How to publish a Linux package to mirror All In One
Posted xgqfrms
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了How to publish a Linux package to mirror All In One相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
 How to publish a Linux package to mirror All In One
How to publish a Linux package to mirror All In One
How to publish a Linux package to mirror All In One
# 获取 IP
$ ping raspberrypi
# SSH, ip ✅
$ ssh pi@192.168.18.135
# SSH, host ✅
$ ssh pi@raspberrypi.local
demos
http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main arm64
# Raspberry Pi 安装中文输入法 chinese input
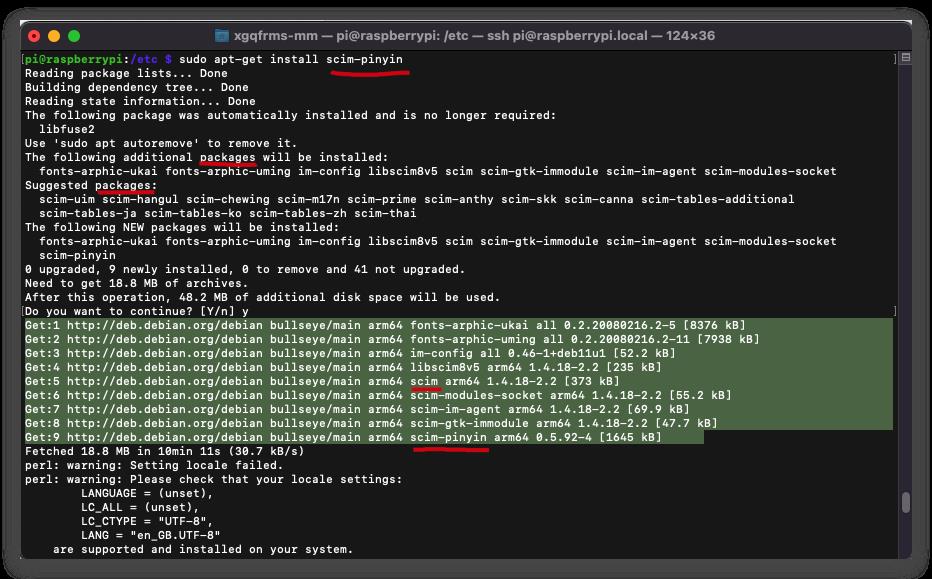
$ sudo apt-get install scim-pinyin
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
The following package was automatically installed and is no longer required:
libfuse2
Use \'sudo apt autoremove\' to remove it.
The following additional packages will be installed:
fonts-arphic-ukai fonts-arphic-uming im-config libscim8v5 scim scim-gtk-immodule scim-im-agent scim-modules-socket
Suggested packages:
scim-uim scim-hangul scim-chewing scim-m17n scim-prime scim-anthy scim-skk scim-canna scim-tables-additional
scim-tables-ja scim-tables-ko scim-tables-zh scim-thai
The following NEW packages will be installed:
fonts-arphic-ukai fonts-arphic-uming im-config libscim8v5 scim scim-gtk-immodule scim-im-agent scim-modules-socket
scim-pinyin
0 upgraded, 9 newly installed, 0 to remove and 41 not upgraded.
Need to get 18.8 MB of archives.
After this operation, 48.2 MB of additional disk space will be used.
Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y
Get:1 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main arm64 fonts-arphic-ukai all 0.2.20080216.2-5 [8376 kB]
Get:2 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main arm64 fonts-arphic-uming all 0.2.20080216.2-11 [7938 kB]
Get:3 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main arm64 im-config all 0.46-1+deb11u1 [52.2 kB]
Get:4 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main arm64 libscim8v5 arm64 1.4.18-2.2 [235 kB]
Get:5 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main arm64 scim arm64 1.4.18-2.2 [373 kB]
Get:6 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main arm64 scim-modules-socket arm64 1.4.18-2.2 [55.2 kB]
Get:7 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main arm64 scim-im-agent arm64 1.4.18-2.2 [69.9 kB]
Get:8 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main arm64 scim-gtk-immodule arm64 1.4.18-2.2 [47.7 kB]
Get:9 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main arm64 scim-pinyin arm64 0.5.92-4 [1645 kB]
Fetched 18.8 MB in 10min 11s (30.7 kB/s)
perl: warning: Setting locale failed.
perl: warning: Please check that your locale settings:
LANGUAGE = (unset),
LC_ALL = (unset),
LC_CTYPE = "UTF-8",
LANG = "en_GB.UTF-8"
are supported and installed on your system.
perl: warning: Falling back to a fallback locale ("en_GB.UTF-8").
locale: Cannot set LC_CTYPE to default locale: No such file or directory
locale: Cannot set LC_ALL to default locale: No such file or directory
Selecting previously unselected package fonts-arphic-ukai.
