mongoDB操作指南
Posted Jeff的技术栈
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mongoDB操作指南相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. docker安装mongoDB
docker pull mongo:5.0
docker run -itd --name mongo:5.0 -p 27017:27017 mongo --auth
-p 27017:27017 :映射容器服务的 27017 端口到宿主机的 27017 端口。外部可以直接通过 宿主机 ip:27017 访问到 mongo 的服务。
--auth:需要密码才能访问容器服务。
$ docker exec -it mongo mongo admin
# 创建一个名为 admin,密码为 123456 的用户。
> db.createUser( user:\'admin\',pwd:\'123456\',roles:[ role:\'userAdminAnyDatabase\', db: \'admin\',"readWriteAnyDatabase"]);
# 尝试使用上面创建的用户信息进行连接。
> db.auth(\'admin\', \'123456\')
2. 库-database
use 数据库名称 //选择和创建数据库的语法格式
注意:在MongoDB中,集台只有在内容插入后才会创建!就是说,创建集合(数据表)后,必须要再插入一个文档(记录),集合才会真正的创建
db //查看当前正在使用的数据库名称
db.user.getDB() //获取库名
db.version() //获取版本
3. 集合-collection
集合,类似关系型数据库中的表。
可以显示的创建,也可以隐式的创建。
3.1 命名规范
1.集合名不能是空字符串""。
2.集合名不能含有\\0字符(空字符),这个字符表示集合名的结尾。
3.集合名不能以"system."开头,这是为系统集合保留的前缀。
4.用户创建的集合名字不能含有保留字符。有些驱动程序的确支持在集合名里面包含,这是因为某些系统生成的集合中包含该字符。除 非你要访问这种系统创建的集合,否则千万不要在名字里出现$。
3.2 增-createCollection
增:
集合创建(显示创建):
db.createCollection("test2")
集合创建(隐士创建):
当向一个集合中插入一个文档的时候,如果集合不存在,则会自动创建集合
注:通常我们使用隐式创建文档即可。
3.3 删-drop
删:
db.集合名.drop()
db.test2.drop()
注:如果成功删除选定集合,则 drop() 方法返回 true,否则返回 false
4. 文档-document
文档(document)的数据结构和 JSON 基本一样。
所有存储在集合中的数据都是 BSON 格式
4.1 命名规范
1)键不能含有\\0 (空字符)。这个字符用来表示键的结尾。
2)"."点和$有特别的意义,只有在特定环境下才能使用。
3)以下划线"_"开头的键是保留的(不是严格要求的)。
4.2 增-insert,insertMany(单个增,批量增)
注:
1.user代表集合名称
2.comment集合如果不存在,则会隐式创建
3.mongo中的数字,默认情况下是double类型,如果要存整型,必须使用函数NumberInt(整型数字),否则取出来就有问题了。
4.插入当前日期使用 new Date()
5.插入的数据没有指定 _id ,会自动生成主键值
6.如果某字段没值,可以赋值为null,或不写该字段。
7.批量插入如果某条数据插入失败,将会终止插入,但已经插入成功的数据不会回滚掉。所以需要处理异常
4.2.1 insertOne-单个增
单个增:
db.user.insertOne([
"name":"jeff004",
"age":18,
])
4.2.2 insertMany-批量增
批量增:
db.user.insertMany([
"name":"ooo","sex":"男",
"name":"xxx","sex":"女"
])
结果:acknowledged:true insertedlds:(Array) 2 Elements
4.2.3 insert-单个增或批量增
//批量增
db.user.insert([
"name":"jeff006",
"age":18,
,
"name":"jeff007",
"age":18,
])
//单个增
db.user.insert(
"name":"jeff008",
"age":18,
)
4.3 查-find
4.3.1 find-查所有,条件查,投影查
db.user.find() //查询集合所有
db.user.find(name:"123"); //条件查询
db.user.findOne(name:"123"); //条件查询,返回符合条件的第一条数据
db.user.find(_id:ObjectId("643622e64a2ad86c86062273")); //_id查询
//投影查
//如果要查询结果返回部分字段,则需要使用投影查询(不显示所有字段,只显示指定的字段)。
//投影查,1:显示 0:不显示,默认 _id 会显示。
db.user.find(name:"123","name":1);
db.user.find(name:"123",name:1,_id:0); //_id不显示
4.3.2 limit,offset翻页查,排序
//limit限制条数,skip跳过条数
db.user.find().limit(10).skip(2)
//排序
db.user.find().sort(age:-1) //-1降序,1升序
db.user.find().sort(age:-1,userid:1) //先按age降序,再按userid生序排列
//排序取第一条
db.user.find().sort(age:-1).limit(1)//max,先排序,再取第一条
db.user.find().sort(age:1).limit(1) //min,先排序,再取第一条
4.3.3 正则模糊查询(相当于like)
db.user.find(name:/正则表达式/)
db.user.find(name:/ef/) //匹配jeff
4.3.4 大于gt,小于lt,大于等于gte,小于等于lte,不等于ne
//大于$gt,小于$lt,大于等于$gte,小于等于$lte,不等于$ne
//不等于
db.user.find(name:$ne:"jeff") //name!=“jeff”的所有
//大于
db.user.find(age:$gt:5) //age大于5的所有
//小于
db.user.find(age:$lt:100) //age小于100的所有
4.3.5 包含查询-\\(in,不包含查询-\\)nin
db.user.find(name:$in:["jeff","chery"]) //user集合中name字段包含的
db.user.find(name:$nin:["jeff","chery"]) ////user集合中name字段不包含的
4.3.6 条件连接-\\(and,\\)or
db.user.find($and:[ , , ])
//name=jeff and age=10
db.user.find($and:[name:"jeff",age:10]) //and
//name正则匹配 and age>5
db.user.find($and:[name:/ef/,age:$gt:5]) //and
//name="jeff" or age>10
db.user.find($or:[name:"jeff",age:$gt:10]) //or
4.4 改-update,updateOne
//默认只修改第一条 $set
db.user.update(name:"123",$set:name:"jeff")
//修改符合条件的所有数据 multi:true
db.user.update(name:"123",$set:name:"jeff",multi:true)
//每次原基础上递增10 $inc
db.user.update(name:"jeff",$inc:age:10)
//$max,$min使用
//解释:age大于小于300则修改,否则不修改
db.user.updateOne(name:"jeff",$max:age:300)
