MySQL8.0 优化器介绍
Posted GreatSQL
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MySQL8.0 优化器介绍相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
- GreatSQL社区原创内容未经授权不得随意使用,转载请联系小编并注明来源。
- GreatSQL是MySQL的国产分支版本,使用上与MySQL一致。
- 作者: 奥特曼爱小怪兽
- 文章来源:GreatSQL社区原创
往期回顾
本篇将进一步深入介绍优化器相关的join优化
为更好的理解本篇内容需要提前看一下以下内容:
- 单表访问的方法,参考《MySQL 是怎样运行的:从根儿上理解 MySQL》第10章"单表访问方法"
- 更多select语句级别的优化细节 见(https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/select-optimization.html)
为了让读者对join优化 有更深的了解,章节里的sql例子,留了一些思考和动手的问题。可能大家得到的答案会不同,但探索未知的过程,方式应该是一样的。
join优化(Join Optimizations)
MySQL可以使用Join Optimizations来改进上次分享过的join algorithms,或者决定如何执行部分查询。本次主要介绍三种经常用到的join Optimizations,更多的 join type 见下面的链接:(https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/explain-output.html#explain-join-types)
index merge
通常MySQL只会对每个表使用一个索引。但是,如果对同一表中的多个列在where后有条件限制,并且没有覆盖所有列的单个索引,无论选哪个索引都不是最佳的。对于这些情况,MySQL支持索引合并 (index merge)。select a,b,c from t where a=x1 and b=x2 and c=x3,这种情况下,建立一个多列的复合索引 index_abc 比使用 index merge +index_a+index_b+index_c 性能更好。
Index merge 支持三种算法 见下表

查询计划使用index merge 时,会在explain sql 的 access type 列 有"index_merge",key 列会 包含所有参与merge的列, key_length 包含一个所用索引的最长关键部分的列表。举个Intersection例子:
Intersection
以下代码块注释中提到的知识点略多
##无论optimizer 是否选择 index merge 取决于index statistics.
## index statistics 是从哪个试图获得呢?mysql.innodb_index_stats 还是 information_schema.statistics
## 还是 information_schema.INNODB_SYS_TABLESTATS?
## 可以参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/ClassicMan/articles/15871403.html
## index_dive eq_range_index_dive_limit 这两个参数有什么作用?
##意味着即使返回相同STATEMENT_DIGEST_TEXT的sql查询语句, WHERE语句后面跟不同的值,得到的查询计划可能是不一样的 ##比如select * from people where name=\'唯一值\';
##select * from people where name=\'超级多的重复值\'
## 同理index statistics 的改变会让同一个查询走不同的执行计划,
## 体现在 select a,b from t where a=1 and b=1 有时走了 index merges,有时没走。
CREATE TABLE `payment` (
`payment_id` smallint unsigned NOT NULL,
`customer_id` smallint unsigned NOT NULL,
`staff_id` tinyint unsigned NOT NULL,
`rental_id` int(DEFAULT NULL,
`amount` decimal(5,2) NOT NULL,
`payment_date` datetime NOT NULL,
`last_update` timestamp NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`payment_id`),
KEY `idx_fk_staff_id` (`staff_id`),
KEY `idx_fk_customer_id` (`customer_id`),
KEY `fk_payment_rental` (`rental_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
## case1 等值查询
SELECT *
FROM sakila.payment
WHERE staff_id = 1
AND customer_id = 75;
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT *
FROM sakila.payment
WHERE staff_id = 1
AND customer_id = 75\\G
**************************** 1. row *****************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: payment
partitions: NULL
type: index_merge
possible_keys: idx_fk_staff_id,idx_fk_customer_id
key: idx_fk_customer_id,idx_fk_staff_id
key_len: 2,1
ref: NULL
rows: 20
filtered: 100
Extra: Using intersect(idx_fk_customer_id,idx_fk_staff_id); Using
where 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.0007 sec)
mysql> EXPLAIN FORMAT=TREE
SELECT *
FROM sakila.payment
WHERE staff_id = 1
AND customer_id = 75\\G
**************************** 1. row ****************************
EXPLAIN: -> Filter: ((sakila.payment.customer_id = 75) and (sakila.payment.staff_id = 1)) (cost=14.48 rows=20)
-> Index range scan on payment using intersect(idx_fk_customer_id,idx_fk_staff_id) (cost=14.48 rows=20)
1 row in set (0.0004 sec)
##注意"Index range scan on payment",两个等值查询条件,为啥触发了rang scan?
## case2 下面的sql范围查询也能用到index merge 吗?执行计划 自己下去测试验证
SELECT *
FROM sakila.payment
WHERE payment_id > 10
AND customer_id = 318;
Union Algorithm
##case1 等值查询
SELECT *
FROM sakila.payment
WHERE staff_id = 1
OR customer_id = 318;
mysql> EXPLAIN
SELECT *
FROM sakila.payment
WHERE staff_id = 1
OR customer_id = 318\\G
**************************** 1. row *****************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: payment
partitions: NULL
type: index_merge
possible_keys: idx_fk_staff_id,idx_fk_customer_id
key: idx_fk_staff_id,idx_fk_customer_id
key_len: 1,2
ref: NULL
rows: 8069
filtered: 100
Extra: Using union(idx_fk_staff_id,idx_fk_customer_id); Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.0008 sec)
mysql> EXPLAIN FORMAT=TREE
SELECT *
FROM sakila.payment
WHERE staff_id = 1
OR customer_id = 318\\G
**************************** 1. row ****************************
EXPLAIN: -> Filter: ((sakila.payment.staff_id = 1) or (sakila.payment.customer_id = 318)) (cost=2236.18 rows=8069)
-> Index range scan on payment using union(idx_fk_staff_id,idx_fk_customer_id) (cost=2236.18 rows=8069)
1 row in set (0.0010 sec)
## case2 范围查询也能用到index merge 吗?执行计划 自己下去测试验证,
## 有主键参与后,和Intersection 章节的case2 执行计划中用到的索引个数有啥不同?
SELECT *
FROM sakila.payment
WHERE payment_id > 15000
OR customer_id = 318;
Sort-Union Algorithm
SELECT *
FROM sakila.payment
WHERE customer_id < 30
OR rental_id < 10;
mysql> EXPLAIN
SELECT *
FROM sakila.payment
WHERE customer_id < 30
OR rental_id < 10\\G
**************************** 1. row *****************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: payment
partitions: NULL
type: index_merge
possible_keys: idx_fk_customer_id,fk_payment_rental
key: idx_fk_customer_id,fk_payment_rental
key_len: 2,5
ref: NULL
rows: 826
filtered: 100
Extra: Using sort_union(idx_fk_customer_id,fk_payment_rental);
Using where 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.0009 sec)
mysql> EXPLAIN FORMAT=TREE
SELECT *
FROM sakila.payment
WHERE customer_id < 30
OR rental_id < 10\\G
**************************** 1. row *****************************
EXPLAIN: -> Filter: ((sakila.payment.customer_id < 30) or (sakila.payment.rental_id < 10)) (cost=1040.52 rows=826)
-> Index range scan on payment using sort_union(idx_fk_customer_id,fk_payment_rental) (cost=1040.52 rows=826)
1 row in set (0.0005 sec)
Multi-Range Read (MRR)
多范围读取(MRR)优化旨在减少对辅助索引进行范围扫描所导致的随机I/O量。优化读取索引
首先,根据行id(InnoDB的聚集索引)对键进行排序,然后按行的存储顺序检索行。多量程读取优化
可以用于范围扫描和使用索引的等值连接。不支持虚拟生成列上的辅助索引。
使用InnoDB进行多范围读取优化的主要用例是用于没有覆盖索引的磁盘绑定查询( disk-bound queries 另外一个层面对disk-bound 的优化,详细可见:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/optimizing-innodb-diskio.html)。优化的效果取决于需要多少行以及存储器的查找时间。MySQL将会估算(estimate)是否有用。然而,成本估算在过于悲观而不是过于乐观的一面,因此可能有必要提供帮助优化器做出正确决策的信息。
有两个 optimizer switches 控制MRR优化
- mrr: Whether the optimizer is allowed to use the Multi-Range Read optimization. The default is ON.
