心灵鸡汤
- 做任何事情,首先要敢想,然后脚踏实地,找准方向。
- 先积淀,再沉淀
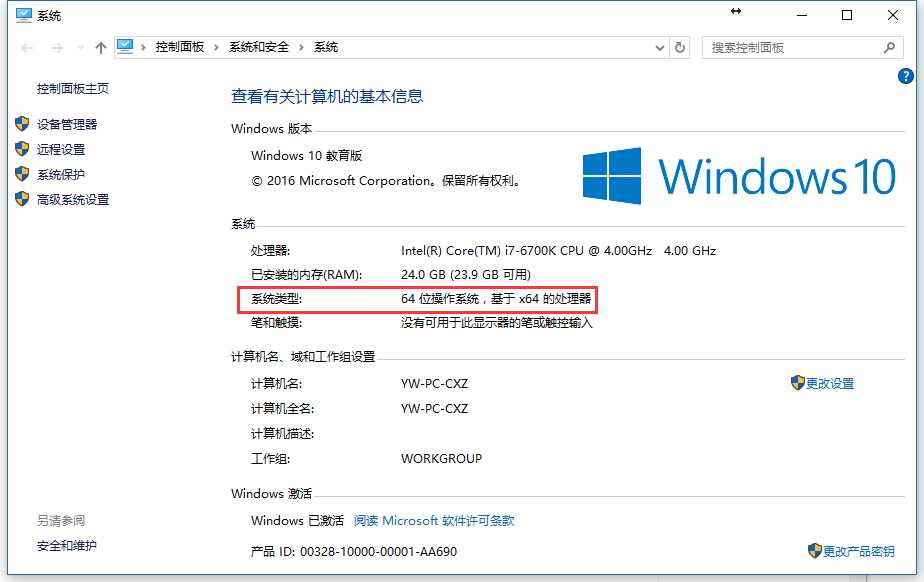
01-Python历史、32bit和64bit区别、系统运行机制浅析