db.user.updateOne(name:"jeff",$min:age:300)
4.5 删-remove
//删除符合条件所有
db.user.remove(name:"jeff")
4.6 统计aggregate聚合函数-count,max,min,avg,sum
//count
db.user.count() //集合全部计数
db.user.count(name:"jeff") //集合条件计数
//avg
db.user.aggregate([
$group : _id : null, avgAge: $avg : "$age"
])
//max
db.user.aggregate([
$group : _id : null, avgAge: $max : "$age"
])
//min
db.user.aggregate([
$group : _id : null, avgAge: $max : "$age"
])
//sum
db.user.aggregate([
$group : _id : null, avgAge: $max : "$age"
])
5. 索引-index
5.1 mongo B-tree与mysql B+tree分析
mongo索引结构:B-Tree
mysql索引结构:B+Tree
B-Tree与B+Tree区别:B+tree只有叶子结点存数据,B-Tree所有节点都存数据
原因:mongo与mysql使用场景不一样,mysql是关系型,mongo是非关系性
至于为什么MongoDB使用B树而不是B +树,可以从其设计的角度考虑它。 MongoDB不是传统的关系数据库,而是以BSON格式(可以认为是JSON)存储的nosql。目的是高性能,高可用性和易于扩展。
Mysql是关系型数据库,最常用的是数据遍历操作(join),而MongoDB它的数据更多的是聚合过的数据,不像Mysql那样表之间的关系那么强烈,因此MongoDB更多的是单个查询。
由于Mysql使用B+树,数据在叶节点上,叶子节点之间又通过双向链表连接,更加有利于数据遍历,而MongoDB使用B树,所有节点都有一个数据字段。只要找到指定的索引,就可以对其进行访问。毫无疑问,单个查询MongoDB平均查询速度比Mysql快。
5.2 索引分类
5.2.1 单字段索引
MongoDB支持在文档的单个字段上创建用户定义的升序/降序索引,称为单字段索引(Single Field Index)。 对于单个字段索引和排序操作,索引键的排序顺序(即升序或降序)并不重要,因为MongoDB可以在任何方向上遍历索引。
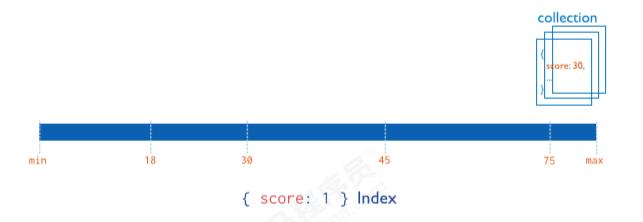
5.2.2 复合索引
MongoDB还支持多个字段的用户定义索引,即复合索引(Compound Index)。
复合索引中列出的字段顺序具有重要意义。例如,如果复合索引由 userid: 1, score: -1 组成,则索引首先按userid正序排序,然后 在每个userid的值内,再在按score倒序排序。
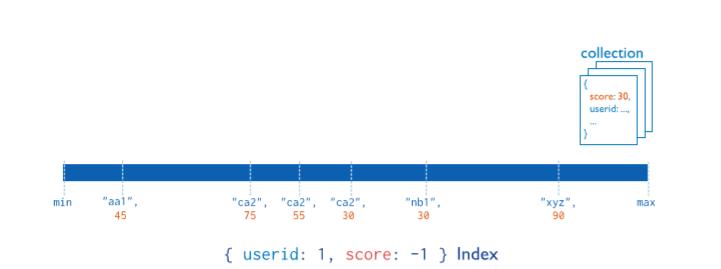
5.2.3 其他索引-地理空间索引,文本索引,哈希索引
地理空间索引(Geospatial Index)、文本索引(Text Indexes)、哈希索引(Hashed Indexes)。
为了支持对地理空间坐标数据的有效查询,MongoDB提供了两种特殊的索引:返回结果时使用平面几何的二维索引和返回结果时使用球面 几何的二维球面索引。

5.3 索引查看
db.user.getIndexes() //查看索引
[
"v" : 2, # mongodb引擎的版本号(不用管)
"key" :
"_id" : 1 # 默认主键
,
"name" : "_id_", # 索引名称
"ns" : "jeff.comment" # 索引的位置
]
5.4 索引创建
db.集合名.createIndex(keys, options)
//升序普通索引
db.user.createIndex(userid:1)
//1升序索引,-1降序索引
db.user.createIndex(name:1,unique:true) //新,推荐
db.user.ensureIndex(name:1,unique:true) //老,不推荐,3.0.0版本前,createIndex的别名
//复合索引
db.user.createIndex(userid:1,name:-1) //先userid升序,再name降序
options参数列表:
options(更多选项)列表:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| background | Boolean | 建索引过程会阻塞其它数据库操作,background可指定以后台方式创建索引,即增加 "background" 可选参数。"background" 默认值为false。 |
| unique | Boolean | 建立的索引是否唯一。指定为true创建唯一索引。默认值为false. |
| name | string | 索引的名称。如果未指定,MongoDB的通过连接索引的字段名和排序顺序生成一个索引名 称。 |
| dropDups | Boolean | 3.0+版本已废弃。在建立唯一索引时是否删除重复记录,指定 true 创建唯一索引。默认值为 false. |
| sparse | Boolean | 对文档中不存在的字段数据不启用索引;这个参数需要特别注意,如果设置为true的话,在索 引字段中不会查询出不包含对应字段的文档.。默认值为 false. |
| expireAfterSeconds | integer | 指定一个以秒为单位的数值,完成 TTL设定,设定集合的生存时间。 |
| v | index version | 索引的版本号。默认的索引版本取决于mongod创建索引时运行的版本。 |
| weights | document | 索引权重值,数值在 1 到 99,999 之间,表示该索引相对于其他索引字段的得分权重。 |
| default_language | string | 对于文本索引,该参数决定了停用词及词干和词器的规则的列表。 默认为英语 |
| language_override | string | 对于文本索引,该参数指定了包含在文档中的字段名,语言覆盖默认的language,默认值为 language. |
提示:
注意在 3.0.0 版本前创建索引方法为 db.collection.ensureIndex() ,之后的版本使用了 db.collection.createIndex() 方法, ensureIndex() 还能用,但只是 createIndex() 的别名。
5.5 索引删除
db.集合名.dropIndex(索引)
//指定删除:删除userid:1索引
db.user.dropIndex(userid:1)
//全部删除:删除集合全部索引,除_id索引
db.user.dropIndexes()
5.6 explain执行计划
分析查询性能 通常使用执行计划来查看查询的情况,如查询耗费的时间、是 否基于索引查询等。
那么,通常,我们想知道,建立的索引是否有效,效果如何,都需要通过执行计划查看。
db.集合名.find(query,options).explain(options)
//eg:
db.user.find("name":"jeff").explain()
6. golang使用mongoDB
6.1 初始化
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/bson"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options"
"log"
)
var Client *mongo.Client
func initMongo(url string) error
clientOptions := options.Client().ApplyURI(url)
client, err := mongo.Connect(context.TODO(), clientOptions)
if err != nil
log.Fatal(err)
// 检测连接
err = client.Ping(context.TODO(), nil)
if err != nil
fmt.Println("连接失败!err:", err)
return err
fmt.Println("Connected to MongoDB!")