- mrr_cost_based: Whether the decision to use the Multi-Range Read optimization is cost based. You can disable this option to always use the optimization when it is supported. The default is ON
可以用MRR() 和NO_MRR() 两个optimizer switches 来控制表级别or 索引级别的 Multi-Range Read ,举个例子:
mysql> EXPLAIN
SELECT /*+ MRR(city) */
*
FROM world.city
WHERE CountryCode BETWEEN \'AUS\' AND \'CHN\'\\G
**************************** 1. row *****************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: city
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: CountryCode
key: CountryCode
key_len: 3
ref: NULL
rows: 812
filtered: 100
Extra: Using index condition; Using MRR
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.0006 sec)
有必要使用MRR()优化器提示或禁用基于MRR_cost_based的优化器开关。
示例中查询的估计行数太小,没有MRR的hint时,基于成本的优化无法使用MRR。
只能显示用hint来干预查询计划使用MRR。
当MRR的优化被使用时, MySQL需要用到random read buffer来存储indexes.
有一个参数可以影响MRR的性能 read_rnd_buffer_size.
Batched Key Access (BKA)
可以简单认为 BKA=BNL+MRR .这使得可以以与非索引连接类似的方式将连接缓冲区用于索引连接,并使用多范围读取优化来减少随机I/O的数量。BKA 用于大量 disk-bound 查询的场景。但是,没有明确的说明来确定优化何时有帮助,何时会导致性能下降。
可以借鉴一下国外知名dba在MySQL 优化方面的blog(http://oysteing.blogspot.com/2012/04/improved-dbt-3-results-with-mysql-565.html)
MRR 在最优时,查询耗时减少20%,最糟糕时查询耗时增加2/3。
BKA 主要的获益在一个相对较窄的查询范围,而其他查询的性能可能会降低,因此默认情况下禁用该优化。
(可以简单理解为 MySQL5.6时,bka优化带来的收益小于bka带来的成本开销)除非确定开启bka能来提升时,再用hint BKA() 来启用。session级别开启:
SET SESSION optimizer_switch = \'mrr=on,mrr_cost_based=off,batched_key_access=on\';
一个使用BKA的例子
mysql> EXPLAIN
SELECT /*+ BKA(ci) */
co.Code, co.Name AS Country,
ci.Name AS City
FROM world.country co
INNER JOIN world.city ci
ON ci.CountryCode = co.Code\\G
**************************** 1. row *****************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: co
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 239
filtered: 100
Extra: NULL
**************************** 2. row *****************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: ci
partitions: NULL
type: ref
possible_keys: CountryCode
key: CountryCode
key_len: 3
ref: world.co.Code
rows: 18
filtered: 100
Extra: Using join buffer (Batched Key Access)
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.0007 sec)
注意看执行计划中Extra 的关键字 "Using join buffer",说明 join_buffer_size 会影响BKA 特性的性能。从全局怎么调整join_buffer_size,并又能充分利用上BKA,是一个极大的挑战。调优最常见的问题,搞定了A sql,又引出了其他问题,比如内存使用率过高。
其他join优化
MySQL 还自动支持其他join 优化,一旦对查询有性能帮助,优化器会自动选择他们,一般不需要手动。
了解一下其他join的优化方式,有助于我们在遇到sql性能问题时,可以适当给与优化器,一些有用的hint。
具体有哪些join 优化方式,可以查看explain 输出中的Extra 的内容说明。本文可能列举的不全,精力有限只做了一些简单的介绍,具体细节需要查看官网,以及大量的实践。
-
Condition Filtering 条件过滤 当一个表有两个或多个与之相关联的条件,并且一个索引可以用于部分条件时,使用条件过滤优化。启用条件过滤后,在估计表的总体过滤时,将考虑其余条件的过滤效果。
-
- Optimizer Switch: condition_fanout_filter – enabled by default
- Optimizer Hints: None
- EXPLAIN Output: None
-
Derived Merge 优化器可以将派生表(derived table)、视图引用和公共表表达式合并到它们所属的查询块中。优化的替代方法是物化表(materialize the table)、视图引用或公共表表达式。
-
- Optimizer Switch: derived_merge – enabled by default.
- Optimizer Hints: MERGE(), NO_MERGE().
- EXPLAIN Output: The query plan reflects that the derived table has been merged
-
Engine Condition Pushdown 此优化将条件向下推到存储引擎。目前仅NDBCluster存储引擎支持它。
-
Index Condition Pushdown
官方文档中给的例子和解释如下:people表中(zipcode,lastname,firstname)构成一个索引 SELECT * FROM people WHERE zipcode=\'95054\' AND lastname LIKE \'%etrunia%\' AND address LIKE \'%Main Street%\';
如果没有使用索引下推技术,则MySQL会通过zipcode=\'95054\'从存储引擎中查询对应的数据,返回到MySQL服务端,然后MySQL服务端基于lastname LIKE \'%etrunia%\'和address LIKE \'%Main Street%\'来判断数据是否符合条件。
如果使用了索引下推技术,则MySQL首先会返回符合zipcode=\'95054\'的索引,然后根据lastname LIKE \'%etrunia%\'和address LIKE \'%Main Street%\'来判断索引是否符合条件。如果符合条件,则根据该索引来定位对应的数据,如果不符合,则直接reject掉。
有了索引下推优化,可以在有like条件查询的情况下,减少回表次数。
该优化也用于二级索引的范围条件。
-
- Optimizer Switch: index_condition_pushdown – enabled by default.
- Optimizer Hints: NO_ICP().
- EXPLAIN Output: The traditional format has Using index condition in the Extra column, and the JSON format sets the index_condition field with the index condition that is pushed
-
Index Extensions InnoDB中的所有二级非唯一索引都将主键列附加到索引中。当启用索引扩展优化时,MySQL会将主键列视为索引的一部分。
-
- Optimizer Switch: use_index_extensions – enabled by default
- Optimizer Hints: None
- EXPLAIN Output: None
-
Index Visibility 当表具有不可见的索引( invisible index)时,默认情况下,优化器在创建查询计划时不会考虑它。如果启用了索引可见性优化器开关,则将考虑不可见的索引。例如,这可以用于测试已添加但尚未可见的索引的效果。
-
- Optimizer Switch: use_invisible_indexes – disabled by default
- Optimizer Hints: None
- EXPLAIN Output: None
-
Loose Index Scan 在某些情况下,MySQL可以使用部分索引来提高聚合数据或包含DISTINCT子句的查询的性能。这要求列用于通过形成多列索引的左前缀以及不用于分组的其他列来分组数据。当存在GROUP BY子句时,只有MIN()和MAX()聚合函数才能使用这个特性。
distinct效率更高还是group by效率更高?
-
- Optimizer Switch: None.
- Optimizer Hints: NO_RANGE_OPTIMIZATION() disables the loose index scan optimization as well as index merges and range scans.
- EXPLAIN Output: The traditional format has Using index for group-by in the Extra column. The JSON format sets the using_index_for_group_by field to true.
-
Range Access Method 范围优化与其他优化略有不同,因为它被认为是一种访问方法。MySQL将只扫描表或索引的一个或多个部分,而不是执行完整的表或索引扫描。范围访问方法通常用于涉及运算符>、>=、<、=<、BETWEEN、IN(),为NULL、LIKE等 range-Optimization 与 index merge Optimization 具有同样的重要性。(https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/range-optimization.html)
-
- Optimizer Switch: None.
- Optimizer Hints: NO_RANGE_OPTIMIZATION() – this also disables the loose index scan and index merge optimizations. It does however not disable the skip scan optimization even though that also uses range access.
- EXPLAIN Output: The access method is set to range. range_optimizer_max_mem_size 可以限制 range access使用的内存。默认是8M
-
Semijoin 半联接优化用于IN和EXIST条件。支持四个策略:
当subquery materialization 开启时, Semijoin 会尽可能的使用 materialization策略。EXISTS 在MySQL8.0.16 以后支持半联接。NOT EXISTS 在MySQL8.0.17 以后支持半联接。每种策略,都可以 以参数的形式,用于SEMIJOIN() and NO_SEMIJOIN() hint
SEMIJOIN(DUPSWEEDOUT):The duplicate weedout strategy executes the semijoin as if it is a normal join and removes the duplicates using a temporary table. EXPLAIN Output: The traditional format has Start temporary and End temporary in the Extra column for the tables involved. The JSON-formatted output uses a block named duplicates_removal
SEMIJOIN(FIRSTMATCH):The first match strategy returns the first match for each value rather than all values. EXPLAIN Output: The traditional format has FirstMatch(...) in the Extra column where the value between parentheses is the name of the reference table. The JSON format sets the value of the first_match field to the name of the reference table
SEMIJOIN(LOOSESCAN):The loose scan strategy uses an index to choose a single value from each of the subquery’s value groups. EXPLAIN Output: The traditional format has LooseScan(m..n) in the Extra column where m and n indicate which parts of the index are used for the loose scan. The JSON format sets the loosescan field equal to true
半连接特别怕 null 值,Oracle 经常在以下方面出问题:
-
- where null in (a,b,c,null), null exists (null) .
