2023-04-19 算法面试中常见的递归和回溯问题
Posted 空無一悟
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2023-04-19 算法面试中常见的递归和回溯问题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
递归和回溯
0 递归与回溯的异同
参考文章
比较
| 递归 | 回溯 | |
|---|---|---|
| 定义 | 为了描述问题的某一状态,必须用到该状态的上一状态,而描述上一状态,又必须用到上一状态的上一状态……这种用自已来定义自己的方法,称为递归定义。形式如 f(n) = n*f(n-1), if n=0,f(n)=1. | 从问题的某一种可能出发, 搜索从这种情况出发所能达到的所有可能, 当这一条路走到” 尽头 “的时候, 再倒回出发点, 从另一个可能出发, 继续搜索. 这种不断” 回溯 “寻找解的方法, 称作” 回溯法 “。 |
| 不同 | 递归是一种算法结构,递归会出现在子程序中自己调用自己或间接地自己调用自己。最直接的递归应用就是计算连续数的阶乘,计算规律:n!=(n-1)!*n。 | 回溯是一种算法思想,可以用递归实现。通俗点讲回溯就是一种试探,类似于穷举,但回溯有“剪枝”功能,比如求和问题。给定7个数字,1 2 3 4 5 6 7,求和等于7的组合,从小到大搜索,选择1+2+3+4 =10>7,已经超过了7,之后的5 6 7就没必要在继续了,这就是一种搜索过程的优化。如果还有不清楚的可以看一下8皇后问题。 |
| 问题举例 | 玩转算法面试第7章_二叉树与递归 | 玩转算法面试第8章_递归与回溯 |
举例
用一个比较通俗的说法来解释递归和回溯:
我们在路上走着,前面是一个多岔路口,因为我们并不知道应该走哪条路,所以我们需要尝试。尝试的过程就是一个函数。
- 我们选择了一个方向,后来发现又有一个多岔路口,这时候又需要进行一次选择。所以我们需要在上一次尝试结果的基础上,再做一次尝试,即在函数内部再调用一次函数,这就是递归的过程。
- 这样重复了若干次之后,发现这次选择的这条路走不通,这时候我们知道我们上一个路口选错了,所以我们要回到上一个路口重新选择其他路,这就是回溯的思想。
1~2 树形问题与回溯
17.电话号码的字母组合
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
示例:
输入:"23"
输出:["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].

class Solution
// 每个按键(数组的下标)对应的可能的字符串,0和1不对应任何字符,所以这里为空
String[] letterMap =
"", // 0
"", // 1
"abc", // 2
"def", // 3
"ghi", // 4
"jkl", // 5
"mno", // 6
"pqrs", // 7
"tuv", // 8
"wxyz" // 9
;
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits)
// 存储最终结果的列表
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
if ("".equals(digits))
return result;
findCombinations(digits, 0, "", result);
return result;
/**
* 寻找digits[index]匹配的字母,获得digits[0...index]对应的解
*
* @param digits 原始数字字符串
* @param index 要看digits的哪一个数字
* @param s s保存了此时从digits[0...index-1]翻译得到的一个字母字符串
* @param result 保存最终可能的字符串
*/
private void findCombinations(String digits, int index, String s, List<String> result)
// 所有数字都遍历完了,递归退出
if (index == digits.length())
result.add(s);
return;
// 拿到index对应的数字字符
char c = digits.charAt(index);
// 获取当前数字字符可能对应的键盘上的字符串
String lettersStr = letterMap[c - \'0\'];
// 第当前数字对应的字符串进行遍历拼接
for (int i = 0; i < lettersStr.length(); i++)
findCombinations(digits, index + 1, s + lettersStr.charAt(i), result);
93.复原IP地址
class Solution
private boolean validId(String ip)
if (ip.length() > 1 && ip.charAt(0) == \'0\')
return false;
if (ip.length() > 3 || Integer.parseInt(ip) > 255)
return false;
return true;
private String concatList(List<String> numList)
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String numStr : numList)
sb.append(numStr).append(".");
// 最后的一个.要去掉
return sb.substring(0, sb.length() - 1);
// 把s分成四分,判断这四份组成的ip的合理性
// 递归过程:不断取字符串的前几个字符,每出现一个合法的字符串就接着往下取
private void findIp(String s, List<String> numList, List<String> result)
if (numList.size() == 4)
result.add(concatList(numList));
// 当s字符串已经被分割成空时,分割完毕,退出本层递归即可
return;
for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++)
if (numList.size() == 3)
// 前面已经分成3份了,这里直接把剩下的作为IP即可
i = s.length();
String tmp = s.substring(0, i);
if (!validId(tmp))
continue;
numList.add(tmp);
// i往后的字符串
findIp(s.substring(i), numList, result);
// 退出上一层递归,就要从numList中删除最后一个num