Client = client
return nil
func main()
url := "mongodb://admin:123456@127.0.0.1:27017"
//初始化
if err := initMongo(url); err != nil
fmt.Println("连接失败!err:", err)
return
6.2 findOne-查询单个
//查询单个
func findOne(detection_coll *mongo.Collection, filter bson.D) (result map[string]interface, err error)
err = detection_coll.FindOne(context.TODO(), filter).Decode(&result)
if err != nil
fmt.Println(err)
return nil, err
return
func main()
url := "mongodb://admin:123456@127.0.0.1:27017"
//初始化
if err := initMongo(url); err != nil
fmt.Println("连接失败!err:", err)
return
// 获取collection
detection_coll := Client.Database("test").Collection("user")
// 查询单条数据
type User struct
Id string `json:"_id"`
Age int `json:"age"`
Name string `json:"name"`
user := User
//查询单个
filter := bson.DKey: "name", Value: "jeff"
data, err := findOne(detection_coll, filter)
if err != nil
fmt.Println(err)
return
fmt.Println(data)
bStr, _ := json.Marshal(data)
_ = json.Unmarshal(bStr, &user)
fmt.Println(user)
6.3 find-查询所有
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo"
"go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options"
"log"
)
type User struct
Id string `json:"_id"`
Age int `json:"age"`
Name string `json:"name"`
//查询所有
func find(detection_coll *mongo.Collection, filter bson.D, reslist []*User) (reqlist []*User, err error)
cur, err := detection_coll.Find(context.TODO(), filter)
if err != nil
return nil, err
if err = cur.Err(); err != nil
return nil, err
err = cur.All(context.Background(), &reslist)
if err != nil
return nil, err
_ = cur.Close(context.Background())
return reslist, nil
func main()
url := "mongodb://admin:123456@127.0.0.1:27017"
//初始化
if err := initMongo(url); err != nil
fmt.Println("连接失败!err:", err)
return
// 获取collection
detection_coll := Client.Database("test").Collection("user")
userList := []*User
//查询所有
filter := bson.DKey: "age", Value: 18
list, err := find(detection_coll, filter, userList)
if err != nil
fmt.Println(err)
return
fmt.Println(list)
for _, one := range list
fmt.Println(one)
6.4 InsertOne-单条插入
//单条插入
func InsertOne(detection_coll *mongo.Collection, info interface) (objectID interface, err error)
objId, err := detection_coll.InsertOne(context.TODO(), info)
if err != nil
return nil, err
fmt.Println("_id:", objId.InsertedID)
return objId, nil
func main()
url := "mongodb://admin:123456@127.0.0.1:27017"
//初始化
if err := initMongo(url); err != nil
fmt.Println("连接失败!err:", err)
return
// 获取collection
detection_coll := Client.Database("test").Collection("user")
userInfo := User
Name: "jeff002",
Age: 20,
objectID, err := InsertOne(detection_coll, userInfo)
if err != nil
fmt.Println(err)
return
fmt.Println(objectID)
6.4 InsertMany-批量插入1
//批量插入
func InsertMany(detection_coll *mongo.Collection, infolist []interface) (count int, err error)
objId, err := detection_coll.InsertMany(context.TODO(), infolist)
if err != nil
return 0, err
return len(objId.InsertedIDs), nil
func main()
url := "mongodb://admin:123456@127.0.0.1:27017"
//初始化
if err := initMongo(url); err != nil
fmt.Println("连接失败!err:", err)
return
// 获取collection
detection_coll := Client.Database("test").Collection("user")
userInfo1 := User
Name: "jeff001",
Age: 20,
userInfo2 := User
Name: "jeff002",
Age: 20,
userList := []UseruserInfo1, userInfo2
list := []interface
bStr, _ := json.Marshal(userList)
_ = json.Unmarshal(bStr, &list)
count, err := InsertMany(detection_coll, list)
if err != nil
fmt.Println(err)
return
fmt.Println(count)
6.5 BulkWrite-批量插入2
//批量插入
func batchSave(detection_coll *mongo.Collection, models []mongo.WriteModel) (insertedCount int64, err error)
opts := options.BulkWrite().SetOrdered(false)
res, err := detection_coll.BulkWrite(context.TODO(), models, opts)
if err != nil
return 0, err
return res.InsertedCount, nil
type User struct
