MySQL8.0 优化器介绍
Posted GreatSQL
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MySQL8.0 优化器介绍相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
- GreatSQL社区原创内容未经授权不得随意使用,转载请联系小编并注明来源。
- GreatSQL是MySQL的国产分支版本,使用上与MySQL一致。
- 作者: 奥特曼爱小怪兽
- 文章来源:GreatSQL社区投稿
上一篇 MySQL8.0 优化器介绍(一)介绍了成本优化模型的三要素:表关联顺序,与每张表返回的行数(过滤效率),查询成本。而join算法又是影响表关联效率的首要因素。
join算法(Join Algorithms)
join在MySQL 是一个如此重要的章节,毫不夸张的说,everything is a join。
截止到本文写作时,MySQL8.0.32 GA已经发行,这里主要介绍三大join:NL(Nested Loop),BNL(Block Nested Loop),HASH JOIN
嵌套循环(Nested Loop)
MySQL5.7之前,都只有NL,它实现简单,适合索引查找。
几乎每个人都可以手动实现一个NL。
SELECT CountryCode,
country.Name AS Country,
city.Name AS City,
city.District
FROM world.country
INNER JOIN world.city
ON city.CountryCode = country.Code
WHERE Continent = \'Asia\';
##执行计划类似如下:
-> Nested loop inner join
-> Filter: (country.Continent = \'Asia\')
-> Table scan on country
-> Index lookup on city using CountryCode
(CountryCode=country.`Code`)
##python 代码实现一个NL
result = []
for country_row in country:
if country_row.Continent == \'Asia\':
for city_row in city.CountryCode[\'country_row.Code\']:
result.append(join_rows(country_row, city_row))
图示化一个NL
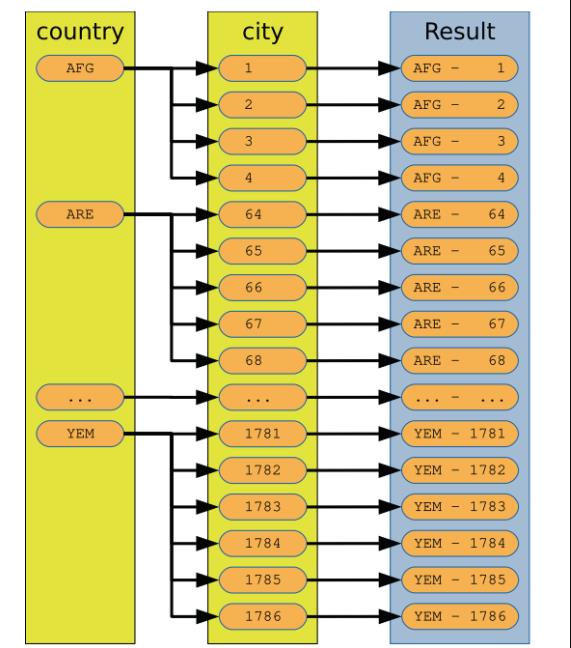
NL的限制:通常多个表join,小表在前做驱动表,被驱动表有索引检索,效率会高一些。(官方手册上没有full outer join ,full join 语法,实际支持full join)
举个例子 多表join 且关联表不走索引:
#人为干预计划,走性能最差的执行路径。
SELECT /*+ NO_BNL(city) */
CountryCode,
country.Name AS Country,
city.Name AS City,
city.District
FROM world.country IGNORE INDEX (Primary)
INNER JOIN world.city IGNORE INDEX (CountryCode)
ON city.CountryCode = country.Code
WHERE Continent = \'Asia\';
SELECT rows_examined, rows_sent,
last_statement_latency AS latency
FROM sys.session
WHERE thd_id = PS_CURRENT_THREAD_ID()\\G
**************************** 1. row ****************************
rows_examined: 208268
rows_sent: 1766
latency: 44.83 ms
##对比一下优化器 自动优化后的
SELECT CountryCode,
country.Name AS Country,
city.Name AS City,
city.District
FROM world.country
INNER JOIN world.city
ON city.CountryCode = country.Code
WHERE Continent = \'Asia\';
SELECT rows_examined, rows_sent,
last_statement_latency AS latency
FROM sys.session
WHERE thd_id = PS_CURRENT_THREAD_ID()\\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
rows_examined: 2005
rows_sent: 1766
latency: 4.36 ms
1 row in set (0.0539 sec)
块嵌套循环(Block Nested Loop)
块嵌套循环算法是嵌套循环算法的扩展。它也被称为BNL算法。连接缓冲区用于收集尽可能多的行,并在第二个表的一次扫描中比较所有行,而不是逐个提交第一个表中的行。这可以大大提高NL在某些查询上的性能。
hash join是在MySQL8.0.18引进的,下面的sql,使用了NO_HASH_JOIN(country,city) 的提示,并且两表的join 字段上的索引被忽略,目的是为了介绍BNL特性。
SELECT /*+ NO_HASH_JOIN(country,city) */
CountryCode,
country.Name AS Country,
city.Name AS City,
city.District