numList.remove(numList.size() - 1);
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s)
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
if ("".equals(s) || s.length() < 4 || s.length() > 12)
return result;
List<String> numList = new ArrayList<>();
findIp(s, numList, result);
return result;
131.分割回文串
验证字符串是否用125.验证回文串的代码
class Solution
/**
* 参考LeetCode125.验证回文串
*/
public boolean isPalindrome(String s)
s = s.toLowerCase();
int l = 0;
int r = s.length() - 1;
while (l < r)
// 只要还没相遇就接着往下走
if (!Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(l)))
// 左边的字符不是字母或数字
l++;
continue;
if (!Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(r)))
// 右边的字符不是字母或数字
r--;
continue;
// 左右两边都是字母或数字,只要不相等就说明不是回文
if (s.charAt(l) != s.charAt(r))
return false;
// 相等地话,继续向中间靠拢
l++;
r--;
return true;
/**
* 获取本次循环中的回文串
*
* @param s 原始字符串
* @param palindromes 本次循环中的回文串
* @param result 存储所有回文串列表的列表
*/
void getAllPalindromes(String s, List<String> palindromes, List<List<String>> result)
if ("".equals(s))
// 当到头时,把回文串列表加入到result中并返回,列表是引用传值,所以必须new一个list
result.add(new ArrayList<>(palindromes));
return;
for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++)
String tmp = s.substring(0, i);
if (!isPalindrome(tmp))
// 不是回文串就直接退出本层递归
continue;
palindromes.add(tmp);
getAllPalindromes(s.substring(i), palindromes, result);
// 退出本层递归,需要移除一个回文串
palindromes.remove(palindromes.size() - 1);
public List<List<String>> partition(String s)
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> palindromes = new ArrayList<>();
getAllPalindromes(s, palindromes, result);
return result;
3 组合
用基于递归的回溯法解决组合问题
46.全排列
class Solution
private void calPermutations(List<Integer> numList, List<Integer> curList, List<List<Integer>> result)
if (numList.size() == 0)
result.add(new ArrayList<>(curList));
return;
for (int i = 0; i < numList.size(); i++)
curList.add(numList.get(i));
List<Integer> numListNext = new ArrayList<>(numList);
numListNext.remove(i);
calPermutations(numListNext, curList, result);
// 递归退出就删除一个元素
curList.remove(curList.size() - 1);
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums)
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> curList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : nums)
numList.add(num);
calPermutations(numList, curList, result);
return result;
47.全排列II
只需要在上面46题的递归退出逻辑上加一句
!result.contains(curList)即可
class Solution
private void calPermutations(List<Integer> numList, List<Integer> curList, List<List<Integer>> result)
if (numList.size() == 0 && !result.contains(curList))
result.add(new ArrayList<>(curList));
return;
for (int i = 0; i < numList.size(); i++)
curList.add(numList.get(i));
List<Integer> numListNext = new ArrayList<>(numList);
numListNext.remove(i);
calPermutations(numListNext, curList, result);
// 递归退出就删除一个元素
curList.remove(curList.size() - 1);
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums)
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> curList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : nums)
numList.add(num);
calPermutations(numList, curList, result);
return result;
4~5 组合问题
利用递归回溯法解决组合问题.