Age int `json:"age"`
Name string `json:"name"`
func main()
url := "mongodb://admin:123456@127.0.0.1:27017"
//初始化
if err := initMongo(url); err != nil
fmt.Println("连接失败!err:", err)
return
// 获取collection
detection_coll := Client.Database("test").Collection("user")
userInfo1 := User
Name: "jeff003",
Age: 20,
userInfo2 := User
Name: "jeff004",
Age: 20,
models := []mongo.WriteModel
mongo.NewInsertOneModel().SetDocument(userInfo1),
mongo.NewInsertOneModel().SetDocument(userInfo2),
count, err := batchSave(detection_coll, models)
if err != nil
fmt.Println(err)
return
fmt.Println(count)
6.6 UpdateMany-批量更新
//批量更新
func updateMany(detection_coll *mongo.Collection, filter, updateData interface) (matchedCount, modifiedCount int64, err error)
result, err := detection_coll.UpdateMany(context.TODO(), filter, updateData)
if err != nil
return 0, 0, err
//matchedCount匹配数
//modifiedCount修改数
return result.MatchedCount, result.ModifiedCount, nil
func main()
url := "mongodb://admin:123456@127.0.0.1:27017"
//初始化
if err := initMongo(url); err != nil
fmt.Println("连接失败!err:", err)
return
// 获取collection
detection_coll := Client.Database("test").Collection("user")
detectionIds := []string"jeff001", "jeff002"
filter := bson.DKey: "name", Value: bson.DKey: "$in", Value: detectionIds
// filter := bson.DKey: "name", Value: "jeff001" //条件
update := bson.D
Key: "$set", Value: bson.D
Key: "age", Value: 89,
,
matchedCount, modifiedCount, err := updateMany(detection_coll, filter, update)
if err != nil
fmt.Println(err)
return
fmt.Println("匹配数:", matchedCount)
fmt.Println("修改数:", modifiedCount)
6.7 DeleteOne-删除一个
//删除一个
func deleteOne(detection_coll *mongo.Collection, filter interface) (deletedCount int64, err error)
result, err := detection_coll.DeleteOne(context.TODO(), filter)
if err != nil
return 0, err
return result.DeletedCount, nil
func main()
url := "mongodb://admin:123456@127.0.0.1:27017"
//初始化
if err := initMongo(url); err != nil
fmt.Println("连接失败!err:", err)
return
// 获取collection
detection_coll := Client.Database("test").Collection("user")
detectionIds := []string"jeff001", "jeff002"
filter := bson.DKey: "name", Value: bson.DKey: "$in", Value: detectionIds
deletedCount, err := deleteOne(detection_coll, filter)
if err != nil
fmt.Println(err)
return
fmt.Println("删除数量:", deletedCount)
6.8 DeleteMany-批量删除
//批量删除
func deleteOne(detection_coll *mongo.Collection, filter interface) (deletedCount int64, err error)
result, err := detection_coll.DeleteMany(context.TODO(), filter)
if err != nil
return 0, err
return result.DeletedCount, nil
func main()
url := "mongodb://admin:123456@127.0.0.1:27017"
//初始化
if err := initMongo(url); err != nil
fmt.Println("连接失败!err:", err)
return
// 获取collection
detection_coll := Client.Database("test").Collection("user")
detectionIds := []string"jeff001", "jeff002"
filter := bson.DKey: "name", Value: bson.DKey: "$in", Value: detectionIds
deletedCount, err := deleteOne(detection_coll, filter)
if err != nil
fmt.Println(err)
return
fmt.Println("删除数量:", deletedCount)
MongoDB——MongoDB安装+增删改查操作
MongoDB安装+MongoDB安装+增删改查操作
MongoDB相关概念
- 业务应用场景
- 传统的关系型数据库(如MySQL),在数据操作的
三高需求以及应对Web2.0的网站需求面前,显得力不从心。 - 解释
三高需求High performance对数据库高并发读写的需求Huge Storage对海量数据的高效率存储和访问的需求High Scalability && High Availability对数据库的高可扩展性和高可用性的需求
- 而MongoDB可应对三高需求
- 具体的应用场景如:
- 社交场景,使用MongoDB存储存储用户信息,以及用户发表的朋友圈信息,通过地理位置索引实现附近的人、地点等功能
- 游戏场景,使用MongoDB存储游戏用户信息,用户的装备、积分等直接以内嵌文档的形式存储,方便查询、高效率存储和访问
- 物流场景,使用MongoDB存储订单信息,订单状态在运送过程中会不断更新,以MongoDB内嵌数组的形式来存储,一次查询就能将订单所有的变更读取出来
- 5)视频直播,使用MongoDB存储用户信息、点赞互动信息等
- 具体的应用场景如:
- 这些应用场景中,数据操作方面的共同特点是:
- 数据量大
- 写入操作频繁(读写都很频繁)
- 价值较低的数据,对事务性要求不高
- 对于这样的数据,我们更适合使用MongoDB来实现数据的存储
- 传统的关系型数据库(如MySQL),在数据操作的
MongoDB简介
- MongoDB是一个开源、高性能、无模式的文档型数据库,当初的设计就是用于简化开发和方便扩展,是NoSQL数据库产品中的一种。是最像关系型数据库(MySQL)的非关系型数据库
