利用python实现IP扫描
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了利用python实现IP扫描相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
需求:写一个脚本,判断192.168.11.0/24网络里,当前在线ip有哪些?
知识点:
1 使用subprocess模块,来调用系统命令,执行ping 192.168.11.xxx 命令
2 调用系统命令执行ping命令的时候,会有返回值(ping的结果),需要用到stdout=fnull, stderr=fnull方法,屏蔽系统执行命令的返回值
常规版本(代码)
import os
import time
import subprocess
def ping_call():
start_time = time.time()
fnull = open(os.devnull, 'w')
for i in range(1, 256):
ipaddr = 'ping 192.168.11.' + str(i)
result = subprocess.call(ipaddr + ' -n 2', shell=True, stdout=fnull, stderr=fnull)
current_time = time.strftime('%Y%m%d-%H:%M:%S', time.localtime())
if result:
print('时间:{} ip地址:{} ping fall'.format(current_time, ipaddr))
else:
print('时间:{} ip地址:{} ping ok'.format(current_time, ipaddr))
print('程序耗时{:.2f}'.format(time.time() - start_time))
fnull.close()
ping_call()执行效果:
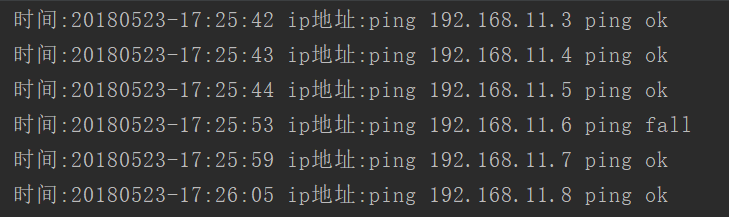
上面的执行速度非常慢,怎么能让程序执行速度快起来?
python提供了进程,线程,协程。分别用这三个对上面代码改进,提高执行效率,测试一波效率
进程池异步执行 -- 开启20个进程
import os
import time
import subprocess
from multiprocessing import Pool
def ping_call(num):
fnull = open(os.devnull, 'w')
ipaddr = 'ping 192.168.11.' + str(num)
result = subprocess.call(ipaddr + ' -n 2', shell=True, stdout=fnull, stderr=fnull)
current_time = time.strftime('%Y%m%d-%H:%M:%S', time.localtime())
if result:
print('时间:{} ip地址:{} ping fall'.format(current_time, ipaddr))
else:
print('时间:{} ip地址:{} ping ok'.format(current_time, ipaddr))
fnull.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.time()
p = Pool(20)
res_l = []
for i in range(1, 256):
res = p.apply_async(ping_call, args=(i,))
res_l.append(res)
for res in res_l:
res.get()
print('程序耗时{:.2f}'.format(time.time() - start_time))执行结果:
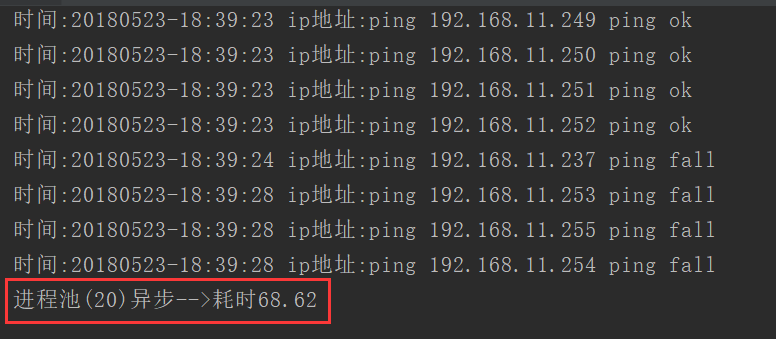
线程池异步执行 -- 开启20个线程
import os
import time
import subprocess
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def ping_call(num):
fnull = open(os.devnull, 'w')
ipaddr = 'ping 192.168.11.' + str(num)
result = subprocess.call(ipaddr + ' -n 2', shell=True, stdout=fnull, stderr=fnull)
current_time = time.strftime('%Y%m%d-%H:%M:%S', time.localtime())
if result:
print('时间:{} ip地址:{} ping fall'.format(current_time, ipaddr))
else:
