1.bin()函数将十进制转换成而进制
2.oct()函数将十进制转换成八进制
3.hex()函数将十进制转换成十六进制
十六进制表示:0-9 a b c d e f
4.数字类型的特性:
只能存放一个值
一经定义,不可更改
直接访问
分类:整型,布尔,浮点,复数
5.字符串类型
引号包含的都是字符串类型
S1=‘hello world‘ s="hello world"
s2="""hello world"""
s3=‘‘‘hello world‘‘‘
单引双引没有区别
6.字符串的常用操作
strip()移除空白,也可以去除其他的字符
slipt()分割,默认以空格分割。也可以以其他的字符分割
len()长度 切片:如print(x[1:3])也是顾头不顾尾
print(x[0:5:2])#0 2 4
capitalize()首字母大写
center()居中显示例如:x=‘hello‘ print(x.center(30,‘#‘))
count():计数,顾头不顾尾,统计某个字符的个数,空格也算一个字符
endswith()以什么结尾
satrtswith()以什么开头
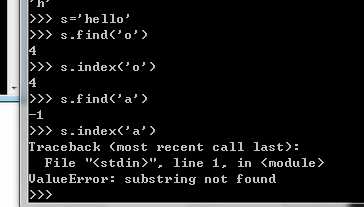
find()查找字符的索引位置,如果是负数,代表查找失败
index()索引
find()和index()的区别,如下图:
format()字符串格式化
1.msg=‘name:{},age:{},sex:{}‘
print(msg.format(‘haiyan‘,18,女))
2.msg=‘name:{0},age:{1},sex:{0}‘
print(msg.format(‘aaaaaa‘,‘bbbbbb‘))
3.msg=‘name:{x},age:{y,sex:{z}‘
print(msg.format(x=‘haiyan‘,y=‘18‘,z=‘女‘))
isdigit()判断是否是数字
islower()判断是否是全部小写
isupper()判断是否是全部大写
lower()全部转换为小写
upper()全部转换为大写
isspace()判断是否是全都是空格
istitle()判断是否是标题(首字母大写)
swapcase()大小写字母翻转
join()连接
repalce()替换
msg=‘hello alex‘
print(msg.replace(‘e‘),‘A‘,1)
print(msg.replace(‘e‘),‘A‘,2)
ljust()左对齐
X=‘ABC‘ print(x.ljust(10,‘*‘))
1.%s,%d
举例1:name=‘egon‘
age=20
print("my name is %s my age is %s" %(name,age))#%s既能接受字符串,也能接受数字
print(‘my name is %s my age is %d’ %(name,age))#%d只能接受数字
举例2:用户信息的显示
1 while True:
2 name=input("name:")
3 age=input("age:")
4 sex=input("sex:")
5 height=input("height:")
6 msg=‘‘‘
7 ------------%s info-----------
8 name:%s
9 age:%s
10 sex:%s
11 height:%s
12 ------------------------------
13 ‘‘‘%(name,name,age,sex,heigth)
14 print(msg)
运行结果如下:

2.字符串方法
# name=‘egon‘ #name=str(‘egon‘)
# print(type(name))
#优先掌握
#1.移除空白strip
# msg=‘ hello ‘
# print(msg)
# print(msg.strip())
# 移除‘*’
# msg=‘***hello*********‘
# msg=msg.strip(‘*‘)
# print(msg)
#移除左边的
# print(msg.lstrip(‘*‘))
#移除右边的
# print(msg.rstrip(‘*‘))
#用处
while True:
name=input(‘user: ‘).strip()
password=input(‘password: ‘).strip()
if name == ‘egon‘ and password == ‘123‘:
print(‘login successfull‘)
#切分split
# info=‘root:x:0:0::/root:/bin/bash‘
# print(info[0]+info[1]+info[2]+info[3])
# user_l=info.split(‘:‘)
# print(user_l[0])
# msg=‘hello world egon say hahah‘
# print(msg.split()) #默认以空格作为分隔符
#cmd=‘download|xhp.mov|3000‘
# cmd_l=cmd.split(‘|‘)
# print(cmd_l[1])
# print(cmd_l[0])
# print(cmd.split(‘|‘,1))
#用处
while True:
cmd=input(‘>>: ‘).strip()
if len(cmd) == 0:continue
cmd_l=cmd.split()
print(‘命令是:%s 命令的参数是:%s‘ %(cmd_l[0],cmd_l[1]))
#长度len
# print(len(‘hell 123‘))
#索引
# 切片:切出子字符串
# msg=‘hello world‘
# print(msg[1:3]) #1 2
# print(msg[1:4]) #1 2 3
# 掌握部分
oldboy_age=84
while True:
age=input(‘>>: ‘).strip()
if len(age) == 0:
continue
if age.isdigit():
age=int(age)
else:
print(‘must be int‘)
#startswith,endswith
# name=‘alex_SB‘
# print(name.endswith(‘SB‘))
# print(name.startswith(‘alex‘))
#replace
# name=‘alex say :i have one tesla,my name is alex‘
# print(name.replace(‘alex‘,‘SB‘,1))
# print(‘my name is %s my age is %s my sex is %s‘ %(‘egon‘,18,‘male‘))
# print(‘my name is {} my age is {} my sex is {}‘.format(‘egon‘,18,‘male‘))
# print(‘my name is {0} my age is {1} my sex is {0}:
{2}‘.format(‘egon‘,18,‘male‘))