77.组合
和46、47差不多,简单适配下即可,通过变化索引的方式去遍历子数组要比新建一个子数组效率高很多
class Solution
private void calCombinations(int[] nums, int start, List<Integer> curList, List<List<Integer>> result, int k)
if (curList.size() == k)
result.add(new ArrayList<>(curList));
return;
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++)
curList.add(nums[i]);
calCombinations(nums,i+1, curList, result, k);
// 递归退出就删除一个元素
curList.remove(curList.size() - 1);
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k)
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> curList = new ArrayList<>();
int[] nums = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
nums[i] = i+1;
calCombinations(nums, 0, curList, result, k);
return result;
39.组合总和
class Solution
private void calCombinations(int[] nums, List<Integer> curList, int start, int target, List<List<Integer>> result)
if (target < 0)
return;
if (target == 0)
result.add(new ArrayList<>(curList));
return;
// 从start开始是为了能重复使用start位置的元素
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++)
curList.add(nums[i]);
// 下一层递归还是用这些元素,通过索引来遍历子数组而不要额外建立空间
calCombinations(nums, curList, i, target - nums[i], result);
// 递归退出就删除一个元素
curList.remove(curList.size() - 1);
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target)
// 排序后输出结果比较统一
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> curList = new ArrayList<>();
calCombinations(candidates, curList, 0, target, result);
return result;
40.组合总和 II
和39类似,就是把i换成i+1,然后再添加到result前判重一下即可
class Solution
private void calCombinations(int[] nums, List<Integer> curList, int start, int target, List<List<Integer>> result)
if (target < 0)
return;
if (target == 0)
if(!result.contains(curList))
result.add(new ArrayList<>(curList));
return;
// 从start开始是为了能重复使用start位置的元素
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++)
curList.add(nums[i]);
// 下一层递归还是用这些元素,通过索引来遍历子数组而不要额外建立空间
calCombinations(nums, curList, i + 1, target - nums[i], result);
// 递归退出就删除一个元素
curList.remove(curList.size() - 1);
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target)
// 排序后输出结果比较统一
Arrays.sort(candidates);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> curList = new ArrayList<>();
calCombinations(candidates, curList, 0, target, result);
return result;
216.组合总和 III
和40题类似。执行用时 : 1 ms , 在所有 Java 提交中击败了 99.29% 的用户
class Solution
private void calCombinations(int[] nums, List<Integer> curList, int start, int target, List<List<Integer>> result, int k)
if (target < 0)
return;
if (target == 0)
if(curList.size() == k)
result.add(new ArrayList<>(curList));
return;
// 从start开始是为了能重复使用start位置的元素
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++)
curList.add(nums[i]);
// 下一层递归还是用这些元素,通过索引来遍历子数组而不要额外建立空间
calCombinations(nums, curList, i + 1, target - nums[i], result, k);
// 递归退出就删除一个元素
curList.remove(curList.size() - 1);
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n)
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> curList = new ArrayList<>();
int[] nums = 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9;
calCombinations(nums, curList, 0, n, result, k);
return result;
78.子集
class Solution
private void calSubsets(int[] nums, int start, List<Integer> curList, List<List<Integer>> result)
if(start == nums.length)
return;
for(int i = start; i < nums.length; i++)
curList.add(nums[i]);
if(!result.contains(curList))
result.add(new ArrayList<>(curList));
calSubsets(nums, i + 1, curList, result);
curList.remove(curList.size() - 1);
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums)