FROM world.country IGNORE INDEX (Primary)
INNER JOIN world.city IGNORE INDEX (CountryCode)
ON city.CountryCode = country.Code
WHERE Continent = \'Asia\';
##使用python伪代码来解释一下 BNL
result = []
join_buffer = []
for country_row in country:
if country_row.Continent == \'Asia\':
join_buffer.append(country_row.Code)
if is_full(join_buffer):
for city_row in city:
CountryCode = city_row.CountryCode
if CountryCode in join_buffer:
country_row = get_row(CountryCode)
result.append(
join_rows(country_row, city_row))
join_buffer = []
if len(join_buffer) > 0:
for city_row in city:
CountryCode = city_row.CountryCode
if CountryCode in join_buffer:
country_row = get_row(CountryCode)
result.append(join_rows(country_row, city_row))
join_buffer = []
图示化一个BNL
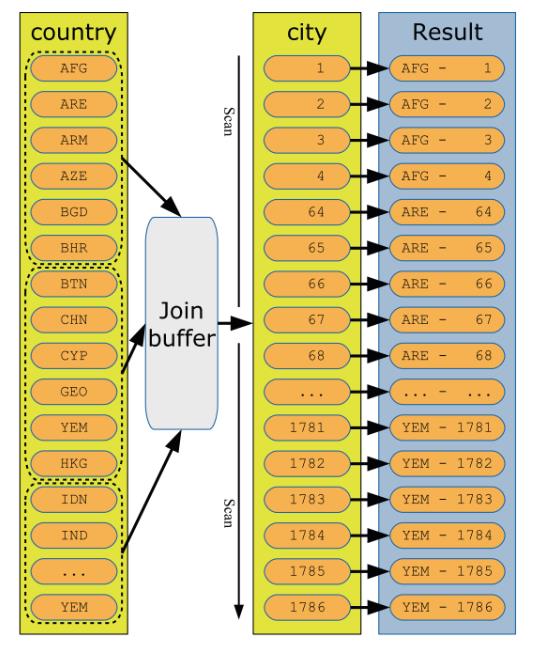
注意图里的join_buffer,在MySQL5.7上使用sysbench压测读写场景,压力上不去,主要就是因为BNL 算法下,join_buffer_size的设置为默认值。适当调整几个buffer后,tps得到显著提高。join buffer对查询影响,也可以用下面的例子做一个量化说明。
SELECT /*+ NO_HASH_JOIN(country,city) */
CountryCode,
country.Name AS Country,
city.Name AS City,
city.District
FROM world.country IGNORE INDEX (Primary)
INNER JOIN world.city IGNORE INDEX (CountryCode)
ON city.CountryCode = country.Code
WHERE Continent = \'Asia\';
SELECT rows_examined, rows_sent,
last_statement_latency AS latency
FROM sys.session
WHERE thd_id = PS_CURRENT_THREAD_ID()\\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
rows_examined: 4318
rows_sent: 1766
latency: 16.87 ms
1 row in set (0.0490 sec)
#人为干预计划,走性能最差的执行路径。
SELECT /*+ NO_BNL(city) */
CountryCode,
country.Name AS Country,
city.Name AS City,
city.District
FROM world.country IGNORE INDEX (Primary)
INNER JOIN world.city IGNORE INDEX (CountryCode)
ON city.CountryCode = country.Code
WHERE Continent = \'Asia\';
SELECT rows_examined, rows_sent,
last_statement_latency AS latency
FROM sys.session
WHERE thd_id = PS_CURRENT_THREAD_ID()\\G
**************************** 1. row ****************************
rows_examined: 208268
rows_sent: 1766
latency: 44.83 ms
在两表join,且join字段不使用索引的前提下,BNL +join_buffer 性能远大于 NL
使用BNL 有几个点需要注意。(我实在懒得全文翻译官方文档了)
- Only the columns required for the join are stored in the join buffer. This means that you will need less memory for the join buffer than you may at first expect. (不需要配置太高buffer)
- The size of the join buffer is configured with the join_buffer_size variable. The value of join_buffer_size is the minimum size of the buffer! Even if less than 1 KiB of country code values will be stored in the join buffer in the discussed example, if join_buffer_size is set to 1 GiB, then 1 GiB will be allocated. For this reason, keep the value of join_buffer_size low and only increase it as needed.