# print(‘my name is {name} my age is {age} my sex is {sex}‘.format(
# sex=‘male‘,
# age=18,
# name=‘egon‘))
# name=‘goee say hello‘
# # print(name.find(‘S‘,1,3)) #顾头不顾尾,找不到则返回-1不会报错,找到了则显示索引
# # print(name.index(‘S‘)) #同上,但是找不到会报错
#
# print(name.count(‘S‘,1,5)) #顾头不顾尾,如果不指定范围则查找所有
#join
# info=‘root:x:0:0::/root:/bin/bash‘
# print(info.split(‘:‘))
# l=[‘root‘, ‘x‘, ‘0‘, ‘0‘, ‘‘, ‘/root‘, ‘/bin/bash‘]
# print(‘:‘.join(l))
#lower,upper
# name=‘eGon‘
# print(name.lower())
# print(name.upper())
#了解部分
#expandtabs
# name=‘egon\\thello‘
# print(name)
# print(name.expandtabs(1))
#center,ljust,rjust,zfill
# name=‘egon‘
# # print(name.center(30,‘-‘))
# print(name.ljust(30,‘*‘))
# print(name.rjust(30,‘*‘))
# print(name.zfill(50)) #用0填充
#captalize,swapcase,title
# name=‘eGon‘
# print(name.capitalize()) #首字母大写,其余部分小写
# print(name.swapcase()) #大小写翻转
# msg=‘egon say hi‘
# print(msg.title()) #每个单词的首字母大写
#在python3中
num0=‘4‘
num1=b‘4‘ #bytes
num2=u‘4‘ #unicode,python3中无需加u就是unicode
num3=‘四‘ #中文数字
num4=‘Ⅳ‘ #罗马数字
#isdigt:str,bytes,unicode
# print(num0.isdigit())
# print(num1.isdigit())
# print(num2.isdigit())
# print(num3.isdigit())
# print(num4.isdigit())
#isdecimal:str,unicode
# num0=‘4‘
# num1=b‘4‘ #bytes
# num2=u‘4‘ #unicode,python3中无需加u就是unicode
# num3=‘四‘ #中文数字
# num4=‘Ⅳ‘ #罗马数字
# print(num0.isdecimal())
# # print(num1.)
# print(num2.isdecimal())
# print(num3.isdecimal())
# print(num4.isdecimal())
#isnumeric:str,unicode,中文,罗马
# num0=‘4‘
# num1=b‘4‘ #bytes
# num2=u‘4‘ #unicode,python3中无需加u就是unicode
# num3=‘四‘ #中文数字
# num4=‘Ⅳ‘ #罗马数字
#
# print(num0.isnumeric())
# # print(num1)
# print(num2.isnumeric())
# print(num3.isnumeric())
# print(num4.isnumeric())
#is其他
# name=‘egon123‘
# print(name.isalnum()) #字符串由字母和数字组成
# name=‘asdfasdfa sdf‘
# print(name.isalpha()) #字符串只由字母组成
#
# name=‘asdfor123‘
# print(name.isidentifier())
name=‘egGon‘
print(name.islower())
# print(name.isupper())
# print(name.isspace())
name=‘Egon say‘
print(name.istitle())
一、列表
作用:多个装备,多个爱好,多门课程,多个女朋友等
定义:[]内可以有多个任意类型的值,逗号分隔
以下是列表的常用操作:
