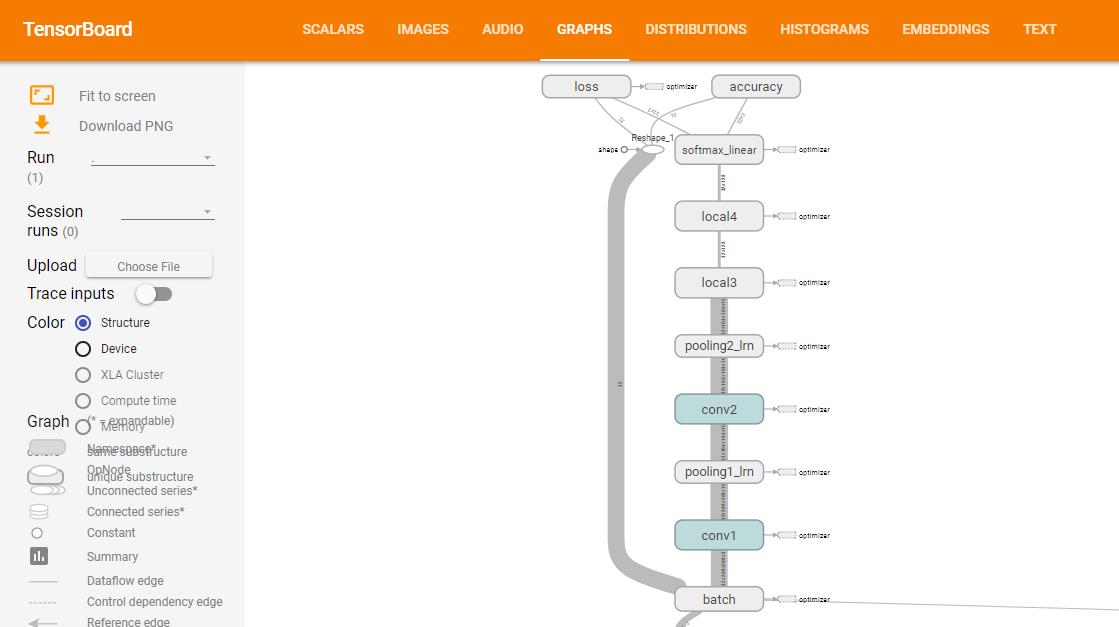
建立神经网络模型,下面要建立的模型如下:
(上图来源:训练网络时,打开tensorboard即可观察网络结构,在下一节模型训练的时候会讲到)
下面为具体步骤:
Step 0:导入相关库
import tensorflow as tfStep 1:定义网络结构
def inference(images, batch_size, n_classes): \'\'\'Build the model Args: images: image batch, 4D tensor, tf.float32, [batch_size, width, height, channels] Returns: output tensor with the computed logits, float, [batch_size, n_classes] \'\'\' #conv1, shape = [kernel size, kernel size, channels, kernel numbers] #卷积层1 with tf.variable_scope(\'conv1\') as scope: #变量初始化 weights = tf.get_variable(\'weights\', shape = [3,3,3, 16], dtype = tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable(\'biases\', shape=[16], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, weights, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding=\'SAME\') pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)#加上偏置 conv1 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name= scope.name)#relu激活函数 #pool1 and norm1 with tf.variable_scope(\'pooling1_lrn\') as scope: pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1,3,3,1],strides=[1,2,2,1], padding=\'SAME\', name=\'pooling1\') norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9.0, beta=0.75,name=\'norm1\') #conv2 with tf.variable_scope(\'conv2\') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable(\'weights\', shape=[3,3,16,16], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable(\'biases\', shape=[16], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, weights, strides=[1,1,1,1],padding=\'SAME\') pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=\'conv2\') #pool2 and norm2 with tf.variable_scope(\'pooling2_lrn\') as scope: norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9.0, beta=0.75,name=\'norm2\') pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(norm2, ksize=[1,3,3,1], strides=[1,1,1,1], padding=\'SAME\',name=\'pooling2\') #local3 #全连接层1 with tf.variable_scope(\'local3\') as scope: reshape = tf.reshape(pool2, shape=[batch_size, -1])#转换为一维 dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value#获取第二维的长度 weights = tf.get_variable(\'weights\', shape=[dim,128], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable(\'biases\', shape=[128], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) local3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weights) + biases, name=scope.name) #local4 with tf.variable_scope(\'local4\') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable(\'weights\', shape=[128,128], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable(\'biases\', shape=[128], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) local4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(local3, weights) + biases, name=\'local4\') # softmax with tf.variable_scope(\'softmax_linear\') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable(\'softmax_linear\', shape=[128, n_classes], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable(\'biases\', shape=[n_classes], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) softmax_linear = tf.add(tf.matmul(local4, weights), biases, name=\'softmax_linear\') return softmax_linear函数介绍:
1)tf.variable_scope
通过
tf.get_variable()为变量名指定命名空间。
2)tf.get_variable
通过所给的名字,创建或者返回一个变量。
以上两个函数详情参考:共享变量:http://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/tensorflow-zh/how_tos/variable_scope.html
3)tf.nn.conv2d
conv2d(
input,
filter,
strides,
padding,
use_cudnn_on_gpu=True,
data_format=\'NHWC\',
name=None
)作用:对给定的4-D输入和卷积核(filter)做2-D的卷积。
输入的张量(tensor)大小为[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels],卷积核(filter/kernel)的大小为[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]。
Strides一般为[1, stride, stride, 1];
padding,取值"SAME", "VALID"。
4)tf.nn.bias_add
bias_add(
value,
bias,
data_format=None,
name=None
)作用:将bias添加至value。
tf.nn.bias_add 是 tf.add 的一个特例,也即 tf.add 支持的操作比 tf.nn.bias_add 更多。二者均支持 broadcasting(广播机制),也即两个操作数最后一个维度保持一致。除了支持最后一个维度保持一致的两个操作数相加外,tf.add 还支持第二个操作数是一维的情况。