(Reading database ... 98715 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../0-fonts-arphic-ukai_0.2.20080216.2-5_all.deb ...
Unpacking fonts-arphic-ukai (0.2.20080216.2-5) ...
Selecting previously unselected package fonts-arphic-uming.
Preparing to unpack .../1-fonts-arphic-uming_0.2.20080216.2-11_all.deb ...
Unpacking fonts-arphic-uming (0.2.20080216.2-11) ...
Selecting previously unselected package im-config.
Preparing to unpack .../2-im-config_0.46-1+deb11u1_all.deb ...
Unpacking im-config (0.46-1+deb11u1) ...
Selecting previously unselected package libscim8v5:arm64.
Preparing to unpack .../3-libscim8v5_1.4.18-2.2_arm64.deb ...
Unpacking libscim8v5:arm64 (1.4.18-2.2) ...
Selecting previously unselected package scim.
Preparing to unpack .../4-scim_1.4.18-2.2_arm64.deb ...
Unpacking scim (1.4.18-2.2) ...
Selecting previously unselected package scim-modules-socket:arm64.
Preparing to unpack .../5-scim-modules-socket_1.4.18-2.2_arm64.deb ...
Unpacking scim-modules-socket:arm64 (1.4.18-2.2) ...
Selecting previously unselected package scim-im-agent.
Preparing to unpack .../6-scim-im-agent_1.4.18-2.2_arm64.deb ...
Unpacking scim-im-agent (1.4.18-2.2) ...
Selecting previously unselected package scim-gtk-immodule:arm64.
Preparing to unpack .../7-scim-gtk-immodule_1.4.18-2.2_arm64.deb ...
Unpacking scim-gtk-immodule:arm64 (1.4.18-2.2) ...
Selecting previously unselected package scim-pinyin.
Preparing to unpack .../8-scim-pinyin_0.5.92-4_arm64.deb ...
Unpacking scim-pinyin (0.5.92-4) ...
Setting up fonts-arphic-uming (0.2.20080216.2-11) ...
Setting up im-config (0.46-1+deb11u1) ...
Setting up fonts-arphic-ukai (0.2.20080216.2-5) ...
Setting up libscim8v5:arm64 (1.4.18-2.2) ...
Setting up scim-modules-socket:arm64 (1.4.18-2.2) ...
Setting up scim (1.4.18-2.2) ...
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/ja_JP (xinput-ja_JP) in auto mode
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/ko_KR (xinput-ko_KR) in auto mode
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/zh_CN (xinput-zh_CN) in auto mode
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/zh_TW (xinput-zh_TW) in auto mode
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/zh_HK (xinput-zh_HK) in auto mode
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/zh_SG (xinput-zh_SG) in auto mode
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim-immodule to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/ja_JP (xinput-ja_JP) in auto mode
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim-immodule to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/ko_KR (xinput-ko_KR) in auto mode
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim-immodule to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/zh_CN (xinput-zh_CN) in auto mode
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim-immodule to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/zh_TW (xinput-zh_TW) in auto mode
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim-immodule to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/zh_HK (xinput-zh_HK) in auto mode
update-alternatives: using /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/scim-immodule to provide /etc/X11/xinit/xinput.d/zh_SG (xinput-zh_SG) in auto mode
Setting up scim-im-agent (1.4.18-2.2) ...
Setting up scim-pinyin (0.5.92-4) ...
Setting up scim-gtk-immodule:arm64 (1.4.18-2.2) ...
Processing triggers for libgtk-3-0:arm64 (3.24.24-4+rpt12+deb11u2) ...
Processing triggers for libgtk2.0-0:arm64 (2.24.33-2+rpt1) ...
Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.31-13+rpt2+rpi1+deb11u5) ...
Processing triggers for man-db (2.9.4-2) ...
Processing triggers for mailcap (3.69) ...
Processing triggers for fontconfig (2.13.1-4.2) ...
Processing triggers for desktop-file-utils (0.26-1) ...
Processing triggers for gnome-menus (3.36.0-1) ...

(How to Add Linux Host to Nagios Monitoring Server Using NRPE Plugin
In our first part of this article, we’ve explained in detail on how to install and configure latest Nagios Core 4.2.0on CentOS 7.2 server. In this article we will show you how to add Remote Linux machine and it’s services to Nagios Monitoring host using NRPE agent.
We hope you already having Nagios installed and running properly. If not, please use the following installation guide to install it on the system.
- Nagios 4.2.0 Installation Guide on RHEL/CentOS 7.x/6.x/5.x & Fedora 24-19
- How to Add Windows Host to Nagios Monitoring Server
Once you’ve installed, you can proceed further to install NRPE agent on your Remote Linux host. Before heading further, let us give you a short description about NRPE.
What is NRPE?
The NRPE (Nagios Remote Plugin Executor) plugin allows you to monitor any remote Linux/Unix services or network devices. This NRPE add-on allows Nagios to monitor any local resources like CPU load, Swap, Memory usage, Online users, etc. on remote Linux machines. After all, these local resources are not mostly exposed to external machines, an NRPE agent must be installed and configured on the remote machines.
Note: The NRPE addon requires that Nagios Plugins must be installed on the remote Linux machine. Without these, the NRPE daemon will not work and will not monitor anything.
Installation of NRPE Plugin
To use the NRPE, you will need to do some additional tasks on both the Nagios Monitoring Host and Remote Linux Host that the NRPE installed on. We will be covering both the installation parts separately.
We assume that you are installing the NRPE on a host that supports TCP wrappers and Xinted daemon installed on it. Today, most of the modern Linux distributions have these two installed by default. If not, we will install it later during the installation when required.
On Remote Linux Host
Please use the below instructions to install Nagios Plugins and NRPE daemon on the Remote Linux Host.
Step 1: Install Required Dependencies
We need to install required libraries like gcc, glibc, glibc-common and GD and its development libraries before installing.
[[email protected]]# yum install -y gcc glibc glibc-common gd gd-devel make net-snmp openssl-devel
-------------- On Fedora 22+ Onwards --------------
[[email protected]]# dnf install -y gcc glibc glibc-common gd gd-devel make net-snmp openssl-devel
Step 2: Create Nagios User
Create a new nagios user account and set a password.
[[email protected]]# useradd nagios
[[email protected]]# passwd nagios
Step 3: Install the Nagios Plugins
Create a directory for installation and all its future downloads.
[[email protected]]# cd /root/nagios
Now download latest Nagios Plugins 2.1.2 package with wget command.
[[email protected] nagios~]# wget https://www.nagios-plugins.org/download/nagios-plugins-2.1.2.tar.gz
Step 4: Extract Nagios Plugins
Run the following tar command to extract the source code tarball.
[[email protected] nagios~]# tar -xvf nagios-plugins-2.1.2.tar.gz
After, extracting one new folder will appear in that directory.
[[email protected] nagios ~]# ls -l
total 2640
drwxr-xr-x. 15 root root 4096 Aug 1 21:58 nagios-plugins-2.1.2
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2695301 Aug 1 21:58 nagios-plugins-2.1.2.tar.gz
Step 5: Compile and Install Nagios Plugins
Next, compile and install using following commands
[[email protected] nagios]# cd nagios-plugins-2.1.2
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# ./configure
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# make
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# make install
Set the permissions on the plugin directory.
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# chown nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# chown -R nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios/libexec
Step 6: Install Xinetd
Most of the systems, its by default installed. If not, install xinetd package using following yum command.
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# yum install xinetd
-------------- On Fedora 22+ Onwards --------------
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# dnf install xinetd
Step 7: Install NRPE Plugin
Download latest NRPE Plugin 3.0 packages with wget command.
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# cd /root/nagios
[[email protected] nagios]# wget http://liquidtelecom.dl.sourceforge.net/project/nagios/nrpe-3.x/nrpe-3.0.tar.gz
Unpack the NRPE source code tarball.