- sum(null) 返回null,count(null) 返回 0
- materialization
- duplicate weedout
- first match
- loose scan (不要和 loose index scan optimization混淆)。
-
Skip Scan
Skip Scan MySQL 8.0.13 引入,工作方式类似loose index scan.当多列索引的第二列上存在范围条件,但第一列上没有条件时使用。Skip Scan将整个索引扫描转换为一系列范围扫描(对索引中第一列的每个值进行一次范围扫描)。
scan in the Extra column, and the JSON format sets the using_index_for_skip_scan field to true
-
- Optimizer Switch: skip_scan – enabled by default.
- Optimizer Hints: SKIP_SCAN(), NO_SKIP_SCAN().
- EXPLAIN Output: The traditional format has Using index for skip
-
Subquery Materialization
子查询物化策略将子查询的结果存储在内部临时表中。如果可能的话,优化器将在临时表上添加一个自动生成的哈希索引,将使其快速连接到查询的其余部分。
当启用了subquery_materialization_cost_based优化器开关(默认开)时,优化器将使用估计的成本来决定是使用Subquery Materialization 还是使用 IN-to-EXIST子查询转换(将IN条件重写为EXISTS)。
当开关关闭时,优化器总是选择Subquery Materialization。
-
- Optimizer Switch: materialization – enabled by default.
- Optimizer Hints: SUBQUERY(MATERIALIZATION).
- EXPLAIN Output: The traditional format has MATERIALIZED as the select type. The JSON format creates a block named materialized_from_subquery.
还有我们可以用哪些方法影响优化器,下篇文章再续。
Enjoy GreatSQL
庖丁解牛|图解 MySQL 8.0 优化器查询转换篇
简介: 本篇介绍子查询、分析表和JOIN的复杂转换过程
一 背景和架构
在《庖丁解牛-图解MySQL 8.0优化器查询解析篇》一文中我们重点介绍了MySQL最新版本8.0.25关于SQL基本元素表、列、函数、聚合、分组、排序等元素的解析、设置和转换过程,本篇我们继续来介绍更为复杂的子查询、分区表和JOIN的复杂转换过程,大纲如下:
Transformation
- remove_redundant_subquery_clause :Permanently remove redundant parts from the query if 1) This is a subquery 2) Not normalizing a view. Removal should take place when a query involving a view is optimized, not when the view is created.
- remove_base_options:Remove SELECT_DISTINCT options from a query block if can skip distinct
- resolve_subquery :Resolve predicate involving subquery, perform early unconditional subquery transformations
- Convert subquery predicate into semi-join, or
- Mark the subquery for execution using materialization, or
- Perform IN->EXISTS transformation, or
- Perform more/less ALL/ANY -> MIN/MAX rewrite
- Substitute trivial scalar-context subquery with its value
- transform_scalar_subqueries_to_join_with_derived:Transform eligible scalar subqueries to derived tables.
- flatten_subqueries :Convert semi-join subquery predicates into semi-join join nests. Convert candidate subquery predicates into semi-join join nests. This transformation is performed once in query lifetime and is irreversible.
- apply_local_transforms :
- delete_unused_merged_columns : If query block contains one or more merged derived tables/views, walk through lists of columns in select lists and remove unused columns.
- simplify_joins : Convert all outer joins to inner joins if possible.
- prune_partitions :Perform partition pruning for a given table and condition.
- push_conditions_to_derived_tables :Pushing conditions down to derived tables must be done after validity checks of grouped queries done by apply_local_transforms();
- Window::eliminate_unused_objects:Eliminate unused window definitions, redundant sorts etc.
二 详细转换过程
1 解析子查询(resolve_subquery)
解析条件中带有子查询的语句,做一些早期的无限制的子查询转换,包括:
- 标记subquery是否变成semi-join
转换判断条件
- 检查OPTIMIZER_SWITCH_SEMIJOIN和HINT没有限制
- 子查询是IN/=ANY和EXIST subquery的谓词
- 子查询是简单查询块而不是UNION
- 子查询无隐形和显性的GROUP BY
- 子查询没有HAVING、WINDOW函数
- Resolve的阶段是Query_block::RESOLVE_CONDITION和Query_block::RESOLVE_JOIN_NEST并且没有用到最新的Hyper optimizer优化器。
- 外查询块可以支持semijoins
- 至少要一个表,而不是类似"SELECT 1"
- 子查询的策略还没有指定Subquery_strategy::UNSPECIFIED
- 父查询也至少有一个表
- 父查询和子查询都不能有straight join
- 父查询块不禁止semijoin
- IN谓词返回值是否是确定的,不是RAND
- 根据子查询判断结果是否需要转成true还是false以及是否为NULL,判断是可以做antijoin还是semijoin
- Antijoin是可以支持的,或者是semijoin
- offset和limit对于semjoin是有效的,offset是从第一行开始,limit也不是0
设置Subquery_strategy::CANDIDATE_FOR_SEMIJOIN并添加sj_candidates
- 标记subquery是否执行时采用materialization方案
- 如果不符合转换semijoin,尝试使用物化方式,转换判断条件
- Optimzier开关subquery_to_derived=on
- 子查询是IN/=ANY or EXISTS谓词
- 子查询是简单查询块而不是UNION
- 如果是[NOT] EXISTS,必须没有聚合
- Subquery谓词在WHERE子句(目前没有在ON子句实现),而且是ANDs or ORs的表达式tree
- 父查询块支持semijoins
- 子查询的策略还没有指定Subquery_strategy::UNSPECIFIED
- 父查询也至少有一个表,然后可以做LEFT JOIN
- 父查询块不禁止semijoin
- IN谓词返回值是否是确定的,不是RAND
- 根据子查询判断结果是否需要转成true还是false以及是否为NULL,判断是可以做antijoin还是semijoin
- 不支持左边参数不是multi-column子查询(WHERE (outer_subq) = ROW(derived.col1,derived.col2))
- 该子查询不支持转换为Derived table(m_subquery_to_derived_is_impossible)
- 设置Subquery_strategy::CANDIDATE_FOR_DERIVED_TABLE并添加sj_candidates
- 如果上面两个策略无法使用,根据类型选择transformer
- Item_singlerow_subselect::select_transformer
- 对于简单的标量子查询,在查询中直接用执行结果代替
select * from t1 where a = (select 1); => select * from t1 where a = 1;