- One join buffer is allocated per join using the block nested loop algorithm.
- Each join buffer is allocated for the entire duration of the query.
- The block nested loop algorithm can be used for full table scans, full index scans, and range scans.(适用table access 方式)
- The block nested loop algorithm will never be used for constant tables as well as the first nonconstant table. This means that it requires a join between two tables with more than one row after filtering by unique indexes to use the block nested loop algorithm
可以通过 optimizer switch 配置BNL() 、 NO_BNL()
BNL 特别擅长在non-indexed joins 的场景,很多时候性能优于hash join。As of version 8.0.20, block nested-loop joins are no longer used; instead, a hash join has replaced it.
哈希join (Hash Join)

Hash Join 作为大杀器在 MySQL8.0.18引入,期间有过引起内存和文件句柄大量消耗的线上问题,但是不妨碍它作为一个join算法的重大突破,特别适合大表与大表的无索引join。某些场景甚至比NL+index join 更快。(当然比起oracle 上的hash join 依然弱爆了,40w * 40w 的大表查询,MySQL优化到极致在10s左右,oracle在1s 水平,相差一个数量级。
思考:MySQL、Oracle都是hash join,为何差距如此大?MySQL hash join 可以哪些方面进行性能提高?
业界主要有两大方向
- 单线程hash优化算法和数据结构
- NUMA架构下,多线程Hash Join的优化主要是能够让读写数据尽量发生在当前NUMA node
参考文档(https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/589601705)
大家不妨看看 MySQL工程师的worklog, 内容很精彩(https://dev.mysql.com/worklog/task/?id=2241)
可以看出国外大厂强大的标准化的it生产能力,一个功能从需求到实现经历了哪些关键步骤。
MySQL 的Hash join是一个内存hash+磁盘hash的混合扩展。为了不让hash join 溢出join buffer,需要加大内存设置,使用磁盘hash时,需要配置更多的文件句柄数。尽管有disk hash ,但实际干活的还是in-memory hash。
内存hash 有两个阶段:
- build phase. One of the tables in the join is chosen as the build table. The hash is calculated for the columns required for the join and loaded into memory.
- probe phase. The other table in the join is the probe input. For this table, rows are read one at a time, and the hash is calculated. Then a hash key lookup is performed on the hashes calculated from the build table, and the result of the join is generated from the matching rows.
当hashes of build table 不足以全部放进内存时,MySQL会自动切换到on-disk的扩展实现(基于 GRACE hash join algorithm)。在build phase阶段,join buffer满,就会发生 in-mem hash 向on-disk hash 转换。
on-disk algorithm 包含3个步骤:
- Calculate the hashes of all rows in both the build and probe tables and store them on disk in several small files partitioned by the hash. The number of partitions is chosen to make each partition of the probe table fit into the join buffer but with a limit of at most 128 partitions.
- Load the first partition of the build table into memory and iterate over the hashes from the probe table in the same way as for the probe phase for the in-memory algorithm. Since the partitioning in step 1 uses the same hash function for both the build and probe tables, it is only necessary to iterate over the first partition of the probe table.
- Clear the in-memory buffer and continue with the rest of the partitions one by one
无论是内存hash还是磁盘hash,都使用xxHash64 hash function。xxHash64有足够快,hash质量好(reducing the number of hash collisions)的特点
BNL不会被选中的时候,MySQL就会选用hash join。
在整理这篇资料时,对要使用的哈希连接算法存在以下要求:
- The join must be an inner join.
- The join cannot be performed using an index, either because there is no available index or because the indexes have been disabled for the query.