[[email protected] nagios]# tar xzf nrpe-3.0.tar.gz
[[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# cd nrpe-3.0
Compile and install the NRPE addon.
[[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# ./configure
[[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make all
Next, install the NRPE plugin daemon, and sample daemon config file.
[[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make install-plugin
[[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make install-daemon
[[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make install-daemon-config
Install the NRPE daemon under xinetd as a service.
[[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make install-xinetd
OR
[[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make install-inetd
Now open /etc/xinetd.d/nrpe file and add the localhost and IP address of the Nagios Monitoring Server.
only_from = 127.0.0.1 localhost <nagios_ip_address>
Next, open /etc/services file add the following entry for the NRPE daemon at the bottom of the file.
nrpe 5666/tcp NRPE
Restart the xinetd service.
[[email protected]]# service xinetd restart
Step 8: Verify NRPE Daemon Locally
Run the following command to verify the NRPE daemon working correctly under xinetd.
[[email protected]]# netstat -at | grep nrpe
tcp 0 0 *:nrpe *:* LISTEN
If you get output similar to above, means it working correctly. If not, make sure to check the following things.
- Check you’ve added nrpe entry correctly in /etc/services file
- The only_from contains an entry for “nagios_ip_address” in the /etc/xinetd.d/nrpe file.
- The xinetd is installed and started.
- Check for the errors in the system log files for about xinetd or nrpe and fix those problems.
Next, verify the NRPE daemon is functioning properly. Run the “check_nrpe” command that was installed earlier for testing purposes.
[[email protected]]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost
You will get a following string on the screen, it shows you what version of NRPE is installed:
NRPE v3.0
Step 9: Configure Firewall Rules
Make sure that the Firewall on the local machine will allow the NRPE daemon to be accessed from remote servers. To do this, run the following iptables command.
-------------- On RHEL/CentOS 6/5 and Fedora --------------
[[email protected]]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 5666 -j ACCEPT
-------------- On RHEL/CentOS 7 and Fedora 19 Onwards --------------
[[email protected]]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=5666/tcp
Run the following command to Save the new iptables rule so it will survive at system reboots.
-------------- On RHEL/CentOS 6/5 and Fedora --------------
[[email protected]]# service iptables save
Step 10: Customize NRPE commands
The default NRPE configuration file that got installed has several command definitions that will be used to monitor this machine. The sample configuration file located at.
[[email protected]]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
The following are the default command definitions that are located at the bottom of the configuration file. For the time being, we assume you are using these commands. You can check them by using the following commands.
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost -c check_users
USERS OK - 1 users currently logged in |users=1;5;10;0
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost -c check_load
OK - load average: 3.90, 4.37, 3.94|load1=3.900;15.000;30.000;0; load5=4.370;10.000;25.000;0; load15=3.940;5.000;20.000;0;
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost -c check_hda1
DISK OK - free space: /boot 154 MB (84% inode=99%);| /boot=29MB;154;173;0;193
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost -c check_total_procs
PROCS CRITICAL: 297 processes
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost -c check_zombie_procs
PROCS OK: 0 processes with STATE = Z
You can edit and add new command definitions by editing the NRPE config file. Finally, you’ve successfully installed and configured NRPE agent on the Remote Linux Host. Now it’s time to install a NRPE component and add some services on your Nagios Monitoring Server…
On Nagios Monitoring Server
Now login into your Nagios Monitoring Server. Here you will need to do following things:
- Install the check_nrpe plugin.
- Create a Nagios command definition using the check_nrpe plugin.
- Create Nagios host and add service definitions for monitoring the remote Linux host.
Step 1: Install NRPE Plugin
Go to the nagios download directory and download latest NRPE Plugin with wget command.
[[email protected]]# cd /root/nagios
[[email protected]]# wget http://liquidtelecom.dl.sourceforge.net/project/nagios/nrpe-3.x/nrpe-3.0.tar.gz
Unpack the NRPE source code tarball.
[[email protected]]# tar xzf nrpe-3.0.tar.gz
[[email protected]]# cd nrpe-3.0
Compile and install the NRPE addon.
