利用C语言实现二维图形的变换
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了利用C语言实现二维图形的变换相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
二维图形由点或直线段组成,直线段可由其端点坐标定义,二维图形的几何变换实际是对点或对直线段端点在变换矩阵的作用下来实现的。设 是原来的点, 是变换之后的点,则几种典型的变换如下:
(a) 平移变换(translation):BM
(b) 比例变换(scale):
(c) 旋转变换(rotation):
好的话再加20分
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct point
float x;
float y;
;
void translation(point*pt, float xp,float yp,int num)//num代表点的个数
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
(pt+i)->x+=xp;
(pt+i)->y+=yp;
void scale(point *pt,float xs,float ys,int num)
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
(pt+i)->x*=xs;
(pt+i)->y*=ys;
void rotation(point *pt,float angle,int num)
int a[2][2];
angle=angle/180*3.141592657;
a[0][0]=cos(angle);
a[0][1]=-sin(angle);
a[1][0]=sin(angle);
a[1][1]=cos(angle);
point* temp;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
temp->x=(pt+i)->x;
temp->y=(pt+i)->y;
(pt+i)->x=temp->x*a[0][0]+a[0][1]*temp->y;
(pt+i)->y*=temp->x*a[1][0]+a[1][1]*temp->y;
int main()
int i=0,N,mode,angle,xp,yp,xk,yk,num;
cout<<"please input the number of point "<<endl;
scanf("%d",&N);
num=N;
point pt[10];
while(N--)
printf("please input points(x,y):\n");
scanf("%f%f",&pt[i].x,&pt[i].y);
i++;
printf("please input motions\n");
printf("0 stand for translation:\n");
printf("1 stand for scale:\n");
printf("2 stand for rotation:\n");
scanf("%d",&mode);
switch(mode)
case 0:
printf("please input the translation in x and y direction respectivly:\n");
cin>>xp>>yp;
translation(pt, xp,yp,num);
break;
case 1:
printf("please input the scale in x and y direction respectivly:\n");
scanf("%f%f",&xk,&yk);
scale(pt, xk,yk,num);
break;
case 2:
printf("please input the angle:\n");
scanf("%f",&angle);
rotation(pt, angle,num);
break;
printf("after translatiton or scale or rotation:\n");
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
printf("%f %f\n",pt[i].x,pt[i].y);
追问
我试了一下怎么不行啊,比例转换那个,出现错误了!还有能不能再VC6.0里实现画图啊!
追答改一下哈。
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct point
float x;
float y;
;
void translation(point*pt, float xp,float yp,int num)//num代表点的个数
for(int i=0;ix+=xp;
(pt+i)->y+=yp;
void scale(point *pt,float xs,float ys,int num)
for(int i=0;ix*=xs;
(pt+i)->y*=ys;
void rotation(point *pt,float angle,int num)
float a[2][2];
angle=angle/180*3.141592657;
a[0][0]=cos(angle);
a[0][1]=-sin(angle);
a[1][0]=sin(angle);
a[1][1]=cos(angle);
point temp;
for(int i=0;ix;
temp.y=(pt+i)->y;
(pt+i)->x=temp.x*a[0][0]+a[0][1]*temp.y;
(pt+i)->y=temp.x*a[1][0]+a[1][1]*temp.y;
int main()
int i=0,N,mode,angle,xp,yp,xk,yk,num;
cout>xp>>yp;
translation(pt, xp,yp,num);
break;
case 1:
printf("please input the scale in x and y direction respectivly:\n");
cin>>xk>>yk;
scale(pt, xk,yk,num);
break;
case 2:
printf("please input the angle:\n");
cin>>angle;
rotation(pt, angle,num);
break;
printf("after translatiton or scale or rotation:\n");
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
printf("%f %f\n",pt[i].x,pt[i].y);
错误 noname.c 3: 无法打开包含文件 'iostream'
怎么回事
再改一下吧
#include
#include
struct point
float x;
float y;
;
void translation(point*pt, float xp,float yp,int num)//num代表点的个数
for(int i=0;ix+=xp;
(pt+i)->y+=yp;
void scale(point *pt,float xs,float ys,int num)
for(int i=0;ix*=xs;
(pt+i)->y*=ys;
void rotation(point *pt,float angle,int num)
float a[2][2];
angle=angle/180*3.141592657;
a[0][0]=cos(angle);
a[0][1]=-sin(angle);
a[1][0]=sin(angle);
a[1][1]=cos(angle);
point temp;
for(int i=0;ix;
temp.y=(pt+i)->y;
(pt+i)->x=temp.x*a[0][0]+a[0][1]*temp.y;
(pt+i)->y=temp.x*a[1][0]+a[1][1]*temp.y;
int main()
int i=0,N,mode,angle,xp,yp,xk,yk,num;
printf("please input the number of point\n ";
scanf("%d",&N);
num=N;
point pt[10];
while(N--)
printf("please input points(x,y):\n");
scanf("%f%f",&pt[i].x,&pt[i].y);
i++;
printf("please input motions\n");
printf("0 stand for translation:\n");
printf("1 stand for scale:\n");
printf("2 stand for rotation:\n");
scanf("%d",&mode);
switch(mode)
case 0:
printf("please input the translation in x and y direction respectivly:\n");
scanf("%f%f",&xp,&yp);
translation(pt, xp,yp,num);
break;
case 1:
printf("please input the scale in x and y direction respectivly:\n");
scanf("%f%f",&xk,&yk);
scale(pt, xk,yk,num);
break;
case 2:
printf("please input the angle:\n");
scanf("%f",&angle);
rotation(pt, angle,num);
break;
printf("after translatiton or scale or rotation:\n");
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
printf("%f %f\n",pt[i].x,pt[i].y);
老哥,你确定没有错误,为什么我一运行就有错误啊!!!