- 它支持的数据结构非常松散,是一种类似于JSON的格式叫BSON,所以它既可以存储比较复杂的数据类型,又相当的灵活。
- MongoDB中的记录是一个文档,它是一个由字段和值对(field:value)组成的数据结构。MongoDB文档类似于JSON对象,即一个文档认为就是一个对象。字段的数据类型是字符型,它的值除了使用基本的一些类型外,还可以包括其他文档、普通数组和文档数组。
体系结构
- MySQL和MongoDB对比
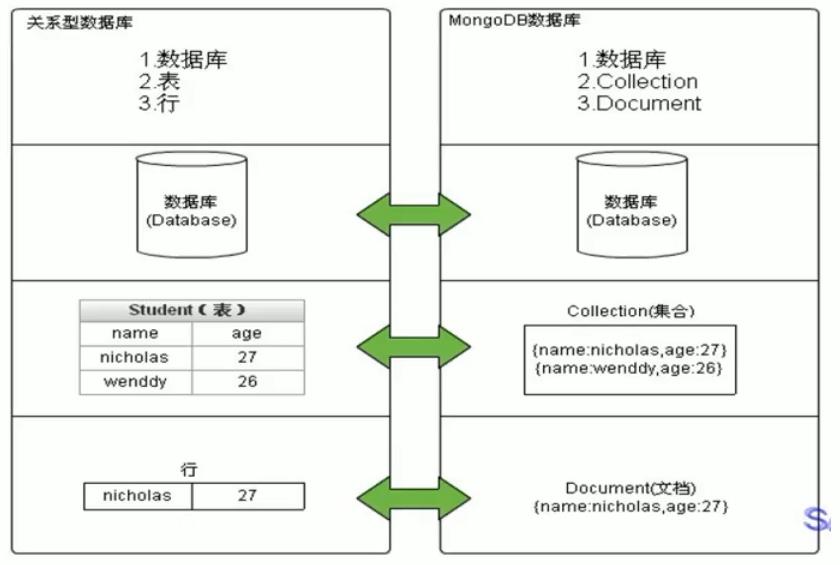
| SQL术语/概念 | MongoDB术语/概念 | 解释/说明 |
|---|---|---|
| database | database | 数据库 |
| table | collection | 数据库表/集合 |
| row | document | 数据记录行/文档 |
| column | field | 数据字段/域 |
| index | index | 索引 |
| table joins | 表连接,MongoDB不支持 | |
| 嵌入文档 | MongoDB通过嵌入式文档来替代多表连接 | |
| primary key | primary key | 主键,MongoDB自动将_id字段设置为主键 |
数据类型
- MongoDB的最小存储单位就是文档(document)对象。文档(document)对象对应于关系型数据库的行。数据在MongoDB中以BSON (Binary-JSON)文档的格式存储在磁盘上。
- BSON (Binary Serialized Document Format)是一种类json的一种二进制形式的存储格式,简称Binary ]SON.BSON和JSON一样,支持内嵌的文档对象和数组对象,但是BSON有JSON没有的一些数据类型,如Date和BinData类型。
- BSON采用了类似于C语言结构体的名称、对表示方法,支持内嵌的文档对象和数组对象,具有轻量性、可遍历性、高效性的三个特点,可以有效描述非结构化数据和结构化数据。这种格式的优点是灵活性高,但它的缺点是空间利用率不是很理想。
- Bson中,除了基本的JSON类型: string,integer,boolean,double,null,array和object,mongo还使用了特殊的数据类型。这些类型包括date,object id,binary data,regular expression和code。每一个驱动都以特定语言的方式实现了这些类型,查看你的驱动的文档来获取详细信息。
BSON数据类型参考列表
| 数据类型 | 描述 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|
| 字符串 | UTF-8字符串都可表示为字符串类型的数据 | “×”: “foobar” |
| 对象ID | 对象id是文档的12字节的唯一ID | “x”:Objectld() |
| 布尔值 | 真或者假:true或者false | “x”:true+ |
| 数组 | 值的集合或者列表可以表示成数组 | “x” :[“a”,“b”,“c”] |
| 32位整数 | 类型不可用。JavaScript仅支持64位浮点数,所以32位整数会被自动转换 | shell是不支持该类型的,shell中默认会转换成64位浮点数 |
| 64位整数 | 不支持这个类型。shell会使用一个特殊的内嵌文档来显示64位整数 | shell是不支持该类型的,shell中默认会转换成64位浮点数 |
| 64位浮点数 | shell中的数字就是这一种类型 | “x”:3.14159,“y”:3 |
| null | 表示空值或者未定义的对象 | “x”:null |
| undefined | 文档中也可以使用未定义类型 | “x”:undefined |
| 符号 | shell不支持,shell会将数据库中的符号类型的数据自动转换成字符串 | |
| 正则表达式 | 文档中可以包含正则表达式,采用JavaScript的正则表达式语法 | “x” : /foobar/i |
| 代码 | 文档中还可以包含JavaScript代码 | “x” : function() /* …… */ |
| 二进制数据 | 二进制数据可以由任意字节的串组成,不过shell中无法使用 | |
| 最大值/最小值 | BSON包括一个特殊类型,表示可能的最大值,shell中没有这个类型。 |
MongoDB数据类型
| 数据类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| String | 字符串。存储数据常用的数据类型。在MongoDB中,UTF-8编码的字符串才是合法的 |
| Integer | 整型数值。用于存储数值。根据你所采用的服务器,可分为32位或64位。 |
| Boolean | 布尔值。用于存储布尔值(真/假) |
| Double | 双精度浮点值。用于存储浮点值 |
| Min/Max keys | 将一个值与BSON(二进制的JSON)元素的最低值和最高值相对比。 |
| Arrays | 用于将数组或列表或多个值存储为—个键。 |
| Timestamp | 时间戳。记录文档修改或添加的具体时间。 |
| Object | 用于内嵌文档。 |
| Null | 用于创建空值。 |
| Symbol | 符号。该数据类型基本上等同于字符串类型,但不同的是,它一般用于采用特殊符号类型的语言。 |
| Date | 日期时间。用UNIX时间格式来存储当前日期或时间。你可以指定自己的日期时间:创建Date对象,传入年月日信息。 |
| Object ID | 对象ID。用于创建文档的 ID。 |
| Binary Data | 二进制数据。用于存储二进制数据。 |
| Code | 代码类型。用于在文档中存储JavaScript代码。 |
| Regular expression | 正则表达式类型。用于存储正则表达式。 |
MongoDB的特点
- MongoDB主要有如下特点:
- 高性能
- MongoDB提供高性能的数据持久性。特别是,对嵌入式数据模型的支持减少了数据库系统上的I/O活动。
- 索引支持更快的查询,并且可以包含来自嵌入式文档和数组的键。(文本索引解决搜索的需求、TTL索引解决历史数据自动过期的需求、地理位置索引可用于构建各种O20应用)
- mmapv1、wiredtiger、mongorocks (rocksdb) . in-memory等多引擎支持满足各种场景需求。
- Gridfs解决文件存储的需求。
- 高可用性
- MongoDB的复制工具称为副本集(replica set),它可提供自动故障转移和数据冗余。
- 高扩展性
- MongoDB提供了水平可扩展性作为其核心功能的一部分。
- 分片将数据分布在一组集群的机器上。(海量数据存储,服务能力水平扩展)
- 从
3.4开始,MongoDB支持基于片键创建数据区域。在一个平衡的集群中,MongoDB将一个区域所覆盖的读写只定向到该区域内的那些片。
- 丰富的查询支持
- MongoDB支持丰富的查询语言,支持读和写操作(CRUD),比如数据聚合、文本搜索和地理空间查询等。
- 其他特点
- 如无模式(动态模式)、灵活的文档模型、
- 高性能
MongoDB安装
#官网下载最新5.0.0安装包
[root@mongodb ~]# wget https://fastdl.mongodb.org/linux/mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel70-5.0.0.tgz
#解压至指定目录中
[root@mongodb ~]# tar xf mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel70-5.0.0.tgz -C /usr/local/
[root@mongodb ~]# mv /usr/local/mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel70-5.0.0/ /usr/local/mongodb
#创建数据/日志目录
[root@mongodb ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/mongodb/data/db
[root@mongodb ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/mongodb/logs
[root@mongodb ~]# touch /usr/local/mongodb/logs/mongodb.log