[[email protected]]# ./configure
[[email protected]]# make all
[[email protected]]# make install-daemon
Step 2: Verify NRPE Daemon Remotely
Make sure that the check_nrpe plugin can communicate with the NRPE daemon on the remote Linux host. Add the IP address in the command below with the IP address of your Remote Linux host.
[[email protected]]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H <remote_linux_ip_address>
You will get a string back that shows you what version of NRPE is installed on the remote host, like this:
NRPE v3.0
If your receive a plugin time-out error, then check the following things.
- Make sure your firewall isn’t blocking the communication between the remote host and the monitoring host.
- Make sure that the NRPE daemon is installed correctly under xinetd.
- Make sure that the remote Linux host firewall rules blocking the monitoring server from communicating to the NRPE daemon.
Adding Remote Linux Host to Nagios Monitoring Server
To add a remote host you need to create a two new files “hosts.cfg” and “services.cfg” under “/usr/local/nagios/etc/” location.
[[email protected]]# cd /usr/local/nagios/etc/
[[email protected]]# touch hosts.cfg
[[email protected]]# touch services.cfg
Now add these two files to main Nagios configuration file. Open nagios.cfg file with any editor.
[[email protected]]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
Now add the two newly created files as shown below.
# You can specify individual object config files as shown below:
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/hosts.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/services.cfg
Now open hosts.cfg file and add the default host template name and define remote hosts as shown below. Make sure to replace host_name, alias and address with your remote host server details.
[[email protected]]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/hosts.cfg
## Default Linux Host Template ##
define host{
name linux-box ; Name of this template
use generic-host ; Inherit default values
check_period 24x7
check_interval 5
retry_interval 1
max_check_attempts 10
check_command check-host-alive
notification_period 24x7
notification_interval 30
notification_options d,r
contact_groups admins
register 0 ; DONT REGISTER THIS - ITS A TEMPLATE
}
## Default
define host{
use linux-box ; Inherit default values from a template
host_name tecmint ; The name we‘re giving to this server
alias CentOS 6 ; A longer name for the server
address 5.175.142.66 ; IP address of Remote Linux host
}
Next open services.cfg file add the following services to be monitored.
[[email protected]]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/services.cfg
define service{
use generic-service
host_name tecmint
service_description CPU Load
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name tecmint
service_description Total Processes
check_command check_nrpe!check_total_procs
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name tecmint
service_description Current Users
check_command check_nrpe!check_users
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name tecmint
service_description SSH Monitoring
check_command check_nrpe!check_ssh
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name tecmint
service_description FTP Monitoring
check_command check_nrpe!check_ftp
}
Now NRPE command definition needs to be created in commands.cfg file.
[[email protected]]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/commands.cfg
Add the following NRPE command definition at the bottom of the file.
###############################################################################
# NRPE CHECK COMMAND
#
# Command to use NRPE to check remote host systems
###############################################################################
define command{
command_name check_nrpe
command_line $USER1$/check_nrpe -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -c $ARG1$
}
Finally, verify Nagios Configuration files for any errors.
[[email protected]]# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
Total Warnings: 0
Total Errors: 0
Restart Nagios:
[[email protected]]# service nagios restart
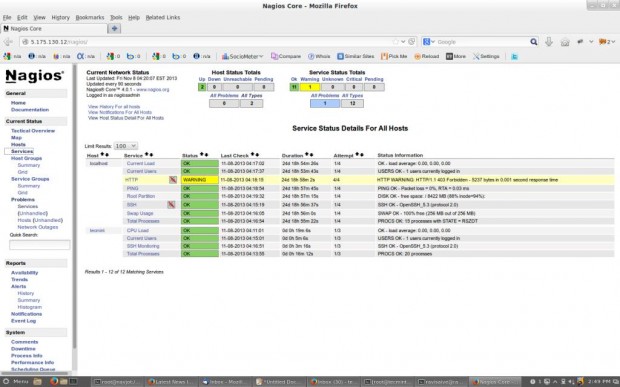
That’s it. Now go to Nagios Monitoring Web interface at “http://Your-server-IP-address/nagios” or “http://FQDN/nagios” and Provide the username “nagiosadmin” and password. Check that the Remote Linux Host was added and is being monitored.