参考技术A c语言环境下的图形变换在不引入opengl之前是相当复杂的,opengl貌似可以直接脱离语言环境直接用自带的函数就能实现各种功能。具体变换就是函数的问题,复杂而麻烦的是如何搭建环境。具体网上搜索示例代码即可。 参考技术B +1二维图形的矩阵变换——在WPF中的应用矩阵变换
原文:二维图形的矩阵变换(三)——在WPF中的应用矩阵变换UIElement和RenderTransform
首先,我们来看看什么样的对象可以进行变换。在WPF中,用于呈现给用户的对象的基类为Visual类,但是Visual对象并不具有变换功能,具有变换功能的是它的子类UIElement。这个类也是非常底层的类了,几乎我们所有的常用控件都是继承自它,也就是说,基本上所有的UI对象都是可以应用变换的。
然后,我们在再来看看UIElement中变换种类。UIElement支持两种变换:RenderTransform和LayoutTransform,其中LayoutTransform是会改变其布局,从而影响相邻的空间大小和位置的,如下图所示。
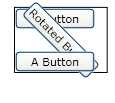
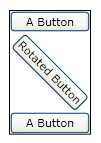
由于我们常用的是RenderTransfrom,并且两种变换的使用方式非常类似,下面的文章中就主要以RenderTransfrom作为介绍对象。下面的例子就简单的演示了其用法:
<StackPanel Orientation="Vertical">
<Button Content="A Button" Opacity="1" />
<Button Content="Rotated Button">
<Button.RenderTransform>
<RotateTransform Angle="45" />
</Button.RenderTransform>
</Button>
<Button Content="A Button" Opacity="1" />
</StackPanel>
矩阵变换MatrixTransform
前面的例子中演示了旋转的变换RotateTransform的用法,其它几种基本变换也有相对的变换类:ScaleTransform 、TranslateTransform 、SkewTransform。我们也可以将多个变换放到一个变换组中实现叠加的效果。
这些基本变换用法相对比较简单,这里就不多介绍了。下面介绍本文的重点:矩阵变换MatrixTransform。它的用法和RotateTransform实际上也差不多:
<Button Content="Rotated Button">
<Button.RenderTransform>
<MatrixTransform x:Name="myMatrixTransform">
<MatrixTransform.Matrix >
<Matrix OffsetX="10" OffsetY="100" />
</MatrixTransform.Matrix>
</MatrixTransform>
</Button.RenderTransform>
</Button>
从上面的代码中可以看到,由于矩阵变换要设置六个值,并且这几个值不容易读,因此在XAML中使用显得非常不直观,大多数的时候我们是在代码中进行设置的。
单单从这个例子来看,是无法看出矩阵变换的什么优越性的。那是因为我们使用的变换比较简单,在前文二维图形的矩阵变换(一)——基本概念中介绍过,任何二维变换的序列均可存储于单个的 Matrix 对象,因此它是可以非常容易实现变换叠加效果的,下面就以我之前的文章用WPF实现一个简单的图片查看器中介绍到的例子用矩阵变换来改写一下。
这个例子的主要功能是实现一个支持鼠标拖动和滚轮缩放的图片查看器,在原文中是靠平移变换和缩放变换叠加实现的,这里用矩阵变换来实现一下。首先还是来看看XAML部分
<Grid>
<Image Source="source.jpg" MouseWheel="Image_MouseWheel" PreviewMouseLeftButtonDown="Image_MouseLeftButtonDown"
PreviewMouseMove="Image_MouseMove">
<Image.RenderTransform>
<MatrixTransform x:Name="transForm" />
</Image.RenderTransform>
</Image>
</Grid>
然后就是事件的实现了:
private
void Image_MouseWheel(object sender, MouseWheelEventArgs e)
{
var center = getPosition(sender, e);
var scale = (e.Delta > 0 ? 1.2 : 1 / 1.2);
var matrix = transForm.Matrix;
matrix.ScaleAt(scale, scale, center.X, center.Y);
transForm.Matrix = matrix;
}
Point dragStart;
private
void Image_MouseLeftButtonDown(object sender, MouseButtonEventArgs e)
{
dragStart = getPosition(sender, e);
}
private
void Image_MouseMove(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
if ((e.LeftButton != MouseButtonState.Pressed))
{
return;
}
var current = getPosition(sender, e);
var offset = current - dragStart;
var matrix = transForm.Matrix;
matrix.Translate(offset.X, offset.Y);
transForm.Matrix = matrix;
dragStart = current;
}
Point getPosition(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
return e.GetPosition(sender as
UIElement) * transForm.Matrix;
}
由于这个例子本身并不复杂,并不能很好的体现矩阵变换的优越性,但还是可见一斑的。原文中是通过平移变换和缩放变换叠加实现的,因此这两个变换是互相影响的,平移的时候需要考虑缩放率、缩放的时候要考虑偏移量,调整相应的参数进行校正。而矩阵变换相对简单得多,只需要产生将变换矩阵和原始变换矩阵相乘即可获得叠加效果。
