编程实现以邻接表或邻接矩阵为存储结构,图的广度和深度优先搜索
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了编程实现以邻接表或邻接矩阵为存储结构,图的广度和深度优先搜索相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
编程实现以邻接表或邻接矩阵为存储结构,图的广度和深度优先搜索。内容包括:
(1)给出图的存储结构,写出该存储结构的特点,并说明采用该存储结构的理由;
(2)给出基于选定的图的存储结构的算法;
(3)列出基于上述存储结构的广度和深度优先搜索的每个步骤;
(4)设计广度和深度优先搜索算法,画出流程图;
(5)写出主程序并显示运行结果
(6)写出至少一个基于图的广度和深度优先搜索算法的应用例子(可只给出应用思路)。
图的遍历演示
以邻接多重表为存储结构,实现连通无向图的深度优先和广度优先遍历.
以用户指定的结点为起点,分别输出每种遍历下的结点访问序列和相应生成树的边集.
*******************************************/
#include<iostream>
# include <string.h>
# include <malloc.h>
# include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int visited[30];
# define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 30
# define OK 1
//typedef int VertexType;
typedef int InfoType;
typedef struct ArcNode //弧
int adjvex;
struct ArcNode *nextarc;
ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode//表头
int data;
ArcNode *firstarc;
VNode,AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
typedef struct//图
AdjList vertices;
int vexnum,arcnum;
int kind;
ALGraph;
void CreateDG(ALGraph &G)
int k,i,v1;
cout<<endl<<"请输入结点个数: ";
cin>>G.vexnum;
cout<<"请输入弧的个数: ";
cin>>G.arcnum;
for(i=1;i<=G.vexnum;i++)//初使化表头
G.vertices[i].data=i;
G.vertices[i].firstarc=NULL;
for(k=1;k<=G.vexnum;k++) //输入边
int v2;
cout<<"请输入与结点"<<k<<"相邻的边数:";
cin>>v2;
cout<<"请输入与第"<<k<<"个结点相连的结点编号: ";
cin>>v1;
ArcNode *p;
p=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
if(!p) exit(-1);
p->adjvex=v1;
p->nextarc=NULL;
G.vertices[k].firstarc=p;
for(int i=1;i<v2;i++)
int m;
cout<<"请输入与第"<<k<<"个结点相连的结点编号: ";
cin>>m;
ArcNode *q;
q=(ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));//动态指针
if(!q) exit(-1);
q->adjvex=m; //顶点给P
q->nextarc=NULL;
p->nextarc=q;
p=q;
//free(q);
//free(p);
void DFS (ALGraph G,int v )//深度搜索
visited[v]=1;
