Python如何查询Mysql
Posted 生活会辜负努力的人,但不会辜负一直努力的人
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python如何查询Mysql相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Python查询Mysql使用 fetchone() 方法获取单条数据, 使用fetchall() 方法获取多条数据。
- fetchone(): 该方法获取下一个查询结果集。结果集是一个对象
- fetchall(): 接收全部的返回结果行.
- rowcount: 这是一个只读属性,并返回执行execute()方法后影响的行数。
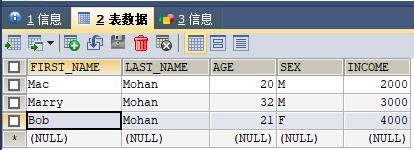
1:使用fetchone()方法获取结果集
import pymysql # 打开数据库连接 db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "123456", "test") # 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标 cursor = db.cursor() # SQL 查询语句 sql = "SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE \\ WHERE INCOME > \'%d\'" % (1000) try: # 执行SQL语句 cursor.execute(sql) print(cursor.rownumber) result = cursor.fetchone() while result!=None: print(result, cursor.rownumber) result = cursor.fetchone() result = cursor.fetchone() print(result, cursor.rownumber) result = cursor.fetchone() print(result, cursor.rownumber) except: print ("Error: unable to fetch data") # 关闭数据库连接 db.close()
输出结果:
0
(\'Mac\', \'Mohan\', 20, \'M\', 2000.0) 1
(\'Marry\', \'Mohan\', 32, \'M\', 3000.0) 2
(\'Bob\', \'Mohan\', 21, \'F\', 4000.0) 3
None 3
None 3
结论:执行cursor.execute(sql)语句后,cursor指向第一条记录之前的位置。
执行cursor.fetchone()语句之后,fetchone()方法返回cursor指向的下一条记录,同时cursor指向当前记录的下一条记录。
当cursor已经指向最后一条记录时,再次执行cursor.fetchone()语句后,结果返回None,cursor不再向前移动。
2:fetchall(): 接收全部的返回结果行
import pymysql # 打开数据库连接 db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "root", "123456", "test") # 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标 cursor = db.cursor() # SQL 查询语句 sql = "SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE \\ WHERE INCOME > \'%d\'" % (1000) try: # 执行SQL语句 cursor.execute(sql) # 获取所有记录列表 results = cursor.fetchall() for row in results: fname = row[0] lname = row[1] age = row[2] sex = row[3] income = row[4] # 打印结果 print("fname=%s,lname=%s,age=%d,sex=%s,income=%d" % (fname, lname, age, sex, income)) except: print ("Error: unable to fetch data") # 关闭数据库连接 db.close()
以上是关于Python如何查询Mysql的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
如何在python中执行mysql查询并将输出作为数据框[重复]