第一、CPU要求不同——由于CPU分别有32位和64位,32位的CPU只支持安装32位系统,而64位的CPU可以同时支持32位系统以及64位系统。
第二、运算速度不同——64位CPU的指令集支持运行64位数据指令,相对来说64位系统比32位系统运行速度快2倍(理论上)。
第三、寻址能力不同——windows 32位操作系统最多能够支持4G内存;而64位系统支持128G++内存
第四、软件兼容性不同——X86代表32位,X64代表64位,以前32位兼容性比64位好,如今,64位系统和32位的兼容性感觉相差无几了,但是遗憾的是,一些32位的软件在64位系统无法运行
02-Python版本的选择
Python发展史
- 1989年,为了打发圣诞节假期,Guido开始写Python语言的编译器。Python这个名字,来自Guido所挚爱的电视剧Monty Python’s Flying Circus。他希望这个新的叫做Python的语言,能符合他的理想:创造一种C和shell之间,功能全面,易学易用,可拓展的语言。
- 1991年,第一个Python编译器诞生。它是用C语言实现的,并能够调用C语言的库文件。从一出生,Python已经具有了:类,函数,异常处理,包含表和词典在内的核心数据类型,以及模块为基础的拓展系统。
- Granddaddy of Python web frameworks, Zope 1 was released in 1999
- Python 1.0 - January 1994 增加了 lambda, map, filter and reduce.
- Python 2.0 - October 16, 2000,加入了内存回收机制,构成了现在Python语言框架的基础
- Python 2.4 - November 30, 2004, 同年目前最流行的WEB框架Django 诞生
- Python 2.5 - September 19, 2006
- Python 2.6 - October 1, 2008
- Python 2.7 - July 3, 2010
- In November 2014, it was announced that Python 2.7 would be supported until 2020, and reaffirmed that there would be no 2.8 release as users were expected to move to Python 3.4+ as soon as possible
- Python 3.0 - December 3, 2008
- Python 3.1 - June 27, 2009