- All joins in the query must have at least one equi-join condition between the two tables in the join, and only columns from the two tables as well as constants are referenced in the condition. (查询中的所有联接必须在联接中的两个表之间至少有一个等联接条件,并且在该条件中仅引用两个表中的列以及常量)
- As of 8.0.20, anti, semi, and outer joins are also supported. If you join the two tables t1 and t2, then examples of join conditions that are supported for hash join include
- t1.t1_val = t2.t2_val
- t1.t1_val = t2.t2_val + 2
- t1.t1_val1 = t2.t2_val AND t1.t1_val2 > 100
- MONTH(t1.t1_val) = MONTH(t2.t2_val)
用一个例子来说明一下hash join:
SELECT CountryCode,
country.Name AS Country,
city.Name AS City,
city.District
FROM world.country IGNORE INDEX (Primary)
INNER JOIN world.city IGNORE INDEX (CountryCode)
ON city.CountryCode = country.Code
WHERE Continent = \'Asia\';
#用一段伪代码翻译一下
result = []
join_buffer = []
partitions = 0
on_disk = False
for country_row in country:
if country_row.Continent == \'Asia\':
hash = xxHash64(country_row.Code)
if not on_disk:
join_buffer.append(hash)
if is_full(join_buffer):
# Create partitions on disk
on_disk = True
partitions = write_buffer_to_disk(join_buffer)
join_buffer = []
else
write_hash_to_disk(hash)
if not on_disk:
for city_row in city:
hash = xxHash64(city_row.CountryCode)
if hash in join_buffer:
country_row = get_row(hash)
city_row = get_row(hash)
result.append(join_rows(country_row, city_row))
else:
for city_row in city:
hash = xxHash64(city_row.CountryCode)
write_hash_to_disk(hash)
for partition in range(partitions):
join_buffer = load_build_from_disk(partition)
for hash in load_hash_from_disk(partition):
if hash in join_buffer:
country_row = get_row(hash)
city_row = get_row(hash)
result.append(join_rows(country_row, city_row))
join_buffer = []
与所使用的实际算法相比,所描述的算法稍微简化了一些。
真正的算法必须考虑哈希冲突,
而对于磁盘上的算法,某些分区可能会变得太大而无法放入连接缓冲区,
在这种情况下,它们会被分块处理,以避免使用比配置的内存更多的内存
图示化一下 in-mem hash 算法:
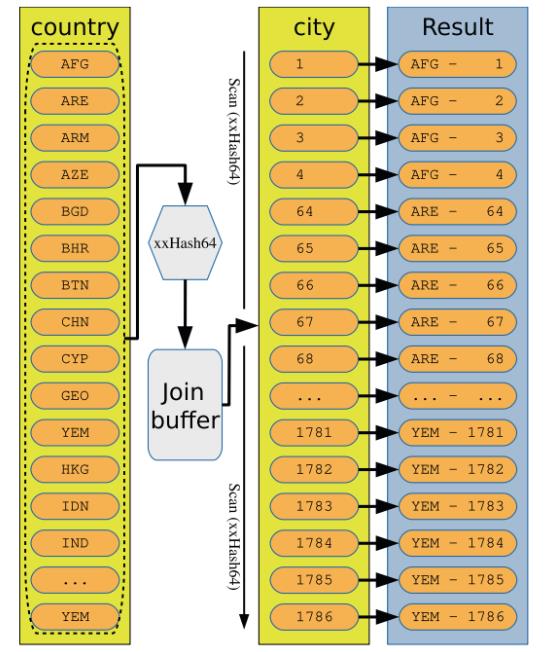
量化一下hash join 的成本
SELECT CountryCode,
country.Name AS Country,
city.Name AS City,
city.District
FROM world.country IGNORE INDEX (Primary)
INNER JOIN world.city IGNORE INDEX (CountryCode)
ON city.CountryCode = country.Code
WHERE Continent = \'Asia\';
SELECT rows_examined, rows_sent,
last_statement_latency AS latency
FROM sys.session
WHERE thd_id = PS_CURRENT_THREAD_ID()\\G
**************************** 1. row ****************************
rows_examined: 4318
rows_sent: 1766
latency: 3.53 ms
从本文的例子中,rows_examined 的角度来看 index_join 下的NL(2005) 优于 无索引join条件下的BNL (4318)= 无索引join条件下的 hash join。但是当数据量发生变化,可能结果就不一样了,现实中也没有绝对的性能好坏规则(如果有,基于规则的成本计算就能很好处理的查询问题,实际上更值得信赖的是成本估算),hash join与NL,BNL 的优越比较,列出几点,当作纸上谈兵 :
-
For a join without using an index, the hash join will usually be much faster than a block nested join unless a LIMIT clause has been added. Improvements of more than a factor of 1000 have been observed.
参考:
(https://mysqlserverteam.com/hash-join-in-mysql-8/)
(https://dev.mysql.com/blog-archive/hash-join-in-mysql-8/)
(http://www.slideshare.net/NorvaldRyeng/mysql-8018-latest-updates-hash-join-and-explain-analyze) -
For a join without an index where there is a LIMIT clause, a block nested loop can exit when enough rows have been found, whereas a hash join will complete the entire join (but can skip fetching the rows). If the number of rows included due to the LIMIT clause is small compared to the total number of rows found by the join, a block nested loop may be faster.