That’s it! for now, in our my up-coming article I will show you how to add Windows host to Nagios monitoring Server. If you’re facing any difficulties while adding remote host to Nagios. Please do comment your queries or problem via comment section, till then stay tuned to Tecmint.com for more such valuable articles.
以上是关于How to publish a Linux package to mirror All In One的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
How to handle Appsettings for .net core 3.1 self contained single file publish
How to handle Appsettings for .net core 3.1 self contained single file publish
Publish to a Linux Production Environment
How to get Mac address in Linux
How to Add Linux Host to Nagios Monitoring Server Using NRPE Plugin
How to Add Linux Host to Nagios Monitoring Server Using NRPE Plugin
In our first part of this article, we’ve explained in detail on how to install and configure latest Nagios Core 4.2.0on CentOS 7.2 server. In this article we will show you how to add Remote Linux machine and it’s services to Nagios Monitoring host using NRPE agent.
We hope you already having Nagios installed and running properly. If not, please use the following installation guide to install it on the system.
- Nagios 4.2.0 Installation Guide on RHEL/CentOS 7.x/6.x/5.x & Fedora 24-19
- How to Add Windows Host to Nagios Monitoring Server
Once you’ve installed, you can proceed further to install NRPE agent on your Remote Linux host. Before heading further, let us give you a short description about NRPE.
What is NRPE?
The NRPE (Nagios Remote Plugin Executor) plugin allows you to monitor any remote Linux/Unix services or network devices. This NRPE add-on allows Nagios to monitor any local resources like CPU load, Swap, Memory usage, Online users, etc. on remote Linux machines. After all, these local resources are not mostly exposed to external machines, an NRPE agent must be installed and configured on the remote machines.
Note: The NRPE addon requires that Nagios Plugins must be installed on the remote Linux machine. Without these, the NRPE daemon will not work and will not monitor anything.
Installation of NRPE Plugin
To use the NRPE, you will need to do some additional tasks on both the Nagios Monitoring Host and Remote Linux Host that the NRPE installed on. We will be covering both the installation parts separately.
We assume that you are installing the NRPE on a host that supports TCP wrappers and Xinted daemon installed on it. Today, most of the modern Linux distributions have these two installed by default. If not, we will install it later during the installation when required.
On Remote Linux Host
Please use the below instructions to install Nagios Plugins and NRPE daemon on the Remote Linux Host.
Step 1: Install Required Dependencies
We need to install required libraries like gcc, glibc, glibc-common and GD and its development libraries before installing.
[[email protected]]# yum install -y gcc glibc glibc-common gd gd-devel make net-snmp openssl-devel -------------- On Fedora 22+ Onwards -------------- [[email protected]]# dnf install -y gcc glibc glibc-common gd gd-devel make net-snmp openssl-devel
Step 2: Create Nagios User
Create a new nagios user account and set a password.
[[email protected]]# useradd nagios [[email protected]]# passwd nagios
Step 3: Install the Nagios Plugins
Create a directory for installation and all its future downloads.
[[email protected]]# cd /root/nagios
Now download latest Nagios Plugins 2.1.2 package with wget command.
[[email protected] nagios~]# wget https://www.nagios-plugins.org/download/nagios-plugins-2.1.2.tar.gz
Step 4: Extract Nagios Plugins
Run the following tar command to extract the source code tarball.
[[email protected] nagios~]# tar -xvf nagios-plugins-2.1.2.tar.gz
After, extracting one new folder will appear in that directory.
[[email protected] nagios ~]# ls -l total 2640 drwxr-xr-x. 15 root root 4096 Aug 1 21:58 nagios-plugins-2.1.2 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2695301 Aug 1 21:58 nagios-plugins-2.1.2.tar.gz
Step 5: Compile and Install Nagios Plugins
Next, compile and install using following commands
[[email protected] nagios]# cd nagios-plugins-2.1.2 [[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# ./configure [[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# make [[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# make install
Set the permissions on the plugin directory.
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# chown nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios [[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# chown -R nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios/libexec
Step 6: Install Xinetd
Most of the systems, its by default installed. If not, install xinetd package using following yum command.
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# yum install xinetd -------------- On Fedora 22+ Onwards -------------- [[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# dnf install xinetd
Step 7: Install NRPE Plugin
Download latest NRPE Plugin 3.0 packages with wget command.
