python中的双向链表实现
Posted F君君
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了python中的双向链表实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
引子
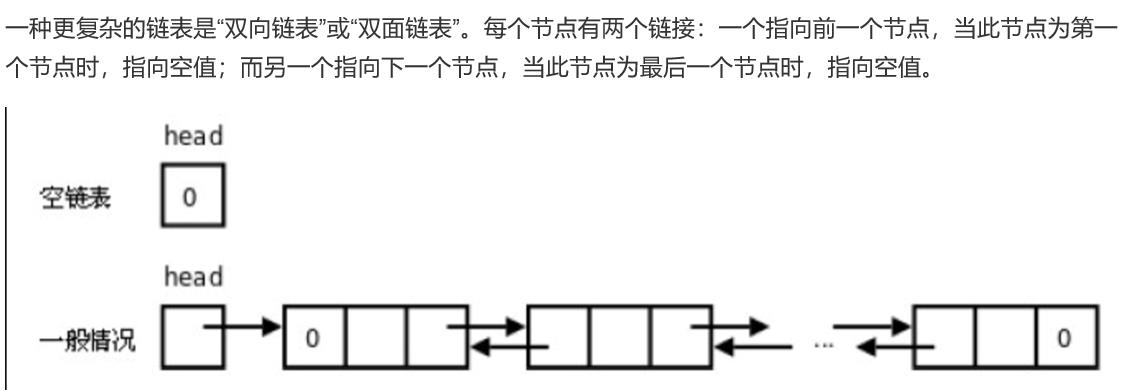
双向链表比之单向链表,多数操作方法的实现都没有什么不同,如is_empty, __len__, traverse, search。这些方法都没有涉及节点的变动,也就可通过继承单向链表来实现即可。
不同之处一是在于节点实现的不同。因为增加了指向前一个节点的前驱区,因此需要为节点添加一个新属性prev,用以指向前一个节点。
另外一点就是在做增删的操作时,需要额外考虑节点的前驱区的指向。其中的remove方法更是需要考虑多种特殊情况。
下面给出代码前,先放一个自己做的图示。(右键选择在新页面打开可看完整图示)
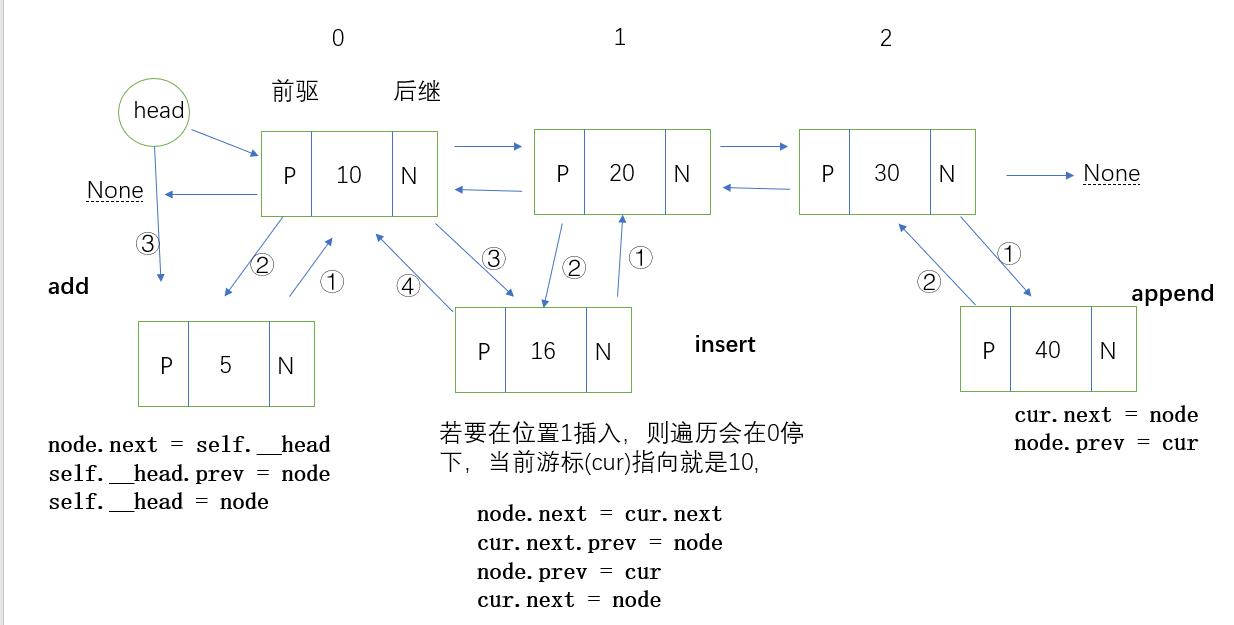
代码
class Node(object): def __init__(self, value): self.value = value # 前驱区 self.prev = None # 后继区 self.next = None class LinkedListTwoway(object): def __init__(self): self.__head = None def is_empty(self): return self.__head is None def __len__(self): count = 0 cur = self.__head while cur: count += 1 cur = cur.next return count def traverse(self): cur = self.__head while cur: print(cur.value) cur = cur.next def add(self, value): node = Node(value) if self.is_empty(): self.__head = node else: # 待插入节点的后继区指向原头节点 node.next = self.__head # 原头节点的前驱区指向待插入节点 self.__head.prev = node self.__head = node def append(self, value): node = Node(value) cur = self.__head if self.is_empty(): self.__head = Node return while cur.next: cur = cur.next cur.next = node node.prev = cur def insert(self, pos, value): if pos <= 0: self.add(value) elif pos > len(self) - 1: self.append(value) else: # 单向链表中为了在特定位置插入,要先在链表中找到待插入位置和其前一个位置 # 双向链表中就不需要两个游标了(当然单向链表中一个游标也是可以只找前一个位置) node = Node(value) count = 0 cur = self.__head while count < pos - 1: count += 1 cur = cur.next # 此时的游标指向pos的前一个位置 # 这里的相互指向需尤为注意,有多种实现,需细细分析 node.next = cur.next cur.next.prev = node node.prev = cur cur.next = node def search(self, value): cur = self.__head while cur: if cur.value == value: return True else: cur = cur.next return False def remove(self, value): if self.is_empty(): return cur = self.__head while cur: if cur.value == value: if cur == self.__head: self.__head = cur.next # 处理链表只有一个节点的特殊情况 if cur.next: cur.next.prev = None else: cur.prev.next = cur.next # 处理待删除节点是最后一个情况 if cur.next: cur.next.prev = cur.prev return else: cur = cur.next
以上是关于python中的双向链表实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章