- Python 3.2 - February 20, 2011
- Python 3.3 - September 29, 2012
- Python 3.4 - March 16, 2014
- Python 3.5 - September 13, 2015
选择Py2.x还是Py3.x?
In summary : Python 2.x is legacy, Python 3.x is the present and future of the language
Python 3.0 was released in 2008. The final 2.x version 2.7 release came out in mid-2010, with a statement of
extended support for this end-of-life release. The 2.x branch will see no new major releases after that. 3.x is
under active development and has already seen over five years of stable releases, including version 3.3 in 2012,
3.4 in 2014, and 3.5 in 2015. This means that all recent standard library improvements, for example, are only
available by default in Python 3.x.
Guido van Rossum (the original creator of the Python language) decided to clean up Python 2.x properly, with less regard for backwards compatibility than is the case for new releases in the 2.x range. The most drastic improvement is the better Unicode support (with all text strings being Unicode by default) as well as saner bytes/Unicode separation.
Besides, several aspects of the core language (such as print and exec being statements, integers using floor division) have been adjusted to be easier for newcomers to learn and to be more consistent with the rest of the language, and old cruft has been removed (for example, all classes are now new-style, "range()" returns a memory efficient iterable, not a list as in 2.x).
So,选择Python3.x
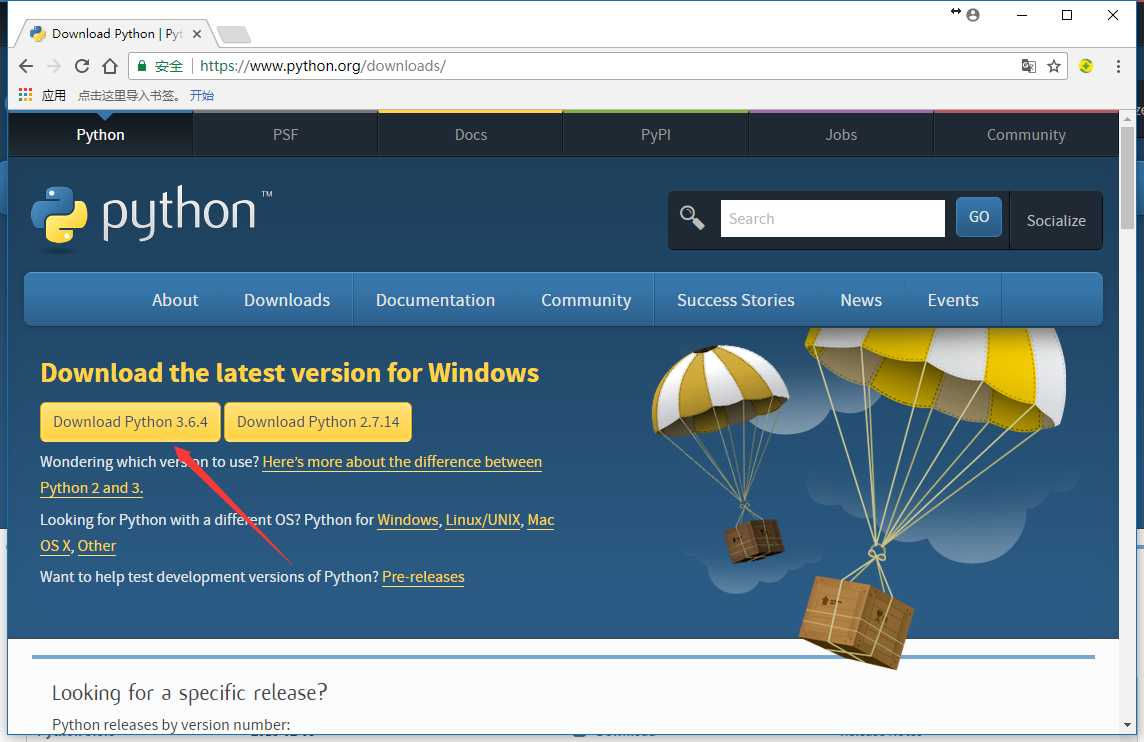
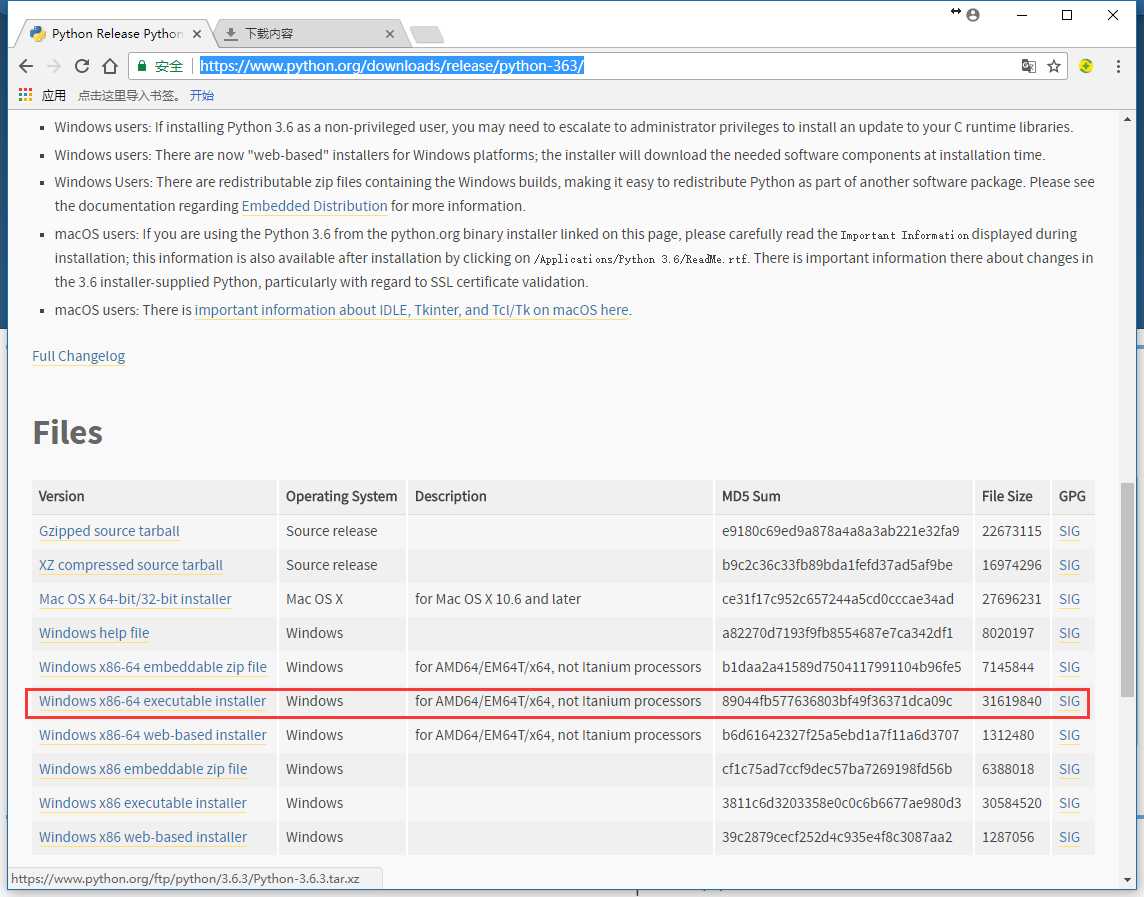
Python的安装
Python 官网:https://www.python.org/
03-第一个Python程序
1 print("Hello World!")
04-文件后缀及环境变量介绍
Windows系统文件按照不同的格式和用途分很多种类,为便于管理和识别,在对文件命名时,是以扩展名加以区分的,即文件名格式为: “主文件名.扩展名”。这样就可以根据文件的扩展名,判定文件的种类,从而知道其格式和用途。详情见百度百科https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%B8%B8%E7%94%A8%E6%96%87%E4%BB%B6%E6%89%A9%E5%B1%95%E5%90%8D/10227127
- 文档文件
- 压缩文件
- 图形文件
- 声音文件
- 动画文件
- 系统文件
- 可执行文件
- 语言文件
- 映像文件
- 备份文件
- 临时文件
- 模板文件
- 批处理文件
环境变量
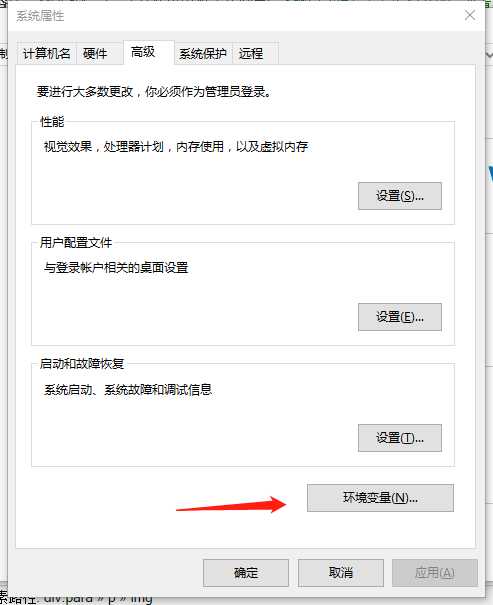
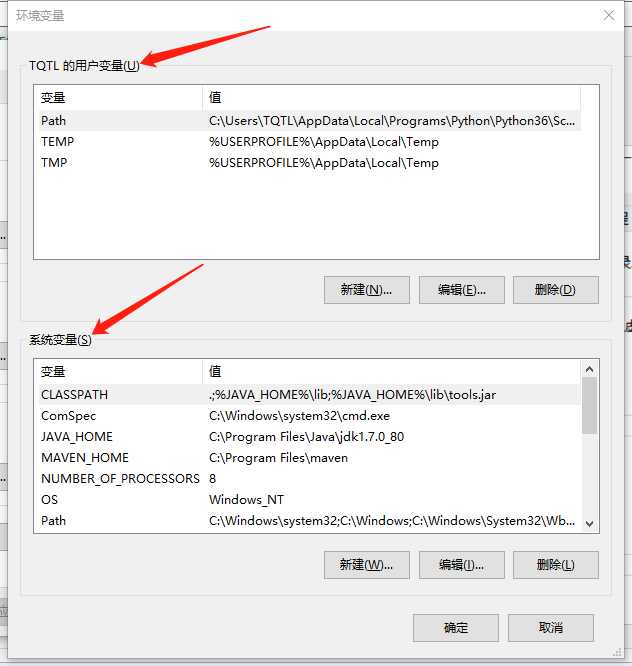
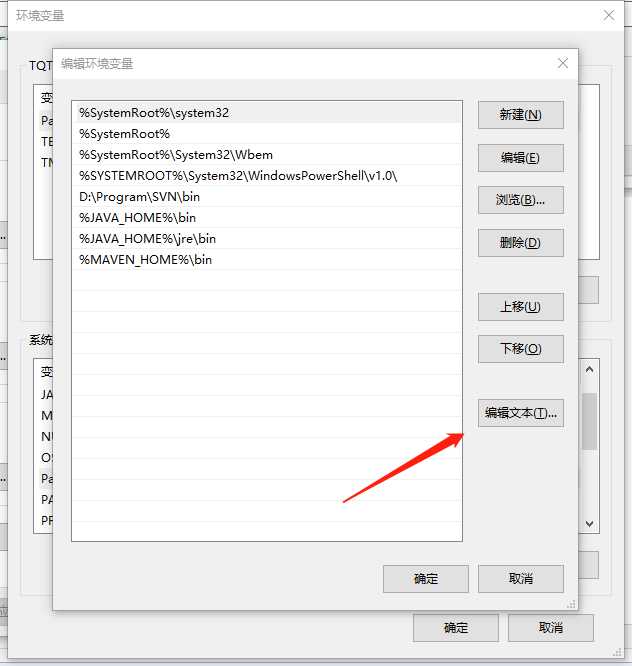
D:\\Program Files\\Python35\\Scripts\\;
D:\\ProgramFiles\\Python35\\;
%SystemRoot%\\system32;%SystemRoot%;%SystemRoot%\\System32\\Wbem;%SYSTEMROOT%\\System32\\WindowsPowerShell\\v1.0\\;
D:\\Program Files\\Python27
05-Python程序语言执行与其他编程语言的简单对比
对比下其它语言的hello world