-
For joins supporting an index, the hash join algorithm can be faster if the index has a low selectivity.
Hash Join 最大的好处在于提升多表无索引关联时的查询性能。具体NL,BNL,HASH JOIN谁更适合用于查询计划,实践才是最好的证明。
同样可以使用HASH_JOIN() 和 NO_HASH_JOIN() 的hint 来影响查询计划。
MySQL8.0 关于支持的三种high-level 连接策略的讨论暂时到此结束。下来可以自己去查一下 anti, semi, and outer joins。
更多细节 参考
(https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/select-optimization.html)(https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/semijoins.html)
还有一些 关于join的lower-level优化值得考虑,下篇文章分解。
Enjoy GreatSQL
mysql中如何查看优化器优化后的执行计划
在开始演示之前,我们先介绍下两个概念。
概念一,数据的可选择性基数,也就是常说的cardinality值。
查询优化器在生成各种执行计划之前,得先从统计信息中取得相关数据,这样才能估算每步操作所涉及到的记录数,而这个相关数据就是cardinality。简单来说,就是每个值在每个字段中的唯一值分布状态。
比如表t1有100行记录,其中一列为f1。f1中唯一值的个数可以是100个,也可以是1个,当然也可以是1到100之间的任何一个数字。这里唯一值越的多少,就是这个列的可选择基数。
那看到这里我们就明白了,为什么要在基数高的字段上建立索引,而基数低的的字段建立索引反而没有全表扫描来的快。当然这个只是一方面,至于更深入的探讨就不在我这篇探讨的范围了。
概念二,关于HINT的使用。
这里我来说下HINT是什么,在什么时候用。
HINT简单来说就是在某些特定的场景下人工协助MySQL优化器的工作,使她生成最优的执行计划。一般来说,优化器的执行计划都是最优化的,不过在某些特定场景下,执行计划可能不是最优化。
比如:表t1经过大量的频繁更新操作,(UPDATE,DELETE,INSERT),cardinality已经很不准确了,这时候刚好执行了一条SQL,那么有可能这条SQL的执行计划就不是最优的。为什么说有可能呢?
来看下具体演示
譬如,以下两条SQL,
A:
select * from t1 where f1 = 20;B:
select * from t1 where f1 = 30;如果f1的值刚好频繁更新的值为30,并且没有达到MySQL自动更新cardinality值的临界值或者说用户设置了手动更新又或者用户减少了sample page等等,那么对这两条语句来说,可能不准确的就是B了。
这里顺带说下,MySQL提供了自动更新和手动更新表cardinality值的方法,因篇幅有限,需要的可以查阅手册。
那回到正题上,MySQL 8.0 带来了几个HINT,我今天就举个index_merge的例子。
示例表结构:
mysql> desc t1;+------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |+------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment || rank1 | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | || rank2 | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | || log_time | datetime | YES | MUL | NULL | || prefix_uid | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | || desc1 | text | YES | | NULL | || rank3 | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | |+------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+7 rows in set (0.00 sec)表记录数:
这里我们两条经典的SQL:
SQL C:
select * from t1 where rank1 = 1 or rank2 = 2 or rank3 = 2;SQL D:
select * from t1 where rank1 =100 and rank2 =100 and rank3 =100;表t1实际上在rank1,rank2,rank3三列上分别有一个二级索引。
那我们来看SQL C的查询计划。
显然,没有用到任何索引,扫描的行数为32034,cost为3243.65。
mysql> explain format=json select * from t1 where rank1 =1 or rank2 = 2 or rank3 = 2\\G*************************** 1. row ***************************EXPLAIN: "query_block": "select_id": 1, "cost_info": "query_cost": "3243.65" , "table": "table_name": "t1", "access_type": "ALL", "possible_keys": [ "idx_rank1", "idx_rank2", "idx_rank3" ], "rows_examined_per_scan": 32034, "rows_produced_per_join": 115, "filtered": "0.36", "cost_info": "read_cost": "3232.07", "eval_cost": "11.58", "prefix_cost": "3243.65", "data_read_per_join": "49K" , "used_columns": [ "id", "rank1", "rank2", "log_time", "prefix_uid", "desc1", "rank3" ], "attached_condition": "((`ytt`.`t1`.`rank1` = 1) or (`ytt`.`t1`.`rank2` = 2) or (`ytt`.`t1`.`rank3` = 2))" 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)我们加上hint给相同的查询,再次看看查询计划。