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> curList = new ArrayList<>();
result.add(new ArrayList<>());
calSubsets(nums, 0, curList, result);
return result;
90.子集II
和上一个题相比就加了个
Arrays.sort(nums);
class Solution
private void calSubsets(int[] nums, int start, List<Integer> curList, List<List<Integer>> result)
if(start == nums.length)
return;
for(int i = start; i < nums.length; i++)
curList.add(nums[i]);
if(!result.contains(curList))
result.add(new ArrayList<>(curList));
calSubsets(nums, i + 1, curList, result);
curList.remove(curList.size() - 1);
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums)
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> curList = new ArrayList<>();
result.add(new ArrayList<>());
calSubsets(nums, 0, curList, result);
return result;
401.二进制手表
class Solution
private void getResult(int[] nums, int start, int k, List<Integer> curList, List<List<Integer>> result)
if(curList.size() == k)
result.add(new ArrayList(curList));
return;
for(int i = start; i < nums.length; i++)
curList.add(nums[i]);
getResult(nums, i + 1, k, curList, result);
curList.remove(curList.size() - 1);
private List<String> trans(List<List<Integer>> result)
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(List<Integer> lightList : result)
int[] flags = new int[10];
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
if(lightList.contains(i))
flags[i] = 1;
else
flags[i] = 0;
int hour = 8 * flags[0] + 4 * flags[1] + 2 * flags[2] + flags[3];
int minute = 32 * flags[4] + 16 * flags[5] + 8 * flags[6] + 4 * flags[7] + 2 * flags[8] + flags[9];
if(hour > 11 || minute > 59)
continue;
if(minute < 10)
list.add(hour + ":0" + minute);
else
list.add(hour + ":" + minute);
Collections.sort(list);
return list;
// 组合问题
public List<String> readBinaryWatch(int num)
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> curList = new ArrayList<>();
// 下标0~3的元素表示上面四个灯,下标4~9的元素表示下面6个灯
int[] nums = 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9;
getResult(nums, 0, num, curList, result);
return trans(result);
6 二维平面的搜索
参考Part2BasicGraph/第06章_图论问题建模和floodfill,这里是floodfill的四连通分量问题,可以用DFS解决,在递归回退时记得要把相关状态重置下
79.单词搜索
class Solution
/**
* 当前点求上右下左四个点时用到的矢量差,dirs 是directions的意思
*/
private int[][] dirs =
-1, 0,
0, 1,
1, 0,
0, -1
;
/**
* 传进来的grid有多少行(Row)多少列(Col)
*/
private int R, C;
/**
* 岛屿网格的情况
*/
private char[][] grid;
private boolean[][] visited;
/**
* 判断第x行第y列的点(x, y)是否在grid所在的范围内
*/
private boolean inArea(int x, int y)
return x >= 0 && x < R && y >= 0 && y < C;
/**
* 图的初始化
*
* @param board 二维的图
* @param word 要找的单词
* @return
*/
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word)
this.grid = board;
if (grid == null)
return false;
R = grid.length;
if (R == 0)
// 如果行数为0说明图为空,直接返回
return false;
C = grid[0].length;
if (C == 0)
// 如果列数为0说明图为空,直接返回
return false;
visited = new boolean[R][C];
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < C; j++)
// 点没有被访问而且字符等于word的第一个字符,才以这个点作为起点进行DFS遍历
if (grid[i][j] == word.charAt(0))
// 以(i,j)作为起点进行DFS,看看遍历结果能否组成提供的单词
List<Character> cList = new ArrayList<>();
cList.add(word.charAt(0));
dfs(i, j, 1, word, cList);
if (cList.size() == word.length())
return true;
// 每次递归DFS遍历完,数组要重新初始化
visited = new boolean[R][C];
return false;
private void dfs(int x, int y, int start, String word, List<Character> cList)
if (cList.size() == word.length())
return;
visited[x][y] = true;
// 遍历节点(x, y)所有的邻接点,判断是陆地的
for (int d = 0; d < dirs.length; d++)
int nextX = x + dirs[d][0];
int nextY = y + dirs[d][1];
// 点(next_x, next_y)必须在grid区域内 + 没被访问过 + 是陆地(点(x, y)是陆地)