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 int main(void) 3 { 4 printf("\\nhello world!"); 5 return 0; 6 }

1 #include <iostream> 2 int main(void) 3 { 4 std::cout<<"Hello world"; 5 }

1 public class HelloWorld{ 2 // 程序的入口 3 public static void main(String args[]){ 4 // 向控制台输出信息 5 System.out.println("Hello World!"); 6 } 7 }

1 <?php 2 echo "hello world!"; 3 ?>

1 puts "Hello world."

1 package main 2 3 import "fmt" 4 5 func main(){ 6 7 fmt.Printf("Hello World!\\n God Bless You!"); 8 9 }
06-变量详解
什么是变量?!
变量 是 为了存储 程序运算过程中的一些中间 结果,为了方便日后调用。
Variables are used to store information to be referenced and manipulatedin a computer program. They also provide a way of labeling data with a descriptive name, so our programs can be understood more clearly by the reader and ourselves. It is helpful to think of variables as containers that hold information. Their sole purpose is to label and store data in memory. This data can then be used throughout your program.
变量的命名规则
1. 要具有描述性,如name = "cuixiaozhao"
2. 变量名只能由数字,字母下划线组成,不可以是空格或特殊字符(#?<.,¥$*!~)
3. 不能以中文为变量名
4. 不能以数字开头
5. 关键字是不能被使用
以下关键字不能声明为变量名
[‘and‘, ‘as‘, ‘assert‘, ‘break‘, ‘class‘, ‘continue‘, ‘def‘, ‘del‘, ‘elif‘, ‘else‘, ‘except‘, ‘exec‘, ‘finally‘, ‘for‘, ‘from‘, ‘global‘, ‘if‘, ‘import‘, ‘in‘, ‘is‘, ‘lambda‘, ‘not‘, ‘or‘, ‘pass‘, ‘print‘, ‘raise‘, ‘return‘, ‘try‘, ‘while‘, ‘with‘, ‘yield‘]
07-变量的重新赋值01
1 #__author__:TQTL 2 #date: 2018/2/27 3 name = "cuixiaozhao" 4 name2 = name 5 print(name,name2) 6 name = "cuixiaosi" 7 print("What is the value of name2 now?") 8 print(name2)
08-变量的重新赋值02
内存何时回收?!
- Python自动回收内存
- 主动释放内存 del age
- 重新建立关系,如age = 28
09-编码部分历史及文件编码简介
Python解释器在加载 .py 文件中的代码时,会对内容进行编码(默认ascill),其中,ASCII(American Standard Code for Information Interchange,美国标准信息交换代码)是基于拉丁字母的一套电脑编码系统,主要用于显示现代英语和其他西欧语言,其最多只能用 8 位来表示(一个字节),即:2**8 = 256-1,所以,ASCII码最多只能表示 255 个符号。
编码发展历程:
- ASCII码表
- 1980年,GB2312
- 1995年,GBK1.0
- 2000年,GB18030
- 万国码,Unicode,支持所有国家和地区的编码
- UTF-8,Unicode的拓展集,可变长的字符编码集
Python2.X 默认编码为ASCII,Python3.x默认是utf-8
#!-*- coding:utf-8 -*-#默认格式,用于声明编码规则
#coding:utf-8
10-注释及简单的文件输入输出

1 #__author__:TQTL 2 #date: 2018/2/27 3 #注意哦,我在此处的作用是"单行注释" 4 name = "cuixiaozhao" 5 name2 = name 6 print(name,name2) 7 name = "cuixiaosi" 8 print("What is the value of name2 now?")#注意哦,我在此处的作用是给这句代码添加"单行注释" 9 print(name2) 10 ‘‘‘ 11 大家好。 12 2018,大家都有加油呀! 13 看到这里,告诉亲,这里面的内容都是"多行注释"! 14 ‘‘‘ 15 """ 16 大家好。 17 2018,大家都有加油呀! 18 看到这里,告诉亲,这里面的内容都是"多行注释"! 19 """

1 #__author__:TQTL 2 #date: 2018/2/27 3 name = input("Please input your name:") 4 print("Hello,"+ name+",欢迎进入Python的世界!")
11-IF语句实现猜年龄

1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 #__author__:TQTL 3 #date: 2018/1/31 4 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 5 true_name = 26#定义一个真实的年龄值 6 input_age = int(input("Please input your name:"))#获取用户输入的年龄值 7 if true_name == input_age:#对两个数值进行大小比较,并给出提示语。 8 print("Yes,you got it!") 9 elif true_name < input_age: 10 print("Your gess is bigger than true age.") 11 else: 12 print("Your gess is smaller than true age.")
12-缩进介绍
Python语言,特点:简单、优雅、明确,所以使用“缩进”代替花括号{}。严格按照缩进进行编码。

1 count = 0 2 while count <3: 3 true_name = 26 4 input_age = int(input("Please input your age:")) 5 if true_name == input_age: 6 print("Yes,you got it!") 7 elif true_name < input_age: 8 print("Your gess is bigger than true age.") 9 else: 10 print("Your gess is smaller than true age.") 11 count +=1 12 else: 13 print("真是个笨蛋!")
13-多分支if语句及作业

1 #__author__:TQTL 2 #date: 2018/2/27 3 socre = 90 4 grade = int(input("Please input your grade:")) 5 if grade > 90: 6 print("A") 7 elif grade > 80: 8 print("B") 9 elif grade > 70: 10 print("C") 11 elif grade > 50: 12 print("D") 13 else: 14 print("滚!")