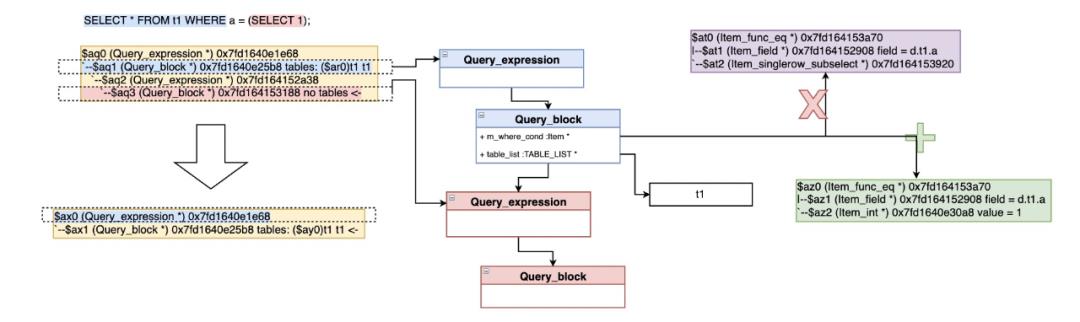
Item_in_subselect/Item_allany_subselect::select_transformer->select_in_like_transformer
- select_in_like_transformer函数来处理 IN/ALL/ANY/SOME子查询转换transformation
- 处理"SELECT 1"(Item_in_optimizer)
- 如果目前还没有子查询的执行方式,也就是无法使用semijoin/antijoin执行的子查询,会做IN->EXISTS的转换,本质是在物化执行和迭代式循环执行中做选择。IN语法代表非相关子查询仅执行一次,将查询结果物化成临时表,之后需要结果时候就去物化表中查找;EXISTS代表对于外表的每一条记录,子查询都会执行一次,是迭代式循环执行。子查询策略设定为Subquery_strategy::CANDIDATE_FOR_IN2EXISTS_OR_MAT
- 重写single-column的IN/ALL/ANY子查询(single_value_transformer)
oe $cmp$ (SELECT ie FROM ... WHERE subq_where ... HAVING subq_having) => - oe $cmp$ (SELECT MAX(...) ) // handled by Item_singlerow_subselect - oe $cmp$ \\<max\\>(SELECT ...) // handled by Item_maxmin_subselect fails=>Item_in_optimizer - 对于已经是materialized方案,不转换 - 通过equi-join转换IN到EXISTS
- 如果是ALL/ANY单值subquery谓词,尝试用MIN/MAX子查询转换
SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE a < ANY (SELECT a FROM t1); => SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE a < (SELECT MAX(a) FROM t1)
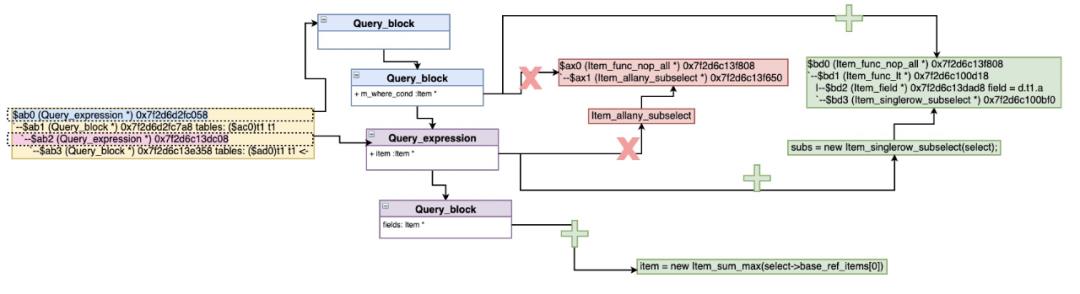
- 不满足上面,调用single_value_in_to_exists_transformer转换IN到EXISTS
- 转换将要将子查询设置为相关子查询,设置UNCACHEABLE_DEPENDENT标识
- 如果子查询包含聚合函数、窗口函数、GROUP语法、HAVING语法,将判断条件加入到HAVING子句中,另外通过ref_or_null_helper来区分NULL和False的结果,如需要处理NULL IN (SELECT ...)还需要封装到Item_func_trig_cond触发器中。
SELECT ... FROM t1 WHERE t1.b IN (SELECT <expr of SUM(t1.a)> FROM t2)
=>
SELECT ... FROM t1 WHERE t1.b IN (SELECT <expr of SUM(t1.a)> FROM t2
[trigcond] HAVING t1.b=ref-to-<expr of SUM(t1.a)>)
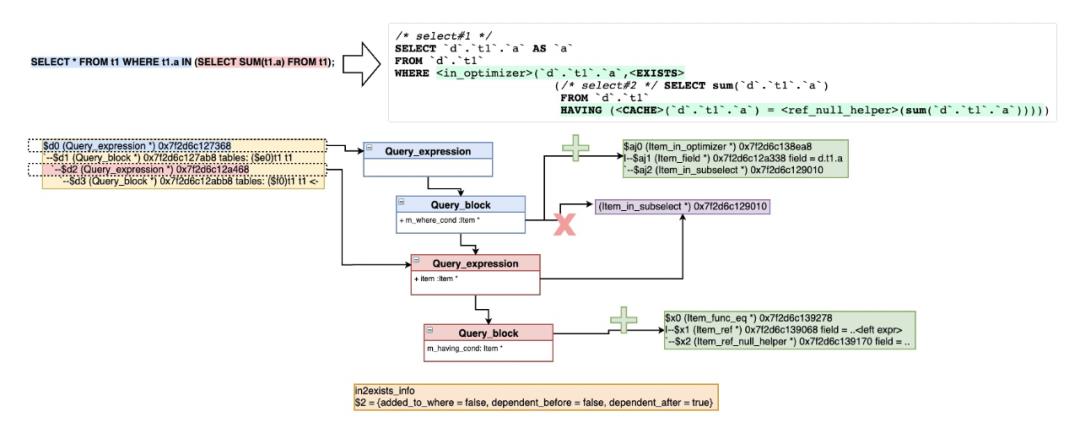
- 如果子查询不包含聚合函数、窗口函数、GROUP语法,会放在WHERE查询条件中,当然如果需要处理NULL情况还是要放入HAVING子句(Item_func_trig_cond+Item_is_not_null_test)。
不需要区分NULL和FALSE的子查询:
SELECT 1 FROM ... WHERE (oe $cmp$ ie) AND subq_where
需要区分的子查询:
SELECT 1 FROM ...
WHERE subq_where AND trigcond((oe $cmp$ ie) OR (ie IS NULL))
HAVING trigcond(@<is_not_null_test@>(ie))
- JOIN::optimize()会计算materialization和EXISTS转换的代价进行选择,设置m_subquery_to_derived_is_impossible = true
- ROW值转换,通过Item_in_optimizer,不支持ALL/ANY/SOME(row_value_transformer)
- Item_in_subselect::row_value_in_to_exists_transformer
for (each left operand)
create the equi-join condition
if (is_having_used || !abort_on_null)
create the "is null" and is_not_null_test items
if (is_having_used)
add the equi-join and the null tests to HAVING
else
add the equi-join and the "is null" to WHERE
add the is_not_null_test to HAVING
- 没有HAVING表达式
(l1, l2, l3) IN (SELECT v1, v2, v3 ... WHERE where) =>
EXISTS (SELECT ... WHERE where and
(l1 = v1 or is null v1) and
(l2 = v2 or is null v2) and
(l3 = v3 or is null v3)
[ HAVING is_not_null_test(v1) and
is_not_null_test(v2) and
is_not_null_test(v3)) ] <-- 保证不为NULL可以去掉HAVING
- 有HAVING表达式
(l1, l2, l3) IN (SELECT v1, v2, v3 ... HAVING having) =>
EXISTS (SELECT ... HAVING having and
(l1 = v1 or is null v1) and
(l2 = v2 or is null v2) and
(l3 = v3 or is null v3) and
is_not_null_test(v1) and
is_not_null_test(v2) and
is_not_null_test(v3))
2 转换的标量子查询转换成Derived Table(transform_scalar_subqueries_to_join_with_derived)
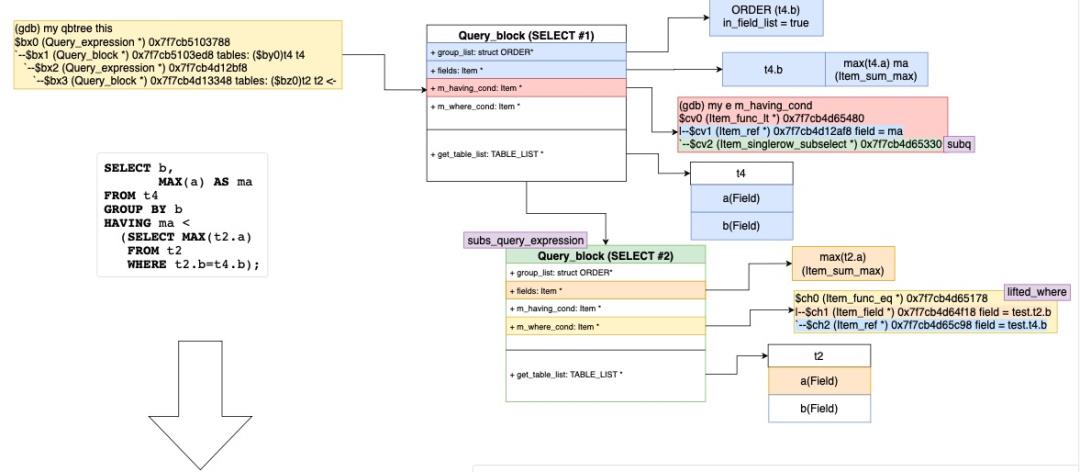
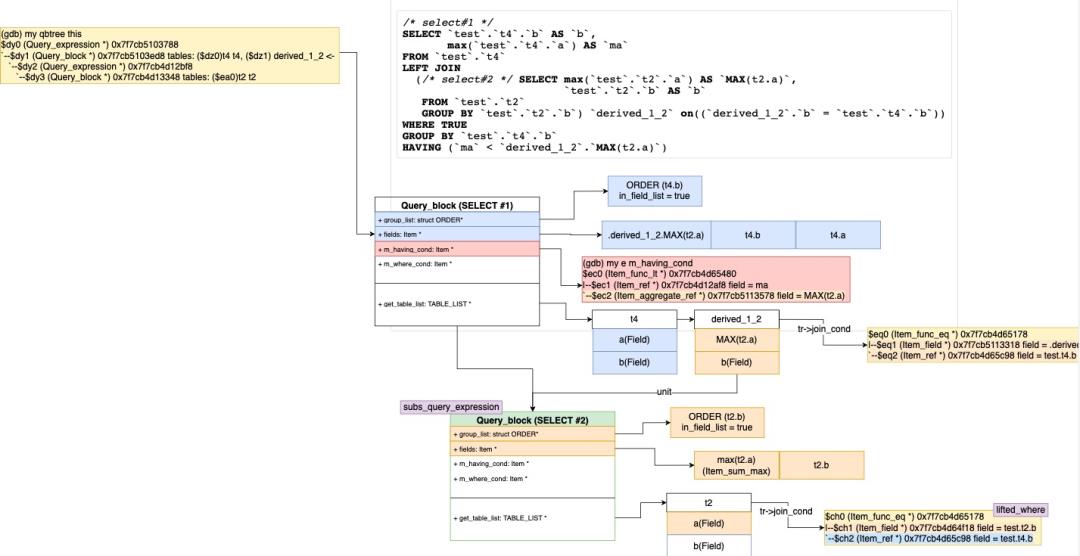
该特性是官方在8.0.16中为了更好的支持Secondary Engine(Heapwave)的分析下推,增强了子查询的转换能力。可以先直观的看下转换和不转换的执行计划的不同:
root:test> set optimizer_switch = 'subquery_to_derived=off'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) root:test> EXPLAIN SELECT b, MAX(a) AS ma FROM t4 GROUP BY b HAVING ma < (SELECT MAX(t2.a) FROM t2 WHERE t2.b=t4.b); +----+--------------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+--------------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+ | 1 | PRIMARY | t4 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | Using temporary | | 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | t2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where | +----+--------------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+ 2 rows in set, 3 warnings (0.00 sec) root:test> set optimizer_switch = 'subquery_to_derived=on'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) root:test> EXPLAIN SELECT b, MAX(a) AS ma FROM t4 GROUP BY b HAVING ma < (SELECT MAX(t2.a) FROM t2 WHERE t2.b=t4.b); +----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+ | 1 | PRIMARY | t4 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | Using temporary | | 1 | PRIMARY | <derived2> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (hash join) | | 2 | DERIVED | t2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using temporary | +----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+ 3 rows in set, 3 warnings (0.01 sec)
