Python 教程——String的内置方法
Posted tinanuaa
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python 教程——String的内置方法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Python为String类型提供了很多很有用的内置方法,这篇文章主要针对Python2.7的内置方法做一个测试列举,展示一下用途。
如果大家想看原版的,可以去这个网址看(https://docs.python.org/2/library/stdtypes.html#string-methods),但是这里是我自己的实践以及一些理解。
1. str.capitalize()
返回第一个字母大写的str
str = "a string" str.capitalize()
\'A string\'
2.str.center(width[, fillchar])
返回一个width宽的string,其中str居中显示,如果有多余的字符,则以fillchar来填充,若没有指定fillchar,则默认使用空格。这个方法主要的功能在于输出一致长度的内容,这边举一个小的应用:
icon = "*" for i in range(1,11,2): if i<=5: out = icon * i else: out = icon print out.center(5)
执行上述代码,则会输出如下的一颗树:

3. str.count(sub[, start[, end]])
返回sub在str内部从start到end为止(不包括end),不重叠出现的次数
a= "abcdefabcdabcccccc" a.count("a") 3 a.count("c",0,12) 2 a="aaaaaaaaaa" a.count("aa") 5
4.str.decode([encoding[, errors]])
在Python中,从Unicode转为其他编码方式成为encode,反之成为decode。所以这个方法返回将用encoding编码的str恢复为unicode,输出是一个unicode的字符串。errors是对于解码过程中出错时候的处理方式,主要有以下几种

5.str.encode([encoding[, errors]])
将str用encoding的编码方式转为字符串。errors和上述表格一致。
现在将4,5 这两个方法结合在一起展示一个例子:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 3 a = "中文" 4 #a.decode("utf-8") 5 a = a.decode("utf-8") 6 #a = a.decode() 7 print a 8 a.encode("utf-8") 9 print a
代码第一行:在python源码中如果使用了中文字符,运行时会有错误,解决的办法是在源码的开头部分加入字符编码的声明,在自带的编辑器内如果不加的话在会出现如下的报错弹出框:
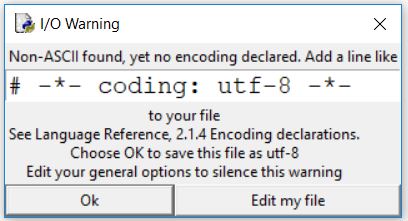
第5行指定了encoding的参数为"utf-8", 则print a的时候可以正常输出中文两个字,如果是第6行这样不指定的,使用的是默认的编码方式,在Python2的自带编辑器内,是ASCII。那么ASCII是无法编码中文的,所以运行时在shell内会输出报错,第8行将unicode又重新编码回普通的string,输出中文两个字。
关于Python中的编码解码问题可以看一下这个链接:https://my.oschina.net/leejun2005/blog/74430
6.str.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]])
判断 str是不是以suffix结尾,start和end指定开始和结尾,不包括end所在的字符。suffix可以是一个tuple,包含多个suffix
a = "abcbcb##" print a.endswith("#") print a.endswith("#",0,-3)
输出
True
False
7.str.expandtabs([tabsize])
根据指定的tabsize来扩展str中的tab,tabsize的默认值是8
这边引用一个stack overflow(https://stackoverflow.com/questions/34546171/python-expandtabs-string-operation)上的一段代码来作为例子:
>>> str = "this is\\tstring" >>> print str.expandtabs(0) this isstring >>> print str.expandtabs(1) this is string >>> print str.expandtabs(2) this is string >>> print str.expandtabs(3) this is string >>> print str.expandtabs(4) this is string >>> print str.expandtabs(5) this is string >>> print str.expandtabs(6) this is string >>> print str.expandtabs(7) this is string >>> print str.expandtabs(8) this is string >>> print str.expandtabs(9) this is string >>> print str.expandtabs(10) this is string >>> print str.expandtabs(11) this is string
8. str.find(sub[, start[, end]])
find 可以找到sub在str(start和end不包括end之间)内的index。如果要判断一个sub是不是在str中,用in
9. str.format(*args, **kwargs)
str中可以用{numeric},或者是{key} 来指代要被格式化的部分,然后在format中,用tuple或者是dict来给str中的那些部分赋值
>>> a = "this is a {0} made by {1}".format("test","tina") >>> a \'this is a test made by tina\' >>> a = "this is a {mode} made by {name}".format(mode = "test",name = "tina") >>> a \'this is a test made by tina\'