[root@mongodb ~]# chmod -R 777 /usr/local/mongodb/logs/mongodb.log
#新建并修改配置文件
[root@mongodb ~]# vim /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongodb.conf
systemLog:
#MongoDB发送所有日志输出的目标指定为文件
destination: file
#Mongod或Mongos应向其发送所有诊断日志记录信息的日志文件的路径
path: "/usr/local/mongodb/logs/mongodb.log"
#当Mongos或mongod实例重新启动时,mongos或mongod会将新条目追加到现有日志文件的>末尾
logAppend: true
storage:
#Mongod实例存储其数据的目录,storage.dbPath设置仅适用于Mongod
dbPath: "/usr/local/mongodb/data/db"
journal:
#启用或禁用持久性日志以确保数据文件保持有效和可恢复
enabled: true
processManagement:
#启用在后台运行Mongos或Mongod进程的守护进程模式
fork: true
net:
#服务实例绑定的IP,默认是localhost
bindIp: localhost,192.168.100.10
#绑定的端口,默认是27017
port: 27017
设置内核参数
- 由于mongodb首先自带大页内存,如果要更改数据库配置文件而不出错,需要关闭大页内存
#临时生效
echo 0 > /proc/sys/vm/zone_reclaim_mode #当某个节点可用内存不足时,系统会从其他节点分配内存。
echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled #关闭大页内存
echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag #关闭大页内存
#永久生效
vim /etc/rc.local
echo 0 > /proc/sys/vm/zone_reclaim_mode
echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag
sh /etc/rc.local #使配置生效
添加环境变量
[root@mongodb ~]# vim /etc/profile
export MONGODB_HOME=/usr/local/mongodb
export PATH=$PATH:$MONGODB_HOME/bin
[root@mongodb ~]# source /etc/profile
启动MongoDB
#通过配置文件启动MongoDB
[root@mongodb ~]# mongod -f /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongodb.conf
[root@mongodb ~]# ps -ef | grep -v grep | grep mongodb
root 1297 1 2 00:36 ? 00:00:02 mongod -f /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongodb.conf
[root@mongodb ~]# ss -lnt
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:27017 *:*
#通过配置文件停止MongoDB
[root@mongodb ~]# mongod -f /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongodb.conf --shutdown
[root@mongodb ~]# curl http://localhost:27017
It looks like you are trying to access MongoDB over HTTP on the native driver port. #代表安装成功
启动Mongodb多进程
- 在单台服务器资源充分的情况下,可以使用多实例,以便充分使用服务器资源
[root@mongodb ~]# cp /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongodb.conf /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongodb1.conf
[root@mongodb ~]# vim /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongodb1.conf
systemLog:
#MongoDB发送所有日志输出的目标指定为文件
destination: file
#Mongod或Mongos应向其发送所有诊断日志记录信息的日志文件的路径
path: "/usr/local/mongodb/logs/mongodb1.log"
#当Mongos或mongod实例重新启动时,mongos或mongod会将新条目追加到现有日志文件的末尾
logAppend: true
storage:
#Mongod实例存储其数据的目录,storage.dbPath设置仅适用于Mongod
dbPath: "/usr/local/mongodb/data/db1"
journal:
#启用或禁用持久性日志以确保数据文件保持有效和可恢复
enabled: true
processManagement:
#启用在后台运行Mongos或Mongod进程的守护进程模式
fork: true
net:
#服务实例绑定的IP,默认是localhost
#bindIp: localhost,192.168.100.10
#绑定的端口,默认是27017
port: 27018
[root@mongodb ~]# touch /usr/local/mongodb/logs/mongodb1.log
[root@mongodb ~]# mkdir /usr/local/mongodb/data/db1
[root@mongodb ~]# chmod 777 /usr/local/mongodb/logs/mongodb1.log
#启动MongoDB
[root@mongodb ~]# mongod -f /usr/local/mongodb/bin/mongodb1.conf
#开启了两个进程
[root@mongodb ~]# ss -lnt
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:27017 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:27018 *:*
关闭MongoDB
- 前台启动关闭
使用 Ctrl + c 即可关闭
- 后台启动关闭
使用 --shutdown 参数即可关闭
#命令启动方式关闭
[root@mongodb mongodb]# bin/mongod --dbpath /usr/local/mongodb/data/db/ --logpath /usr/local/mongodb/logs/mongodb.log --logappend --port 27017 --bind_ip 0.0.0.0 --fork --shutdown
#配置文件启动方式的关闭
[root@mongodb mongodb]# bin/mongod -f bin/mongodb.conf --shutdown
- kill命令关闭
通过 kill -9 的方式强制关闭进程,一般这种方式不怎么推荐
#查看MongoDB运行的进程信息
ps -ef | grep -v grep | grep mongodb
#kill -9 强制关闭
kill -9 pid
- MongoDB函数关闭
连接到MongoDB服务后,切换到 admin 数据库,并使用相关函数关闭服务
#连接MongoDB
bin/mongo
#切换 admin 数据库
use admin
#执行以下函数(2选1)即可关闭服务
db.shutdownServer()
db.runCommand("shutdown")
基本常用命令
选择和创建数据库
- 选择和创建数据库
use 数据库名称
- 如果数据库不存在则自动创建,例如,以下语句创建
pakho数据库