if (inArea(nextX, nextY) && !visited[nextX][nextY] && grid[nextX][nextY] == word.charAt(start))
cList.add(grid[nextX][nextY]);
dfs(nextX, nextY, start + 1, word, cList);
if (cList.size() == word.length())
break;
// 状态重置:列表和访问数组
cList.remove(cList.size() - 1);
visited[nextX][nextY] = false;
/**
* char[][] board = \'A\', \'B\', \'C\', \'E\', \'S\', \'F\', \'C\', \'S\', \'A\', \'D\', \'E\', \'E\';
* String word = "ABCCED";
* <p>
* char[][] board = \'C\', \'A\', \'A\', \'A\', \'A\', \'A\', \'B\', \'C\', \'D\';
* String word = "AAB";
* <p>
* char[][] board = \'A\',\'B\',\'C\',\'E\',\'S\',\'F\',\'E\',\'S\',\'A\',\'D\',\'E\',\'E\';
* String word = "ABCEFSADEESE";
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
char[][] board = \'C\', \'A\', \'A\', \'A\', \'A\', \'A\', \'B\', \'C\', \'D\';
String word = "AAB";
System.out.println(new Solution().exist(board, word));
7 floodfill(实际就是DFS)
二维图的搜索实际就是DFS
200.岛屿数量
实际就是DFS求连通分量的个数
public class Solution
/**
* 当前点求上右下左四个点时用到的矢量差,dirs 是directions的意思
*/
private int[][] dirs =
-1, 0,
0, 1,
1, 0,
0, -1
;
/**
* 传进来的grid有多少行(Row)多少列(Col)
*/
private int R, C;
/**
* 岛屿网格的情况
*/
private char[][] grid;
private boolean[][] visited;
/**
* 连通分量的个数
*/
private int cCount = 0;
/**
* 判断第x行第y列的点(x, y)是否在grid所在的范围内
*/
private boolean inArea(int x, int y)
return x >= 0 && x < R && y >= 0 && y < C;
public int numIslands(char[][] grid)
this.grid = grid;
if (grid == null)
return 0;
R = grid.length;
if (R == 0)
// 如果行数为0说明图为空,直接返回
return 0;
C = grid[0].length;
if (C == 0)
// 如果列数为0说明图为空,直接返回
return 0;
visited = new boolean[R][C];
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < C; j++)
// 点没有被访问而且字符等于word的第一个字符,才以这个点作为起点进行DFS遍历
if (grid[i][j] == \'1\' && !visited[i][j])
dfs(i, j);
cCount++;
return cCount;
private void dfs(int x, int y)
visited[x][y] = true;
// 遍历节点(x, y)所有的邻接点,判断是陆地的
for (int d = 0; d < dirs.length; d++)
int nextX = x + dirs[d][0];
int nextY = y + dirs[d][1];
// 点(next_x, next_y)必须在grid区域内 + 没被访问过 + 是陆地(点(x, y)是陆地)
if (inArea(nextX, nextY) && !visited[nextX][nextY] && grid[nextX][nextY] == \'1\')
dfs(nextX, nextY);
139.被围绕的区域
class Solution
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict)
boolean[] visited = new boolean[s.length() + 1];
return dfs(s, 0, wordDict, visited);
private boolean dfs(String s, int start, List<String> wordDict, boolean[] visited)
visited[start] = true;
for (int i = start; i < s.length(); i++)
// 防止递归回退的时候再次经过这个字符
if (visited[i + 1])
continue;
String substr = s.substring(start, i + 1);
if (wordDict.contains(substr))
if (i + 1 == s.length() || dfs(s, i + 1, wordDict, visited))
return true;
return false;
/**
* 输入: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet", "code"] 输出: true
* <p>
* 输入:"aaaaaaa" 输出:["aaaa","aaa"]
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
String s = "aaaaaaa";
String[] words = "aaaa", "aaa";
List<String> wordDict = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(words));
System.out.println(new Solution().wordBreak(s, wordDict));
417.太平洋大西洋水流问题
遍历每个点,DFS找到既能到达太平洋又能到达大西洋的点加入到结果中即可
class Solution
/**
* 当前点求上右下左四个点时用到的矢量差,dirs 是directions的意思
*/
private int[][] dirs =
-1, 0,
0, 1,
1, 0,
0, -1
;
/**
* 传进来的grid有多少行(Row)多少列(Col)
*/
private int R, C;
/**
* 岛屿网格的情况
*/
private int[][] grid;
private boolean[][] visited;
/**
* 判断第x行第y列的点(x, y)是否在grid所在的范围内
*/
private boolean inArea(int x, int y)
return x >= 0 && x < R && y >= 0 && y < C;
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] matrix)
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
this.grid = matrix;
if (grid == null)