cout<<G.vertices[v].data<<" ";
ArcNode *x;
x=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
if(!x) exit(-1);
x=G.vertices[v].firstarc;
int w;
for (;x;x=x->nextarc)
w=x->adjvex;
if(visited[w]==0)
DFS(G,w);
void DFSB (ALGraph G,int v)//深度搜索的边集
visited[v]=1;
ArcNode *y;
y=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
if(!y) exit(-1);
y=G.vertices[v].firstarc;
int u=G.vertices[v].data;
int w;
for(;y;y=y->nextarc)
w=y->adjvex;
if(visited[w]==0)
cout<<u<<"--->"<<w<<endl;
DFSB(G,w);
typedef struct QNode
int data;
QNode *next;
QNode,*QueuePtr;
typedef struct
QueuePtr front;
QueuePtr rear;
LinkQueue;
void InitQueue (LinkQueue &Q)//建立一个空队列
Q.front=Q.rear=(QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(!Q.front) exit(-1);
Q.front->next=NULL;
void EnQueue (LinkQueue &Q,int e)//进队
QNode *p;
p=(QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(!p) exit(-1);
p->data=e;
p->next=NULL;
Q.rear->next=p;
Q.rear=p;
//free(p);
int DeQueue (LinkQueue &Q,int &e)//出队
if(Q.front==Q.rear)
return -1;
QNode *p;
p=(QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(!p) exit(-1);
p=Q.front->next;
e=p->data;
Q.front->next=p->next;
if(Q.rear==p)
Q.rear=Q.front;
free(p);
return e;
int QueueEmpty (LinkQueue Q)//判断队列是否为空
if(Q.front==Q.rear)
return 1;
return 0;
void BFS(ALGraph G,int v)//广度搜索
int u;
LinkQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
if(visited[v]==0)
visited[v]=1;
cout<<G.vertices[v].data<<" ";
EnQueue(Q,v);
while(QueueEmpty(Q)!=1)
DeQueue(Q,u);
ArcNode *z;
z=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
if(!z) exit(-1);
z=G.vertices[u].firstarc;
/*
for(int w=z->adjvex;w>=0;w=z->nextarc->adjvex)
if(visited[w]==0)
visited[w]=1;
cout<<w<<" ";
EnQueue(Q,w);
*/
int w;
for(;z;z=z->nextarc)
w=z->adjvex;
if(visited[w]==0)
visited[w]=1;
cout<<w<<" ";
EnQueue(Q,w);