use pakho
- 查看有权限查看的所有的数据库命令
show dbs
或
show databases
注意:在MongoDB中,集合只有在内容插入后才会创建! 就是说创建集合(数据表)后要再插入一个文档(记录),集合才会真正创建。
- 查看当前正在使用的数据库命令
db
MongoDB中默认的数据库为test,如果你没有选择数据库,集合将存放在test数据库中
- 数据库名可以是满足以下条件的任意UTF-8字符串
- 不能是空字符串(" ")
- 不得含有
''(空格) 、.、$、/、\\和0(空字符) - 应全部小写
- 最多64字节
- 有一些数据库名是保留的,可以直接访问这些有特殊作用的数据库
admin:从权限的角度来看,这是"root"数据库。要是将一个用户添加到这个数据库,这个用户自动继承所有数据库的权限。一些特定的服务器端命令也只能从这个数据库运行,比如列出所有的数据库或者关闭服务器local:这个数据永远不会被复制,可以用来存储限于本地单台服务器的任意集合config:当Mongo用于分片设置时,config数据库在内部使用,用于保存分片的相关信息。
数据库的删除
- MongoDB删除数据库的语法格式如下
- 提示:主要用来删除已经持久化的数据库
db.dropDatabase()
集合操作
- 集合,类似关系型数据库中的表
- 可以显示的创建,也可以隐式的创建
集合的显示创建(了解)
- 基本语法格式
db.createCollection("name")
- 参数说明
- name:要创建的集合名称
- 例如:创建一个名为
shabi的普通集合
> db.createCollection("shabi")
"ok" : 1
- 查看当前库中的表:
show tables命令
> show collections
shabi
> show tables
shabi
集合的隐式创建
- 当向一个集合中插入一个文档的时候,如果集合不存在,则会自动创建集合
集合的删除
- 集合删除语法格式如下
db.collection.drop()
或
db.集合.drop()
- 返回值
- 如果成功删除选定集合,则drop()方法返回
true,否则返回false - 例如:要删除
shabi集合
- 如果成功删除选定集合,则drop()方法返回
> db.shabi.drop()
true
文档基本CRUD
- 文档(document)的数据结构和JSON基本—样。
- 所有存储在集合中的数据都是BSON格式。
文档的插入
单个文档插入
- 使用
insert()或save()方法向集合中插入文档,语法如下:
db.collection.insert(
<document or array of documents>,
writeConcern: <document>,
ordered: <boolean>
)
- 参数说明
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
document | document or array | 要插入到集合中的文档或文档数组(json格式) |
writeConcern 插入时的性能级别 | document | Optional. A document expressing the write concern. Omit to use thedefault write concern. See Write Concern.Do not explicitly set the writeconcern for the operation if run in a transaction.To use write concernwith transactions, see Transactions and Write Concern. |
ordered是否排序 | boolean | 可选,如果为真,则按顺序插入数组中的文档,如果其中一个文档出现错误,MongoDB将返回而不处理数组中的其余文档。如果为假,则执行无序插入,如果其中—个文档出现错误,则继续处理数组中的主文档,在版本2.6+中默认为true |
- 向
comment的集合(表)中插入一条测试数据:
> db.comment.insert('articleid':'100','content':'你多少脑子不好使','userid':'200','createdatetime':new Date(),'likenum':NumberInt(10),'state':null)
- comment集合如果不存在,则会隐式创建
- mongo中的数字,默认情况下是double类型,如果要存整型,必须使用函数NumberInt(整型数字否则取出来就有问题了
- 插入当前日期使用
new Date() - 插入的数据没有指定
_id,会自动生成主键值 - 如果某字段没值,可以赋值为
null,或不写该字段
- 执行后,如下,说明插入一个数据成功了
WriteResult( "nInserted" : 1 )
批量插入
- 语法如下
db.collection.insertMany(
[ <document 1> , <document 2>, ... ],
writeConcern: <document>,
ordered: <boolean>
)
- 参数说明
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
document | document | 要插入到集合中的文档或文栏数组。((json格式) |
writeConcern | document | Optional. A document expressing the write concern. Omit to use thedefault write concern. See Write Concern.Do not explicitly set the writeconcern for the operation if run in a transaction.To use write concernwith transactions, see Transactions and Write Concern. |
ordered | boolean | 可选。一个布尔值,指定Mongod实例应执行有序插入还是无序插入。默认为true。 |
- 批量插入多条文章评论
db.comment.insertMany([ "_id":"1","articleid":"100001","content":"我们不应该把清晨浪费在手机上,健康很重要,一杯温水幸福你我他","userid":"1002","createdatetime":new Date("2020-08- 05T22:08:15.522Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(1000),"state":"1",
"_id":"2","articleid":"100001","content":"我夏天空腹喝凉白开,冬天喝温开水","userid":"1005","createdatetime":new Date("2020-08-05T23:58:51.485Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(888),"state":"1",
"_id":"3","articleid":"100001","content":"我一直喝凉开水,冬天夏天都喝。","userid":"1004","createdatetime":new Date("2020-08-06T01:05:06.321Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(666),"state":"1",
"_id":"4","articleid":"100001","content":"专家说不能空腹吃饭,影响健康。","userid":"1003","createdatetime":new Date("2020-08-06T08:18:35.288Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(2000),"state":"1",
"_id":"5","articleid":"100001","content":"研究表明,刚烧开的水千万不能喝,因为烫嘴","userid":"1003","createdatetime":new Date("2020-08-06T11:01:02.521Z"),"likenum":NumberInt(3000),"state":"1" ]);
