Python3 爬虫Beautiful Soup库的使用
Posted 奔跑的金鱼
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python3 爬虫Beautiful Soup库的使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
之前学习了正则表达式,但是发现如果用正则表达式写网络爬虫,那是相当的复杂啊!于是就有了Beautiful Soup
简单来说,Beautiful Soup是python的一个库,最主要的功能是从网页抓取数据。
Beautiful Soup提供一些简单的、python式的函数用来处理导航、搜索、修改分析树等功能。它是一个工具箱,通过解析文档为用户提供需要抓取的数据,因为简单,所以不需要多少代码就可以写出一个完整的应用程序。
安装Beautiful Soup
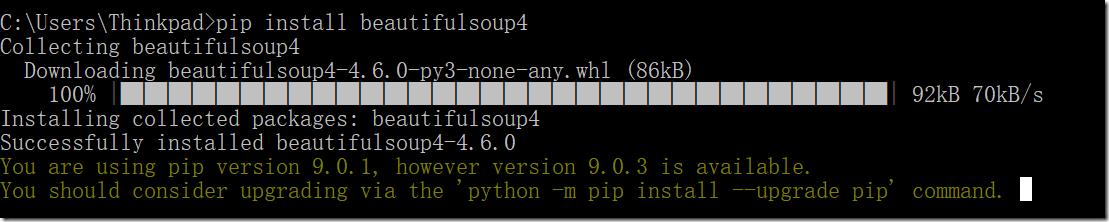
使用命令安装
pip install beautifulsoup4
出现上述截图表示已经成功安装
Beautiful Soup的使用
1.首先必须先导入BS4库
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
2.定义html内容(为后边的例子演示做准备)
下面的一段HTML代码将作为例子被多次用到.这是 爱丽丝梦游仙境的 的一段内容(以后内容中简称为 爱丽丝 的文档):
html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse\'s story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse\'s story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """
3.创建beautifulsoup 对象
#创建BeautifulSoup对象 soup = BeautifulSoup(html) """ 若html内容存在文件a.html中,那么可以这么创建BeautifulSoup对象 soup = BeautifulSoup(open(a.html)) """
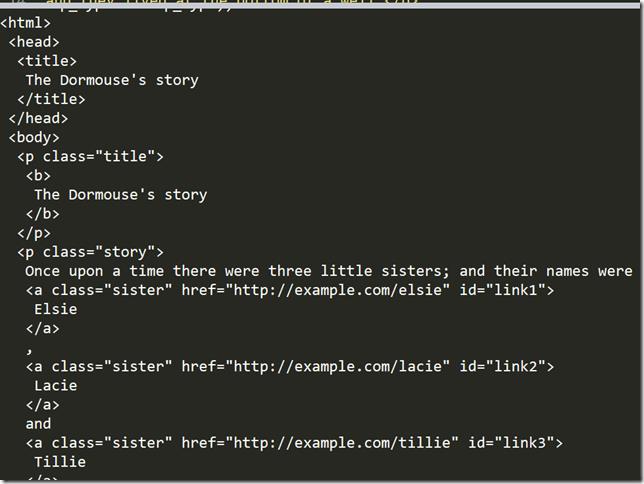
4.格式化输出
#格式化输出 print(soup.prettify())
输出结果:
5.Beautiful Soup将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构
每个节点都是Python对象,所有对象可以归纳为4种:
- Tag
- NavigableString
- BeautifulSoup
- Comment
(1)Tags
Tags是 HTML 中的一个个标签,例如:
<title></title>
<a></a>
<p></p>
…
等都是标签
下面感受一下怎样用 Beautiful Soup 来方便地获取 Tags
#获取tags print(soup.title) #运行结果:<title>The Dormouse\'s story</title> print(soup.head) #运行结果:<head><title>The Dormouse\'s story</title></head> print(soup.a) #运行结果:<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a> print(soup.p) #运行结果:<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse\'s story</b></p>
不过有一点是,它查找的是在所有内容中的第一个符合要求的标签,看<a>标签的输出结果就可以明白了!