[[email protected] nagios-plugins-2.1.2]# cd /root/nagios [[email protected] nagios]# wget http://liquidtelecom.dl.sourceforge.net/project/nagios/nrpe-3.x/nrpe-3.0.tar.gz
Unpack the NRPE source code tarball.
[[email protected] nagios]# tar xzf nrpe-3.0.tar.gz [[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# cd nrpe-3.0
Compile and install the NRPE addon.
[[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# ./configure [[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make all
Next, install the NRPE plugin daemon, and sample daemon config file.
[[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make install-plugin [[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make install-daemon [[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make install-daemon-config
Install the NRPE daemon under xinetd as a service.
[[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make install-xinetd OR [[email protected] nrpe-3.0]# make install-inetd
Now open /etc/xinetd.d/nrpe file and add the localhost and IP address of the Nagios Monitoring Server.
only_from = 127.0.0.1 localhost <nagios_ip_address>
Next, open /etc/services file add the following entry for the NRPE daemon at the bottom of the file.
nrpe 5666/tcp NRPE
Restart the xinetd service.
[[email protected]]# service xinetd restart
Step 8: Verify NRPE Daemon Locally
Run the following command to verify the NRPE daemon working correctly under xinetd.
[[email protected]]# netstat -at | grep nrpe tcp 0 0 *:nrpe *:* LISTEN
If you get output similar to above, means it working correctly. If not, make sure to check the following things.
- Check you’ve added nrpe entry correctly in /etc/services file
- The only_from contains an entry for “nagios_ip_address” in the /etc/xinetd.d/nrpe file.
- The xinetd is installed and started.
- Check for the errors in the system log files for about xinetd or nrpe and fix those problems.
Next, verify the NRPE daemon is functioning properly. Run the “check_nrpe” command that was installed earlier for testing purposes.
[[email protected]]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost
You will get a following string on the screen, it shows you what version of NRPE is installed:
NRPE v3.0
Step 9: Configure Firewall Rules
Make sure that the Firewall on the local machine will allow the NRPE daemon to be accessed from remote servers. To do this, run the following iptables command.
-------------- On RHEL/CentOS 6/5 and Fedora -------------- [[email protected]]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 5666 -j ACCEPT -------------- On RHEL/CentOS 7 and Fedora 19 Onwards -------------- [[email protected]]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=5666/tcp
Run the following command to Save the new iptables rule so it will survive at system reboots.
-------------- On RHEL/CentOS 6/5 and Fedora -------------- [[email protected]]# service iptables save
Step 10: Customize NRPE commands
The default NRPE configuration file that got installed has several command definitions that will be used to monitor this machine. The sample configuration file located at.
[[email protected]]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
The following are the default command definitions that are located at the bottom of the configuration file. For the time being, we assume you are using these commands. You can check them by using the following commands.
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost -c check_users USERS OK - 1 users currently logged in |users=1;5;10;0
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost -c check_load OK - load average: 3.90, 4.37, 3.94|load1=3.900;15.000;30.000;0; load5=4.370;10.000;25.000;0; load15=3.940;5.000;20.000;0;
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost -c check_hda1 DISK OK - free space: /boot 154 MB (84% inode=99%);| /boot=29MB;154;173;0;193
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost -c check_total_procs PROCS CRITICAL: 297 processes
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost -c check_zombie_procs PROCS OK: 0 processes with STATE = Z
You can edit and add new command definitions by editing the NRPE config file. Finally, you’ve successfully installed and configured NRPE agent on the Remote Linux Host. Now it’s time to install a NRPE component and add some services on your Nagios Monitoring Server…
On Nagios Monitoring Server
Now login into your Nagios Monitoring Server. Here you will need to do following things:
- Install the check_nrpe plugin.
- Create a Nagios command definition using the check_nrpe plugin.
- Create Nagios host and add service definitions for monitoring the remote Linux host.
Step 1: Install NRPE Plugin
Go to the nagios download directory and download latest NRPE Plugin with wget command.
[[email protected]]# cd /root/nagios [[email protected]]# wget http://liquidtelecom.dl.sourceforge.net/project/nagios/nrpe-3.x/nrpe-3.0.tar.gz
Unpack the NRPE source code tarball.
