LRU缓存替换策略及C#实现
Posted 黑洞视界
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LRU缓存替换策略及C#实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
LRU缓存替换策略
缓存是一种非常常见的设计,通过将数据缓存到访问速度更快的存储设备中,来提高数据的访问速度,如内存、CPU缓存、硬盘缓存等。
但与缓存的高速相对的是,缓存的成本较高,因此容量往往是有限的,当缓存满了之后,就需要一种策略来决定将哪些数据移除出缓存,以腾出空间来存储新的数据。
这样的策略被称为缓存替换策略(Cache Replacement Policy)。
常见的缓存替换策略有:FIFO(First In First Out)、LRU(Least Recently Used)、LFU(Least Frequently Used)等。
今天给大家介绍的是LRU算法。
核心思想
LRU算法基于这样一个假设:如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高。
大部分情况下这个假设是成立的,因此LRU算法也是比较常用的缓存替换策略。
基于这个假设,我们在实现的时候,需要维护一个有序的数据结构,来记录数据的访问历史,当缓存满了之后,就可以根据这个数据结构来决定将哪些数据移除出缓存。
不适用场景
但如果数据的访问模式不符合LRU算法的假设,那么LRU算法就会失效。
例如:数据的访问模式是周期性的,那么LRU算法就会把周期性的数据淘汰掉,这样就会导致缓存命中率的下降。
换个说法比如,如果现在缓存的数据只在白天被访问,晚上访问的是另一批数据,那么在晚上,LRU算法就会把白天访问的数据淘汰掉,第二天白天又会把昨天晚上访问的数据淘汰掉,这样就会导致缓存命中率的下降。
后面有时间会给大家介绍LFU(Least Frequently Used)算法,以及LFU和LRU的结合LFRU(Least Frequently and Recently Used)算法,可以有效的解决这个问题。
算法基本实现
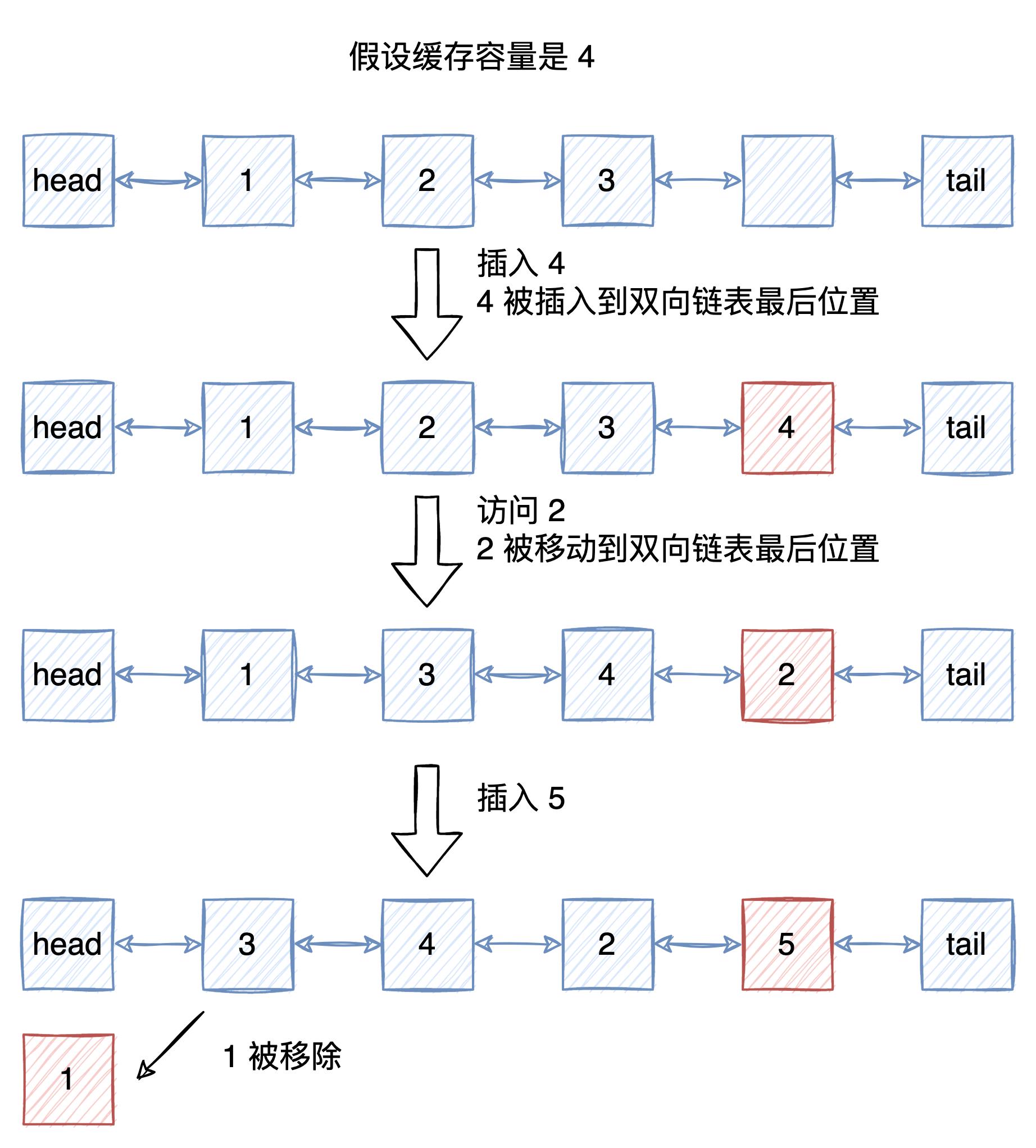
上文提到,LRU算法需要维护一个有序的数据结构,来记录数据的访问历史。通常我们会用双向链表来实现这个数据结构,因为双向链表可以在O(1)的时间复杂度内往链表的头部或者尾部插入数据,以及在O(1)的时间复杂度内删除数据。
我们将数据存储在双向链表中,每次访问数据的时候,就将数据移动到链表的尾部,这样就可以保证链表的尾部就是最近访问的数据,链表的头部就是最久没有被访问的数据。
当缓存满了之后,如果需要插入新的数据,因为链表的头部就是最久没有被访问的数据,所以我们就可以直接将链表的头部删除,然后将新的数据插入到链表的尾部。
如果我们要实现一个键值对的缓存,我们可以用一个哈希表来存储键值对,这样就可以在O(1)的时间复杂度内完成查找操作,.NET 中我们可以使用 Dictionary。
同时我们使用 LinkedList 来作为双向链表的实现,存储缓存的 key,以此记录数据的访问历史。
我们在每次操作 Dictionary 进行插入、删除、查找的时候,都需要将对应的 key 也插入、删除、移动到链表的尾部。
// 实现 IEnumerable 接口,方便遍历
public class LRUCache<TKey, TValue> : IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>
private readonly LinkedList<TKey> _list;
private readonly Dictionary<TKey, TValue> _dictionary;