10. str.index(sub[, start[, end]])
和find一样,获取sub在str中的index,但是如果找不到的话,会raise valueError()
11. str.isalnum()
判断str是不是只包含数字或者字母,并且长度至少为1,如果是的话则返回True,否则False
>>> a= "123" >>> a.isalnum() True >>> a = "123abc" >>> a.isalnum() True >>> a = "abc" >>> a.isalnum() True >>> a = "" >>> a.isalnum() False >>> a = "+-^&*(123" >>> a.isalnum() False >>> a = "1" >>> a.isalnum() True >>> a = "a" >>> a.isalnum() True
12. str.isalpha()
如果str中只包含字母,并且长度大于1,则返回True,否则返回False
>>> a="" >>> a.isalpha() False >>> a="a" >>> a.isalpha() True >>> a = "1" >>> a.isalpha() False
13. str.isdigit()
判断str中是否只有数字并且长度大于等于1,是的话返回True,否则返回False
>>> a="" >>> a.isdigit() False >>> a="a" >>> a.isdigit() False >>> a = "1" >>> a.isdigit() True
14. str.islower()
如果str中全是小写字符并且str至少包含一个小写字母,则返回True,否则返回False
15. str.isspace()
如果str中全是空格并且str的长度大于等于1,则返回True,否则返回False
16. str.istitle()
如果str中的每个word都首字母大写而且str至少包含一个大写字母,则返回True,否则返回False
>>> a = "this is a test string" >>> a.istitle() False
17. str.isupper()
如果str中的字母都是大写,并且str中至少包含一个大写字母 ,则返回True,否则返回False
>>> a= "123" >>> a.isupper() False >>> a = "123A" >>> a.isupper() True >>> a="abc" >>> a.isupper() False
18. str.join(iterable)
iterable是一个序列的迭代器,如果这个序列包含了string和unicode之外的类型,则join会出错,如果序列中包含了unicode,则最后返回一个unicode。这个方法将序列中的每个元素用str来连接起来
>>> a = [1,2,3,4,5] >>> \',\'.join(a) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#93>", line 1, in <module> \',\'.join(a) TypeError: sequence item 0: expected string, int found >>> a = [\'a\',\'b\',\'c\'] >>> \',\'.join(a) \'a,b,c\'
19. str.ljust(width[, fillchar])
返回一个width长的string,其中str左对齐,剩余的位置用fillchar补齐,fillchar默认是空格。如果width<len(str) ,则返回str
>>> a = "if you know what i mean" >>> a.ljust(40,\'*\') \'if you know what i mean*****************\' >>> a.ljust(40) \'if you know what i mean \' >>> a.ljust(2) \'if you know what i mean\'
20. str.lower()
将str中的字母都换为小写字母再返回,数字无所谓大写小写,会保持不变
21. str.lstrip([chars])
从左边开始,将str中的chars的位置删除,直到遇到第一个不符合的位置为止,如果不提供chars,则删除空格。如果从左边开始的第一个字符不符合chars中的任何一个,则不会删除任何字符
>>> a = \' this is a test \' >>> a.lstrip() \'this is a test \' >>> a.lstrip(\'a\') \' this is a test \' >>> a.lstrip(\'t\') \' this is a test \' >>> a = \'www.example.com\' >>> a.lstrip(\'a\') \'www.example.com\' >>> a.lstrip(\'cmowz.\') \'example.com\'
22. str.partition(sep)
将str用sep分隔,并且返回一个包含三个元素的Tuple,即sep之前的部分,sep 和sep之后的部分; 如果在str中没有找到sep,则返回str和两个空的string组成的元组
23. str.replace(old, new[, count])
将str中old的部分用new来替换,如果count这个参数也提供了,那么只有前count个old会被替换
>>> a = "aaaaaaa" >>> a.replace(\'a\',\'t\') \'ttttttt\' >>> a.replace(\'a\',\'t\',3) \'tttaaaa\'
24. str.rfind(sub[, start[, end]])
返回str的start 和end(不包括end)之间包含了sub的最大的index,如果没找到则返回-1
25. str.rindex(sub[, start[, end]])
和rfind的功能一致,但是如果没有找到会报valueError的错
26. str.rjust(width[, fillchar])
返回一个width宽的string,其中str居右对齐,如果有多余的字符位置,则用fillchar补齐;如果width<len(str),则返回str。fillchar的默认值是一个空格
27. str.rpartition(sep)