[[email protected]]# tar xzf nrpe-3.0.tar.gz [[email protected]]# cd nrpe-3.0
Compile and install the NRPE addon.
[[email protected]]# ./configure [[email protected]]# make all [[email protected]]# make install-daemon
Step 2: Verify NRPE Daemon Remotely
Make sure that the check_nrpe plugin can communicate with the NRPE daemon on the remote Linux host. Add the IP address in the command below with the IP address of your Remote Linux host.
[[email protected]]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H <remote_linux_ip_address>
You will get a string back that shows you what version of NRPE is installed on the remote host, like this:
NRPE v3.0
If your receive a plugin time-out error, then check the following things.
- Make sure your firewall isn’t blocking the communication between the remote host and the monitoring host.
- Make sure that the NRPE daemon is installed correctly under xinetd.
- Make sure that the remote Linux host firewall rules blocking the monitoring server from communicating to the NRPE daemon.
Adding Remote Linux Host to Nagios Monitoring Server
To add a remote host you need to create a two new files “hosts.cfg” and “services.cfg” under “/usr/local/nagios/etc/” location.
[[email protected]]# cd /usr/local/nagios/etc/ [[email protected]]# touch hosts.cfg [[email protected]]# touch services.cfg
Now add these two files to main Nagios configuration file. Open nagios.cfg file with any editor.
[[email protected]]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
Now add the two newly created files as shown below.
# You can specify individual object config files as shown below: cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/hosts.cfg cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/services.cfg
Now open hosts.cfg file and add the default host template name and define remote hosts as shown below. Make sure to replace host_name, alias and address with your remote host server details.
[[email protected]]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/hosts.cfg
## Default Linux Host Template ##
define host{
name linux-box ; Name of this template
use generic-host ; Inherit default values
check_period 24x7
check_interval 5
retry_interval 1
max_check_attempts 10
check_command check-host-alive
notification_period 24x7
notification_interval 30
notification_options d,r
contact_groups admins
register 0 ; DONT REGISTER THIS - ITS A TEMPLATE
}
## Default
define host{
use linux-box ; Inherit default values from a template
host_name tecmint ; The name we‘re giving to this server
alias CentOS 6 ; A longer name for the server
address 5.175.142.66 ; IP address of Remote Linux host
}
Next open services.cfg file add the following services to be monitored.
[[email protected]]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/services.cfg
define service{
use generic-service
host_name tecmint
service_description CPU Load
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name tecmint
service_description Total Processes
check_command check_nrpe!check_total_procs
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name tecmint
service_description Current Users
check_command check_nrpe!check_users
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name tecmint
service_description SSH Monitoring
check_command check_nrpe!check_ssh
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name tecmint
service_description FTP Monitoring
check_command check_nrpe!check_ftp
}
Now NRPE command definition needs to be created in commands.cfg file.
[[email protected]]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/commands.cfg
Add the following NRPE command definition at the bottom of the file.
###############################################################################
# NRPE CHECK COMMAND
#
# Command to use NRPE to check remote host systems
###############################################################################
define command{
command_name check_nrpe
command_line $USER1$/check_nrpe -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -c $ARG1$
}
Finally, verify Nagios Configuration files for any errors.
[[email protected]]# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg Total Warnings: 0 Total Errors: 0
Restart Nagios:
[[email protected]]# service nagios restart
That’s it. Now go to Nagios Monitoring Web interface at “http://Your-server-IP-address/nagios” or “http://FQDN/nagios” and Provide the username “nagiosadmin” and password. Check that the Remote Linux Host was added and is being monitored.
That’s it! for now, in our my up-coming article I will show you how to add Windows host to Nagios monitoring Server. If you’re facing any difficulties while adding remote host to Nagios. Please do comment your queries or problem via comment section, till then stay tuned to Tecmint.com for more such valuable articles.
以上是关于How to publish a Linux package to mirror All In One的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
How to handle Appsettings for .net core 3.1 self contained single file publish
How to handle Appsettings for .net core 3.1 self contained single file publish
Publish to a Linux Production Environment
How to get Mac address in Linux
How to Add Linux Host to Nagios Monitoring Server Using NRPE Plugin