这个时候用到了index_merge,union了三个列。扫描的行数为1103,cost为441.09,明显比之前的快了好几倍。
mysql> explain format=json select /*+ index_merge(t1) */ * from t1 where rank1 =1 or rank2 = 2 or rank3 = 2\\G*************************** 1. row ***************************EXPLAIN: "query_block": "select_id": 1, "cost_info": "query_cost": "441.09" , "table": "table_name": "t1", "access_type": "index_merge", "possible_keys": [ "idx_rank1", "idx_rank2", "idx_rank3" ], "key": "union(idx_rank1,idx_rank2,idx_rank3)", "key_length": "5,5,5", "rows_examined_per_scan": 1103, "rows_produced_per_join": 1103, "filtered": "100.00", "cost_info": "read_cost": "330.79", "eval_cost": "110.30", "prefix_cost": "441.09", "data_read_per_join": "473K" , "used_columns": [ "id", "rank1", "rank2", "log_time", "prefix_uid", "desc1", "rank3" ], "attached_condition": "((`ytt`.`t1`.`rank1` = 1) or (`ytt`.`t1`.`rank2` = 2) or (`ytt`.`t1`.`rank3` = 2))" 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)我们再看下SQL D的计划:
不加HINT,
mysql> explain format=json select * from t1 where rank1 =100 and rank2 =100 and rank3 =100\\G*************************** 1. row ***************************EXPLAIN: "query_block": "select_id": 1, "cost_info": "query_cost": "534.34" , "table": "table_name": "t1", "access_type": "ref", "possible_keys": [ "idx_rank1", "idx_rank2", "idx_rank3" ], "key": "idx_rank1", "used_key_parts": [ "rank1" ], "key_length": "5", "ref": [ "const" ], "rows_examined_per_scan": 555, "rows_produced_per_join": 0, "filtered": "0.07", "cost_info": "read_cost": "478.84", "eval_cost": "0.04", "prefix_cost": "534.34", "data_read_per_join": "176" , "used_columns": [ "id", "rank1", "rank2", "log_time", "prefix_uid", "desc1", "rank3" ], "attached_condition": "((`ytt`.`t1`.`rank3` = 100) and (`ytt`.`t1`.`rank2` = 100))" 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)加了HINT,
mysql> explain format=json select /*+ index_merge(t1)*/ * from t1 where rank1 =100 and rank2 =100 and rank3 =100\\G*************************** 1. row ***************************EXPLAIN: "query_block": "select_id": 1, "cost_info": "query_cost": "5.23" , "table": "table_name": "t1", "access_type": "index_merge", "possible_keys": [ "idx_rank1", "idx_rank2", "idx_rank3" ], "key": "intersect(idx_rank1,idx_rank2,idx_rank3)", "key_length": "5,5,5", "rows_examined_per_scan": 1, "rows_produced_per_join": 1, "filtered": "100.00", "cost_info": "read_cost": "5.13", "eval_cost": "0.10", "prefix_cost": "5.23", "data_read_per_join": "440" , "used_columns": [ "id", "rank1", "rank2", "log_time", "prefix_uid", "desc1", "rank3" ], "attached_condition": "((`ytt`.`t1`.`rank3` = 100) and (`ytt`.`t1`.`rank2` = 100) and (`ytt`.`t1`.`rank1` = 100))" 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)对比下以上两个,加了HINT的比不加HINT的cost小了100倍。