将str在sep最后一次出现的位置分隔,并且返回一个包含三个元素的Tuple,即sep之前的部分,sep 和sep之后的部分; 如果在str中没有找到sep,则返回两个空的string和str组成的元组
28. str.rsplit([sep[, maxsplit]])
用sep作为分隔符分割str,返回一个包含分割之后各个词的list。如果sep没有提供,则用空格来分割。如果制定了maxsplit,则只有右侧的maxsplit个词被分割出来。和split的区别只有一个是从左,一个是从右。
>>> a = \'this.is a test.for the rsplit\' >>> a.rsplit(\' \') [\'this.is\', \'a\', \'test.for\', \'the\', \'rsplit\'] >>> a.rsplit(\' \',2) [\'this.is a test.for\', \'the\', \'rsplit\'] >>> a.rsplit(\' \',1) [\'this.is a test.for the\', \'rsplit\']
29. str.rstrip([chars])
从右边开始,将str中的chars的位置删除,直到遇到第一个不符合的位置为止,如果不提供chars,则删除空格。如果从右边开始的第一个字符不符合chars中的任何一个,则不会删除任何字符
30. str.split([sep[, maxsplit]])
用sep作为分隔符分割str,返回一个包含分割之后各个词的list。如果sep没有提供,则用空格来分割。如果制定了maxsplit,则只有左侧的maxsplit个词被分割出来。连续的spe不会作为一个sep来处理,而是当做sep之间是一个空的字符,如下所示
>>> a.split(\',\') [\'1\', \'\', \'2\']
sep可以包括多个字符,如‘<>’。如果sep没有指定的话,则用空格来作为分隔符,并且连续的空格被认定为一个,如下所示:
>>> a=\' \' >>> a.split() [] >>> a = \'this is a test code for split with whitespace\' >>> a.split() [\'this\', \'is\', \'a\', \'test\', \'code\', \'for\', \'split\', \'with\', \'whitespace\']
31. str.splitlines([keepends])
根据换行标志来分割string,\'\\r\' , \'\\n\', \'\\r\\n\' 是常用的换行符(boundaries)
>>> \'ab c\\n\\nde fg\\rkl\\r\\n\'.splitlines() [\'ab c\', \'\', \'de fg\', \'kl\'] >>> \'ab c\\n\\nde fg\\rkl\\r\\n\'.splitlines(True) [\'ab c\\n\', \'\\n\', \'de fg\\r\', \'kl\\r\\n\'] >>> "".splitlines() [] >>> "One line\\n".splitlines() [\'One line\'] >>> \'\'.split(\'\\n\') [\'\'] >>> \'Two lines\\n\'.split(\'\\n\') [\'Two lines\', \'\']
32. unicode.splitlines([keepends])
与上一个string的splitlines基本一致,除了unicode使用的换行符更多一些,如下表所示:
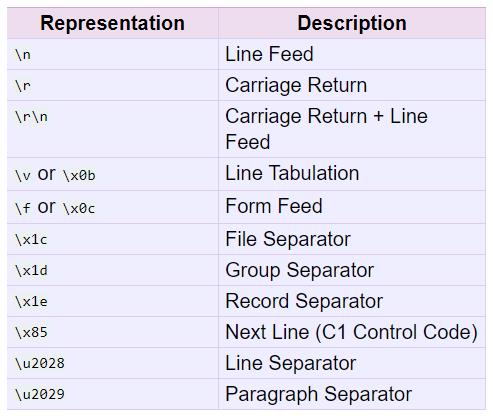
33. str.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]])
判断 str是不是以suffix开始,start和end指定开始和结尾,不包括end所在的字符。prefix可以是一个tuple,包含多个prefix
34. str.strip([chars])
删除str中包含的chars,如果chars没有提供,则删除str中的空格。chars可以是一个字符串,包含多个要删除的字符
35. str.swapcase()
将str中的大写字母和小写字母反转,即大写改小写,小写改大写
36. str.title()
将str转为title格式
>>> a = \'this is a title\' >>> a.title() \'This Is A Title\'
37. str.translate(table[, deletechars])
删除str中的deletechars,并且将剩余的字符用table的对应关系来对应为另一个字符。可以用maketrans来生成一个翻译的table,也可以指定为None,当这个table指定为None时,这个方法只是简单地执行删除字符的操作。
38. str.upper()
将str中的字符转为大写格式。需要注意一点,str.upper().isupper() 可能为False,比如当str中含有数字字符时,或者当Unicode
39. str.zfill(width)
返回一个width长的string,如果str的长度小于width,则在左侧填充0,如果str的长度大于width,则返回str
>>> a=\'this\' >>> a.zfill(10) \'000000this\'
40. unicode.isnumeric()
如果unicode内部只有数字,则返回True,否则返回False。 Numeric指数字字符以及Unicode中的数字类型,如 U+2155, VULGAR FRACTION ONE FIFTH.
>>> u = u\'1.2345\' >>> u.isnumeric() False >>> u=u\'12345\' >>> u.isnumeric() True
41. unicode.isdecimal()
如果unicode内部只有数字,则返回True,否则返回False。 Numeric指数字字符以及Unicode中的数字类型,如 U+2155, VULGAR FRACTION ONE FIFTH.
isnumeric 和 isdecimal 的区别详见这个链接:http://www.runoob.com/python/att-string-isnumeric.html,最后的笔记列表有较为详细的介绍。
如果有问题的地方,欢迎大家批评指正。
以上是关于Python 教程——String的内置方法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章