private readonly int _capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity)
_capacity = capacity;
_list = new LinkedList<TKey>();
_dictionary = new Dictionary<TKey, TValue>();
public TValue Get(TKey key)
if (_dictionary.TryGetValue(key, out var value))
// 在链表中删除 key,然后将 key 添加到链表的尾部
// 这样就可以保证链表的尾部就是最近访问的数据,链表的头部就是最久没有被访问的数据
// 但是在链表中删除 key 的时间复杂度是 O(n),所以这个算法的时间复杂度是 O(n)
_list.Remove(key);
_list.AddLast(key);
return value;
return default;
public void Put(TKey key, TValue value)
if (_dictionary.TryGetValue(key, out _))
// 如果插入的 key 已经存在,将 key 对应的值更新,然后将 key 移动到链表的尾部
_dictionary[key] = value;
_list.Remove(key);
_list.AddLast(key);
else
if (_list.Count == _capacity)
// 缓存满了,删除链表的头部,也就是最久没有被访问的数据
_dictionary.Remove(_list.First.Value);
_list.RemoveFirst();
_list.AddLast(key);
_dictionary.Add(key, value);
public void Remove(TKey key)
if (_dictionary.TryGetValue(key, out _))
_dictionary.Remove(key);
_list.Remove(key);
public IEnumerator<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>> GetEnumerator()
foreach (var key in _list)
yield return new KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>(key, _dictionary[key]);
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
return GetEnumerator();
var lruCache = new LRUCache<int, int>(4);
lruCache.Put(1, 1);
lruCache.Put(2, 2);
lruCache.Put(3, 3);
lruCache.Put(4, 4);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", lruCache));
Console.WriteLine(lruCache.Get(2));
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", lruCache));
lruCache.Put(5, 5);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", lruCache));
lruCache.Remove(3);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", lruCache));