5)tf.nn.relu
relu(
features,
name=None
)作用:是计算激活函数relu,即max(features, 0)。
6)tf.nn.max_pool
max_pool(
value,
ksize,
strides,
padding,
data_format=\'NHWC\',
name=None
)作用:计算池化区域中元素的最大值
输入参数:
value: 一个四维的Tensor。数据维度是 [batch, height, width, channels]。数据类型是float32,float64,qint8,quint8,qint32。
ksize: 一个长度不小于4的整型数组。每一位上面的值对应于输入数据张量中每一维的窗口对应值。
strides: 一个长度不小于4的整型数组。该参数指定滑动窗口在输入数据张量每一维上面的步长。
padding: 一个字符串,取值为 SAME 或者 VALID 。
name: (可选)为这个操作取一个名字。
7)tf.nn.lrn
作用:局部响应归一化
Step 2:定义损失函数
def losses(logits, labels): \'\'\'Compute loss from logits and labels Args: logits: logits tensor, float, [batch_size, n_classes] labels: label tensor, tf.int32, [batch_size] Returns: loss tensor of float type \'\'\' with tf.variable_scope(\'loss\') as scope:#sparse 不需要one hot encoding cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits\\ (logits=logits, labels=labels, name=\'xentropy_per_example\') loss = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name=\'loss\') tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+\'/loss\', loss) return loss函数介绍:
1) tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits
sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
_sentinel=None,
labels=None,
logits=None,
name=None
)
作用:计算logits和labels之间的softmax交叉熵。
第一个参数logits:就是神经网络最后一层的输出,如果有batch的话,它的大小就是[batchsize,num_classes],单样本的话,大小就是num_classes。
第二个参数labels以前也必须是[batch_size, num_classes]否则无法做Cross Entropy(softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits的用法),这个函数改为限制更强的[batch_size],而值必须是从0开始编码的int32或int64,而且值范围是[0, num_class)。
2) tf.reduce_mean
作用:计算输入tensor的均值
3)tf.summary.scalar
scalar(
name,
tensor,
collections=None,
family=None
)作用:输出一个包含单个标量值的
Summaryprotocol buffer 。
Step 3:定义训练方法
def trainning(loss, learning_rate): \'\'\'Training ops, the Op returned by this function is what must be passed to \'sess.run()\' call to cause the model to train. Args: loss: loss tensor, from losses() Returns: train_op: The op for trainning \'\'\' with tf.name_scope(\'optimizer\'): optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= learning_rate) global_step = tf.Variable(0, name=\'global_step\', trainable=False) train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step= global_step) return train_op函数介绍:
1)tf.train.AdamOptimizer
__init__(
learning_rate=0.001,
beta1=0.9,
beta2=0.999,
epsilon=1e-08,
use_locking=False,
name=\'Adam\'
)作用:利用Adam algorithm来
2)optimizer.minimize
minimize(
loss,
global_step=None,
var_list=None,
gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
aggregation_method=None,
colocate_gradients_with_ops=False,
name=None,
grad_loss=None
)作用:最小化loss。
global_step: Optional Variable to increment by one after the variables have been updated.
Step4:定义评估方法
def evaluation(logits, labels): """Evaluate the quality of the logits at predicting the label. Args: logits: Logits tensor, float - [batch_size, NUM_CLASSES]. labels: Labels tensor, int32 - [batch_size], with values in the range [0, NUM_CLASSES). Returns: A scalar int32 tensor with the number of examples (out of batch_size) that were predicted correctly. """ with tf.variable_scope(\'accuracy\') as scope: correct = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits, labels, 1) correct = tf.cast(correct, tf.float16) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(correct) tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+\'/accuracy\', accuracy) return accuracy函数介绍:
1)tf.nn.in_top_k
in_top_k(
predictions,
targets,
k,
name=None
)作用:返回targets是否位于前K个predictions中,True或者False。
Predictions:float32类型的Tensor,大小为batch_sizexclasses
Targets:必须是int32或者int64的Tensor。类id组成的batch_size大小的向量。
说明:
代码来自:https://github.com/kevin28520/My-TensorFlow-tutorials,略有修改
函数作用主要参考tensorflow官网。https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/master/api_docs/
以上是关于Kaggle上使用Tensorboard的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章