另外,由于矩阵变换还可以应用于Point,因此非常方便实现一些附加功能的,例如,我们要获取放大后的图像在原始图像的位置时,只需要取屏幕上四周的四个点,对档期变换矩阵的逆矩阵相乘即可。其它的就不一一列举了,要实现完整的图片查看器,矩阵变换比平移变换和缩放变换叠加要方便太多。
矩阵变换的动画
在WPF中,变换过程是可以非常容易的改成动画的炫酷效果的,但不知道为什么,系统并没有提供动画效果的矩阵变换的内置实现。不过这个并不难解决,Google了一下就发现在Stack overflow上已经有人实现了,原文地址如下:Smooth animation using MatrixTransform?,为了防止方校长哪天爱心泛滥把这个网站改成寻人启事了,这里还是转录一下。

public class MatrixAnimation : MatrixAnimationBase { public Matrix? From { set { SetValue(FromProperty, value); } get { return (Matrix?)GetValue(FromProperty); } } public static DependencyProperty FromProperty = DependencyProperty.Register("From", typeof(Matrix?), typeof(MatrixAnimation), new PropertyMetadata(null)); public Matrix? To { set { SetValue(ToProperty, value); } get { return (Matrix?)GetValue(ToProperty); } } public static DependencyProperty ToProperty = DependencyProperty.Register("To", typeof(Matrix?), typeof(MatrixAnimation), new PropertyMetadata(null)); public IEasingFunction EasingFunction { get { return (IEasingFunction)GetValue(EasingFunctionProperty); } set { SetValue(EasingFunctionProperty, value); } } public static readonly DependencyProperty EasingFunctionProperty = DependencyProperty.Register("EasingFunction", typeof(IEasingFunction), typeof(MatrixAnimation), new UIPropertyMetadata(null)); public MatrixAnimation() { } public MatrixAnimation(Matrix toValue, Duration duration) { To = toValue; Duration = duration; } public MatrixAnimation(Matrix toValue, Duration duration, FillBehavior fillBehavior) { To = toValue; Duration = duration; FillBehavior = fillBehavior; } public MatrixAnimation(Matrix fromValue, Matrix toValue, Duration duration) { From = fromValue; To = toValue; Duration = duration; } public MatrixAnimation(Matrix fromValue, Matrix toValue, Duration duration, FillBehavior fillBehavior) { From = fromValue; To = toValue; Duration = duration; FillBehavior = fillBehavior; } protected override Freezable CreateInstanceCore() { return new MatrixAnimation(); } protected override Matrix GetCurrentValueCore(Matrix defaultOriginValue, Matrix defaultDestinationValue, AnimationClock animationClock) { if (animationClock.CurrentProgress == null) { return Matrix.Identity; } var normalizedTime = animationClock.CurrentProgress.Value; if (EasingFunction != null) { normalizedTime = EasingFunction.Ease(normalizedTime); } var from = From ?? defaultOriginValue; var to = To ?? defaultDestinationValue; var newMatrix = new Matrix( ((to.M11 - from.M11) * normalizedTime) + from.M11, ((to.M12 - from.M12) * normalizedTime) + from.M12, ((to.M21 - from.M21) * normalizedTime) + from.M21, ((to.M22 - from.M22) * normalizedTime) + from.M22, ((to.OffsetX - from.OffsetX) * normalizedTime) + from.OffsetX, ((to.OffsetY - from.OffsetY) * normalizedTime) + from.OffsetY); return newMatrix; } }
以上是关于利用C语言实现二维图形的变换的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