return result;
R = grid.length;
if (R == 0)
// 如果行数为0说明图为空,直接返回
return result;
C = grid[0].length;
if (C == 0)
// 如果列数为0说明图为空,直接返回
return result;
visited = new boolean[R][C];
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < C; j++)
// 点没有被访问而且字符等于word的第一个字符,才以这个点作为起点进行DFS遍历
boolean pacific = dfs(i, j, true);
visited = new boolean[R][C];
boolean atlantic = dfs(i, j, false);
visited = new boolean[R][C];
if (pacific && atlantic)
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(i);
list.add(j);
result.add(list);
return result;
/**
* dfs遍历看起点是否能到到
*
* @param x 行
* @param y 列
* @param pacific true代表检查能否到达太平洋(),false代表检查能否到到大西洋
* @return 是否能到达太平洋或大西洋
*/
private boolean dfs(int x, int y, boolean pacific)
if (pacific)
// 检查能否到达太平洋
if (x == 0 || y == 0)
return true;
else
// 检查大西洋
if (x == R - 1 || y == C - 1)
return true;
visited[x][y] = true;
for (int d = 0; d < dirs.length; d++)
int nextX = x + dirs[d][0];
int nextY = y + dirs[d][1];
// 点(next_x, next_y)必须在grid区域内 + 没被访问过 + 往地处流 + 能到达边界
if (inArea(nextX, nextY) && !visited[nextX][nextY] && grid[nextX][nextY] <= grid[x][y] && dfs(nextX, nextY, pacific))
return true;
// 到最后都没能到达边界,则说明无法到到,退出即可
return false;
public static void main(String[] args)
int[][] matrix =
1, 2, 2, 3, 5,
3, 2, 3, 4, 4,
2, 4, 5, 3, 1,
6, 7, 1, 4, 5,
5, 1, 1, 2, 4
;
System.out.println(new Solution().pacificAtlantic(matrix));
8 递归回溯法是人工智能的基础
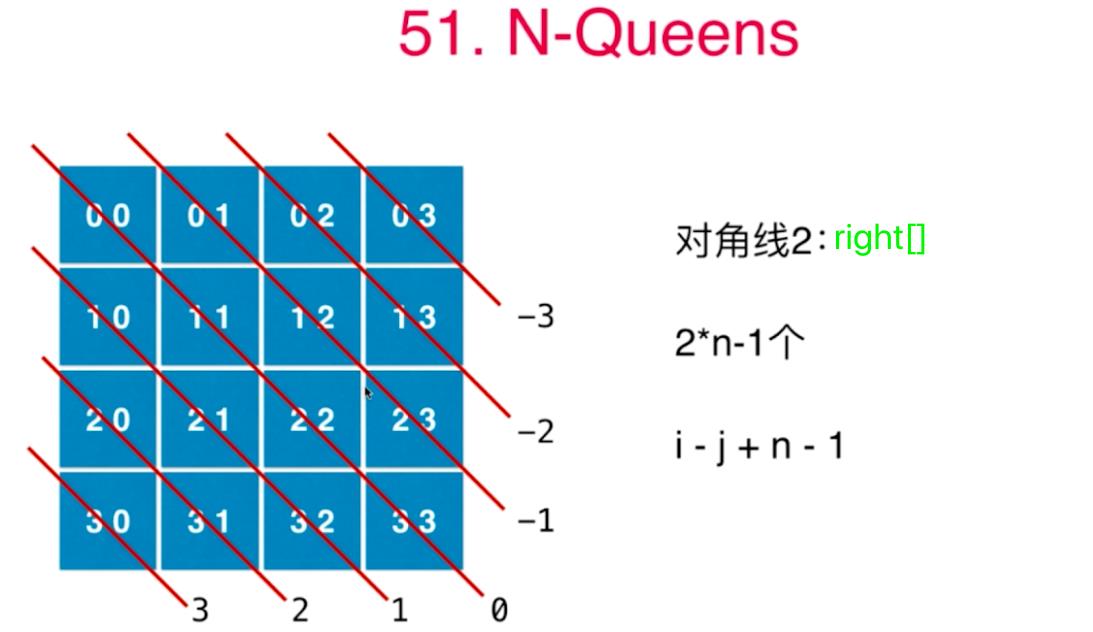
51.N皇后问题
图中的i是下面的r,
class Solution
boolean[] col = null;
boolean[] left = null;
boolean[] right = null;
List<List<String>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n)
// col[i]表示第i列被占用
col = new boolean[n];
// 左倾对角线
left = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
// 右倾对角线
right = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
// 二维平面
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
// 回溯法求解问题
backTrack(board, 0, n);
return ret;
// i代表行,j代表列
void backTrack(char[][] board, int i, int n)
if (i >= n)
// 找到能一个能摆放皇后的位置,加入到结果列表中
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
list.add(new String(board[j]));
ret.add(list);
return;
// 初始化棋盘啥都不放
Arrays.fill(board[i], \'.\');
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (!col[j] && !left[i + j] && !right[i - j + n - 1])
// 一、尝试在当前位置摆放皇后
// 摆放皇后
board[i][j] = \'Q\';
// 列占用
col[j] = true;
// 左倾对角线的规律
left[i + j] = true;
// 右倾对角线的规律
right[i - j + n - 1] = true;
// 二、递归求解其合法性
backTrack(board, i + 1, n);
// 三、递归回退过程中需要恢复初始的状态
// 拿走皇后
board[i][j] = \'.\';
// 列占用解除
col[j] = false;
// 左对角线占用解除
left[i + j] = false;
// 右对角线占用解除
right[i - j + n - 1] = false;
类似问题还有52和37
52.N皇后II
把51返回的ret改成
ret.size()即可
class Solution
boolean[] col = null;
boolean[] left = null;
boolean[] right = null;
List<List<String>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
public int totalNQueens(int n)
// col[i]表示第i列被占用
col = new boolean[n];
// 左倾对角线
left = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
// 右倾对角线
right = new boolean[2 * n - 1];
// 二维平面
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
// 回溯法求解问题
backTrack(board, 0, n);
// 和51题唯一不同的地方
return ret.size();
// i代表行,j代表列
void backTrack(char[][] board, int i, int n)
if (i >= n)
// 找到能一个能摆放皇后的位置,加入到结果列表中
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
list.add(new String(board[j]));
ret.add(list);
return;
// 初始化棋盘啥都不放
Arrays.fill(board[i], \'.\');
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (!col[j] && !left[i + j] && !right[i - j + n - 1])
// 一、尝试在当前位置摆放皇后
// 摆放皇后
board[i][j] = \'Q\';
// 列占用
col[j] = true;
// 左倾对角线的规律