我们可以使用type来验证以下这些标签的类型
#看获取Tags的数据类型 print(type(soup.title)) #运行结果:<class \'bs4.element.Tag\'>
对于Tags,还有2个属性,name跟attrs
#查看Tags的两个属性name、attrs print(soup.a.name) #运行结果:a print(soup.a.attrs) #运行结果:{\'href\': \'http://example.com/elsie\', \'class\': [\'sister\'], \'id\': \'link1\'}
从上面的输出结果我们可以看到标签<a>的attrs属性输出结果是一个字典,我们要想获取字典中的具体的值可以这样
p = soup.a.attrs print(p[\'class\']) #print(p.get(\'class\')) 与上述方法等价 #运行结果:[\'sister\']
(2)NavigableString
我们已经获取了Tags了,那么我们如何来获取Tags中的内容呢?
#获取标签内部的文字(NavigableString) print(soup.a.string) #运行结果:Elsie
同样的,我们也可以通过type来查看他的类型
print(type(soup.a.string)) #运行结果:<class \'bs4.element.NavigableString\'>
(3)BeautifulSoup
soup本身也是有这两个属性的,只是比较特殊而已
#查看BeautifulSoup的属性 print(soup.name) #运行结果:[document] print(soup.attrs) #运行结果:{}
(4)Comment
我们把上述html中的这一段修改为下面这个样子(把<a></a>标签中的内容修改为注释内容)
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>
我们可以使用Comment同样提取被注释的内容
#获取标签内部的文字 print(soup.a.string) #运行结果:Elsie
查看其类型
print(type(soup.a.string))
#运行结果:<class \'bs4.element.Comment\'>
6.遍历文档树
(1)直接子节点
.contens属性
tag的contents属性可以将tag的子节点以列表的方式输出
print(soup.head.contents) #运行结果:[<title>The Dormouse\'s story</title>] #获取列表中的内容 print(soup.head.contents[0]) #运行结果:<title>The Dormouse\'s story</title>
.children属性
children生成的是一个list生成器对象,我们可以通过遍历获取所有子节点
print(soup.html.children) #运行结果:<list_iterator object at 0x05730670> print(type(soup.head.contents)) #运行结果:<class \'list\'> #遍历子节点 for children in soup.html.children: print(children) """ 运行结果: <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse\'s story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> </body> """
(2)所有子孙节点
.descendants 属性
contents 和 .children 属性仅包含tag的直接子节点,.descendants 属性可以对所有tag的子孙节点进行递归循环,和 children类似,我们也需要遍历获取其中的内容。
#.descendants 属性 for child in soup.descendants: print(child) """ 运行结果: <html><head><title>The Dormouse\'s story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse\'s story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> </body></html> <head><title>The Dormouse\'s story</title></head> <title>The Dormouse\'s story</title> The Dormouse\'s story <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse\'s story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> </body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse\'s story</b></p> <b>The Dormouse\'s story</b> The Dormouse\'s story <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a> Elsie , <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> Lacie and <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a> Tillie ; and they lived at the bottom of a well. <p class="story">...</p> ...
(3)节点内容
.string属性
如果一个标签里面没有标签了,那么 .string 就会返回标签里面的内容。如果标签里面只有唯一的一个标签了,那么 .string 也会返回最里面的内容。例如
print(soup.title.string) #运行结果:The Dormouse\'s story print(soup.head.string) #运行结果:The Dormouse\'s story
如果tag包含了多个子节点,tag就无法确定,string 方法应该调用哪个子节点的内容, .string 的输出结果是 None
print(soup.html.string) #运行结果:None
(4)多个内容
.strings属性
获取多个内容,不过需要遍历获取,repr函数返回一个对象的string格式
for string in soup.strings: print(repr(string)) # "The Dormouse\'s story" # \'\\n\' # \'\\n\' # "The Dormouse\'s story" # \'\\n\' # \'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\\n\' # \',\\n\' # \'Lacie\' # \' and\\n\' # \'Tillie\' # \';\\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.\' # \'\\n\' # \'...\' # \'\\n\'
.stripped_strings属性