- transform_scalar_subqueries_to_join_with_derived具体转换的过程如下:
- 首先从JOIN条件、WHERE条件、HAVING条件和SELECT list中收集可以转换的标量子查询(Item::collect_scalar_subqueries)。
- 遍历这些子查询,判断是否可以增加一个额外的转换(transform_grouped_to_derived):把隐性的GROUP BY标量子查询变成Derived Table。
SELECT SUM(c1), (SELECT SUM(c1) FROM t3) scalar FROM t1;
转换为=>
SELECT derived0.summ, derived1.scalar
FROM (SELECT SUM(a) AS summ FROM t1) AS derived0
LEFT JOIN
(SELECT SUM(b) AS scalar FROM t3) AS derived1
ON TRUE
执行计划如下:
explain SELECT SUM(a), (SELECT SUM(c1) FROM t3) scalar FROM t1;
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | <derived3> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | PRIMARY | <derived4> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (hash join) |
| 4 | DERIVED | t3 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 3 | DERIVED | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+
- 收集唯一的聚合函数Item列表(collect_aggregates),这些Item将会被新的Derived Table的列代替。
- 还需要添加所有引用到这些Item的fields,包括直接在SELECT列表的,Window函数参数、ORDER by、Partition by包含的,还有该查询块中ORDER BY的列,因为他们都会引动到Derived Table里。
- 创建Derived Table需要的Query_expression/Query_block(create_query_expr_and_block)。
- 添加Derived Table到查询块和top_join_list中。
- 保留旧的子查询单元块,如果包含可以转化的Derived的移到Derived Table下面的Query_block,如果不包含,保留到原来的子查询块中。
- 将之前的聚合函数Item列表插入到Derived Table的查询块中。
- 收集除GROUP AGG表达式中的列,由于这些fields已经移动到Derived Table中,删除不合理的fields引用。
- 收集所有唯一的列和View的引用后,将他们加到新的Derived Table列表中。
- 对新的新的Derived Table进行flatten_subqueries/setup_tables
- 重新resolve_placeholder_tables,不处理进行转换后的子查询。
- 处理Derived Table中,新加入的HAVING条件中的聚合函数Item,并通过Item_aggregate_refs引用到new_derived->base_ref_items而不是之前的父查询块base_ref_items。
- 永久代替父查询块中的聚合函数列表,变成Derived Table的列,并删除他们。
- 之前保存和加入到Derived Table的唯一的列和View的引用,也要替换新的fields代替他们的引用。
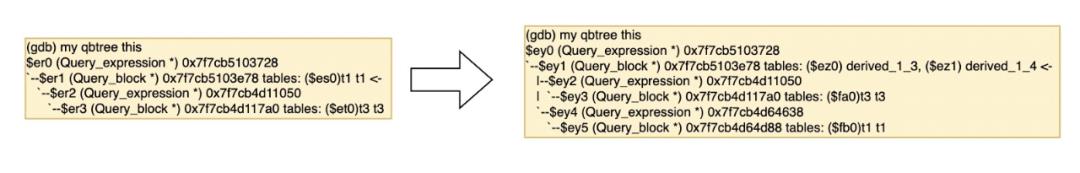
- 但目前不支持HAVING表达式中包含该子查询,其实也是可以转换的。
SELECT SUM(a), (SELECT SUM(b) FROM t3) scalar
FROM t1
HAVING SUM(a) > scalar;
转换为=>
SELECT derived0.summ, derived1.scalar
FROM (SELECT SUM(a) AS summ FROM t1) AS derived0
LEFT JOIN
(SELECT SUM(b) AS scalar FROM t3) AS derived1
ON TRUE
WHERE derived0.sum > derived1.scalar;
- 接下来遍历所有可以转换的子查询,把他们转换成derived tables,并替换相应的表达式变成列(transform_subquery_to_derived)。
- 生成derived table的TABLE_LIST(synthesize_derived)。
- 将可以移动到derived table的where_cond设置到join_cond上。
- 添加derived table到查询块的表集合中。
- decorrelate_derived_scalar_subquery_pre
- 添加非相关引用列(NCF)到SELECT list,这些条件被JOIN条件所引用,并且还有另外一个fields包含了外查询相关的列,我们称之为'lifted_where'
- 添加COUNT(*)到SELECT list,这样转换的查询块可以进行cardinality的检查。比如没有任何聚合函数在子查询中。如果确定包含聚合函数,返回一行一定是NCF同时在GROUP BY列表中。
- 添加NCF到子查询的GROUP列表中,如果已经在了,需要加到最后,如果发生GROUP BY的列由于依赖性检查失败,还要加Item_func_any_value(非聚合列)到SELECT list。对于NCF会创建 derived.field和derived.`count(field)` 。
- 设置物化的一些准备(setup_materialized_derived)。
- decorrelate_derived_scalar_subquery_post:
- 创建对应的'lifted_fields'。
- 更新JOIN条件中相关列的引用,不在引用外查询而换成Derived table相关的列。
- 代替WHERE、JOIN、HAVING条件和SELECT list中的子查询的表达式变成对应的Derived Table里面列。
下面图解该函数的转换过程和结果:
3 扁平化子查询(flatten_subqueries)
该函数主要是将Semi-join子查询转换为nested JOIN,这个过程只有一次,并且不可逆。
- 简单来讲步骤可以简化理解为:
- 创建SEMI JOIN (it1 ... itN)语以部分,并加入到外层查询块的执行计划中。
- 将子查询的WHERE条件以及JOIN条件,加入到父查询的WHERE条件中。
- 将子查询谓词从父查询的判断谓词中消除。
- 由于MySQL在一个query block中能够join的tables数是有限的(MAX_TABLES),不是所有sj_candidates都可以做因此做flatten_subqueries 的,因此需要有优先级决定的先后顺序先unnesting掉,优先级规则如下:
- 相关子查询优先于非相关的
- inner tables多的子查询大于inner tables少的
- 位置前的子查询大于位置后的
subq_item->sj_convert_priority =
(((dependent * MAX_TABLES_FOR_SIZE) + // dependent subqueries first
child_query_block->leaf_table_count) *
65536) + // then with many tables
(65536 - subq_no); // then based on position
- 另外,由于递归调用flatten_subqueries是bottom-up,依次把下层的子查询展开到外层查询块中。
for SELECT#1 WHERE X IN (SELECT #2 WHERE Y IN (SELECT#3)) :
Query_block::prepare() (select#1)
-> fix_fields() on IN condition
-> Query_block::prepare() on subquery (select#2)
-> fix_fields() on IN condition
-> Query_block::prepare() on subquery (select#3)
<- Query_block::prepare()
<- fix_fields()
-> flatten_subqueries: merge #3 in #2
<- flatten_subqueries
<- Query_block::prepare()
<- fix_fields()
-> flatten_subqueries: merge #2 in #1
- 遍历子查询列表,删除Item::clean_up_after_removal标记为Subquery_strategy::DELETED的子查询,并且根据优先级规则设置sj_convert_priority。根据优先级进行排序。
- 遍历排序后的子查询列表,对于Subquery_strategy::CANDIDATE_FOR_DERIVED_TABLE策略的子查询,转换子查询([NOT] {IN, EXISTS})为JOIN的Derived table(transform_table_subquery_to_join_with_derived)
FROM [tables] WHERE ... AND/OR oe IN (SELECT ie FROM it) ...