输出:
[1, 1] [2, 2] [3, 3] [4, 4] // 初始化
2 // 访问 2
[1, 1] [3, 3] [4, 4] [2, 2] // 2 移动到链表尾部
[3, 3] [4, 4] [2, 2] [5, 5] // 插入 5
[4, 4] [2, 2] [5, 5] // 删除 3
算法优化
上面的实现中,对缓存的查询、插入、删除都会涉及到链表中数据的删除(移动也是删除再插入)。
因为我们在 LinkedList 中存储的是 key,所以我们需要先通过 key 在链表中找到对应的节点,然后再进行删除操作,这就导致了链表的删除操作的时间复杂度是 O(n)。
虽然 Dictionary 的查找、插入、删除操作的时间复杂度都是 O(1),但因为链表操作的时间复杂度是 O(n),整个算法的最差时间复杂度是 O(n)。
算法优化的关键在于如何降低链表的删除操作的时间复杂度。
优化思路:
- 在 Dictionary 中存储 key 和 LinkedList 中节点的映射关系
- 在 LinkedList 的节点中存储 key-value
也就是说,我们让两个本来不相关的数据结构之间产生联系。
不管是在插入、删除、查找缓存的时候,都可以通过这种联系来将时间复杂度降低到 O(1)。
- 通过 key 在 Dictionary 中找到对应的节点,然后再从 LinkedList 节点中取出 value,时间复杂度是 O(1)
- LinkedList 删除数据之前,先通过 key 在 Dictionary 中找到对应的节点,然后再删除,这样就可以将链表的删除操作的时间复杂度降低到 O(1)
- LinkedList 删除头部节点时,因为节点中存储了 key,所以我们可以通过 key 在 Dictionary 中删除对应的节点,时间复杂度是 O(1)
public class LRUCache_V2<TKey, TValue> : IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>
private readonly LinkedList<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>> _list;
private readonly Dictionary<TKey, LinkedListNode<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>> _dictionary;
private readonly int _capacity;
public LRUCache_V2(int capacity)
_capacity = capacity;
_list = new LinkedList<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>();
_dictionary = new Dictionary<TKey, LinkedListNode<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>>();
public TValue Get(TKey key)
if (_dictionary.TryGetValue(key, out var node))
_list.Remove(node);
_list.AddLast(node);
return node.Value.Value;
return default;
public void Put(TKey key, TValue value)
if (_dictionary.TryGetValue(key, out var node))
