Python学习函数参数传递方法四种(位置,关键字,默认值,包裹位置,包裹关键字传递)
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python学习函数参数传递方法四种(位置,关键字,默认值,包裹位置,包裹关键字传递)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 位置传递:
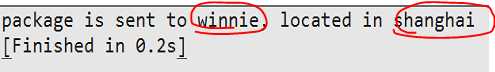
#--coding:utf-8-- def send(name,address): return ‘package is sent to %s, located in %s‘ %(name, address) print(send(‘winnie‘,‘shanghai‘))
2. 关键字传递
def run(name,length, date): return ‘%s ran %s on %s‘ %(name,length,date) #关键字传递时,可以无视参数顺序,名字对了就行。 print(run(length = ‘5km‘,date =‘11/29/2016‘,name = ‘winnie‘)) #关键字和位置混用,但要注意位置参数要出现在关键字前面。 如果不,那编译器不知道除了几个有名字的,位置的顺序。 print(run(‘winnie‘,length = ‘5km‘,date =‘11/29/2016‘))
winnie ran 5km on 11/29/2016 winnie ran 5km on 11/29/2016 [Finished in 0.2s]
3. 默认值参数
# 3. 默认值参数: 可以给出参数默认值 # 我们跑团每周二的例行约跑 def runWeekly(name,length, time = ‘Tuesday 5:00PM‘): return ‘%s ran %s on %s‘ %(name,length,time)
调用:
print(runWeekly(‘jin‘,‘5km‘)) print(runWeekly(‘jin‘,‘5km‘,‘Wednesday‘)) print(runWeekly(‘jin‘,time = ‘5km‘,‘Wednesday‘)) #Error
File "C:\\pytest\\Sele\\tem1111.py", line 20 print(runWeekly(‘jin‘,time = ‘5km‘,‘Wednesday‘)) SyntaxError: non-keyword arg after keyword arg [Finished in 0.2s with exit code 1]
4. 包裹传递
# 4. 包裹传递 (*/**) # 参数被 collect收集,type: tuple def subselect(*collect): print collect print type(collect) # 参数被 aa收集,type: dict def packing(**aa): #print test print type(aa) print aa
调用:
subselect([‘ppe-test-1‘,‘dddd‘]) packing(a=1,b=2,sub=[11,22])
输出:
<type ‘tuple‘>
<type ‘dict‘>
{‘a‘: 1, ‘b‘: 2, ‘sub‘: [11, 22]}
[Finished in 0.2s]
5. 解包
# 5.Unpacking with */** tuple1 = [‘test1‘,‘test2‘,‘test3‘] dictionary1 = {‘at‘:‘88wi‘,‘b‘:‘secondParam‘,‘third‘:‘winnie‘} print ‘dictionary1 ‘, dictionary1 def useDict(at,b,third): print at , b ,third useDict(**dictionary1) #把字典参数解包 此时相当于关键字参数传递 名字和函数定义的参数名必须要一一对应 useDict(*tuple1) #把元组解包 此时相当于位置参数传递
以上是关于Python学习函数参数传递方法四种(位置,关键字,默认值,包裹位置,包裹关键字传递)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章