=>
FROM (tables) LEFT JOIN (SELECT DISTINCT ie FROM it) AS derived
ON oe = derived.ie WHERE ... AND/OR derived.ie IS NOT NULL ...
- 设置策略为Subquery_strategy::DERIVED_TABLE
- semijoin子查询不能和antijoin子查询相互嵌套,或者外查询表已经超过MAX_TABLE,不做转换,否则标记为Subquery_strategy::SEMIJOIN策略。
- 判断子查询的WHERE条件是否为常量。如果判断条件永远为FALSE,那么子查询结果永远为空。该情况下,调用Item::clean_up_after_removal标记为Subquery_strategy::DELETED,删除该子查询。
- 如果无法标记为Subquery_strategy::DELETED/设置Subquery_strategy::SEMIJOIN策略的重新标记会Subquery_strategy::UNSPECIFIED继续下一个。
- 替换外层查询的WHERE条件中子查询判断的条件(replace_subcondition)
- 子查询内条件并不永远为FALSE,或者永远为FALSE的情况下,需要改写为antijoin(antijoin情况下,子查询结果永远为空,外层查询条件永远通过)。此时将条件改为永远为True。
- 子查询永远为FALSE,且不是antijoin。那么将外层查询中的条件改成永远为False。
- Item_subselect::EXISTS_SUBS不支持有聚合操作
- convert_subquery_to_semijoin函数解析如下模式的SQL
- IN/=ANY谓词
- 如果条件满足解关联,解关联decorrelate_condition
- 添加解关联的内表表达式到 SELECT list
- 收集FROM子句中的外表相关的 derived table或join条件
- 去掉关联标识UNCACHEABLE_DEPENDENT,更新used table
- Derived table子查询增加SELECT_DISTINCT标识
- 转换子查询成为一个derived table,并且插入到所属于的查询块FROM后(transform_subquery_to_derived)
- 创建derived table及其join条件
- 遍历父查询块的WHERE,替换该子查询的Item代替成derived table(replace_subcondition)
- 遍历排序后的子查询列表,对于Subquery_strategy::CANDIDATE_FOR_SEMIJOIN策略的子查询。
- 判断是否可以转换为semijoin
- 遍历排序后的子查询列表,对于Subquery_strategy::SEMIJOIN的子查询,开始转换为semijoin/antijoin(convert_subquery_to_semijoin)
- convert_subquery_to_semijoin函数解析如下模式的SQL
- IN/=ANY谓词
SELECT ...
FROM ot1 ... otN
WHERE (oe1, ... oeM) IN (SELECT ie1, ..., ieM
FROM it1 ... itK
[WHERE inner-cond])
[AND outer-cond]
[GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
=>
SELECT ...
FROM (ot1 ... otN) SJ (it1 ... itK)
ON (oe1, ... oeM) = (ie1, ..., ieM)
[AND inner-cond]
[WHERE outer-cond]
[GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
- EXISTS谓词
SELECT ...
FROM ot1 ... otN
WHERE EXISTS (SELECT expressions
FROM it1 ... itK
[WHERE inner-cond])
[AND outer-cond]
[GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
=>
SELECT ...
FROM (ot1 ... otN) SJ (it1 ... itK)
[ON inner-cond]
[WHERE outer-cond]
[GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
- NOT EXISTS谓词
SELECT ...
FROM ot1 ... otN
WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT expressions
FROM it1 ... itK
[WHERE inner-cond])
[AND outer-cond]
[GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
=>
SELECT ...
FROM (ot1 ... otN) AJ (it1 ... itK)
[ON inner-cond]
[WHERE outer-cond AND is-null-cond(it1)]
[GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
- NOT IN谓词
SELECT ...
FROM ot1 ... otN
WHERE (oe1, ... oeM) NOT IN (SELECT ie1, ..., ieM
FROM it1 ... itK
[WHERE inner-cond])
[AND outer-cond]
[GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
=>
SELECT ...
FROM (ot1 ... otN) AJ (it1 ... itK)
ON (oe1, ... oeM) = (ie1, ..., ieM)
[AND inner-cond]
[WHERE outer-cond]
[GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
- 查找可以插入semi-join嵌套和其生成的条件的位置,比如对于 t1 LEFT JOIN t2, embedding_join_nest为t2,t2也可以是nested,如t1 LEFT JOIN (t2 JOIN t3))
- 生成一个新的semijoin嵌套的TABLE_LIST表
- 处理Antijoin
- 将子查询中潜在的表合并到上述join表(TABLE_LIST::merge_underlying_tables)
- 将子查询的叶子表插入到当前查询块的叶子表后面,重新设置子查询的叶子表的序号和依赖的外表。将子查询的叶子表重置。
- 如果是outer join的话,在join链表中传递可空性(propagate_nullability)
- 将内层子查询中的关联条件去关联化,这些条件被加入到semijoin的列表里。这些条件必须是确定的,仅支持简单判断条件或者由简单判断条件组成的AND条件(Query_block::decorrelate_condition)
- 判断左右条件是否仅依赖于内外层表,将其表达式分别加入到semijoin内外表的表达式列表中(decorrelate_equality)
- 解关联内层查询的join条件(Query_block::decorrelate_condition)
- 移除该子查询表达式在父查询的AST(Query_express::exclude_level)
- 根据semi-join嵌套产生的WHERE/JOIN条件更新对应的table bitmap(Query_block::fix_tables_after_pullout)
- 将子查询的WHERE条件上拉,更新使用表的信息(Item_cond_and::fix_after_pullout())
- 根据semijoin的条件列表创建AND条件,如果有条件为常量True,则去除该条件;如果常量为False,则整个条件都去除(Query_block::build_sj_cond)
- 将创建出来的semijoin条件加入到外层查询的WHERE条件中
- 最后遍历排序后的子查询列表,对于没有转换的子查询,对于Subquery_strategy::UNSPECIFIED的策略,执行IN->EXISTS改写(select_transformer),如果确实原有的子查询已经有替代的Item,调用replace_subcondition解析并把他们加入到合适的WHERE或者ON子句。
- 清除所有的sj_candidates列表
- Semi-join有5中执行方式,本文并不介绍Optimizer和Execution过程,详细可以参考引用文章中关于semijoin的介绍,最后引入下控制semijoin优化和执行的优化器开关,其中semijoin=on/off是总开关。
SELECT @@optimizer_switch\\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
@@optimizer_switch: ......
materialization=on,semijoin=on,loosescan=on,
firstmatch=on,
subquery_materialization_cost_based=on,
......