node.Value = new KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>(key, value);
_list.Remove(node);
_list.AddLast(node);
else
if (_list.Count == _capacity)
_dictionary.Remove(_list.First.Value.Key);
_list.RemoveFirst();
var newNode = new LinkedListNode<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>(new KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>(key, value));
_list.AddLast(newNode);
_dictionary.Add(key, newNode);
public void Remove(TKey key)
if (_dictionary.TryGetValue(key, out var node))
_dictionary.Remove(key);
_list.Remove(node);
public IEnumerator<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>> GetEnumerator()
return _list.GetEnumerator();
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
return GetEnumerator();
进一步优化
因为我们对 双向链表 的存储需求是定制化的,要求节点中存储 key-value,直接使用 C# 的 LinkedList 我们就需要用 KeyValuePair 这样的结构来间接存储,会导致一些不必要的内存开销。
我们可以自己实现一个双向链表,这样就可以直接在节点中存储 key-value,从而减少内存开销。
public class LRUCache_V3<TKey, TValue>
private readonly DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue> _head;
private readonly DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue> _tail;
private readonly Dictionary<TKey, DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue>> _dictionary;
private readonly int _capacity;
public LRUCache_V3(int capacity)
_capacity = capacity;
_head = new DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue>();
_tail = new DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue>();
_head.Next = _tail;
_tail.Previous = _head;
_dictionary = new Dictionary<TKey, DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue>>();
public TValue Get(TKey key)
if (_dictionary.TryGetValue(key, out var node))
RemoveNode(node);