print('时间:{} ip地址:{} ping ok'.format(current_time, ipaddr))
fnull.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.time()
thread_pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(20)
ret_lst = []
for i in range(1, 256):
ret = thread_pool.submit(ping_call, i)
ret_lst.append(ret)
thread_pool.shutdown()
for ret in ret_lst:
ret.result()
print('线程池(20)异步-->耗时{:.2f}'.format(time.time() - start_time))执行结果:
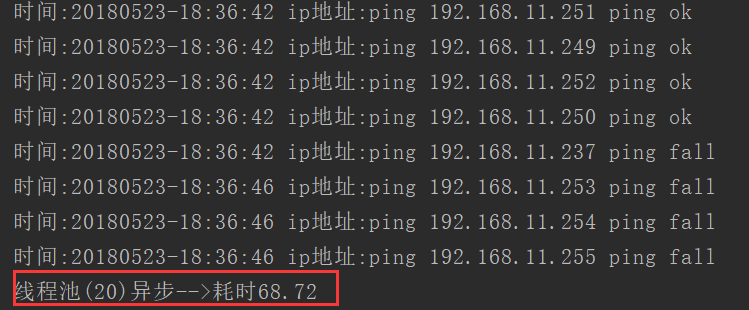
协程执行---(执行多个任务,遇到I/O操作就切换)
使用gevent前,需要pip install gevent
from gevent import monkey;monkey.patch_all()
import gevent
import os
import time
import subprocess
def ping_call(num):
fnull = open(os.devnull, 'w')
ipaddr = 'ping 192.168.11.' + str(num)
result = subprocess.call(ipaddr + ' -n 2', shell=True, stdout=fnull, stderr=fnull)
current_time = time.strftime('%Y%m%d-%H:%M:%S', time.localtime())
if result:
print('时间:{} ip地址:{} ping fall'.format(current_time, ipaddr))
else:
print('时间:{} ip地址:{} ping ok'.format(current_time, ipaddr))
fnull.close()
def asynchronous(): # 异步
g_l = [gevent.spawn(ping_call, i) for i in range(1, 256)]
gevent.joinall(g_l)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.time()
asynchronous()
print('协程执行-->耗时{:.2f}'.format(time.time() - start_time))执行结果:
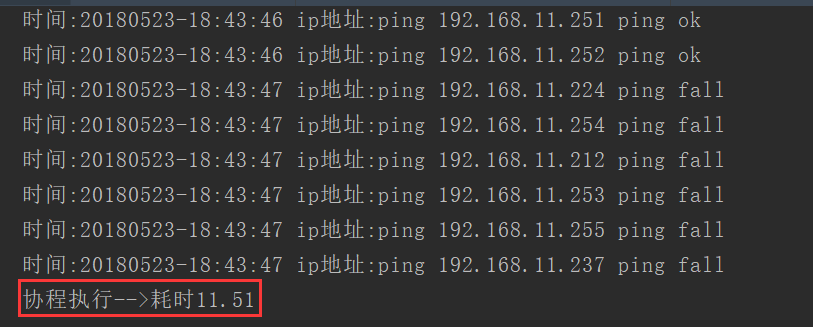
遇到I/O操作,协程的效率比进程,线程高很多!
总结:python中,涉及到I/O阻塞的程序中,使用协程的效率最高
最后附带协程池代码
gevent.pool
from gevent import monkey;monkey.patch_all()
import gevent
import os
import time
import subprocess
import gevent.pool
def ping_call(num):
fnull = open(os.devnull, 'w')
ipaddr = 'ping 192.168.11.' + str(num)
result = subprocess.call(ipaddr + ' -n 2', shell=True, stdout=fnull, stderr=fnull)
current_time = time.strftime('%Y%m%d-%H:%M:%S', time.localtime())
if result:
print('时间:{} ip地址:{} ping fall'.format(current_time, ipaddr))
else:
print('时间:{} ip地址:{} ping ok'.format(current_time, ipaddr))
fnull.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.time()
res_l = []
p = gevent.pool.Pool(100)
for i in range(1, 256):
res_l.append(p.spawn(ping_call, i))
gevent.joinall(res_l)
print('协程池执行-->耗时{:.2f}'.format(time.time() - start_time))执行结果:
以上是关于利用python实现IP扫描的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章