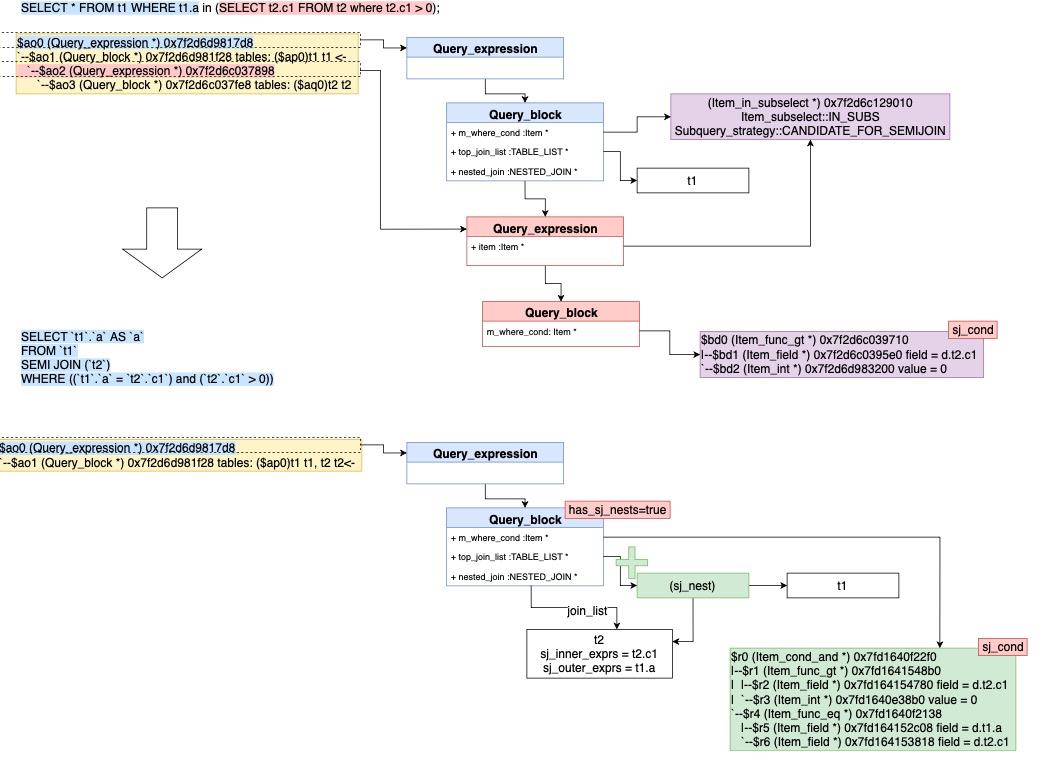
- 下图举例说明该转换过程:
SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE t1.a in (SELECT t2.c1 FROM t2 where t2.c1 > 0); => /* select#1 */ SELECT `t1`.`a` AS `a` FROM `t1` SEMI JOIN (`t2`) WHERE ((`t1`.`a` = `t2`.`c1`) and (`t2`.`c1` > 0)) 执行计划如下: explain SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE t1.a in (SELECT t2.c1 FROM t2 where t2.c1 > 0); +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where; Start temporary | | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50.00 | Using where; End temporary; Using join buffer (hash join) | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
4 应用当前查询块转换(apply_local_transforms)
该函数在flattern subqueries之后,bottom-up调用,主要分几个步骤:
删除无用列(delete_unused_merged_columns)
如果查询块已经删除了一些derived tables/views,遍历SELECT列表的列,删除不必要的列
简化JOIN(simplify_joins)
该函数会把Query_block中的top_join_list的嵌套join的简化为扁平化的join list。嵌套连接包括table1 join table2,也包含table1, (table2, table3)这种形式。如果所示的简化过程:
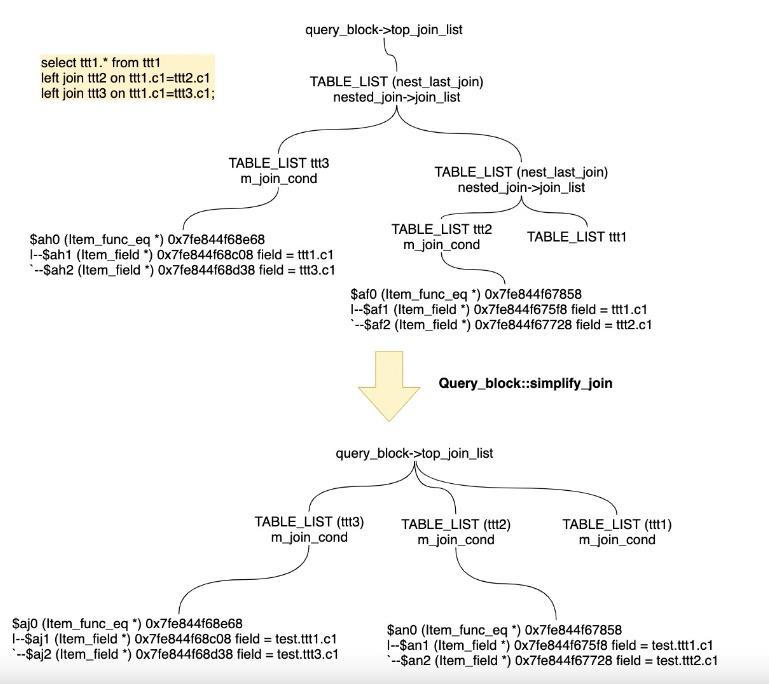
分区表的静态剪枝(prune_partitions)
由于剪枝根据HASH/RANGE/LIST及二级分区都有不同,这里简单介绍下剪枝过程,现有prune_partitions是在prepare和optimize阶段会被调用,某些常量子查询被评估执行完。
struct TABLE {
......
partition_info *part_info{nullptr}; /* Partition related information */
/* If true, all partitions have been pruned away */
bool all_partitions_pruned_away{false};
......
}
SQL tranformation phase
SELECT_LEX::apply_local_transforms
--> prune_partitions
for example, select * from employee where company_id = 1000 ;
SQL optimizer phase
JOIN::prune_table_partitions
--> prune_partitions
------> based on tbl->join_cond_optim() or JOIN::where_cond
for example, explain select * from employee where company_id = (select c1 from t1);
- 举例下面RANGE剪枝的过程:
root:ref> CREATE TABLE R2 (
-> a INT,
-> d INT
-> ) PARTITION BY RANGE(a) (
-> PARTITION p20 VALUES LESS THAN (20),
-> PARTITION p40 VALUES LESS THAN (40),
-> PARTITION p60 VALUES LESS THAN (60),
-> PARTITION p80 VALUES LESS THAN (80),
-> PARTITION p100 VALUES LESS THAN MAXVALUE
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.09 sec)
root:ref> Select * From R2 where a > 40 and a < 80;
- 剪枝详细过程如下:
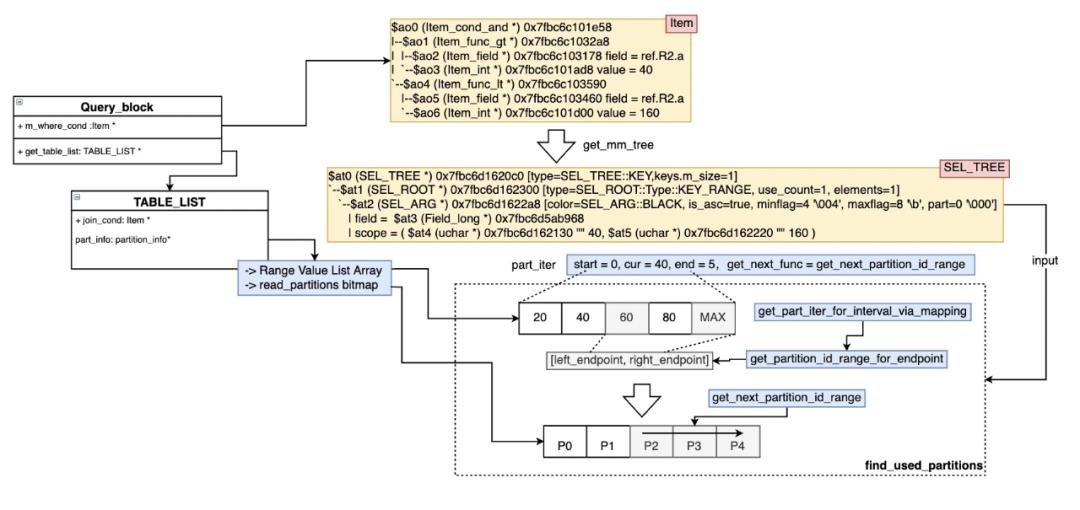
- 由于剪枝需要根据不同条件产生的pruning结果进行交集,因此剪枝过程中需要使用read_partitions这样的bitmap来保存是否使用该对应分区。另外剪枝过程类似迭代判断,因此引入了part_iterator来保存开始、结束和当前,以及对应需要获取区间范围的endpoint函数和获取下一个值next的迭代器函数。这里巧妙的运用了指针,来兼容不同分区类型Hash/Range/List类型,如下图所示:
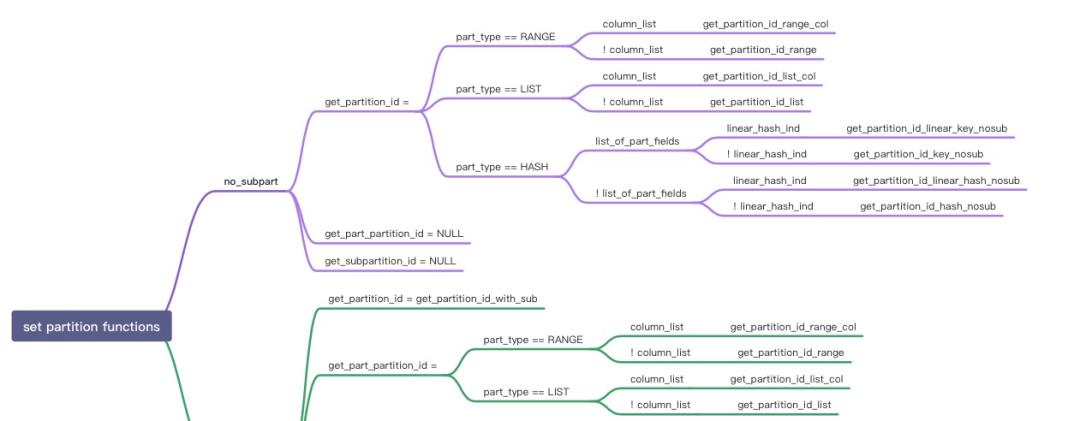
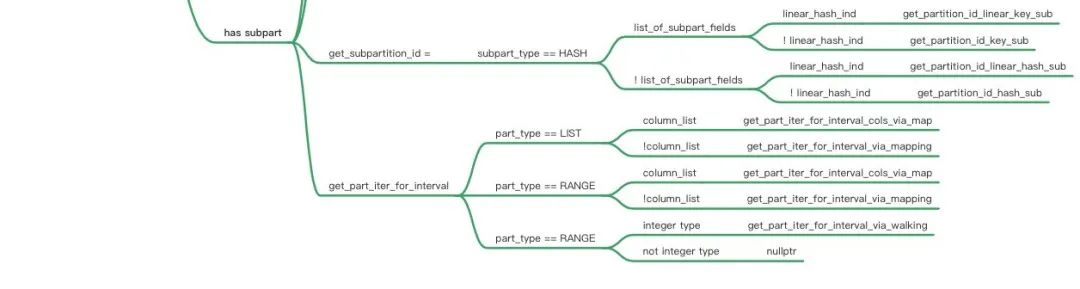
- 获取join_cond或者m_where_cond的SEL_TREE红黑树(get_mm_tree)
- 调用find_used_partitions来获取满足的分区,对于SEL_TREE的每个区间(interval):1. 获取区间的左右端点 2.从左边继续获取下一个满足的分区,直到到右边端点结束,每次调用完满足条件的分区需要使用bitmap_set_bit设置该分区在part_info->read_partitions上的位点。
- find_used_partitions是根据SEL_TREE的结构进行递归,如图从左到右遍历next_key_part(and condition),然后再遍历SEL_TREE的左右(也就是上下方向,or condition)深度递归。
(start)
| $
| Partitioning keyparts $ subpartitioning keyparts
| $
| ... ... $
| | | $
| +---------+ +---------+ $ +-----------+ +-----------+
\\-| par1=c1 |--| par2=c2 |-----| subpar1=c3|--| subpar2=c5|
+---------+ +---------+ $ +-----------+ +-----------+
| $ | |
| $ | +-----------+
| $ | | subpar2=c6|