AddLastNode(node);
return node.Value;
return default;
public void Put(TKey key, TValue value)
if (_dictionary.TryGetValue(key, out var node))
RemoveNode(node);
AddLastNode(node);
node.Value = value;
else
if (_dictionary.Count == _capacity)
var firstNode = RemoveFirstNode();
_dictionary.Remove(firstNode.Key);
var newNode = new DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue>(key, value);
AddLastNode(newNode);
_dictionary.Add(key, newNode);
public void Remove(TKey key)
if (_dictionary.TryGetValue(key, out var node))
_dictionary.Remove(key);
RemoveNode(node);
private void AddLastNode(DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue> node)
node.Previous = _tail.Previous;
node.Next = _tail;
_tail.Previous.Next = node;
_tail.Previous = node;
private DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue> RemoveFirstNode()
var firstNode = _head.Next;
_head.Next = firstNode.Next;
firstNode.Next.Previous = _head;
firstNode.Next = null;
firstNode.Previous = null;
return firstNode;
private void RemoveNode(DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue> node)
node.Previous.Next = node.Next;
node.Next.Previous = node.Previous;
node.Next = null;
node.Previous = null;
internal class DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue>
public DoubleLinkedListNode()
public DoubleLinkedListNode(TKey key, TValue value)
Key = key;
Value = value;
public TKey Key get; set;
public TValue Value get; set;
public DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue> Previous get; set;
public DoubleLinkedListNode<TKey, TValue> Next get; set;
Benchmark
使用 BenchmarkDotNet 对3个版本进行性能测试对比。
[MemoryDiagnoser]
public class WriteBenchmarks