"acknowledged" : true,
"insertedIds" : [
"1",
"2",
"3",
"4",
"5"
]
文档的基本查询
- 查询数据的语法格式如下:
db.co1lection.find(<query>,[projection])
- 参数
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
query | document | 可选,使用查询运算符指定选择筛选器,若要返回集合中的所有文档,请省略此参数或传递空文档() |
projection | document | 可选,指定要在与查询筛选器匹配的文档中返回的字段(投影),若要返回匹配文档中的所有字段,请省略此参数 |
查询所有
- 如果我们要查询
spit集合的所有文档,我们可以输入以下命令
db.comment.find()
或
db.comment.find()
- 这里你会发现每条文档会有一个叫_id的字段,这个相当于我们原来关系数据库中表的主键,当你在插入文档记录时没有指定该字段,MongoDB会自动创建,其类型是ObjectID类型
- 如果我们在插入文档记录时指定该字段也可以,其类型可以是ObjectID类型,也可以是MongoDB支持的任意类型
- 如果我想按一定条件来查询,比如我想查询userid为1003的记录,怎么办?很简单!只要在
find()中添加参数即可,参数也是json格式,如下:
db.comment.find(userid:'1003')
- 如果你只需要返回符合条件的第一条数据,我们可以使用
findOne命令来实现,语法和find一样 - 如:查询用户编号是1003的记录,但只最多返回符合条件的第一条记录:
db.comment.findOne(userid:'1003')
投影查询
- 如果要查询结果返回部分字段,则需要使用投影查询(不显示所有字段,只显示指定的字段)
- 如:查询结果只显示
_id、userid、nickname
db.comment.find(articleid:"100001",articleid:1,_id:0)
文档的更新
- 更新文档的语法:
db.collection.update(query, update, options)
#或
db.collection.update(
<query>,
<update>,
upsert: <boolean>,
multi: <boolean>,
writeConcern: <document>,
collation: <document>,
arrayFilters:
[ <filterdocument1>, ... ],
hint: <document|string> #Available starting in MongoDB 4.2
)
覆盖修改
- 如果我们想修改
_id为1的记录,点赞量为1001,输入以下语句:- 执行后,我们会发现,这条文档除了likenum字段其它字段都不见了
db.comment.update(_id:"1",likenum:NumberInt(1001))
局部修改
- 为了解决这个问题,我们需要使用修改器
$set来实现,命令如下 - 我们想修改_id为2的记录,浏览量为889,输入以下语句:
db.comment.update(_id:"2",$set:likenum:NumberInt(889))
批量修改
- 更新所有用户为1003的用户的昵称为凯撒大帝
- 提示:如果不加后面的参数,则只更新符合条件的第一条记录
#默认只修改第一条数据
db.comment.update(userid:"1003",$set:nikename:"凯撒2")
#修改所有符合条件的数据
db.comment.update(userid:"1003",$set:nikename:"凯撒大帝",multi:teue)
列值增长的修改
- 如果我们想实现对某列值在原有值的基础上进行增加或减少,可以使用
$inc运算符来实现- 需求:对3号数据的点赞数,每次递增1
db.comment.update(_id:"3",$inc:likenum:NumberInt(1))
删除文档
- 删除文档的语法结构:
db.集合名称.remove(条件)
- 以下语句可以将数据全部删除,请慎用
db.comment.remove()
- 如果删除_id=1的记录,输入以下语句
db.comment.remove(_id:"1")
文档的分页查询
统计查询
- 统计查询使用
count()方法,语法如下:
db.collection.count(query,options)
- 参数
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
query | document | 查询选择条件 |
option | document | 可选,用于修改计数的额外选项 |
- 统计所有记录数:
- 统计comment集合的所有的记录数
db.comment.count()
- 按条件统计记录数
- 例如:统计userid为1003的记录条数
db.comment.count(userid:"1003")
- 默认情况下
count()方法返回符合条件的全部记录条数
分页列表查询
- 可以使用
limit()方法来读取指定数量的数据,使用skip()方法来跳过指定数量的数据 - 基本语法如下所示:
db.collection_name.find().limit(number).skip(number)
- 如果你想返回指定条数的记录,可以在
find方法后调用limit来返回结果(TopN),默认值20,例如:
db.comment.find().limit(3)
skip方法同样接受一个数字参数作为跳过的记录条数,(前N个不要),默认值是0
db.comment.find().skip(3)
排序查询
sort()方法对数据进行排序,sort()方法可以通过参数指定排序的字段,并使用1和-1来指定排序的方式,其中1为升序排列,而-1是用于降序排列- 语法格式如下:
db.collection_name.find().sort(key:1)
或
db.集合名称.find().sort(排序方式)
- 例如:
- 对
userid降序排列,并对访问量进行升序排列
- 对
db.comment.find().sort(userid:-1,likenum:1)
文档的更多查询
正则的复杂条件查询
- MongoDB的模糊查询是通过正则表达式的方式实现的。格式为:
db.collection.find(field:/正则表达式/)
或
db.集合.find(字段:/正则表达式/)
- 正则表达式是js的语法,直接量的写法
- 例如,要查询评论内容包含 “开水” 的所有文档,代码如下:
db.comment.find(content:/开水/)
- 如果要查询评论内容中以 “专家” 开头的,代码如下:
db.comment.find(content:/^专家/)
比较查询
<<=>>=这个操作符也是很常用的
db.集合名称.find( "field" : $gt: value ) // 大于: field > value
db.集合名称.find( "field" : $lt: value ) // 小于: field < value
db.集合名称.find( "field" : $gte: value ) // 大于等于: field >= value
db.集合名称.find( "field" : $lte: value ) // 小于等于: field <= value
db.集合名称.find( "field" : $ne: value ) // 不等于: field != value
- 查询评论点赞数量大于700的记录
db.comment.find(likenum:$gt:NumberInt(700))
包含查询
- 包含使用
$in操作符 - 示例:查询评论的集合中userid字段包含1003或1004的文档
db.comment.find(userid:$in:["1003","1004"])
- 不包含使用
$nin操作符 - 示例:查询评论集合中userid字段不包含1003和1004的文档
db.comment.find(userid:$nin:["1003","1004"])
条件连接查询
- 我们如果需要查询同时满足两个以上条件,需要使用$and操作符将条件进行关联(相当于SQL的and)
- 格式为:
$and:[ , , 以上是关于mongoDB操作指南的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章