| $ | +-----------+
| $ |
| $ +-----------+ +-----------+
| $ | subpar1=c4|--| subpar2=c8|
| $ +-----------+ +-----------+
| $
| $
+---------+ $ +------------+ +------------+
| par1=c2 |------------------| subpar1=c10|--| subpar2=c12|
+---------+ $ +------------+ +------------+
| $
... $
例如第一行(par1=c1 and par2=c2 and subpar1=c3 and subpar2=c5)的遍历的stack将是:
in find_used_partitions(key_tree = "subpar2=c5") (***)
in find_used_partitions(key_tree = "subpar1=c3")
in find_used_partitions(key_tree = "par2=c2") (**)
in find_used_partitions(key_tree = "par1=c1")
in prune_partitions(...)
然后是继续下面的条件,以此类推
or(par1=c1 and par2=c2 and subpar1=c3 and subpar2=c6)
or(par1=c1 and par2=c2 and subpar1=c4 and subpar2=c8)
or(par1=c2 and subpar1=c10 and subpar2=c12)
- 下图来展示了pruning的结构和过程:
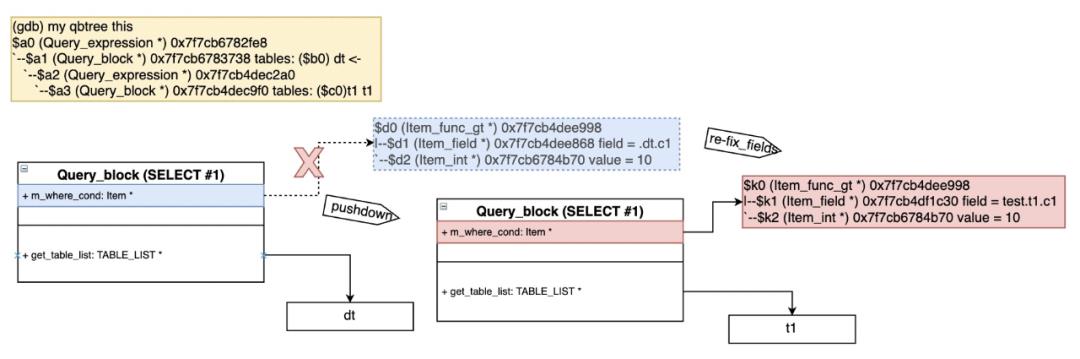
5 下推条件到Derived Table(push_conditions_to_derived_tables)
该函数将条件下推到derived tables,详细见WL#8084 - Condition pushdown to materialized derived table。
root:test> set optimizer_switch = 'derived_merge=off'; // 关闭dervied_merge 测试下推能力
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
root:test> EXPLAIN FORMAT=tree SELECT * FROM (SELECT c1,c2 FROM t1) as dt WHERE c1 > 10;
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| EXPLAIN |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| -> Table scan on dt (cost=2.51..2.51 rows=1)
-> Materialize (cost=2.96..2.96 rows=1)
-> Filter: (t1.c1 > 10) (cost=0.35 rows=1)
-> Table scan on t1 (cost=0.35 rows=1)
|
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
过程如下:
- 遍历derived table列表,判断是否可以下推(can_push_condition_to_derived),如果包括下面的情况则不能下推:
- Derived table有UNION
- Derived table有LIMIT
- Derived table不能是outer join中的内表,会导致更多NULL补偿的行
- 不能是CTE包含的Derived table
- 创建可以下推到的Derived table的where cond(Condition_pushdown::make_cond_for_derived)
- 保留剩余不能下推的条件(Condition_pushdown::get_remainder_cond)
- Top-down递归调用push_conditions_to_derived_tables
详细图解该过程如下:
三 综述
两篇文章重点介绍了下优化器的基于规则的优化部分,并没有涉及更多的基于代价的优化,可以看到对于直接运用规则优化带来执行的加速,那么可以直接转换,尤其是对于查询结构上面的变化类转换,如merge_derived。对于运用规则优化无法判断是否带来执行的加速,那么优化器会保留一些临时结构,为后续的代价估算提供更多选择,如IN/EXIST/Materialized转换。当然还有一些,又改变查询结构又无法判定是否规则转换带来的执行加速,MySQL目前还不支持。文章虽然详尽,但无法覆盖全部情况,也是为了抛砖引玉,还需要读者自己通过调试的方法更进一步了解某一类SQL的具体过程。
四 参考资料
《WL#13520: Transform correlated scalar subqueries》
《WL#8084 - Condition pushdown to materialized derived table》
《WL#2980: Subquery optimization: Semijoin》
- WL#3740: Subquery optimization: Semijoin: Pull-out of inner tables
- WL#3741: Subquery optimization: Semijoin: Duplicate elimination strategy
- WL#3750: Subquery optimization: Semijoin: First-match strategy
- WL#3751: Subquery optimization: Semijoin: Inside-out strategy
《WL#4389: Subquery optimizations: Make IN optimizations also handle EXISTS》
《WL#4245: Subquery optimization: Transform NOT EXISTS and NOT IN to anti-join》
《WL#2985: Perform Partition Pruning of Range conditions》
《MySQL · 源码分析 · Semi-join优化执行代码分析》
《MySQL·源码分析·子查询优化源码分析》《Optimizing Subqueries, Derived Tables, View References, and Common Table Expressions》
原文链接
本文为阿里云原创内容,未经允许不得转载。
以上是关于MySQL8.0 优化器介绍的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章