// 保证写入的数据有一定的重复性,借此来测试LRU的最差时间复杂度
private const int Capacity = 1000;
private const int DataSize = 10_0000;
private List<int> _data;
[GlobalSetup]
public void Setup()
_data = new List<int>();
var shared = Random.Shared;
for (int i = 0; i < DataSize; i++)
_data.Add(shared.Next(0, DataSize / 10));
[Benchmark]
public void LRUCache_V1()
var cache = new LRUCache<int, int>(Capacity);
foreach (var item in _data)
cache.Put(item, item);
[Benchmark]
public void LRUCache_V2()
var cache = new LRUCache_V2<int, int>(Capacity);
foreach (var item in _data)
cache.Put(item, item);
[Benchmark]
public void LRUCache_V3()
var cache = new LRUCache_V3<int, int>(Capacity);
foreach (var item in _data)
cache.Put(item, item);
public class ReadBenchmarks
// 保证写入的数据有一定的重复性,借此来测试LRU的最差时间复杂度
private const int Capacity = 1000;
private const int DataSize = 10_0000;
private List<int> _data;
private LRUCache<int, int> _cacheV1;
private LRUCache_V2<int, int> _cacheV2;
private LRUCache_V3<int, int> _cacheV3;
[GlobalSetup]
public void Setup()
_cacheV1 = new LRUCache<int, int>(Capacity);
_cacheV2 = new LRUCache_V2<int, int>(Capacity);
_cacheV3 = new LRUCache_V3<int, int>(Capacity);
_data = new List<int>();
var shared = Random.Shared;
for (int i = 0; i < DataSize; i++)
int dataToPut = shared.Next(0, DataSize / 10);
int dataToGet = shared.Next(0, DataSize / 10);
_data.Add(dataToGet);
_cacheV1.Put(dataToPut, dataToPut);
_cacheV2.Put(dataToPut, dataToPut);
_cacheV3.Put(dataToPut, dataToPut);
[Benchmark]
public void LRUCache_V1()
foreach (var item in _data)
_cacheV1.Get(item);
[Benchmark]
public void LRUCache_V2()
foreach (var item in _data)
_cacheV2.Get(item);
[Benchmark]
