如何利用百度地图获取一种类型POI的统计数据
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何利用百度地图获取一种类型POI的统计数据相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 12345678/***根据中心点、半径和检索词发起周边检索*异步函数,返回结果在BMKPoiSearchDelegate的onGetPoiResult通知*@paramoption周边搜索的搜索参数类(BMKNearbySearchOption)*@paramindex页码,如果是第一次发起搜索,填0,根据返回的结果可以去获取第n页的结果,页码从0开始*@return成功返回YES,否则返回NO*/-(BOOL)poiSearchNearBy:(BMKNearbySearchOption*)option;12345678910111213141516171819_searcher=[[BMKPoiSearchalloc]init];_searcher.delegate=self;BMKNearbySearchOption*option=[[BMKNearbySearchOptionalloc]init];option.pageIndex=0;//起始页option.pageCapacity=30;//每页条数option.location=_locationCoordinate;//中心点option.keyword=self.keywordTF.text;//关键词option.sortType=BMK_POI_SORT_BY_DISTANCE;//根据距离排序option.radius=3000;//半径BOOLflag=[_searcherpoiSearchNearBy:option];if(flag)NSLog(@"周边检索发送成功");elseNSLog(@"周边检索发送失败");12345678910111213141516171819202122//实现PoiSearchDeleage处理回调结果-(void)onGetPoiResult:(BMKPoiSearch*)searcherresult:(BMKPoiResult*)poiResulterrorCode:(BMKSearchErrorCode)errorCodeif(errorCode==BMK_SEARCH_NO_ERROR)//在此处理正常结果_result=poiResult;[_mapViewremoveAnnotations:[_mapViewannotations]];for(inti=0;i<poiResult.poiInfoList.count;i++)BMKPoiInfo*info=[poiResult.poiInfoListobjectAtIndex:i];BMKPointAnnotation*annotation=[[BMKPointAnnotationalloc]init];annotation.title=info.name;annotation.subtitle=info.address;annotation.coordinate=info.pt;[_mapViewaddAnnotation:annotation];self.resultNumLabel.text=FORMATSTRING(@"共找到“%@”相关%d个结果",self.keywordTF.text,poiResult.currPoiNum);elseself.resultNumLabel.text=FORMATSTRING(@"抱歉,未找到“%@”相关的结果",self.keywordTF.text);百度地图POI数据爬取,突破百度地图API爬取数目“400条“的限制11。
1.POI爬取方法说明
1.1AK申请
登录百度账号,在百度地图开发者平台的API控制台申请一个服务端的ak,主要用到的是Place API.检校方式可设置成IP白名单,IP直接设置成了0.0.0.0/0比较方便。
Place API 提供的接口用于返回查询某个区域的某类POI数据,且提供单个POI的详情查询服务,用户可以使用C#、C++、Java,Python等开发语言发送请求,接收json、xml的数据。关于Place API的具体使用可以参考:Place API Web服务API
1.2爬取方式
百度地图将POI数据划分为多个类别,我想要爬取某个城市的所有类别的POI名称和经纬度信息。爬取时,先将类别存储在一个“POI总表.csv”文件中,再逐类别爬取POI数据。POI总表包含POI类别、POI类别对应的编码、各类POI记录条数。
Place API提供了3种爬取区域POI信息的方式:(1)城市内检索 (2)矩形检索 (3)圆形区域检索。这里,POI信息的爬取主要使用城市内检索和矩形检索两种方式。

1.2.1城市内检索
城市内检索主要的请求参数是query查询的类别、region查询的城市名称。将查询得到json格式的数据,解码为utf-8编码方式后存储在content中。通过正则表达式可以得到POI的名称和经纬度信息。
reg = r\'"name":"([\\d\\D]*?)",[\\d\\D]*?"lat":([\\d\\D]*?),[\\d\\D]*?"lng":([\\d\\D]*?)},\'
pattern = re.compile(reg)
items = re.findall(pattern,content)

1.2.2矩形检索