void BFSB (ALGraph G,int v)//广度搜索的边集
int u;
LinkQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
if(visited[v]==0)
visited[v]=1;
EnQueue(Q,v);
while(QueueEmpty(Q)!=1)
DeQueue(Q,u);
ArcNode *r;
r=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
if(!r) exit(-1);
r=G.vertices[u].firstarc;
int w;
for(;r!=NULL;r=r->nextarc)
w=r->adjvex;
if(visited[w]==0)
visited[w]=1;
cout<<u<<"--->"<<w<<endl;
EnQueue(Q,w);
int main()
int i;
ALGraph G;
CreateDG(G);
int x;
cout<<"请输入结点数:";
cin>>x;
cout<<"邻接表为:"<<endl;
for(int j=1;j<=x;j++)
cout<<G.vertices[j].data<<" ";
ArcNode *p;
p=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
if(!p) exit(-1);
p=G.vertices[j].firstarc;
while(p)
cout<<p->adjvex<<" ";
p=p->nextarc;
cout<<endl;
cout<<"请输入第一个要访问的结点序号:"<<endl;
int n;
cin>>n;
for( i=0;i<30;i++)
visited[i]=0;
cout<<"广度搜索:"<<endl;
BFS(G,n);
for( i=0;i<30;i++)
visited[i]=0;
cout<<endl;
cout<<"边集:"<<endl;
BFSB(G,n);
for( i=0;i<30;i++)
visited[i]=0;
cout<<"深度搜索:"<<endl;
DFS(G,n);
for( i=0;i<30;i++)
visited[i]=0;
cout<<endl;
cout<<"边集:"<<endl;
DFSB(G,n);
//system("pause");
return 0;
前几天上机刚好做了这个,个人感觉很完美,尽管老师说用的是邻接表而不是多重表,太简单,但还不错,界面输入过程比较繁琐,要严格按照提示来输入,是无向图,等级太低,没办法把执行结果粘出来,应该能看懂吧本回答被提问者采纳
图的存储与实现,使用邻接矩阵
一、实现思想
图的邻接矩阵表示法,也叫数组表示法。用一个一维数组存储图中的顶点,用一个二维数组存储图中的边,即各个顶点直接的边的关系,这个二维数组就叫「邻接矩阵」。
不用代码的话,我们都比较熟悉,图的深度遍历和广度遍历。但是用代码怎么实现,这就要考虑存储一个图了,这个正是本博客的重点。
设图G=(V,E),有n个顶点,则邻接矩阵是一个 n X n的二维数组。V代表一个点集,E代表一个边集。
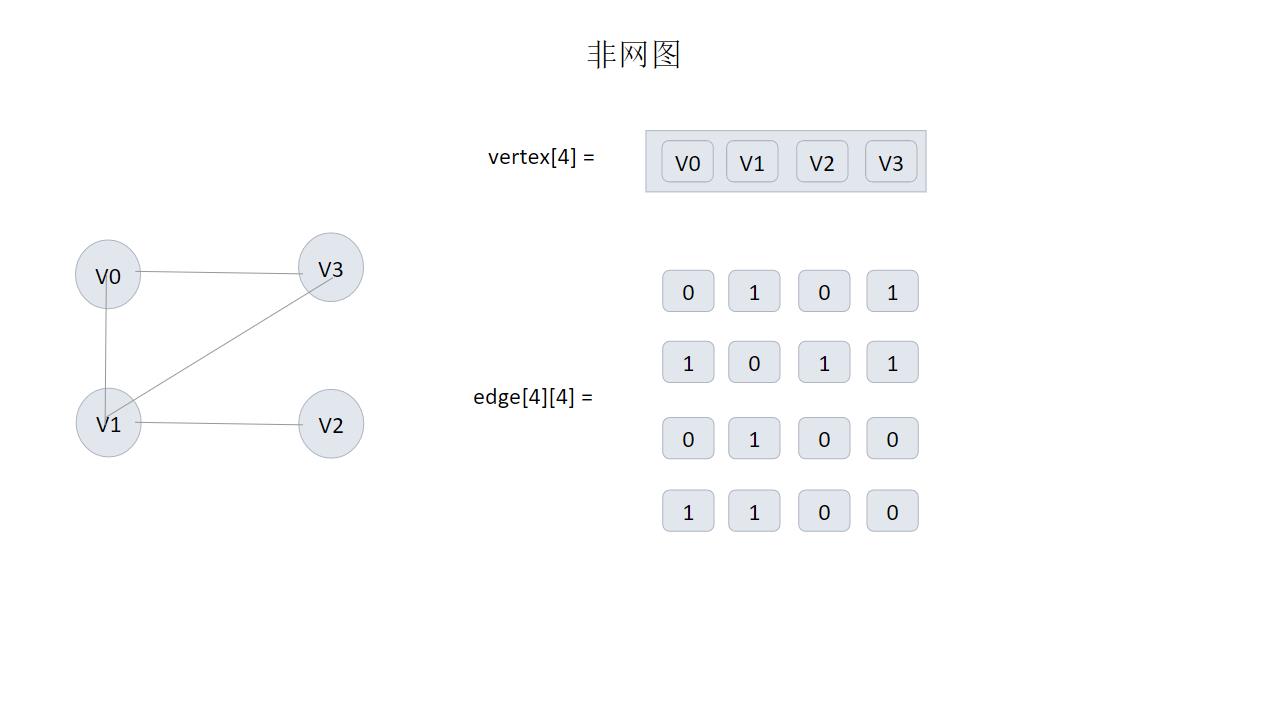
- 对于非网图(没有权值的有向、无向图)
= = 1 若(vi,vj) 属于 E
edge[i][j]
= = 0 否则
这条公式很精辟,因为概括地很好,既包括了有向图,也包括了无向图。其实本质上,我们在置1的时候,考虑的是连通性,如果某个点可以到另一个点,那么二维数组的某个位置就可以置1了。
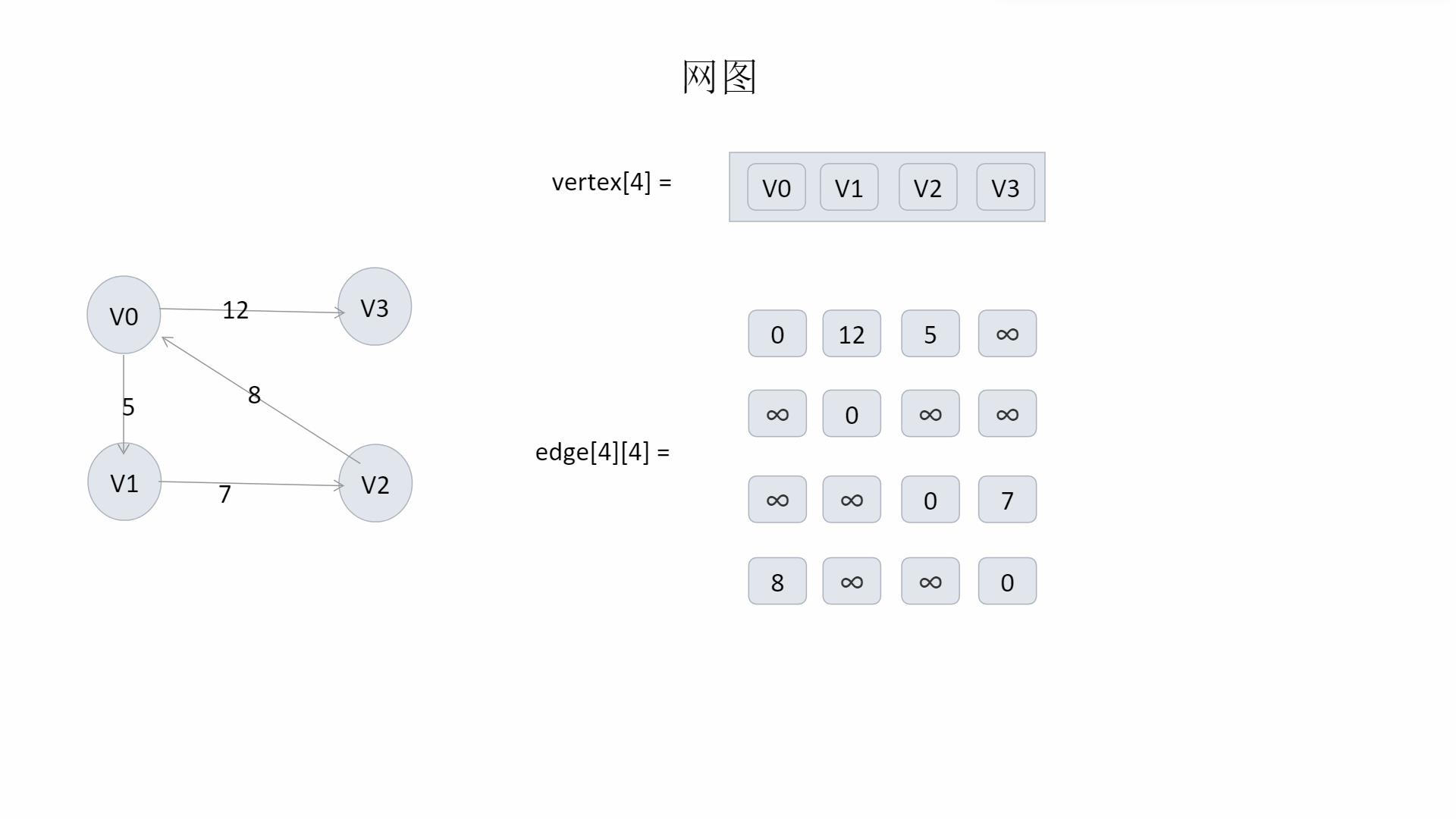
- 对于网图(有权值的有向、无向图)
= w(ij) 若(vi,vj)属于 E。w(ij)代表某条边的权值
edge[i][j] = 0 若 i = j
= ∞ 否则
以上是关于编程实现以邻接表或邻接矩阵为存储结构,图的广度和深度优先搜索的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章