总结下,就是说表的cardinality值影响这张的查询计划,如果这个值没有正常更新的话,就需要手工加HINT了。相信MySQL未来的版本会带来更多的HINT。
1,slow_query_log
这个参数设置为ON,可以捕获执行时间超过一定数值的SQL语句。
2,long_query_time
当SQL语句执行时间超过此数值时,就会被记录到日志中,建议设置为1或者更短。
3,slow_query_log_file
记录日志的文件名。
4,log_queries_not_using_indexes
这个参数设置为ON,可以捕获到所有未使用索引的SQL语句,尽管这个SQL语句有可能执行得挺快。
二、检测mysql中sql语句的效率的方法
1、通过查询日志
(1)、Windows下开启MySQL慢查询
MySQL在Windows系统中的配置文件一般是是my.ini找到[mysqld]下面加上
代码如下
log-slow-queries = F:/MySQL/log/mysqlslowquery。log
long_query_time = 2
(2)、Linux下启用MySQL慢查询
MySQL在Windows系统中的配置文件一般是是my.cnf找到[mysqld]下面加上
代码如下
log-slow-queries=/data/mysqldata/slowquery。log
long_query_time=2
说明
log-slow-queries = F:/MySQL/log/mysqlslowquery。
为慢查询日志存放的位置,一般这个目录要有MySQL的运行帐号的可写权限,一般都将这个目录设置为MySQL的数据存放目录;
long_query_time=2中的2表示查询超过两秒才记录;
2.show processlist 命令
SHOW PROCESSLIST显示哪些线程正在运行。您也可以使用mysqladmin processlist语句得到此信息。
各列的含义和用途:
ID列
一个标识,你要kill一个语句的时候很有用,用命令杀掉此查询 /*/mysqladmin kill 进程号。
user列
显示单前用户,如果不是root,这个命令就只显示你权限范围内的sql语句。
host列
显示这个语句是从哪个ip的哪个端口上发出的。用于追踪出问题语句的用户。
db列
显示这个进程目前连接的是哪个数据库。
command列
显示当前连接的执行的命令,一般就是休眠(sleep),查询(query),连接(connect)。
time列
此这个状态持续的时间,单位是秒。
state列
显示使用当前连接的sql语句的状态,很重要的列,后续会有所有的状态的描述,请注意,state只是语句执行中的某一个状态,一个 sql语句,以查询为例,可能需要经过copying to tmp table,Sorting result,Sending data等状态才可以完成
info列
显示这个sql语句,因为长度有限,所以长的sql语句就显示不全,但是一个判断问题语句的重要依据。
这个命令中最关键的就是state列,mysql列出的状态主要有以下几种:
Checking table
正在检查数据表(这是自动的)。
Closing tables
正在将表中修改的数据刷新到磁盘中,同时正在关闭已经用完的表。这是一个很快的操作,如果不是这样的话,就应该确认磁盘空间是否已经满了或者磁盘是否正处于重负中。
Connect Out
复制从服务器正在连接主服务器。
Copying to tmp table on disk
由于临时结果集大于tmp_table_size,正在将临时表从内存存储转为磁盘存储以此节省内存。
Creating tmp table
正在创建临时表以存放部分查询结果。
deleting from main table
服务器正在执行多表删除中的第一部分,刚删除第一个表。
deleting from reference tables
服务器正在执行多表删除中的第二部分,正在删除其他表的记录。
Flushing tables
正在执行FLUSH TABLES,等待其他线程关闭数据表。
Killed
发送了一个kill请求给某线程,那么这个线程将会检查kill标志位,同时会放弃下一个kill请求。MySQL会在每次的主循环中检查kill标志位,不过有些情况下该线程可能会过一小段才能死掉。如果该线程程被其他线程锁住了,那么kill请求会在锁释放时马上生效。
Locked
被其他查询锁住了。
Sending data
正在处理SELECT查询的记录,同时正在把结果发送给客户端。
Sorting for group
正在为GROUP BY做排序。
Sorting for order
正在为ORDER BY做排序。
Opening tables
这个过程应该会很快,除非受到其他因素的干扰。例如,在执ALTER TABLE或LOCK TABLE语句行完以前,数据表无法被其他线程打开。正尝试打开一个表。
Removing duplicates
正在执行一个SELECT DISTINCT方式的查询,但是MySQL无法在前一个阶段优化掉那些重复的记录。因此,MySQL需要再次去掉重复的记录,然后再把结果发送给客户端。
Reopen table
获得了对一个表的锁,但是必须在表结构修改之后才能获得这个锁。已经释放锁,关闭数据表,正尝试重新打开数据表。
Repair by sorting
修复指令正在排序以创建索引。
Repair with keycache
修复指令正在利用索引缓存一个一个地创建新索引。它会比Repair by sorting慢些。
Searching rows for update
正在讲符合条件的记录找出来以备更新。它必须在UPDATE要修改相关的记录之前就完成了。
Sleeping
正在等待客户端发送新请求.