left[i + j] = true;
// 右倾对角线的规律
right[i - j + n - 1] = true;
// 二、递归求解其合法性
backTrack(board, i + 1, n);
// 三、递归回退过程中需要恢复初始的状态
// 拿走皇后
board[i][j] = \'.\';
// 列占用解除
col[j] = false;
// 左对角线占用解除
left[i + j] = false;
// 右对角线占用解除
right[i - j + n - 1] = false;
37.解数独
class Solution
final int N = 9;
int[] row = new int [N], col = new int [N];
//ones数组表示0~2^9 - 1的整数中二进制表示中1的个数:如ones[7] = 3 ones[8] = 1
//map数组表示2的整数次幂中二进制1所在位置(从0开始) 如 map[1] = 0,map[2] = 1, map[4] = 2
int[] ones = new int[1 << N], map = new int[1 << N];
int[][] cell = new int[3][3];
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board)
init();
int cnt = fill_state(board);
dfs(cnt, board);
void init()
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) row[i] = col[i] = (1 << N) - 1;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
cell[i][j] = (1 << N) - 1;
//以上2个循环把数组的数初始化为二进制表示9个1,即一开始所以格子都可填
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) map[1 << i] = i;
//统计0~2^9 - 1的整数中二进制表示中1的个数
for(int i = 0; i < 1 << N; i++)
int n = 0;
for(int j = i; j != 0; j ^= lowBit(j)) n++;
ones[i] = n;
int fill_state(char[][] board)
int cnt = 0; //统计board数组空格(\'.\')的个数
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++)
if(board[i][j] != \'.\')
int t = board[i][j] - \'1\';
//数独中 i,j位置为数组下标,修改row col cell数组中状态
change_state(i, j, t);
else cnt++;
return cnt;
boolean dfs(int cnt, char[][] board)
if(cnt == 0) return true;
int min = 10, x = 0, y = 0;
//剪枝,即找出当前所以空格可填数字个数最少的位置 记为x y
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++)
if(board[i][j] == \'.\')
int k = ones[get(i, j)];
if(k < min)
min = k;
x = i;
y = j;
//遍历当前 x y所有可选数字
for(int i = get(x, y); i != 0; i ^= lowBit(i))
int t = map[lowBit(i)];
change_state(x, y, t);
board[x][y] = (char)(\'1\' + t);
if(dfs(cnt - 1, board)) return true;
//恢复现场
change_state(x, y, t);
board[x][y] = \'.\';
return false;
void change_state(int x, int y, int t)
row[x] ^= 1 << t;
col[y] ^= 1 << t;
cell[x / 3][y / 3] ^= 1 << t;
//对维护数组x行,y列的3个集合(行、列、九宫格)进行&运算
//就可以获得可选数字的集合(因为我们用1标识可填数字)
int get(int x, int y)
return row[x] & col[y] & cell[x / 3][y / 3];
int lowBit(int x)
return -x & x;
java——递归(动态规划,回溯)
最近刷面试题经常刷到递归方面的算法,一直以为都是递归,后来发现竟然都有具体的叫法,所以写了这篇博客来牢记以下
1. 五大常用算法
(1) 分治算法
把一个复杂的问题分成两个或多个相同或者相似的子问题,然后不断地细分,直到最后的子问题可以很简单地求解出来,原问题的解就是自问题的合并。比如常见的快速排序算法和归并算法
分治法的核心思想就是把大的难解的问题不断分割,分而治之。
(2) 动态规划
类似于分治法,将带求解的问题分化成几个小问题,每个小问题的解会影响原问题的解。
先求每个子问题的局部解,然后通过决策保留那些可能达到最优解的局部解
能够分解成若干子问题,且子问题之间有交叉
(3) 回溯算法
类似于一个枚举的过程,其实也是一个建树的过程,是树的深度优先搜索。
在搜索尝试过程中,发现当前节点已经不能满足求解条件时,就返回其父节点,继续尝试别的路径
(4) 分支界限法
类似于回溯算法,不过不是深度优先搜索,而是广度优先搜索,一般是用到queue(先进先出)来对每一个节点进行判断。
(5) 贪心算法
在问题求解时,总是找到局部最优解,而不是整体上最优。
贪心算法的前提:局部最优策略能最终产生全局的最优解
2. 递归(个人感觉这个学会了,算法只是如何调用递归)
先上一个最简单的递归代码,斐波那契数列
public class Fibo { public int[] array = new int[100];{ array[0]=0; array[1]=1; array[2]=1;} public int Fibonacci(int n){ if(n==1||n==2){ return 1; }else{ return this.array[n]=Fibonacci(n-1)+Fibonacci(n-2); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Fibo fb = new Fibo(); System.out.println(fb.Fibonacci(3)); } }
当然,也可以来个伪递归,就是建立一个数组,把答案先预存起来,然后直接返回结果。剑指offer上很多直接递归是通不过的,必须要伪递归才可以
再来个青蛙跳台阶的代码,题目同样是剑指offer上的
