Python处理命令行参数
Posted 头痛不头痛
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python处理命令行参数相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 将命令行参数保存在列表中,注意argv[0]是程序本身的名字:
import sys print(sys.argv) print(sys.argv[1])
python argv.py localhost 3306
[\'argv.py\', \'localhost\', \'3306\']
localhost
2. 使用sys.stdin和fileinput读取标准输入,并打印在终端类似shell中的管道
import sys for line in sys.stdin: print(line,end="")
可以像shell脚本一样,通过标准输入给程序输入内容
python read_stdin.py </etc/passwd
python read_stdin.py -
cat /etc/passwd |python read_stdin.py
将标准输入保存在一个列表中
import sys
def get_content():
return sys.stdin.readlines()
print(get_content())
python readlines_stdin.py <test/1.txt
[\'hello\\n\', \'world\\n\']
3. 利用fileinput读取标准输入
#/usr/bin/env python
#coding=utf-8
import fileinput
for line in fileinput.input():
print(line,end="")
python file_input1.py /etc/passwd
python file_input1.py </etc/passwd
python file_input1.py /etc/passwd /etc/my.cnf
fileinput常用于从文件中读取内容
import fileinput
for line in fileinput.input():
meta = [fileinput.filename(), fileinput.fileno(), fileinput.filelineno(),
fileinput.isfirstline(), fileinput.isstdin()]
print(*meta, end="")
print()
print(line, end="")

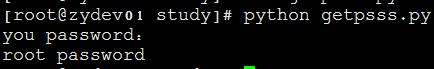
4. 使用getpass读取密码:
import getpass user=getpass.getuser() passwd=getpass.getpass(\'you password: \') print(user,passwd)
可以避免输入密码被看见
5.使用argparse解析命令行参数
agrparse能够根据从sys.arg中解析参数,并自动生成帮助信息
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
def _argparse():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="This is description")
parser.add_argument(\'--host\', action=\'store\',
dest=\'server\',default="localhost", help=\'connect to host\')
parser.add_argument(\'-t\', action=\'store_true\',
default=False, dest=\'boolean_switch\', help=\'Set a switch to true\')
return parser.parse_args()
def main():
parser = _argparse()
print(parser)
print(\'host =\', parser.server)
print(\'boolean_switch=\', parser.boolean_switch)
if __name__ == \'__main__\':
main()
格式:rgumentParser.add_argument(name or flags...[, action][, nargs][, const][, default][, type][, choices][, required][, help][, metavar][, dest])
name:参数的名字
action: 遇到参数时的动作,默认为store,store_xx,表示将参数转换为xx
nargs:参数的个数
dest:解析后的参数的名字
type:参数的类型

6. 使用Click创建命令行解析
Click比较argparse更加的快速和简单
pip inst click
import click
@click.command()
@click.option(\'--count\', default=1, help=\'Number of greetings.\')
@click.option(\'--name\', prompt=\'Your name\',
help=\'The person to greet.\')
def hello(count, name):
"""Simple program that greets NAME for a total of COUNT times."""
for x in range(count):
click.echo(\'Hello %s!\' % name)
if __name__ == \'__main__\':
hello()
commond让函数成为命令行接口
option:增加命令行选项
echo:输出结果
prompt:如果没有指定name这个参数时,会进入交互模式下输入

也可以像Linux中的fc一样进入默认编辑器
import click message = click.edit() print(message,end="")
7. 使用prompt_toolkit打造交互式命令行工具
pip install prompt_toolkit
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
while True:
user_input = prompt(\'>\')
print(user_input)
Linux下的快捷键都可以使用,输入时退格键,也不会出现乱码
加入历史输入功能
from __future__ import unicode_literals
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
from prompt_toolkit.history import FileHistory
while True:
user_input = prompt(\'>\',
history=FileHistory(\'history.txt\'),
)
print(user_input)
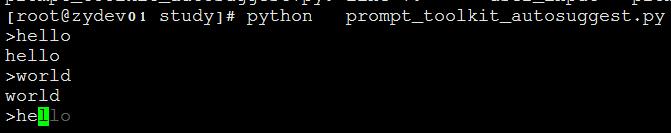
加入自动提示功能
from __future__ import unicode_literals
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
from prompt_toolkit.history import FileHistory
from prompt_toolkit.auto_suggest import AutoSuggestFromHistory
while True:
user_input = prompt(\'>\',
history=FileHistory(\'history.txt\'),
auto_suggest=AutoSuggestFromHistory(),
)
print(user_input)
会以按字体进行提示
加入自动补全功能:
from __future__ import unicode_literals
from prompt_toolkit import prompt
from prompt_toolkit.history import FileHistory
from prompt_toolkit.auto_suggest import AutoSuggestFromHistory
from prompt_toolkit.contrib.completers import WordCompleter
SQLCompleter = WordCompleter([\'select\', \'from\', \'insert\', \'update\', \'delete\', \'drop\'],
ignore_case=True)
while True:
user_input = prompt(\'SQL>\',
history=FileHistory(\'history.txt\'),
auto_suggest=AutoSuggestFromHistory(),
completer=SQLCompleter,
)
print(user_input)
按tab键就可以自动补全

以上是关于Python处理命令行参数的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章