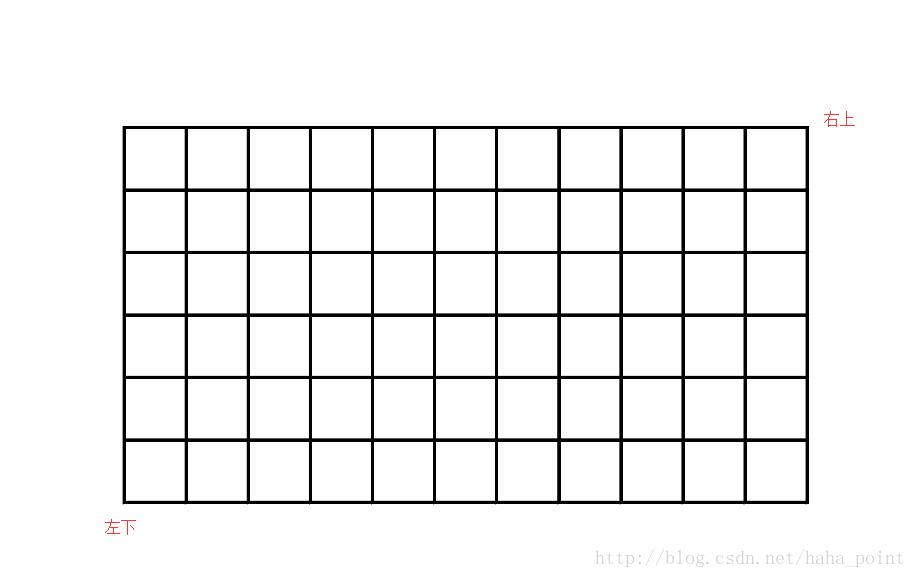
矩形检索的主要请求参数是query查询的类别、bounds查询区域的左下、右上经纬度。lat,lng(左下角坐标),lat,lng(右上角坐标)。查询得到的结果与城市范围内检索结果相似。
通过两种方式实现POI的区域检索都很便捷,但是当城市较大,某一类POI信息数量大时,由于百度API的限制,1.2.1城市内检索最多只能返回400条POI数据,会造成查不全的现象。这时,可以利用矩形检索,将区域的外包矩形划分为多个小网格,并确保每个网格中该类别POI数据的条数不会超过400条,这样逐个小网格进行矩形检索,最终得到城市区域某一类别POI的所有数据。
2.Python代码实现
2.1 城市内检索
城市区域内检索通过正则表达式re获取需要的信息,当该城市某一类POI数量大于400时,可使用划分为网格的矩形检索进行POI爬取,以保证爬取到完整的POI数据。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
import codecs
import urllib
import urllib2
import re
import pandas as pd
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding(\'utf-8\')
user_agent = \'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.2)\'
headers = {\'User-Agent\':user_agent}
inpath = \'POI总表.csv\'
path = unicode(inpath, \'utf-8\')
poi_list = pd.read_csv(path)
api_key="" #输入AK
for poi in range(len(poi_list)):
outpath = \'+str(poi)+\'_\'+poi_list.iloc[poi, 1] + \'.csv\'
path = unicode(outpath, \'utf-8\')
with open(path, \'w\') as f:
f.write(codecs.BOM_UTF8)
f.write(\'id,name,lat,lng\\n\')
i=1
j=1
try:
for i in range(int(poi_list.iloc[poi,4])/10+2):
url = "http://api.map.baidu.com/place/v2/search?q="+poi_list.iloc[poi,3]+"&page_size=10&page_num="
url = url+str(i-1) + "&scope=1®ion=%E6%AD%A6%E7%A9%B4&city_limit=true&coord_type=1&output=json&ak="
+api_key # ak需输入申请的ak
request = urllib2.Request(url, headers=headers)
response = urllib2.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode("utf-8")
# print content
reg = r\'"name":"([\\d\\D]*?)",[\\d\\D]*?"lat":([\\d\\D]*?),[\\d\\D]*?"lng":([\\d\\D]*?)},\'
pattern = re.compile(reg)
items = re.findall(pattern,content)
for item in items:
# print "name:",item[0]
# print "lat:",item[1]
# print "lng:",item[2]
savestr = str(j)+\',\'+str(item[0])+\',\'+str(item[1])+\',\'+str(item[2])
j += 1
f.write(savestr)
except urllib2.URLError, e:
if hasattr(e, "code"):
print e.code
if hasattr(e, \'reason\'):
print e.reason
finally:
f.close()
2.2 矩形区域检索
BaiduPOI通过url获取POI数据,LocaDiv划分网格,逐个网格爬取POI数据。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import json import codecs import os import urllib2 import sys import time reload(sys) sys.setdefaultencoding(\'utf8\') class BaiDuPOI(object): def __init__(self, itemy, loc): self.itemy = itemy self.loc = loc def urls(self): api_key = baidu_api urls = [] for pages in range(0, 20): url = \'http://api.map.baidu.com/place/v2/search?query=\' + self.itemy + \'&bounds=\' + self.loc + \'&page_size=20&page_num=\' + str( pages) + \'&output=json&ak=\' + api_key urls.append(url) return urls def baidu_search(self): json_sel = [] for url in self.urls(): json_obj = urllib2.urlopen(url) data = json.load(json_obj) for item in data[\'results\']: jname = item["name"] jlat = item["location"]["lat"] jlng = item["location"]["lng"] js_sel = jname + \',\' + str(jlat) + \',\' + str(jlng) json_sel.append(js_sel) return json_sel class LocaDiv(object): def __init__(self, loc_all): self.loc_all = loc_all def lat_all(self): lat_sw = float(self.loc_all.split(\',\')[0]) lat_ne = float(self.loc_all.split(\',\')[2]) lat_list = [] for i in range(0, int((lat_ne - lat_sw + 0.0001) / 0.1)): # 0.1为网格大小,可更改 lat_list.append(lat_sw + 0.1 * i) # 0.05 lat_list.append(lat_ne) return lat_list def lng_all(self): lng_sw = float(self.loc_all.split(\',\')[1]) lng_ne = float(self.loc_all.split(\',\')[3]) lng_list = [] for i in range(0, int((lng_ne - lng_sw + 0.0001) / 0.1)): # 0.1为网格大小,可更改 lng_list.append(lng_sw + 0.1 * i) # 0.1为网格大小,可更改 lng_list.append(lng_ne) return lng_list def ls_com(self): l1 = self.lat_all() l2 = self.lng_all() ab_list = [] for i in range(0, len(l1)): a = str(l1[i]) for i2 in range(0, len(l2)): b = str(l2[i2]) ab = a + \',\' + b ab_list.append(ab) return ab_list def ls_row(self): l1 = self.lat_all() l2 = self.lng_all() ls_com_v = self.ls_com() ls = [] for n in range(0, len(l1) - 1): for i in range(0 + len(l1) * n, len(l2) + (len(l2)) * n - 1): a = ls_com_v[i] b = ls_com_v[i + len(l2) + 1] ab = a + \',\' + b ls.append(ab) return ls if __name__ == \'__main__\': # ak baidu_api ="" # 这里填入你的百度API的ak print "开始爬取数据,请稍等..." start_time = time.time() loc = LocaDiv(\'29.8255, 115.367400, 30.2194, 115.8287\') locs_to_use = loc.ls_row() for loc_to_use in locs_to_use: par = BaiDuPOI(u\'购物\', loc_to_use) # 请修改爬取的类别 a = par.baidu_search() doc = open(\'zhengfujigou.csv\', \'a+\') doc.write(codecs.BOM_UTF8) for ax in a: doc.write(ax) doc.write(\'\\n\') doc.close() end_time = time.time() print "购物爬取完毕,用时%.2f秒" % (end_time - start_time)
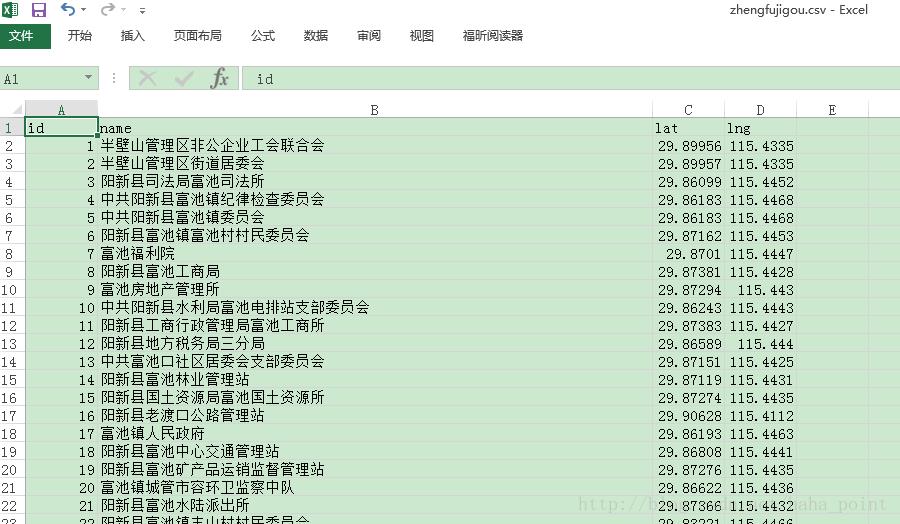
2.3爬取结果示例
---------------------
作者:haha_point
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/haha_point/article/details/78079614
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
以上是关于如何利用百度地图获取一种类型POI的统计数据的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章