System lock
正在等待取得一个外部的系统锁。如果当前没有运行多个mysqld服务器同时请求同一个表,那么可以通过增加--skip-external-locking参数来禁止外部系统锁。
Upgrading lock
INSERT DELAYED正在尝试取得一个锁表以插入新记录。
Updating
正在搜索匹配的记录,并且修改它们。
User Lock
正在等待GET_LOCK()。
Waiting for tables
该线程得到通知,数据表结构已经被修改了,需要重新打开数据表以取得新的结构。然后,为了能的重新打开数据表,必须等到所有其他线程关闭这个表。以下几种情况下会产生这个通知:FLUSH TABLES tbl_name, ALTER TABLE, RENAME TABLE, REPAIR TABLE, ANALYZE TABLE,或OPTIMIZE TABLE。
waiting for handler insert
INSERT DELAYED已经处理完了所有待处理的插入操作,正在等待新的请求。
大部分状态对应很快的操作,只要有一个线程保持同一个状态好几秒钟,那么可能是有问题发生了,需要检查一下。
还有其他的状态没在上面中列出来,不过它们大部分只是在查看服务器是否有存在错误是才用得着。
例如如图:
3、explain来了解SQL执行的状态
explain显示了mysql如何使用索引来处理select语句以及连接表。可以帮助选择更好的索引和写出更优化的查询语句。
使用方法,在select语句前加上explain就可以了:
例如:
explain select surname,first_name form a,b where a.id=b.id
结果如图
EXPLAIN列的解释
table
显示这一行的数据是关于哪张表的
type
这是重要的列,显示连接使用了何种类型。从最好到最差的连接类型为const、eq_reg、ref、range、indexhe和ALL
possible_keys
显示可能应用在这张表中的索引。如果为空,没有可能的索引。可以为相关的域从WHERE语句中选择一个合适的语句
key
实际使用的索引。如果为NULL,则没有使用索引。很少的情况下,MYSQL会选择优化不足的索引。这种情况下,可以在SELECT语句 中使用USE INDEX(indexname)来强制使用一个索引或者用IGNORE INDEX(indexname)来强制MYSQL忽略索引
key_len
使用的索引的长度。在不损失精确性的情况下,长度越短越好
ref
显示索引的哪一列被使用了,如果可能的话,是一个常数
rows
MYSQL认为必须检查的用来返回请求数据的行数
Extra
关于MYSQL如何解析查询的额外信息。将在表4.3中讨论,但这里可以看到的坏的例子是Using temporary和Using filesort,意思MYSQL根本不能使用索引,结果是检索会很慢
extra列返回的描述的意义
Distinct
一旦MYSQL找到了与行相联合匹配的行,就不再搜索了
Not exists
MYSQL优化了LEFT JOIN,一旦它找到了匹配LEFT JOIN标准的行,就不再搜索了
Range checked for each Record(index map:#)
没有找到理想的索引,因此对于从前面表中来的每一个行组合,MYSQL检查使用哪个索引,并用它来从表中返回行。这是使用索引的最慢的连接之一
Using filesort
看到这个的时候,查询就需要优化了。MYSQL需要进行额外的步骤来发现如何对返回的行排序。它根据连接类型以及存储排序键值和匹配条件的全部行的行指针来排序全部行
Using index
列数据是从仅仅使用了索引中的信息而没有读取实际的行动的表返回的,这发生在对表的全部的请求列都是同一个索引的部分的时候
Using temporary
看到这个的时候,查询需要优化了。这里,MYSQL需要创建一个临时表来存储结果,这通常发生在对不同的列集进行ORDER BY上,而不是GROUP BY上
Where used
使用了WHERE从句来限制哪些行将与下一张表匹配或者是返回给用户。如果不想返回表中的全部行,并且连接类型ALL或index,这就会发生,或者是查询有问题不同连接类型的解释(按照效率高低的顺序排序)
const
表中的一个记录的最大值能够匹配这个查询(索引可以是主键或惟一索引)。因为只有一行,这个值实际就是常数,因为MYSQL先读这个值然后把它当做常数来对待
eq_ref
在连接中,MYSQL在查询时,从前面的表中,对每一个记录的联合都从表中读取一个记录,它在查询使用了索引为主键或惟一键的全部时使用
ref
这个连接类型只有在查询使用了不是惟一或主键的键或者是这些类型的部分(比如,利用最左边前缀)时发生。对于之前的表的每一个行联合,全部记录都将从表中读出。这个类型严重依赖于根据索引匹配的记录多少—越少越好
range
这个连接类型使用索引返回一个范围中的行,比如使用>或<查找东西时发生的情况
index
这个连接类型对前面的表中的每一个记录联合进行完全扫描(比ALL更好,因为索引一般小于表数据)
ALL
这个连接类型对于前面的每一个记录联合进行完全扫描,这一般比较糟糕,应该尽量避免
以上是关于MySQL8.0 优化器介绍的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章