public void LRUCache_V3()
foreach (var item in _data)
_cacheV3.Get(item);
写入性能测试结果:
| Method | Mean | Error | StdDev | Median | Gen0 | Gen1 | Allocated |
|------------ |----------:|----------:|----------:|----------:|---------:|---------:|----------:|
| LRUCache_V1 | 16.890 ms | 0.3344 ms | 0.8012 ms | 16.751 ms | 750.0000 | 218.7500 | 4.65 MB |
| LRUCache_V2 | 7.193 ms | 0.1395 ms | 0.3958 ms | 7.063 ms | 703.1250 | 226.5625 | 4.22 MB |
| LRUCache_V3 | 5.761 ms | 0.1102 ms | 0.1132 ms | 5.742 ms | 585.9375 | 187.5000 | 3.53 MB |
查询性能测试结果:
| Method | Mean | Error | StdDev | Gen0 | Allocated |
|------------ |----------:|----------:|----------:|--------:|----------:|
| LRUCache_V1 | 19.475 ms | 0.3824 ms | 0.3390 ms | 62.5000 | 474462 B |
| LRUCache_V2 | 1.994 ms | 0.0273 ms | 0.0242 ms | - | 4 B |
| LRUCache_V3 | 1.595 ms | 0.0187 ms | 0.0175 ms | - | 3 B |
06 | 链表(上):如何实现LRU缓存淘汰算法?
我们先来讨论一个经典的链表应用场景,那就是 LRU 缓存淘汰算法。
缓存的大小有限,当缓存被用满时,哪些数据应该被清理出去,哪些数据应该被保留?这就需要缓存淘汰策略来决定。
常见的策略有三种:
先进先出策略 FIFO(First In,First Out)、最少使用策略 LFU(Least Frequently Used)、最近最少使用策略 LRU(Least Recently Used)。
三种最常见的链表结构,它们分别是:单链表、双向链表和循环链表。
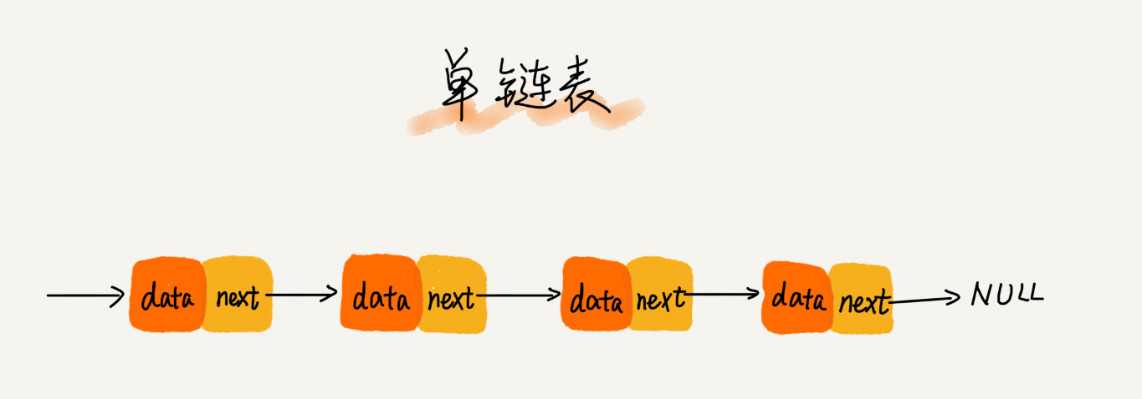
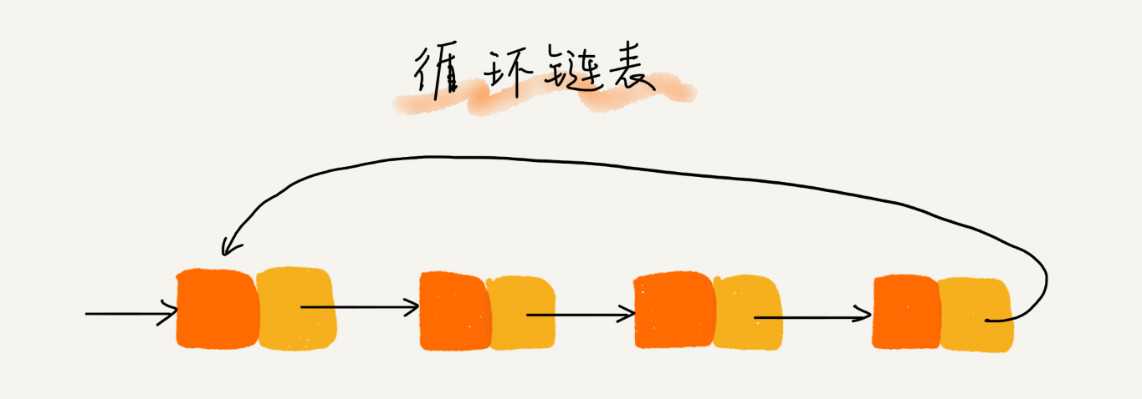
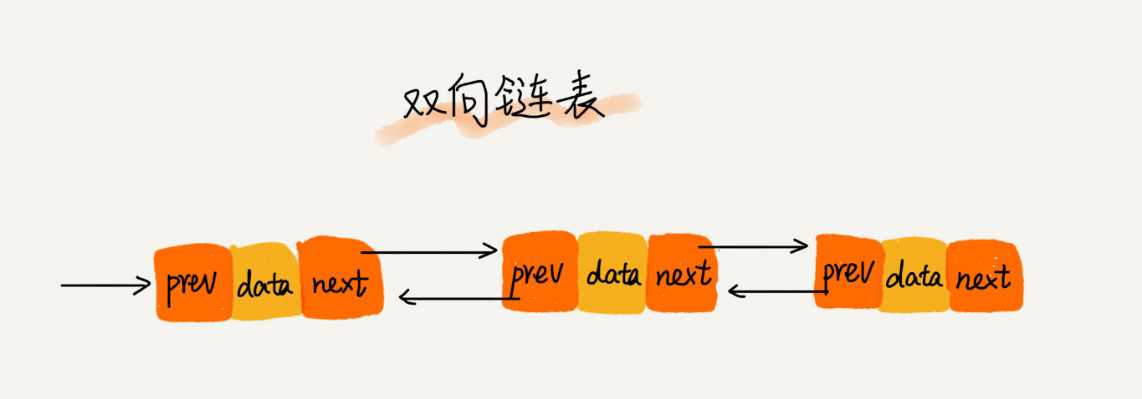
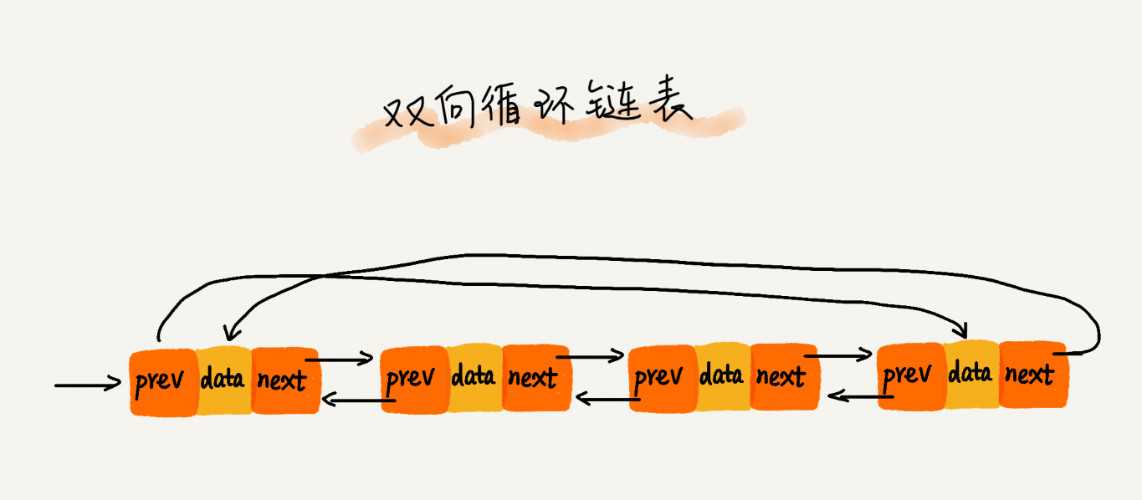
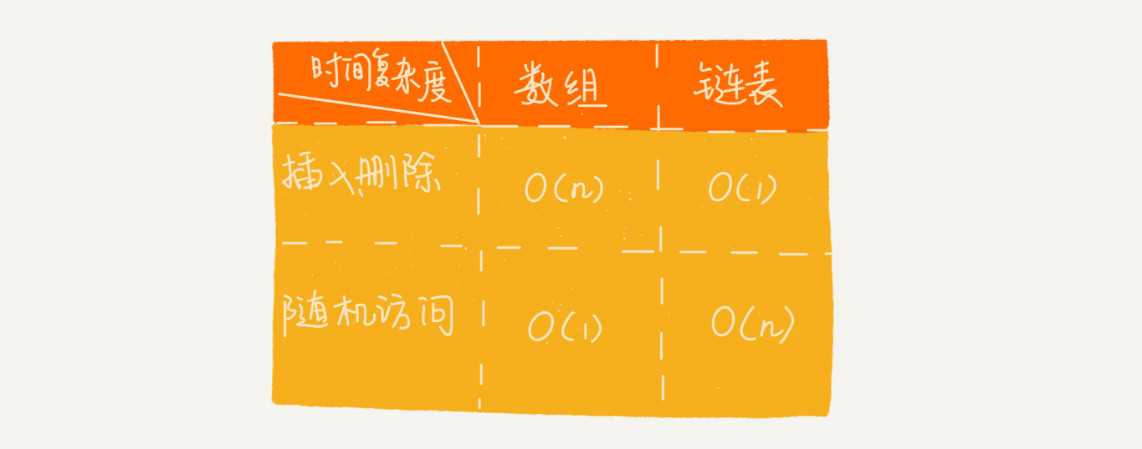
数组简单易用,在实现上使用的是连续的内存空间,可以借助 CPU 的缓存机制,预读数组中的数据,所以访问效率更高。而链表在内存中并不是连续存储,所以对 CPU 缓存不友好,没办法有效预读.
数组的缺点是大小固定,一经声明就要占用整块连续内存空间。如果声明的数组过大,系统可能没有足够的连续内存空间分配给它,导致“内存不足(out of memory)”。如果声明的数组过小,则可能出现不够用的情况。这时只能再申请一个更大的内存空间,把原数组拷贝进去,非常费时。链表本身没有大小的限制,天然地支持动态扩容,我觉得这也是它与数组最大的区别。
以上是关于LRU缓存替换策略及C#实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章