输出的字符串中可能包含了很多空格或空行,使用 .stripped_strings 可以去除多余空白内容
for string in soup.stripped_strings: print(repr(string)) # "The Dormouse\'s story" # "The Dormouse\'s story" # \'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\' # \',\' # \'Lacie\' # \'and\' # \'Tillie\' # \';\\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.\' # \'...\'
(5)父节点
.parent 属性
p = soup.p print(p.parent.name) #运行结果:body
(6)全部父节点
.parents属性
通过元素的 .parents 属性可以递归得到元素的所有父辈节点
#首先打印出子节点 content = soup.head.title.string print("子节点内容:%s"%content) #遍历其父节点 for parent in content.parents: print(parent.name) """ #运行结果: 子节点内容:The Dormouse\'s story title head html [document] """
(7)兄弟节点
.next_sibling .previous_sibling 属性
兄弟节点可以理解为和本节点处在统一级的节点,.next_sibling 属性获取了该节点的下一个兄弟节点,.previous_sibling 则与之相反,如果节点不存在,则返回 None
注:实际文档中的tag的 .next_sibling 和 .previous_sibling 属性通常是字符串或空白,因为空白或者换行也可以被视作一个节点,所以得到的结果可能是空白或者换行
#获取该节点的下一兄弟节点 print(soup.p.next_sibling) #运行结果:返回空白 #获取该节点的上一兄弟节点 print(soup.p.previous_sibling) #运行结果:返回空白 #下一个节点的下一个兄弟节点 print(soup.p.next_sibling.next_sibling) #运行结果: """ <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> """
(8)全部兄弟节点
.next_siblings .previous_siblings 属性
属性通过 .next_siblings 和 .previous_siblings 属性可以对当前节点的兄弟节点迭代输出
for content in soup.a.next_siblings: print(repr(content)) """ 运行结果: \',\\n\' <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> \' and\\n\' <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a> \';\\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.\' """
(9)前后节点
next_element .previous_element 属性
与 .next_sibling .previous_sibling 不同,它并不是针对于兄弟节点,而是在所有节点,不分层次
比如 head 节点为
<head><title>The Dormouse\'s story</title></head>
那么它的下一个节点便是 title,它是不分层次关系的
print(soup.head.next_element) #运行结果:<title>The Dormouse\'s story</title>
(10)所有前后节点
next_elements .previous_elements 属性
通过 .next_elements 和 .previous_elements 的迭代器就可以向前或向后访问文档的解析内容,就好像文档正在被解析一样
content = soup.a.next_elements for element in content: print(repr(element)) """ 运行结果: \'Elsie\' \',\\n\' <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> \'Lacie\' \' and\\n\' <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a> \'Tillie\' \';\\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.\' \'\\n\' <p class="story">...</p> \'...\' \'\\n\' """
7.搜索文档树
(1)find_all(name,attrs,recursive,next,**kwargs)
find_all() 方法搜索当前tag的所有tag子节点,并判断是否符合过滤器的条件
①name参数
name 参数可以查找所有名字为 name 的tag,字符串对象会被自动忽略掉
A.传字符串
#传入字符串查找p标签 print(soup.find_all(\'b\')) #运行结果:[<b>The Dormouse\'s story</b>]
B.传正则表达式
如果传入正则表达式作为参数,Beautiful Soup会通过正则表达式的 match() 来匹配内容.下面例子中找出所有以b开头的标签,这表示<body>和<b>标签都应该被找到
import re for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile(\'^b\')): print(tag.name) #运行结果: # body # b
C.传列表
content = soup.find_all(["a","b"]) print(content) """ #运行结果: [<b>The Dormouse\'s story</b>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>] """
D.传True
True 可以匹配任何值,下面代码查找到所有的tag,但是不会返回字符串节点
for tag in soup.find_all(True): print(tag.name) """ 运行结果: html head title body p b p a a a p """
E.传方法
如果没有合适过滤器,那么还可以定义一个方法,方法只接受一个元素参数 [4] ,如果这个方法返回 True 表示当前元素匹配并且被找到,如果不是则反回 False
下面方法校验了当前元素,如果包含 class 属性却不包含 id 属性,那么将返回 True:
#定义函数,Tag的属性只有id def has_id(tag): return tag.has_attr(\'id\') content = soup.find_all(has_id) print(content) """ 运行结果: [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>] """
②keyword参数