//一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。 //求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法 public class JumpFloor { public int Jump(int target){ if(target==0){ return 0; }else if(target==1){ return 1; }else if(target==2){ return 2; }else{ int[] array = new int[target+1]; array[0]=0; array[1]=1; array[2]=2; for(int i=3;i<array.length;i++){ array[i]=array[i-1]+array[i-2]; } return array[target]; } } //一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级,跳3个,4个......n-1个。 //求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法 public int JumpII(int target){ if(target==0){ return 0; }else if(target==1){ return 1; }else if(target==2){ return 2; }else{ int[] array = new int[target+1]; array[0]=0; array[1]=1; array[2]=2; int sum = 3; for(int i=3;i<array.length;i++){ array[i]=sum+1; sum = sum+array[i]; } return array[target]; } } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub JumpFloor jf = new JumpFloor(); System.out.println(jf.Jump(3)); System.out.println(jf.JumpII(3)); } }
这里也是用伪递归来实现的
3. 递归的本质
其实递归的本质就是找到前后的联系,找到递归的公式
例如 F(n) = F(n-1) + F(n-2) 等等
递归的一般情况是
(1). if(满足递归结束条件),返回值
(2). else,继续递归
4. 回溯的本质,其实是在递归基础上进行了改进
(1). if(不满足继续递归查找的条件,通常是界限判断),返回
(2). if(满足查找条件),记录下来,继续往下
(3). 加入这个节点,更新条件和值
(4). 递归左边
(5).递归右边
(6). 删除这个节点(回溯)
来个例子,例子是中兴的一道笔试题,我对其进行了改进。其实所有这类的能量补给,血条补给都是相同的解法。
import java.util.ArrayList;
//输入 //补给站个数,[补给站距离],[补给站能量],目的地距离(总共需要能量),初始能量 //3, [5, 7, 10], [2, 3, 5], 15, 5 //5, [10, 20, 22, 23, 26], [10, 2, 5, 1, 1], 30, 10
//输出
//所有可以到达的方案,到达不了返回-1
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner; public class PowerGain { private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> listAll = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); private ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> minNumber(int n, int[] distince, int[] judce, int left, int right, int destination, int power){ //System.out.println(left+" "+destination+" "+power); if( left>right || power<=0){ return listAll; } //if(power>=distince[left]){ list.add(left); //} if(power>=destination){ listAll.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list)); //return listAll; } int newleft = left+1; //不喝继续前行,喝了继续前行 minNumber(n, distince, judce, newleft, n, destination-distince[left], power-distince[left]); minNumber(n, distince, judce, newleft, n, destination-distince[left], power-distince[left]+judce[left]); list.remove(list.size()-1); return listAll; } public void outPrint(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> tempAll){ if(tempAll.size()==0){ System.out.println(-1); return; } for(int i=0;i<tempAll.size();i++){ ArrayList<Integer> temp = tempAll.get(i); for(int j=1;j<temp.size();j++){ System.out.print(temp.get(j)); if(j!=temp.size()-1){ System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String st = input.nextLine(); String[] sarray = st.split(", "); int n = Integer.parseInt(sarray[0]); int[] distince = new int[n+1]; int[] judce = new int[n+1]; int index = 1; //sarray下标 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(i==0){ distince[i] = Integer.parseInt(sarray[index].substring(1)); judce[i] = Integer.parseInt(sarray[index+n].substring(1)); }else if(i==n-1){ distince[i] = Integer.parseInt(sarray[index].substring(0, sarray[index].length()-1)); judce[i] = Integer.parseInt(sarray[index+n].substring(0, sarray[index+n].length()-1)); }else{ distince[i] = Integer.parseInt(sarray[index]); judce[i] = Integer.parseInt(sarray[index+n]); } index++; } index = 2*n+1; int destination = Integer.parseInt(sarray[index]); int power = Integer.parseInt(sarray[index+1]); //长度分段 judce[n] = 0; distince[n]=destination-distince[n-1]; for(int i=n-1;i>0;i--){ distince[i]=distince[i]-distince[i-1]; } PowerGain m = new PowerGain(){}; ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = m.minNumber(n, distince, judce, 0, n, destination, power); m.outPrint(result); } }
以上是关于2023-04-19 算法面试中常见的递归和回溯问题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章