1 l=[1,2,3] #l=list([1,2,3]) 2 # print(type(l)) 3 4 #pat1===》优先掌握部分 5 # 索引:l=[1,2,3,4,5] 6 print(l[0]) 7 # 切片 8 l=[‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘,‘f‘] 9 10 # print(l[1:5]) 11 # print(l[1:5:2]) 12 # print(l[2:5]) 13 # print(l[-1]) 14 15 16 #了解 17 # print(l[-1:-4]) 18 # print(l[-4:]) 19 # l=[‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘,‘f‘] 20 # print(l[-2:]) 21 22 # 追加 23 # hobbies=[‘play‘,‘eat‘,‘sleep‘,‘study‘] 24 # hobbies.append(‘girls‘) 25 # print(hobbies) 26 27 # 删除 28 hobbies=[‘play‘,‘eat‘,‘sleep‘,‘study‘] 29 # x=hobbies.pop(1) #不是单纯的删除,是删除并且把删除的元素返回,我们可以用一个变量名去接收该返回值 30 # print(x) 31 # print(hobbies) 32 33 # x=hobbies.pop(0) 34 # print(x) 35 # 36 # x=hobbies.pop(0) 37 # print(x) 38 39 #队列:先进先出 40 queue_l=[] 41 #入队 42 # queue_l.append(‘first‘) 43 # queue_l.append(‘second‘) 44 # queue_l.append(‘third‘) 45 # print(queue_l) 46 #出队 47 # print(queue_l.pop(0)) 48 # print(queue_l.pop(0)) 49 # print(queue_l.pop(0)) 50 51 52 #堆栈:先进后出,后进先出 53 # l=[] 54 # #入栈 55 # l.append(‘first‘) 56 # l.append(‘second‘) 57 # l.append(‘third‘) 58 # #出栈 59 # print(l) 60 # print(l.pop()) 61 # print(l.pop()) 62 # print(l.pop()) 63 64 #了解 65 # del hobbies[1] #单纯的删除 66 # hobbies.remove(‘eat‘) #单纯的删除,并且是指定元素去删除 67 68 69 # 长度 70 # hobbies=[‘play‘,‘eat‘,‘sleep‘,‘study‘] 71 # print(len(hobbies)) 72 73 # 包含in 74 # hobbies=[‘play‘,‘eat‘,‘sleep‘,‘study‘] 75 # print(‘sleep‘ in hobbies) 76 77 # msg=‘hello world egon‘ 78 # print(‘egon‘ in msg) 79 80 81 ##pat2===》掌握部分 82 hobbies=[‘play‘,‘eat‘,‘sleep‘,‘study‘,‘eat‘,‘eat‘] 83 # hobbies.insert(1,‘walk‘) 84 # hobbies.insert(1,[‘walk1‘,‘walk2‘,‘walk3‘]) 85 # print(hobbies) 86 87 # print(hobbies.count(‘eat‘)) 88 # print(hobbies) 89 # hobbies.extend([‘walk1‘,‘walk2‘,‘walk3‘]) 90 # print(hobbies) 91 92 hobbies=[‘play‘,‘eat‘,‘sleep‘,‘study‘,‘eat‘,‘eat‘] 93 # print(hobbies.index(‘eat‘)) 94 95 96 #pat3===》了解部分 97 hobbies=[‘play‘,‘eat‘,‘sleep‘,‘study‘,‘eat‘,‘eat‘] 98 # hobbies.clear() 99 # print(hobbies) 100 101 # l=hobbies.copy() 102 # print(l) 103 104 # l=[1,2,3,4,5] 105 # l.reverse() 106 # print(l) 107 108 l=[100,9,-2,11,32] 109 l.sort(reverse=True) 110 print(l)