注意:如果一个指定名字的参数不是搜索内置的参数名,搜索时会把该参数当作指定名字tag的属性来搜索,如果包含一个名字为 id 的参数,Beautiful Soup会搜索每个tag的”id”属性
print(soup.find_all(id="link3")) # 运行结果:[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
如果传入 href 参数,Beautiful Soup会搜索每个tag的”href”属性
import re print(soup.find_all(href=re.compile("lacie"))) # 运行结果:[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]
使用多个指定名字的参数可以同时过滤tag的多个属性
import re print(soup.find_all(href=re.compile("lacie"),id="link2")) # 运行结果:[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]
使用class过滤的时候,class不是python的关键字,加个下划线即可
print(soup.find_all("a",class_="sister")) # 运行结果:[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
③text参数
通过 text 参数可以搜搜文档中的字符串内容.与 name 参数的可选值一样, text 参数接受 字符串 , 正则表达式 , 列表, True
#传入字符串 print(soup.find_all(text="Lacie")) # 运行结果:[\'Lacie\'] #传入列表 print(soup.find_all(text=["Lacie","Tillie"])) # 运行结果:[\'Lacie\', \'Tillie\'] #传入正则表达式 import re print(soup.find_all(text=re.compile("Dormouse"))) # 运行结果:["The Dormouse\'s story", "The Dormouse\'s story"]
④limit参数
find_all()参数在大量查询的时候可能会变慢,所以我们引入了limit函数,该函数可以限制返回的结果
print(soup.find_all("a")) """ 运行结果: [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>] """ print(soup.find_all("a",limit=2)) """ 运行结果: [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>] """
⑤recursive参数
recursive被翻译为递归循环的意思
调用tag的 find_all() 方法时,Beautiful Soup会检索当前tag的所有子孙节点,如果只想搜索tag的直接子节点,可以使用参数 recursive=False .
print(soup.html.find_all("title")) # 运行结果:[<title>The Dormouse\'s story</title>] print(soup.html.find_all("title",recursive=False)) # 运行结果:[]
(2)find( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
它与 find_all() 方法唯一的区别是 find_all() 方法的返回结果是值包含一个元素的列表,而 find() 方法直接返回结果
(3)find_parents() find_parent()
find_all() 和 find() 只搜索当前节点的所有子节点,孙子节点等. find_parents() 和 find_parent() 用来搜索当前节点的父辈节点,搜索方法与普通tag的搜索方法相同,搜索文档搜索文档包含的内容
(4)find_next_siblings() find_next_sibling()
这2个方法通过 .next_siblings 属性对当 tag 的所有后面解析的兄弟 tag 节点进行迭代, find_next_siblings() 方法返回所有符合条件的后面的兄弟节点,find_next_sibling() 只返回符合条件的后面的第一个tag节点
(5)find_previous_siblings() find_previous_sibling()
这2个方法通过 .previous_siblings 属性对当前 tag 的前面解析的兄弟 tag 节点进行迭代, find_previous_siblings() 方法返回所有符合条件的前面的兄弟节点, find_previous_sibling() 方法返回第一个符合条件的前面的兄弟节点
(6)find_all_next() find_next()
这2个方法通过 .next_elements 属性对当前 tag 的之后的 tag 和字符串进行迭代, find_all_next() 方法返回所有符合条件的节点, find_next() 方法返回第一个符合条件的节点
(7)find_all_previous() 和 find_previous()
这2个方法通过 .previous_elements 属性对当前节点前面的 tag 和字符串进行迭代, find_all_previous() 方法返回所有符合条件的节点, find_previous()方法返回第一个符合条件的节点
8.CSS选择器
我们在写 CSS 时,标签名不加任何修饰,类名前加点,id名前加 #,在这里我们也可以利用类似的方法来筛选元素,用到的方法是 soup.select(),返回类型是 list
(1)通过标签名查找
print(soup.select(\'title\')) # 运行结果:[][<title>The Dormouse\'s story</title>] print(soup.select(\'b\')) # 运行结果:[<b>The Dormouse\'s story</b>]
(2)通过类名查找
print(soup.select(".sister")) """ [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>] """
(3)通过类名查找
print(soup.select("#link1")) # 运行结果:[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>]
(4)组合查找
print(soup.select("p #link1")) # 运行结果:[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>]
(5)属性查找
查找时还可以加入属性元素,属性需要用中括号括起来,注意属性和标签属于同一节点,所以中间不能加空格,否则会无法匹配到。
print(soup.select(\'a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]\')) # 运行结果:[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>]
以上是关于Python3 爬虫Beautiful Soup库的使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章